The Mantoux test, the side effects of which can occur in children and adults, is considered safe for health.
However, doctors say: the administration of tuberculin may be accompanied by the appearance of unwanted symptoms and complications. More details later in the material.
Why is the Mantoux test dangerous?
The Mantoux test is not a vaccination, as many parents mistakenly believe. It is an immunological test. The essence is the intradermal injection of tuberculin (the protein component of killed tuberculosis bacteria). In the presence of immunity, a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction develops , which is manifested by the formation of an infiltrate and local redness of the skin. Since the test is immunological, Mantoux may be dangerous for a child due to the development of allergic reactions.
The test involves the introduction of an isolated antigen, and not live pathogenic bacteria, so it is impossible to get tuberculosis from Mantoux.
Expert opinion
Lyudmila Sokolova
Pediatrician, doctor of the highest category
Ask a Question
After performing Mantoux, the injection site can be wetted with water, but wiping with a towel is not recommended, as the risk of tissue damage and secondary bacterial infection increases.
“Should I wet it or not?” That is the question!
Get wet! Tuberculin is injected intradermally, and human skin is a fairly dense membrane. Therefore, water is not a hindrance to tuberculin! Feel free to bathe your child.
Many parents may object to the author of the article, saying that all nurses and pediatricians do not allow this. The thing is that stereotypes are outdated. Previously, a cutaneous tuberculin test was performed - the Pirquet reaction. In this test, a drop of tuberculin was applied to the forearm and a scratch was made on the skin through the solution. And it was categorically impossible to wet Pirquet’s sample.
Recently, on the World Wide Web and in the press, there have been articles stating that the results of the Mantoux test can be influenced by worms, time of year, viral infections, allergies, and so on. Indeed, asthmatics and allergy sufferers may experience redness, swelling and pain in the arm after the Mantoux test, but these phenomena gradually fade away.
When the Mantoux reaction is carried out during an exacerbation of diseases, its results can indeed vary within 1-2 millimeters. However, a positive test always indicates that the body has already “seen” Koch’s bacillus and “remembered” it.
Side effects and consequences
After intradermal administration of tuberculin for diagnostic purposes, negative consequences do not always develop. The reaction to the Mantoux test in children is characterized by general and local manifestations. They are accompanied by changes of varying severity. A hyperergic Mantoux reaction often develops with infiltration and hyperemia of the skin more than 16 mm in diameter.
It manifests itself against the background of allergies or high immune tension, which indicates the presence of a tuberculosis infection in the child. A hyperergic reaction after the administration of tuberculin requires diagnosis of the causes followed by the appointment of therapeutic measures.
After examination by a doctor and exclusion of contraindications for the diagnosis of tuberculosis, all children are prescribed the Mantoux test. Side effects after intradermal injection of tuberculin include the following conditions:
- Allergic reactions - in the presence of increased sensitization of the child’s body after the introduction of a foreign protein substance, immune cells (eosinophils, basophils) begin to produce biologically active compounds. This leads to various reactions in the form of skin rash, itching, and local swelling of soft tissues.
- Lymphadenitis is a reactive inflammation of regional (axillary) lymph nodes on the side of intradermal injection of tuberculin. They increase in size, become painful, and the skin over them turns red.
- Lymphangitis is an inflammatory reaction that affects the lymphatic vessels of the forearm and shoulder. It is accompanied by skin hyperemia, the appearance of infiltrates in the form of strands, a local increase in temperature, as well as pain.
- Skin rash , the origin of which cannot be determined. It appears in children without allergies. It is believed that this is the result of the peculiarities of the functioning of the child’s immune system.
- General reactions - weakness, increased body temperature, headaches, aches in muscles and joints, drowsiness, loss of appetite, unstable stool.
Complications after Mantoux are rare in children. They usually occur in children with allergies, contraindications, and individual characteristics of the immune system. However, this may interfere with the correct interpretation of test results and require the use of additional methods for diagnosing tuberculosis.
Negative consequences can develop if the reaction technique is incorrect (subcutaneous injection of a solution with tuberculin). Mechanical damage to the skin in the area of administration of the immunobiological drug, exposure to aggressive chemical compounds or physical factors increases the likelihood of negative consequences.
Causes
Side effects of compound samples are usually caused by the following factors:
- Negligence of the baby's parents towards contraindications.
- Individual intolerance by a child to one or another component of a pharmaceutical product.
- The “button” (Mantoux graft) was damaged by soap or water. In such situations, the wet sample should be dried immediately using an absorbent cloth. You cannot wipe it with a towel.
- The child damaged the “button” by scratching or pressing.
It is strictly prohibited to test yourself at home without a doctor.
The cause of undesirable consequences from manipulation may be the drug itself, namely, an allergy to its components.
Another important reason is the introduction of an expired or low-quality vaccine into the body. Tuberculin becomes unusable two hours after opening the ampoule. If for any reason it is used later, a negative reaction from the body is inevitable: the consequences of Mantoux will bring significant discomfort to the child and a lot of trouble to the parents.
Side effects are also caused by:
- Improper transportation and storage of the medical product. The Mantoux test is sensitive to temperature - it must be stored in the range from plus 2 to plus 8 degrees. Under no circumstances should the drug be overheated or cooled. If it freezes, it should be thrown away immediately.
- Exceeding the permissible dose or, conversely, administering a smaller amount of the drug than required. The nurse may make a mistake due to inexperience or negligence and, instead of the standard dose of 0.1 ml, administer a larger or smaller amount of the drug.
- The drug has already expired. It is very important to check whether the period of use has expired before giving the injection.
- Incorrect administration of the drug. The nurse may use an unsterilized needle or gloves or forget to disinfect the area on the skin where the sample is being administered. Also, some unscrupulous health workers reuse disposable syringes or use reusable needles, although this is strictly prohibited.
It is important for medical staff to strictly follow the rules that are standard for all types of injections:
- the manipulation is performed with a disposable syringe, which is removed from the package immediately before the sample;
- Only a sterile needle should be immersed in the vaccine container. Ideally, there are disposable vials with the required dosage of the drug;
- The injection site is wiped for disinfection with a cotton pad soaked in alcohol;
- The nurse must wear sterile gloves, which must be replaced after each manipulation.
Side effects can appear for both subjective and objective reasons. They can be caused by the characteristics of the body and the human factor. At pharmaceutical enterprises, drug production technology is often violated. Even the most qualified medical staff cannot fix this.
Allergy
If there is sensitization (hypersensitivity) of the immune system, a child may be allergic to Mantoux. The main reason for the development of the pathological condition is the peculiarity of the functioning of the immune system, which is realized at the genetic level. If one or both parents have an allergy, then with a high degree of probability it will manifest itself in the child. Typically, a reaction develops after the body comes into contact with other allergens (certain foods, house dust, plant pollen, medications).
There are several types of allergies possible:
- allergic dermatitis with skin rash, itching;
- urticaria with changes on the skin resembling a nettle burn;
- angioedema angioedema.
Less commonly, severe systemic reactions, in particular anaphylactic shock, may develop after vaccination. The condition is accompanied by a critical decrease in blood pressure and multiple organ failure. It poses a threat to the child’s life and requires urgent treatment.
If a post-vaccination Mantoux allergy develops as a side effect, the child is prescribed antihistamines . Depending on the patient’s age, tablets, capsules, syrup or suspension are given (L-cet, Suprastin, Astemizole, etc.). With the help of antiallergic medications, it is possible to prevent the development of allergic reactions in children with hypersensitivity. For this purpose, drugs are given on the eve of the test, as well as within 2 days after intradermal administration of tuberculin.
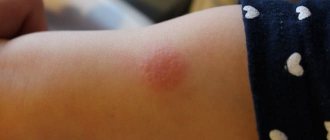
A common condition is urticaria - an allergic reaction to Mantoux in a child. The photo shows changes on the skin that resemble a nettle burn.
Hives
Normal reaction in children
The result of the tuberculin test is assessed 3 days after administration. In this case, it is important to distinguish infiltration (a place of accumulation of lymphocytes, characterized by compaction) from hyperemia (overflow of blood vessels, the thickness of the skin remains the same). To assess the response, the transverse infiltrate is measured.
The results may be as follows:
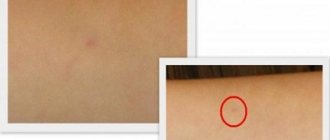
- negative test . The papule is completely absent, the size of the point at the injection site does not exceed 1 mm.
- doubtful _ The diameter of the infiltrate is 2-4 mm. Hyperemia is observed - overflow of blood vessels, accompanied by redness of the skin.
- positive _ The size of the infiltrate is 5 mm or more.
A large papule does not always indicate the presence of tuberculosis. Sometimes a false positive reaction is observed. It can be caused by allergies, recent infectious diseases or vaccinations, or improper handling of the injection site. To understand what's wrong, you need to contact a phthisiatrician.
A number of diagnostic measures may be prescribed:
- analysis of urine, blood and feces;
- fluorography;
- Diaskintest (the main alternative to the Mantoux test);
- CT scan;
- polymerase chain reaction;
- linked immunosorbent assay.
Normally, the Mantoux reaction remains doubtful or positive for up to 3 years.
The result of the first tuberculin test depends on the presence or absence of a scar on the forearm after BCG vaccination. In the first case, the reaction may be positive, in the second – doubtful. The diameter of the infiltrate is directly proportional to the size of the scar after BCG and can reach 15 mm. During the 2nd and 3rd years of life, the Mantoux reaction does not increase; it decreases or remains the same size.
Starting from the age of 4, the tuberculin test result must be negative. If it remains so for up to 7 years, revaccination with BCG is carried out. Indications for the procedure are the need for repeated anti-tuberculosis vaccination, contact with infected patients, diagnosis of an active form of tuberculosis.
Temperature
In a small number of cases, the temperature may rise after a Mantoux test (not vaccination!). This occurs within several days after the test , and the indicator can reach 40 ° C. When such a reaction to Mantoux develops, the child’s temperature rises as a result of an overly active immune response to the intradermal injection of the antigen.
Immune cells begin to produce biologically active compounds (prostaglandins), which affect the thermoregulation center of the medulla oblongata. The development of the reaction is determined by the individual, genetically inherited characteristics of the child.
The development of intoxication with hyperthermia (pronounced increase in temperature) is also possible after secondary bacterial infection of tissues in the area of administration of the immunobiological drug.
When the temperature rises after Mantoux, you should perform several simple measures:
- In case of low-grade fever (not higher than 37.5°C), no additional measures are taken; the child is monitored.
- If the temperature is 38°C or higher , children's antipyretics are prescribed in the appropriate age-appropriate dosage (Paracetamol, Ibuprofen).
- If the temperature rises above 39° C , the general condition of the child worsens with severe weakness, body aches, headaches, and impaired consciousness, emergency medical care is required.
If a child’s temperature rises after Mantoux vaccination, Komarovsky recommends taking the measures shown in the video. They are the same regardless of whether the temperature rises from an immunological test or after vaccination.
Reference materials (download)
| # | File | file size |
| 1 | Detection and diagnosis of tuberculosis in children entering and studying in educational institutions. Clinical recommendations. 2017 | 817 KB |
| 2 | If you refuse to perform a Mantoux test, clarifications of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated July 13, 2016 | 79 KB |
| 3 | All about the Mantoux test | 169 KB |
| 4 | Disease history. Primary tuberculosis. complex of the 1st segment of the right lung in the infiltration stage. complicated by polyserositis. Pediatrics | 95 KB |