Roseola is a viral disease that affects children of different ages; it occurs quite often. Roseola is difficult to diagnose, and its symptoms are similar to other diseases, so it is extremely difficult to determine the presence of roseola. Knowing the causes and symptoms of roseola, you can recognize it and go to the hospital in time. If treatment is not started immediately, the disease will progress. A specialist will help determine your baby’s condition and prescribe appropriate treatment.
general information
Sudden exanthema, namely roseola infantum, is an infectious disease of herpetic origin. Scientific medicine has not fully studied this disease. To make an accurate diagnosis, differential diagnosis is necessary. The reason for this is that similar symptoms can be encountered with completely different childhood diseases, such as acute respiratory disease or allergies. The symptoms of infantile roseola are very similar to those of rubella, which is why this disease is called pseudorubella.
Infantile roseola is one of the most common viral diseases that affects children under 3 years of age. Typically, roseola infantum occurs in children between six months and 2 years of age. Children get pseudorubella once in a lifetime. At the age of 4 to 5 years, antibodies are detected in children. Seasonal characteristics: spring, early summer and autumn. To a greater extent, sudden exanthema resolves without complications within a period of 4 to 6 days.
The main causative agent of childhood roseola is the sixth type of herpes, less often - the seventh herpes virus. From 5 to 15 days is the incubation period. Between 6 and 24 months of life is the time of maximum manifestation. Roseola is a disease exclusively for children. It occurs in both girls and boys in exactly the same way.
Treatment of roseola in children
Effective treatment consists of controlling the temperature and making the child comfortable. Replication of herpes viruses type 6 and 7 is suppressed by ganciclovir, cidofovir and foscarnet. Acyclovir is not used in this case. A qualified pediatrician or infectious disease specialist can prescribe medications. In pediatric practice, antiviral drugs are rarely used to combat common exanthema. They can be used when roseola is complicated by neurological symptoms or other manifestations of herpetic infection. During the fever phase, children feel satisfactory, but if there is a risk of febrile seizures, it is advisable to use ibuprofen or paracetamol. All patients must comply with the drinking regime. Doctors recommend not to self-medicate and take medications after the temperature drops. This is especially true for antibacterial drugs. Otherwise, the rash can be confused with allergic manifestations.
Causes
Despite the fact that infantile roseola is a widespread disease, newborn children have maternal antibodies that protect their body. But by 4-6 months of life, the amount of antibodies in the baby rapidly decreases and the child involuntarily becomes susceptible to a viral disease.
- Most often, the virus can be transmitted through airborne infection of healthy children from a sick child.
- Children can become infected through direct contact with a virus carrier through kissing and salivation.
- Sudden exanthema in children can occur through everyday life through contaminated household items or toys.
Subsequently, after the illness, a fairly strong, stable type-specific immunity is intensively developed. Children aged 5 years and older are not prone to infection. By this age, children have already formed antibodies to the roseola virus. It doesn’t matter what form the disease took – be it a clear clinical picture or an asymptomatic course of the disease.
Is it possible to bathe a child with roseola?
Roseola or the sixth disease in children (as it is called in medicine) has an original clinical picture. It is accompanied by a high temperature, but no other signs of the disease are observed. Antipyretics are ineffective, so they should be used only as prescribed by a specialist. It is not recommended to bathe a child with roseola and walk with him; water procedures can be carried out only after the temperature has normalized. The patient is prescribed bed rest in a well-ventilated room.
Symptoms
When infected with infantile roseola virus in children, symptoms are expressed as follows:
- A sharp increase in body temperature, sometimes reaching 41 degrees. Most often, children experience symptoms of fever - maintaining body temperature can last for hours (short) or several weeks (long). Fever can be subfebrile (up to 38 degrees), moderate (febrile - up to 39 degrees), pyretic (high - up to 41 degrees) and hyperpyretic (excessive - over 41 degrees). Often, both parents and pediatricians consider this painful condition of children as ARVI or teething.
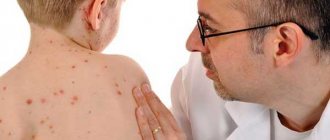
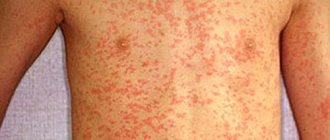
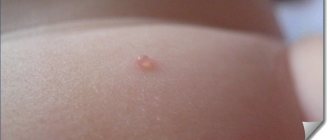
- A skin rash of varying intensity is formed. As a rule, these are pink pale spots with a diameter of 4 to 6 mm. There is a border of white halo around some spots. The rash quickly spreads throughout the child’s body. Starting on the child's back, it actively appears in the area of the child's chest and on the tummy. Appears in the crooks of the arms. The areas of the face and legs are practically not affected by pseudorubella; in rare cases, minor rashes occur. Based on these symptomatic signs, the disease is called roseola or sudden exanthema.
- Sudden exanthema rashes disappear almost without a trace on the second or third day. In rare cases, some skin changes in the form of peeling are left. Soon these affected areas will be restored.
Infantile roseola disease can occur with either small, non-serious rashes or absolutely no rashes. Parents do not always know that the child has suffered from sudden exanthema if roseola manifests itself as symptoms in the form of a rash during the night, and by the morning of the rash has disappeared without a trace.
Fever in babies
Dear reader, I'm interested
fever
in children
is precisely because it allows parents
to feel
like they are in the “skin”
of resuscitators
.
Since this
the condition includes
dynamic observation
, with the need
to monitor
and
adjust
therapy every 2-3 hours.
And managing febrile
patient always mobilizes
the sound
logical
thinking
of adults.
I will explain it primitively
, but
in an intelligible way
- so that the article can be
transferred
to practice.
Fever
is
a syndrome
of many diseases.
It is a natural
process
of non-specific
control of
the pathogen
that produces
primary pyrogens.
Accompanied by an increase in temperature
body, chills and fever.
At high temperatures
body - becomes
pathological
, often with
the need for medicinal
support.
If this is a defense mechanism, how does it work?
1. Some pathogens die when
temperatures up to
39
C. Most often
the bacteria
are
Treponema pallidum (the causative agent of syphilis).
Pale spirochete. Viruses almost never die from high temperatures, this is
a common misconception .
2. Increases the permeability of histohematic
barriers.
What allows the immune system
work more
efficiently
.
Of course, this was not intended
the effectiveness of the use
also
increases .
3. The rate of interferon synthesis
.
Which activates many
immune factors.
This happens due to an increase in the rate of biochemical reactions in general (you probably heated reagents in chemistry lessons to speed up their interaction - the same principle applies here).
The mechanism of FEVER at the biochemical level:
The pathogen releases substances ( primary pyrogens
):
- toxins
- cell wall fragments
- viral proteins
Which stimulates the production
endogenous pyrogens (
secondary pyrogens
):
- Interleukin – 1, interleukin – 6
- Tumor necrosis factor (beta)
Secondary pyrogens penetrate
through
the BBB
, affecting the membrane of neurons
of the thermoregulatory
center
of the hypothalamus
.
Which works on the principle of a thermostat
.
Hypothalamus
– changes
set point
to
higher
values.
Thus, the brain considers
the usual body temperature
to be unacceptably low
and begins
to increase
.
Due to the mediators of fever
-
prostaglandins E2
, to a lesser extent E1.
That is, for the body, it is essentially formed
new
physiological NORM
.
Which indicates
the
naturalness
of the process itself.
Which temperature should I lower and which should I not?
The following types of temperature increase are distinguished:
1. Low-grade fever
– up to 38 C.
2. Febrile
– 38-39 C.
3. Pyretic
– 39-41 S.
4. Hyperpyretic, hyperthermic
– up to 41-42 C.
For all international
standards,
an increase
in temperature above
38.5 C
already requires the use of
antipyretics
.
And according to my observations
in relation to children, this is
absolutely
correct.
But there are nuances
that are important to consider.
- Some children tolerate
a rise in
temperature extremely difficult
.
Even in the absence of any pathology
of internal organs.
The nature of the fever in such children is always malignant
- the so-called
WHITE FEVER
.
With such an individual peculiarity
low-grade fever requires a decrease - Hemorrhagic
syndrome is a frequent companion to fever.
Therefore, children with vasculitis, thrombocytopenia
, liver diseases, and deficiency of
clotting
need to reduce any increase in temperature, preferably not with medications, but
with physical cooling methods
. - The child has a history of hypoxia
during childbirth,
intrauterine
hypoxia,
cephalohematomas, epilepsy, and traumatic brain injury. It also requires a decrease in temperature - at the level of low-grade fever. - Anatomical disorders
in the structure of the heart, the presence
of anatomical
pathologies of cerebral vessels - requires
a decrease in temperature
at the level
of subfebrinopathy
.
- Some diseases
also cause very
severe
physiological reactions when
the temperature rises
and require
immediate
reduction.
( 38.0 for ARVI is one thing,
38.0 for bacterial
meningitis
).
Stages of fever and treatment tactics:
“Parent, when you have a fever, focus on your sensations
child - and not on
readings
.
You intuitively
know what to do.”
1. Chills
- indicates that
the temperature
is rising.
Clinically manifested by shivering thermogenesis and a subjective feeling of cold.
- The child should be covered with a LIGHT sheet, and should not be wrapped up under any circumstances.
- You need to wear woolen socks on your feet, and you can put a heating pad on your calf muscles (temperature - 45-50 C - no more than 30 minutes).
- Give - a warm drink, preferably fortified and containing fast carbohydrates. Warm sweet jelly, warm fruit drink.
- Eliminate all drafts in the room, this “depresses” the patient.
- Bed rest. It is better to lie half-lying or half-sitting, with the head end elevated.
- Inhaling camphor has some calming effects. So objects in the room can be treated with camphor alcohol. Do not give camphor internally, do not bring it to the child’s nose.
- As a rule, the child does not want to eat - but if the desire arises, he needs to be fed something that evokes positive emotions in him: chocolate is almost ideal, hematogen is wonderful, applesauce.
2. Heat -
usually indicates
that the temperature has reached its maximum values. And here the main task is to accelerate convection and sweating.
- The child needs to be revealed
- Remove the heating pad from your feet, take off your socks
- The child should be wiped with warm water. Warm - because it reduces the temperature, precisely due to evaporation from the surface of the body. You can add vodka to the water - 1 tablespoon of vodka per 250 ml of water (vodka is not absorbed by the skin). You need to wipe the natural skin folds: armpits; inguinal folds. And also the torso and back.
This simple physical method often allows you to do without antipyretics. Capable of lowering body temperature by 1-2 degrees C.
- If a headache develops against the background of fever, then it is necessary to apply cold. ATTENTION! After 2 layers of towels, you apply an ice pack to the back of the head; no more than 15 minutes. Can be repeated after 45 minutes. This usually relieves the headache.
- The drink should already be at room temperature - containing natural salicylates, just RASPBERRY JAM ideally diluted in water.
Life-threatening condition against the background of HEAT.
Usually during a fever the child is crimson and red.
– His hands and feet
are warm.
But it happens that the child turns pale
hands and feet become “
icy”.
A complaint of unbearable headache may develop. If you see something like this, call an ambulance
help.
The only thing that can alleviate
this condition is the use of
antispasmodics
.
And it’s not easy to break
drotaverine
tablet to help - and not harm.
In old manuals
USSR –
the use
of Corvalol
for
acceptable – 1 drop/year of life. But I have always had ampoule no-spa, and I cannot say anything about the effectiveness and safety of Corvalol.
Antipyretics in pediatric practice.
Allowed
: Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Metamizole sodium
Lucky combination.
Prohibited
:
Aspirin, Nimesulide
.
Doses
for drugs should be
age-
appropriate the frequency
of administration of drugs should not exceed
4-6 times a day, and no more than 1 time in 2-3 hours.
The effectiveness of the antipyretic is assessed after 1 hour. There is no need to give antipyretics every 15 minutes if you don’t see the effect (kill the liver with paracetamol; the heart with ibuprofen; hematopoiesis with analgin).
If there is no effect from the antipyretic, call an ambulance.
For children, an ambulance is “bent over” so that a fever resistant to antipyretics is a serious reason to call. But don’t call for a “sneeze” - please.
If a doctor or paramedic administered an antipyretic and left without waiting for the clinical effect; leave a complaint through the dispatch service - all conversations there are recorded.
In case of complications in the child, this will be your proof. But it’s better to ask: “Let’s wait for the effect.”
Stages of temperature reduction:
Lytic is considered natural
temperature decrease - no more than
1-2 degrees in 4 hours
.
The child actively
sweats, drinks a lot, and begins to “play pranks.”
The skin is pink, the limbs are warm
.
is considered pathological - a sharp decrease in elevated temperature. The temperature can drop by 4 - 5 degrees in 1 hour. The condition is correctly considered as COLLAPSE.
- the child turns pale.
- hands and feet are cold
- profuse sweating
- When standing up, fainting may develop.
- The skin is damp, cold, sticky.
- Vomiting occurs due to changes in the autoregulation of brain vessels.
What to do during a CRISIS?
- lay with elevated
; if vomiting occurs, turn your head to the side. - cover with a warm blanket
- Give hot, strong, sweet tea
. - CALLING AN AMBULANCE
is mandatory.
Usually a crisis develops
against the background
of an overdose of antipyretics, or active loss of water and electrolytes (diarrhea and vomiting).
Note:
If the child’s body temperature rises above 38.5 for more than 3 days. This is a reason to be examined by a pediatrician. That is, you need emergency housing assistance, and if this is not possible, an ambulance.
Of course I’m primitive, but the best is the enemy of the good.
Dear reader, I ask you to read my articles. The fact is that I turned off all advertising on my channel so that the “scoundrels” would not dare accuse me of CLICKBAIT. And I am disabled - my pension is 8,000 rubles a month; I live in St. Petersburg. And this is a rather “expensive” city.
I ask you, if you specifically like my articles, if you have the desire and opportunity, transfer money to “Yandex Money”, to the number410019363239625
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5c7250f55ec51000c77757fd/lihoradka-u-malyshei-5ce1108aea066d00c401cdca
What does baby roseola look like?
Below you can see a photo of sudden exanthema in children. If you look closely, it becomes clear why many people call this disease pseudorubella. Therefore, when a child exhibits symptoms of rashes similar to those in the photo, it is necessary to make a differential diagnosis, from rubella and from other similar diseases, which are given in the diagnosis section.
Treatment and prevention
Before taking any independent actions, you must remember that self-medication is highly discouraged. It is imperative to contact your local doctor. After the examination, the doctor gives certain instructions:
- children with high body temperature should not be in contact with other children and must be isolated until complete recovery;
- if there is no fever and the elevated temperature does not cause problems or inconvenience to the child, then there is no need for drug treatment;
- You can lower the fever by lightly bathing the child in warm water; if the baby begins to feel cold, you need to slightly increase the water temperature;
- Do not use alcohol-containing solutions for rubbing the body;
- in rare cases, anticonvulsant medications are prescribed to lower the temperature and for prevention purposes;
- in order to eliminate or prevent seizures, it is necessary to turn the baby on his side, loosen the clothes around the neck, place a pillow under the head, and nothing should be in the mouth.
Sudden exanthema has no specific treatment. To significantly alleviate the painful condition of children with high temperatures, antipyretic drugs such as Nurofen or paracetamol are given. For the symptomatic treatment of pseudorubella, a child with immunosuppression is additionally prescribed drugs such as Acyclovir or Foscarnet.
To summarize, it is worth recalling that roseola infantum should be correctly diagnosed. In addition, we must remember that treatment for this disease is not always necessary, and for the purpose of prevention, it is necessary to monitor the baby and the children with whom he communicates more often.
Diagnostics
The reasons for the appearance may be different, but whatever they are, you should always consult a doctor; a pediatric specialist will confirm the presence of the disease. If the temperature is more than 38 degrees, the baby may be given an antipyretic before the doctor arrives. A professional will examine your child and give the necessary treatment to eliminate the disease.
You should contact the clinic immediately if symptoms similar to roseola appear, as the disease can be confused with other similar ailments. A doctor must be called home, as the child may be a carrier and transmitter of the disease.