Herpes type 6 in a child is most often detected between the ages of two and seven years. There is a high risk of intrauterine infection. Up to six months during breastfeeding, the herpes virus is suppressed by antibodies from mother's milk.
The highest risk of developing infection occurs during the period from six months to a year. The amount of antibodies in mother's milk gradually decreases, and the child's immunity is not yet at the proper level.
Detection of a herpes virus after the end of breastfeeding clearly signals a decrease in immunity.
The structure of herpes virus type 6 is similar to cytomegalovirus. Nevertheless, it is customary to consider two varieties of it:
- neurotropic, which in the future may lead to the development of multiple sclerosis,
- lymphotropic, which can lead to sudden exanthema of a newborn baby, or to a disease of the lymphatic system.
Herpes virus type 6 in children - what is it?
This virus belongs to the group of herpes viruses that are pathogenic for humans. It has some differences in biological and genetic properties. It is a medium-sized virus containing DNA. The structure of HHV6 is most similar to cytomegalovirus.
There are two types of herpesvirus type 6:
- A (neurotropic) – participates in the development of multiple sclerosis;
- B (lymphotropic) - is one of the causes of diseases of the lymphatic system, sudden exanthema of newborns.
The pathogen has a tropism for lymphocytes - this means that in a child’s body, type 6 herpes primarily affects these blood cells and tissues. The life cycle of the virus - from reproduction to death - is about 5 days.
How does the virus enter a child's body?
The prevalence of the pathogen is widespread. Antibodies to it are found in 90% of children over two years of age. This means that primary infection occurs at a very early age. The herpes virus is found in saliva and nasopharyngeal mucus, so the main route of transmission to the baby is through airborne droplets. Intrauterine infection of the fetus occurs less frequently. Breast milk does not transmit type 6 herpes. Children in hospitals can become infected through contaminated instruments.
In the first six months of life in children, the herpes virus type 6 is suppressed by maternal antibodies obtained from milk. When the level of these antibodies decreases or is completely absent, corresponding manifestations develop. If a 6-month-old child develops herpes, this indicates a marked decrease in immune defense or the absence of antibodies in the mother. Children aged six months to one year are most vulnerable, since maternal antibodies are no longer present, and the child’s own immune system has not yet fully formed.
After entering the body, the herpes virus may not be activated immediately, but remain dormant in lymphocytes and monocytes. Reactivation of the infection occurs with decreased immunity, intense emotional and physical overload.
Risk factors
Children with reduced immunity, undergoing chemotherapy, infected with HIV, and suffering from autoimmune diseases are at risk.
Particular attention should be paid to children under one year of age who have not had this virus, since their body has not yet developed antibodies.
Breasts are at risk of getting the virus in 3 cases:
- the mother suffered from herpes during pregnancy. Possible intrauterine infection
- during childbirth. The rash appears immediately after birth or within two years,
- The baby is bottle-fed.
Symptoms
Infection with herpes type 6 in a child occurs with any contact with the virus, but clinical manifestations do not occur in all children. This depends on the state of immunity, the nature of feeding, the presence of concomitant pathologies, and the characteristics of the course of pregnancy and childbirth.
Children under 3 years old
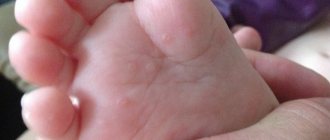
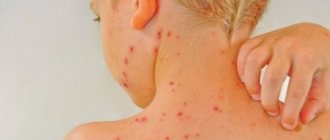
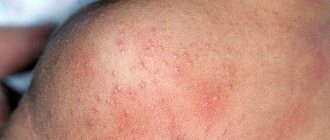
The most common manifestation of herpes type 6 in children is sudden exanthema of the newborn. This name is due to the acute appearance of the first signs of the disease. It occurs against the background of apparent complete health. The baby's temperature rises sharply, reaching 39-40*C. Against this background, there is a lack of appetite, anxiety, and lethargy. The baby sleeps poorly, cries often, and there is increased sensitivity to bright light and loud sounds.
At the height of the fever, vomiting and loose stools often appear. Upon examination, redness of the conjunctiva and mucous membrane of the pharynx, enlarged lymph nodes in the neck and behind the ears are detected. The high fever continues for 3 days.
Then the temperature drops and a rash appears on the skin. It is represented by small spotted pink rashes that do not merge with each other. Rashes appear on the back, skin of the abdomen, and sometimes spread to the limbs. After three days, the rash disappears without a trace.
This manifestation of herpes type 6 in children is very similar in symptoms to rubella, as a result of which erroneous diagnoses are common.
Children over five years old
In children who begin to attend organized groups, the disease develops like infectious mononucleosis. Herpes in the throat in children is manifested by the following symptoms:
- mild fever;
- redness of the mucous membrane of the pharynx;
- enlargement of all groups of lymph nodes;
- enlarged liver and spleen.
A small patient complains of a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, weakness, and lack of appetite. Herpes, like in small children, occurs quickly, symptoms disappear within 5-7 days.
In adolescence, the disease caused by HHV-6 practically does not manifest itself and proceeds latently or like a common ARVI.
Diagnostics
Laboratory confirmation of the diagnosis is quite difficult, since the disease progresses quickly and does not have specific symptoms. Diagnosis of herpes type six in children is based on confirmation of infection.
What tests to take
To detect herpes in the body, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- blood serum examination using ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) - antibodies to HHV-6 are detected;
- study of nasopharyngeal mucus using polymerase chain reaction - the genetic material of the herpes virus type 6 is detected;
- cultivation method - allows you to identify the virus itself in lymphocytes;
- examination of serum using the immunofluorescence method - specific antibodies are detected.
Thus, to make a diagnosis, you need to take a nasal swab and blood.
Interpretation of analyzes
The results of the diagnosis of the disease may vary.
- Serum testing to detect antibodies to herpes in the blood. Immunoglobulins, or antibodies, are formed in the body immediately after infection. During latent infection, without clinical manifestations, class G immunoglobulins are detected. Acute infection leads to the formation of class M immunoglobulins.
- When performing PCR of nasopharyngeal mucus, positive DNA of the herpes virus type 6 is detected. This means that the baby is not only infected, but is also in the stage of acute illness. When the pathogen goes into a dormant state, its DNA is absent in the nasopharyngeal mucus and saliva.
- General clinical blood tests reveal signs of inflammation. These include an increase in ESR, an increase in the number of leukocytes due to lymphocytes.
The cultivation method is quite complex and requires special nutrient media, so under normal conditions it is not used to identify human herpes virus type 6 in a child.
Diet
If you follow it, the child will tolerate the disease more easily and recover faster. When properly organizing nutrition for a child, parents should remember that herpes viruses are sensitive to two proteins:
- arginine – chocolate, nuts, seeds, grains and legumes containing it can “awaken” the virus,
- lysine - it is present in shrimp, sea fish, milk, natural yogurt and is especially necessary for a child during the course of an illness.
To strengthen the immune system, children should include ginger, lemon, onion and garlic in their diet at least once a day.
If the mucous membranes of the mouth are affected, it is recommended to follow a gentle diet and remove sour, spicy, salty and sweet foods from the children's menu.
After eating, the child must rinse his mouth.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for herpes type 6 in children. In children with an initially compromised immune system, antiviral drugs are prescribed in the form of tablets or solutions:
- "Foscarnet";
- "Acyclovir";
- "Ganciclovir";
- "Valvir."
The doctor prescribes the dosage and duration of medication based on the child’s condition, age, body weight and the presence of concomitant diseases.
For other children, herpes can be treated symptomatically:
- antipyretics - Ibuprofen, Cefekon, Panadol;
- immunomodulators – “Cycloferon”, “Anaferon”;
- vitamin complexes – “Complivit”, “Vitrum”;
- rinses and throat sprays - “Tantum-verde”, “Aqualor-throat”.
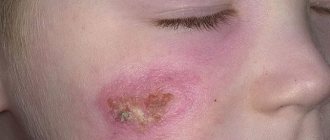
The duration of drug therapy in children with herpes type 6 depends on the severity of clinical manifestations. Local treatment for roseola in children is not required. Heavy rashes are treated with an antiseptic to prevent secondary infection.
The baby requires daily hygienic skin treatment. If he is already receiving complementary foods, you should limit their use during the fever. The optimal diet is milk and cereals, a small amount of fruit. The room where the baby is located must be ventilated and wet cleaned daily.
For older children, a light milk-vegetable diet and bed rest until the temperature normalizes are recommended. Daily cleaning and ventilation of the room is also required.
Mode and nutrition↑
Fighting a herpetic infection takes a lot of resources from the baby’s body, so it is important to provide the baby with proper nutrition and create a regime that is optimal for a speedy recovery.
The diet of a sick child must be balanced: he must receive vitamin-rich vegetables, fruits, meat and fish products, and slow carbohydrates. At the same time, it is important to take into account the baby’s appetite - if there is no appetite, you should not force feed the child; as soon as the fever subsides, he will ask to eat on his own. If a baby gets sick, it is important to continue breastfeeding if possible, which can be supplemented with the baby’s usual complementary foods. At the same time, it is important to refrain from introducing new complementary foods into the baby’s diet during the illness.
Foods rich in fast carbohydrates and fats stimulate the activity of the virus; during illness, their consumption should be limited.
During illness, bed or semi-bed rest is recommended; overwork, physical and psychological stress are excluded.
Complications
In most cases, type 6 herpes infection occurs without any consequences. Compromised children may develop seizures due to fever, which can subsequently trigger epilepsy. The incidence of this complication is about 30%. To prevent seizures, antipyretics should be used promptly.
With a decrease in immune status, the infection is often combined with cytomegalovirus, together they lead to the development of possible complications:
- encephalitis;
- hepatitis;
- pneumonia.
The development of encephalitis is considered the most severe complication of herpes type 6 and occurs due to the penetration of the virus into the brain. Subsequently, disturbances in the child’s mental development are possible. To confirm this complication, a computed tomography scan is necessary.
With the development of mononucleosis-like syndrome, a secondary infection may occur - in this case, a complication becomes a sore throat. To treat it, broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs are used.
Herpetic infection caused by HHV-6 is most pronounced before the age of 5 years. Older children get sick like ARVI, or don’t get sick at all. The disease is subject to mainly symptomatic treatment. Antiviral therapy is recommended for children with low immunity, as they are more likely to develop complications.
Traditional medicine recipes
Herpetic colds are treatable. The main thing is to notice the signs in a timely manner and start it at the first symptoms.
Traditional methods of treating children:
- baking soda - dries the skin, neutralizes acids, relieves irritation. You need to add water or lemon juice to the paste. Lubricate the affected areas of the body and leave for 10 minutes. and after this time wash it off,
- a compress of cold water will reduce swelling, relieve redness due to the outflow of blood,
- ice - compresses made from it will dry out the herpes and relieve inflammation. You need to freeze the water in the molds. Wrap an ice cube in a soft cloth and place on the affected area for 10 minutes. For facial rashes, ice is prepared from brewed coffee. It will prevent the virus from developing and spreading further,
- egg white – heals herpes in 3-4 days. The white is separated from the yolk and ulcers are treated with it,
- garlic – disinfects, helps fight herpes. Its antibacterial properties prevent the appearance of rashes. It relieves swelling and speeds up healing. Cut a clove of garlic and apply it to sore areas near the mouth or on the cheeks. To avoid damaging the skin with juice, lubricate the affected area with oil. The juice of two cloves of garlic, to which 15 grams of ash and 10 grams of honey are added, will also cure a rash around the lips. The composition is applied to the area of the rash,
- Honey – treats throat infections. Give the baby 2 tsp to suck. in a day. The rash will become softer and it will be easier for the child to swallow. They also treat rashes on the face. Prepare the composition: 15 g honey, 100 g yogurt, 0.5 tsp. instant coffee, 15 grams of flour. Mix all this and apply the paste to the bubbles daily.
Carefully! Honey is an allergenic product. The child should not have a reaction to it,
- Propolis is a good treatment for sore throats. Lubricate the bubbles with its tincture (dilute 1:1 with glycerin). It will help if 3 r. gargle with it a day (0.5 tsp per 1 cup of warm water),
- Chamomile decoction (infusion) – treats rashes in the mouth and on the gums. Infuse 1 tbsp. boiling water with 1 tbsp. l. chamomile flowers. Add 1 tbsp to the decoction. l. propolis tinctures. Apply the solution to the affected skin for 3-5 rubles. in a day. At the same time, give 1 tbsp orally. l. 3 times a day. Or 10 grams of dry chamomile, pour 0.25 liters of water and boil over low heat for 5 minutes. Strain, rinse your mouth with the broth up to 5 times a day,
- celandine - its juice is used to treat wounds. 3 cauterizations are done per day,
- essential oils - tea tree oil is used to treat the throat. Add 10 drops of oil to 1 glass of warm water. Give to your child as a gargle 3 times a day. If the face is affected, an oil swab can be applied to the sore spots. Eucalyptus, lavender, mint, and lemon balm oils will also get rid of vesicles. They treat the affected areas many times, applying them for 1 minute. If you combine fir oil with sea buckthorn oil and lubricate your throat with this mixture more often, then in 3-4 days you can forget about the disease,
- aloe – its juice is recommended to lubricate the blisters on the cheeks and nasolabial triangle. It is also recommended to apply the leaf of this plant to the hearth for 30 minutes,
- golden mustache – treats herpes on the nose. It is advisable to cauterize the rash with its juice 3 times a day.