The Mantoux test is the main method of examining a person for tubercle bacilli. The Mantoux test technique is a skin injection that allows one to detect the presence of a specific reaction of the body’s immune system to tuberculin. This is a kind of immunological test with which you can obtain information about the presence of tuberculosis in the body.
Execution method
For the first time, the Mantoux reaction is assessed in one-year-old children.
Previously, the test is uninformative: the body is not mature enough to demonstrate the required response. The test is placed subcutaneously. Exactly 0.1 ml of tuberculin is injected. The accuracy of the dosage is important - the results of Mantoux are assessed as a response to the introduction of a clearly established number of tuberculin units.
special instructions
The test is performed if the following conditions are met:
- the last vaccination is at least 4-6 weeks old;
- the injection is done with a tuberculin syringe;
- the needle is inserted with the bevel upward, and the skin is slightly pulled back, ensuring that the drug penetrates the epithelium and not under it.
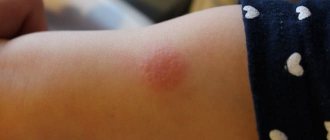
A small bump immediately forms at the injection site, which will change shape within 2 days. It should not be combed or covered with a band-aid.
It is not recommended after tuberculin administration until the reaction is checked:
- stay in the sun for a long time;
- comb the papule (lump at the injection site);
- wet it;
- be physically active.
Application of purified allergen
The Mantoux vaccination is administered using tuberculin. A clear, colorless liquid is used in standard dilution. The powder is available in gray or cream color and is accompanied by an ampoule containing 1 ml of solvent.
The authenticity of the vaccine is determined experimentally. Transparency and color are determined in accordance with the General Pharmacopoeia Monograph “Transparency and degree of turbidity of a liquid”, while only a sterile solution is used for testing.
The drug is non-toxic, the activity index is 0.95-1.05. The medicine is packaged in cardboard containers. One dose of the drug contains 10 IU of purified substance.
To carry out the test, use the recommended dose diluted in 0.1 ml. The results of the Mantoux test performed using tuberculin are necessary to obtain a complete clinical picture of the disease. When interpreting Mantoux’s results, they take into account the fact that the drug does not cause the formation of anti-tuberculosis immunity in the body of a healthy person. Tuberculin only affects patients sensitized by Mycobacterium tuberculosis or the BCG vaccine.
Diagnostic results
After birth, a healthy child is given a vaccine against tuberculosis. This procedure is mandatory because the baby’s fragile body cannot resist the disease on its own. To check that the body is protected from tuberculosis, a mantoux test is done. Let's consider the possible results of the test.
Negative
If the result is negative, there are no dangerous Koch bacilli in the body. However, immunity to tuberculosis has not yet developed. The diameter of the papule is less than 1 mm. There is no redness around the injection site.
If at the age of 7 and 14 the test shows a negative test, then the person is revaccinated again. This could have happened due to the use of low-quality drugs or irregularities in vaccination techniques.
Positive
If the reaction is positive, the child’s body fights the introduced microorganisms. It is worth knowing that in the absence of BCG vaccination, such a result may indicate tuberculosis.
Some worried parents begin to measure the “button” on their own, making serious mistakes. The convex part of the papule should be measured.
Diagnostic results
After birth, a healthy child is given a vaccine against tuberculosis. This procedure is mandatory because the baby’s fragile body cannot resist the disease on its own. To check that the body is protected from tuberculosis, a mantoux test is done. Let's consider the possible results of the test.
Negative
If the result is negative, there are no dangerous Koch bacilli in the body. However, immunity to tuberculosis has not yet developed. The diameter of the papule is less than 1 mm. There is no redness around the injection site.
If at the age of 7 and 14 the test shows a negative test, then the person is revaccinated again. This could have happened due to the use of low-quality drugs or irregularities in vaccination techniques.
Positive
If the reaction is positive, the child’s body fights the introduced microorganisms. It is worth knowing that in the absence of BCG vaccination, such a result may indicate tuberculosis.
Some worried parents begin to measure the “button” on their own, making serious mistakes. The convex part of the papule should be measured.
Features of Mantoux
The test is first performed on children aged 12 months. If after the BCG vaccination, which is given to newborn children, their body has developed immunity against Koch's bacillus, then after tuberculin is administered to the baby, immune cells begin to attack it, causing an inflammatory reaction at the site of injection of the substance.
There are situations when doctors prescribe Mantoux once every 6 months, starting from the age of 6 months.
In such cases, indications for its implementation may include:
- the presence of medical indicators or refusal of parents to vaccinate their newborn child with BCG;
- frequent pneumonia or chronic bronchitis;
- diagnosing a child with HIV;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs by the baby.
Mantoux is considered a safe research method. But there are times when a baby develops a complication after the administration of tuberculin or the result turns out to be false. Therefore, before performing the test, the doctor will check the patient for possible contraindications.
These include:
- exacerbation of any infectious or chronic disease;
- skin pathologies;
- epilepsy or other somatic disease;
- bronchial asthma;
- allergy.
Also, the test is not carried out if quarantine is introduced in the children's group that the child attends due to any infectious disease. A temporary medical exemption is given if the baby has received any vaccination within the past 1-2 months.
Conclusions after testing
To evaluate the results of Mantoux, use the recommendations approved by the rules of Sanpin 3.1.2. 31114-13 “Prevention of tuberculosis.” The test results are only 80% effective.
Sometimes the doctor concludes that the result is a false positive. If on the third day the test is interpreted as positive, the child is sent to a tuberculosis clinic for further examination by a TB specialist.
Deciphering the reliability of the result in a child under 12 months presents certain difficulties.
In a six-month-old baby, the reaction is false negative, because the immune system has its own developmental characteristics. It is not always possible to correctly decipher the test result, since the reaction to tuberculin may be a manifestation of the individual sensitivity of the body.
A distorted test result is recorded if the child has had the flu or ARVI, or suffers from food or drug allergies. Worm infestation also affects the Mantoux result. Increased background radiation, environmental pollution, and emissions from chemical production have an adverse effect.
To accurately determine the results of tuberculin diagnostics, you should follow the rules for conducting it, use a high-quality drug, and avoid inaccuracies when performing the test.
Standard guidelines
The optimal button size ranges from 5 to 12 mm. But if the answer is doubtful, negative, the pediatrician takes into account the time that has passed since the last BCG vaccination.
The main landmarks are highlighted:
- 1 year has passed since the last vaccination. The optimal papule size is from 5 to 15 mm. The appearance of compaction and redness is considered a normal reaction of the body.
- 2 years have passed since the last vaccination. The infiltrate should become smaller or remain the same. If the diameter of the injection site increases by more than 5 mm, a repeat test is prescribed.
- 3-5 years have passed since the last test. The maximum permissible diameter of a papule is 8 mm, the norm is up to 5 mm. In children with strong immunity, a few days after the injection, only a dot is noticeable at the site of the papule. There is no redness or bulge observed. If the swelling increases, a full examination of the person is carried out.
The final result can be affected by: hemodialysis, violation of vaccine storage conditions, and the use of low-quality syringes.
Antihistamines before Mantoux
The body's reaction to the Mantoux test may be non-standard. This often happens if the child is prone to allergies.
In order to avoid an allergic reaction, it is necessary to use special medications, but it is recommended to take them only as prescribed by a doctor, according to the following scheme:
- Three days before the Mantoux test.
- Next time on the day the test is taken.
- Every day until the results are assessed.
The most popular drugs prescribed in this case: Fenistil, Suprastin, Zyrtec. It is important to understand that taking these medications does not in any way affect the final result.
An allergic reaction may prevent adequate assessment of redness after the injection. Therefore, in such cases, taking antihistamines to prevent allergies is justified.
Contraindications
There are a number of contraindications for performing the Mantoux test:
- skin diseases;
- acute or chronic diseases in the acute stage - the test can be performed no earlier than 30 days after the disappearance of symptoms;
- epilepsy;
- allergic conditions in the acute stage or intolerance to the components of the sample;
- colds;
- vaccination with preventive vaccinations less than 4 weeks ago.
The immune system may falsely react to tuberculin within a month after vaccination or illness. In this regard, a period of 30 days arose, which was recommended to be maintained before revaccination. It is better to vaccinate the baby after the Mantoux test, which is allowed immediately after measuring the reaction.
Mantoux test: evaluation of results in children
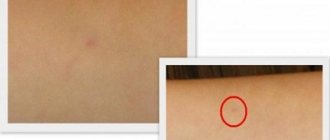
All parents whose child has been vaccinated should know how to measure Mantoux. The place where the vaccine was injected is called a papule. Redness around the papule is called hyperemia. Depending on the body's reaction, the intensity of the size of redness varies. But it does not affect the result in any way. Only the footprint size is evaluated as a result. There are only 4 options for final measurements:
- 0-1 mm - negative;
- 2-4 mm - doubtful;
- 5 mm - positive;
- from 17 mm - hyperergic.
These results are deciphered as follows:
- “doubtful” means that the baby is considered to be at risk;
- “positive” means that the baby has a high risk of disease, additional examination needs to be carried out;
- “hyperergic” means the presence of disease.
The Mantoux norm in children is the size of the seal. Doctors evaluate the Mantoux reaction over time. All results are compared with those made in previous years. An alarming sign is if a child develops a large papule after vaccination. Parents should be alert if the area of compaction increases sharply. That is, the compaction becomes more than 6 mm, compared to previous samples.
False negative and false positive response
The Mantoux norm is not tied to the age or gender of the patient.
The standards are the same for adults and children. The nuances of the body’s response to Mantoux in a child is a recent vaccination against tuberculosis. The less time has passed since BCG, the larger the diameter of the compaction will be. This means that the body has responded to vaccination. When assessing the Mantoux test, there are no clear numbers and standards. Each lump is individual for each patient. It should be noted that the Mantoux reaction in a 3-year-old child is expressed differently than in a 5- or 6-year-old child. But at the same time, there are no separate norms, depending on the age of the child. The Mantoux test may give a false negative answer. This means that unification has been found, but the reaction is negative. The child may be given a false positive diagnosis. This means that the child is healthy, but the Mantoux reaction is positive. The reasons for this discrepancy are recent hemodialysis, immunodeficiency, low-quality tuberculin, irregularities in the test, and oncological diseases.
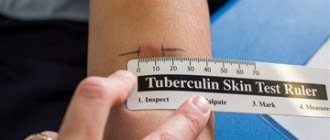
How to measure your results yourself
You can measure the papule yourself at home. To measure, you must use a plastic transparent ruler. It must be placed across the forearm. Only the compaction needs to be measured. Size in millimeters means total. Everyone knows that the main cause of tuberculosis is a wet cough with sputum production. If the baby has a lingering cough and the test response is negative, this indicates tuberculosis.
- Mantoux vaccination for children is completely safe.
- It helps determine the occurrence of tuberculosis. This vaccination should never be neglected.
- When conducting a test, you must follow all the above rules. The vaccination site must be properly cared for.
- In this case, the vaccination will show the most accurate result.
- Vaccination assessments can be done at home using a clear plastic ruler.
When vaccinating, special instructions must be followed. Vaccination is carried out if the necessary conditions are met. The Mantoux test is performed after vaccination for 6 weeks. Injections are carried out using a turbocharged syringe. When an injection is given, the needle is placed with the cut side up, and the patient’s skin is slightly pulled back. This is necessary for the medication to penetrate the epithelium.
When the vaccine is given, a small bump forms at the injection site. It changes shape within 48 hours. During this time, it should not be combed or covered with a band-aid. The patient who has received the vaccine should not be in the sun for a long time. It is strictly forbidden to comb the area of the seal. The Mantoux sample must not be wetted. The child should not be physically active until the result is assessed.
Negative result
The Mantoux reaction at 1 year of age has its own characteristics: it is considered negative in the absence of redness or when a papule of 0-1 mm in size appears.
If the baby is not infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the reaction indicates the absence of lymphocytes that took part in the elimination of Koch's bacillus. The Mantoux test does not always show the correct result, since technical errors cannot be excluded when performing it.
A negative result can be recorded in a patient for several years, but if the Mantoux test is performed on a child who has had a viral infection, incorrect data are often obtained.
A negative reaction to Mantoux in a child indicates good health - the patient’s immune system responds to the action of tuberculin.
In a child aged 7 years, the appearance of a negative Mantoux result can be caused by the following reasons:
- improper storage of tuberculin preparation;
- individual resistance of the body to the causative agent of consumption;
- a reduced number of T-lymphocytes and a deficiency of microelements, which caused a weakening of the immune system and its reaction to the administration of tuberculin.
In some cases, lymphocytes do not cope with their functions and do not interact with the administered drug, so the doctor registers a negative reaction to the test.
Is Diaskintest dangerous?
There are several myths associated with tuberculin diagnostics. The most unfounded and frightening of them is the danger of contracting tuberculosis due to the administration of the drug. In fact, this is impossible even if the injection technique was violated.
The fact is that Diaskintest is a sterile drug. It contains absolutely no microorganisms.
In order for an immune reaction to occur, the introduction of mycobacterial antigen proteins is sufficient. In this case, the tuberculosis bacilli themselves are not needed. The drug contains only two antigens, which by themselves cannot cause disease.
Moreover, Diaskintest is administered intradermally. All drugs with this method of administration do not enter the bloodstream. This means that Diaskintest can only cause a local reaction.
The only danger in this case is the occurrence of a nonspecific allergy to a foreign protein. But, as a rule, it is local in nature and does not pose a threat to the body.
Why is a tuberculosis test necessary?
The Mantoux test is a special test that is performed to determine the results of immunity to tuberculosis pathogens. Tuberculin is injected under the baby's skin - this is a special element that includes an extract from the causative agents of tuberculosis. T-lymphocytes, the so-called immune cells, react to this element.
But not all cells “notice” the presence of tuberculin in the body, but only those that come into contact with Koch’s bacillus. Lymphocytes tend to accumulate at the site of drug vaccination. Outwardly, it looks like the formation of a compaction, that is, papules. It is by its size that it is determined what correspondence the Mantoux reaction has to the norm in a child. It is not necessary to conduct a preventive examination. There is now a widespread belief that not everyone needs vaccinations. Therefore, many parents write a refusal to vaccinate. In Russia, tuberculosis is considered a common disease, so it is better not to refuse vaccination.
Psychological attitude and conversation with the child
Preparing a child for Mantoux is very important. It's no secret that most young children are afraid of injections. Few people know that, basically, this fear comes from ignorance. The child, in fact, experiences stress when mom and dad take him to the doctor, who injects something into his arm. He doesn’t understand why this is being done, why it hurts. In order to prevent the child from worrying his nerves once again, you need to explain what the doctor will do and how, but not limit yourself to simply “it doesn’t hurt, like a mosquito bites,” if the child is very sensitive to pain, you need to tell the truth, which will be unpleasant.
How to check the Mantoux test in a child
The Mantoux diagnostic method is based on assessing the dimensional characteristics of the dermatological reaction to subcutaneous injection of tuberculin. This is a drug that is an extract from mycobacterium tuberculosis artificially cultivated in a nutrient medium. The grown microorganisms are inactivated, the protein complex is thoroughly purified using chemical and thermal treatment methods. The resulting extract is preserved on a phenol base and stabilized.
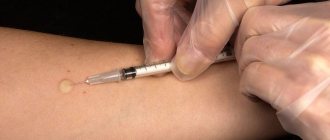
The manipulation is carried out with a disposable tuberculin syringe with a volume of 0.1 mm. The drug is injected subcutaneously from the inside of the forearm
It is important to monitor the integrity of the dermis in the area of the planned injection. The procedure itself is painless
After the injection is given, the medical worker is obliged to tell the patient and accompanying adults about the rules for caring for the “button”.
On what day are the Mantoux test results assessed in children? Mantoux must be measured after 72 hours from the date of tuberculin administration. At this time the reaction reaches its peak. It can manifest itself in the form of hyperemia (redness) around the injection site or in the formation of a compaction - papules. The latter is the focus of antibodies or T-lymphocytes, which store the memory of the encounter with the virus. If there are a lot of them, then there is a high probability that the child is infected with Koch's bacillus. It is the papule that domestic pediatricians take as the basis for measurements.
The specialist examines and feels the area of the seal, after which a regular transparent ruler is applied to the “button”. Place the measuring device at the sample site perpendicular to the shoulder line. It is advisable to do this in bright light so that the boundaries of the compaction are clearly visible. Then the doctor measures and writes down the diameter of the compacted area.
Why measure the Mantoux test?
In addition to identifying the disease at an early stage, measuring the papule can help specialists assess whether the BCG vaccine was successfully administered, whether the child has developed immunity, and how likely he is to become infected in the future.
Often, a specialist will pay attention to redness around the “button”. If it is pronounced, it is noted in the child’s medical record.
Such observation will allow us to further identify a possible increased, nonspecific allergy to tuberculin.
When and how to correctly measure Mantoux in a child
Any parent can use the method described above to measure Mantoux in a child at home before going to the doctor. The reaction to Mantoux appears immediately or within the first 24 hours after administration of the tuberculin test. However, the most objective result can be obtained on the third day.
Appearance of the papule one day after injection
Parents are interested in the question of what the Mantoux reaction should be 24 hours after its administration in order to notice deviations from the norm in time.
After tuberculin is administered, a chemical reaction develops in the patient’s body, causing characteristic changes to appear on the skin.
There is no reaction to Mantoux on the first day. Slight redness of the skin may occur.
On the second day a small papule appears. Education has clear boundaries and does not cause inconvenience to the child. If Mantoux does not bother the patient on the first day, then in the next day the dense nodule may fester, and a slight swelling appears around the injection site.
After Mantoux vaccination for a child, the reddened papule is very noticeable, and it becomes necessary to find out the cause of the development of inflammation on the skin.
The Mantoux result is deciphered by the doctor 72 hours after the test. The papule changes its color: if on day 1 it was invisible, then when pressed, the dense nodule becomes dark red, and after a few days it turns pale.
The Mantoux vaccination is tested in most children according to the instructions within the prescribed time frame, but it may look different on the first day and increase depending on the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Combination of CRP and ESR tests
The ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) test is one of the oldest and simplest methods for detecting inflammation, which is still performed in hematology laboratories.
The C-reactive protein test is a newer and more accurate method of detecting inflammation in the body.
Advantages of the CRP test compared to the ESR test
| Property | C-reactive protein | ESR |
| Speed of response to inflammation | Increases within a few hours after the onset of the pathological process | Increases slowly – over several days/weeks |
| Inflammation test sensitivity | High | Not high enough. With minor inflammation, the test may be false negative. |
| Specificity | Does not give false positive results | The results of the analysis are affected by changes in the number and shape of red blood cells. In patients suffering from anemia, the ESR test may be false positive |
The clinical information provided by both of these tests is complementary to each other. Therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, it makes sense to conduct both studies simultaneously.
Read more about ESR analysis: here
CRP + ESRDifferential diagnosis
| Pathology | SRB | ESR |
| Aseptic tissue damage | Promoted | Norm |
| Viral diseases | Normal/slightly increased | High |
| Chronic arthritis | Normal/slightly increased | High |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Elevated/high | High |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) | Normal/slightly increased | Very high |
| Ulcerative colitis | Normal/slightly increased | Promoted |
| Crohn's disease | Elevated/high | High |
| Anemia with low red blood cell levels | Norm | High |
| Sickle cell anemia | Norm | Low |
Variants of reaction to the sample in the table
Mantoux results may be as follows:
| Sample option | Appearance | Meaning |
| Negative | There are no traces of the injection, or redness of the skin at the injection site up to 1 mm | No infection. Repeated Mantoux is required, revaccination is indicated. |
| Doubtful | The presence of hyperemia at the injection site in the absence of compaction, or the size of the papule is 2-4 mm | A repeat injection of tuberculin is required. |
| Positive | Sealing from 5 mm | The size of the “button” is 5-12 mm – the norm. More than 12 mm – tuberculosis is possible. |
If there is a papule on the forearm, measure its width - the diameter perpendicular to the axis of the arm. If there is only redness of the skin (without thickening in the center), measure the size of the hyperemia. Sometimes Mantoux looks different - a papule appears on the forearm, around which there is a circle of larger diameter reddened skin
In this case, only the inner diameter of the ring is measured, that is, the width of the “button” is taken into account
Norm of reaction by age
The reaction to Mantoux is determined by the age of the child and the date of vaccination against tuberculosis (see also: would it be better to test the child’s blood for tuberculosis instead of the Mantoux test?). The size of the scar after vaccination is of great importance in the dynamics of assessing the results. For example, if a child’s scar diameter is 6-8 mm, the papule after Mantoux in such a child can reach 15 mm.
In children who were vaccinated against tuberculosis in the first week after birth, a positive reaction is considered normal during the first three years of life. At the same time, the papule should decrease in size every year, and thus, by the age of seven it becomes almost invisible.
At 7 years of age, vaccination is repeated, after which the cycle is renewed. By the age of 10, immunity weakens, the child has a weak positive reaction, and at 13 years the result becomes doubtful.
The evaluation of the results of the norm is carried out in accordance with the designations presented in the table below.
| Age | Maximum allowable scar size | Limit standard for seal size |
| 1 year | About 6mm | 5-10 mm |
| 2 years | Up to 8 mm | Up to 16 mm |
| 3 years | Up to 6 mm | Up to 9 mm |
| 4 years | Up to 5 mm | Up to 8 mm |
| 5 years | 2-5 mm | Up to 8 mm |
| 6 years | 2mm | Up to 4 mm |
| 7-9 years | 6-8 mm | Up to 16 mm |
| 10-12 years | 2-4 mm | Up to 6 mm |
| 13-14 years old | 2 mm | Up to 4 mm |
Assessing the reaction of the sample by age makes it possible to identify a turn in time. The variation of the Mantoux tuberculin test refers to small patients who had a negative or questionable result during the first 5-10 years of life, but in one year the reaction changed by more than 6 mm. These dynamics may indicate recent infection. The reliability of such conclusions is verified using other diagnostic methods.
Questionable result
In a 2-year-old child, the diameter of the papule may increase by 3-5 mm, and the doctor suggests a high probability of infection with tuberculosis.
A reaction is considered questionable if redness of any size appears, but there is no compaction. A “button” measuring two mm is measured with a transparent ruler and the diameter of the infiltrate is determined.
A questionable result after testing a child 2-3 years old sometimes occurs as a manifestation of a post-vaccination allergy. It is necessary to collect anamnesis and assess the patient’s condition day by day before deciding on his observation in a tuberculosis dispensary.
A questionable Mantoux reaction in children is recorded in registration card No. 063/u. The nurse indicates the number, series and expiration date of tuberculin, and the date of the test. The presence of somatic pathology and the allergic status of the patient is of great importance for the size of the papules.
A Mantoux size of 2 cm in some cases is equated to a negative result. A papule enlarged by 3 mm is not evidence of the development of tuberculosis infection.
If the child has not been vaccinated with the BCG vaccine, the appearance of certain changes on the skin after Mantoux is considered as infection with Koch's bacillus, although in some cases the fact of infection is questioned. The study of Mantoux results in children is carried out dynamically, observing the timing and frequency of BCG vaccinations.
Which is better - mantu or diaskintest
At the moment, there are two main methods for determining immunity to tuberculosis using antigen diagnostics - Diaskintest and Mantoux test. Each of them has its positive and negative sides.
The Mantoux test is performed using a protein extract made from several strains of mycobacteria. The drug used for the test contains proteins that are present in both “wild” and vaccine strains.
The Mantoux test causes an immune reaction both during infection with tuberculosis and after the BCG vaccine. In addition, it may react to the presence of other mycobacteria that do not cause tuberculosis.
Thus, the Mantoux test has less specificity than the Diaskintest. When performing it, it is difficult to distinguish post-vaccination immunity from that acquired during primary tuberculosis. These are the main disadvantages of the Mantoux test.
Diaskintest is made by growing strains of bacteria that express only two Koch bacilli antigens.
These antigens are found in “wild” strains, but are absent in vaccine strains. Diaskintest causes an immune reaction only in those infected with tuberculosis.
There are no post-vaccination reactions, no cross-reactions with other mycobacteria. All these are the benefits of Diaskin.
The disadvantage is that the antigens of this test do not appear immediately after infection with tuberculosis. That is, when a primary outbreak occurs, the Mantoux test will respond faster than the Diaskintest.
In many countries, Diaskintest is used as the first-line method for diagnosing primary tuberculosis.
However, it is worth remembering that this method does not recognize immunity that occurs immediately after infection. In addition, the Mantoux test is still used to determine the strength of immunity after the BCG vaccine, which Diaskintest cannot do.
How and when to make Mantoux
Parents should know how often the Mantoux test is performed on children and at what age. According to the schedule, diagnostics are carried out as follows:
- healthy children vaccinated with BCG - once a year up to 15 years of age;
- children at risk - twice a year up to 15 years of age.
The risk group includes babies with weakened immune systems and who have not been vaccinated with BCG. And also those who come into contact with tuberculosis patients in the family or in society.
When it is better to do the Mantoux test for a child, parents decide based on the recommendations of the attending physician. The pediatrician first examines the child and studies the results of blood and urine tests.
Important! The test is performed only on a healthy baby. If he has recently been ill, then the procedure is possible no earlier than a month after recovery.
Description of the procedure
According to the instructions, the purified tuberculin preparation is dissolved in a special colorless solution containing a preservative and stabilizer. One dose (0.1 ml) of the drug corresponds to two tuberculin units (2TU).
Before the procedure, open the ampoule and draw 0.2 ml of solution into a special disposable syringe (1.0 ml) with a thin needle. (You cannot use syringes intended for insulin injections, as well as syringes that have expired.) Before injection, 0.1 ml of solution is released, therefore, only 0.1 ml of solution is injected.
It is recommended to sit the child on a chair. The area of the inner surface of the forearm of the left hand is wiped with an alcohol solution and dried
The nurse performing the procedure slightly stretches the skin on the forearm with his hand from below, inserts a needle intradermally, carefully releasing 0.1 ml of solution from the syringe (1 dose, 2TE). A small (8-10 mm) papule forms at the injection site
Is it possible to wet the injection site?
The injection site does not require special care: sealing with a plaster, applying a bandage, or treating with disinfectant solutions. The opinion that the injection site should not be wet is erroneous. You can and should bathe your child. Just do not steam for a long time in hot water and do not use a washcloth at the injection site. It is necessary to monitor the hygiene of the child’s body, as well as to ensure that he does not scratch the injection site and does not introduce an infection.
But the Pirquet test, by the way, does not allow the test site to be wetted, since tuberculin is applied to the skin, slightly “scratching” it (scarifying).
Running the test
The Mantoux test is given to a child at the age of 6 only after examination by a doctor. The manipulation is performed by a nurse who has permission to conduct the test.
The inner surface of the forearm is treated with a 70% alcohol solution. The required dose of vaccine is drawn into the syringe. The sample is placed intradermally. The patient is administered 1 dose of the drug - 2 TEPPD-L.
During the manipulation, it is necessary to follow the Mantoux test technique; the result is assessed after 72 hours. Tuberculin diagnostics identifies high-risk groups for consumption, as well as people infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
When summing up young children, the nurse follows a certain algorithm of action specified in the job description. She explains to the patient the purpose of the study and obtains his consent to perform the Mantoux test.
When assessing the result, the vaccination card indicates the date of the test, the number and series of the drug. The patient is explained the rules of behavior during the procedure. It is not recommended to wet the injection site with water or lubricate it with cosmetics.
Parents are explained what the vaccination should look like after 72 hours if all hygiene requirements are met. It is not allowed to treat the vaccination site with iodine or other disinfectants.
Side effects, contraindications to the procedure
The most common complication as a result of the Mantoux reaction is the development of allergic reactions. They are expressed by swelling in the respiratory tract, damage to the kidneys and liver, as well as the human circulatory system, which in some cases leads to death.
Other types of side effects of this test include:
- inflammatory reactions at the injection site;
- the development of itching, which provokes the appearance of painful scratching, as a result of which hyperergic processes are formed;
- temperature increase up to 40°C;
- renal failure;
- blood oxidation.
The appearance of a cough after the procedure is not considered a side effect, since it is not related to the components of the vaccine. The consequences of rubbing, contact with water and lubrication with various means should also not be considered complications of the Mantoux test, since this is a problem of irresponsible attitude towards this type of tuberculosis prevention.
Doctors strongly do not recommend changing your diet for some time after the test. This is necessary so that when allergic processes develop, their etiology can be differentiated.
The Mantoux reaction has a number of contraindications for which it should not be used.
These include:
- phases of exacerbation of inflammatory diseases;
- diseases of the skin or subcutaneous fat;
- epilepsy;
- rheumatic diseases;
- bronchial asthma.
If it is impossible to carry out the Mantoux test, the doctor may allow the use of Diaskintest as an alternative. This is a specific test of an immunological nature, in which protein structures of an agent are injected under the skin of a person to determine the interferon response. A positive result indicates the presence of Koch's bacillus in the body at the initial or active stage of the disease.
Do not forget that the Mantoux test is a mandatory method for preventing the tuberculosis epidemic, as well as identifying the disease in the early stages.
Its implementation can only be prescribed by a doctor, who takes into account the individual structure of the body and contraindications to the procedure. This is necessary to prevent the development of severe complications, which will make the examination as safe and comfortable as possible for the patient.
Hyperergic test
A hyperergic reaction occurs when there is excessive immune activation of the human body. This is a variant of deviation, which is often accompanied not only by the occurrence of infiltration, but also by the development of vesicles, inflammation of regional lymph nodes, and foci of necrosis in the area of tuberculin injection.
Most often, this version of the Mantoux test is observed during an active tuberculosis process in the body. In this case, clinical symptoms of the disease can be detected in the child (prolonged cough, low-grade body temperature, general weakness, weight loss).
In this case, the child is sent for consultation to a specialized medical institution, where a bacteriological analysis of sputum, chest radiography, and a set of laboratory tests are performed. After diagnosis, a course of combination chemotherapy is prescribed.
Positive response to the Mantoux test
In some patients, a positive reaction to the administration of tuberculin is recorded, which deserves some assessment by a phthisiatrician.
A weakly positive reaction to the administration of the drug is observed after a few days, the infiltrate measures up to 9 mm in diameter. The doctor refers the patient for consultation to the tuberculosis dispensary.
Mantoux 5 mm, in some cases, is considered normal, and the size of the papule may decrease over the years, or it may disappear completely.
Often, a child’s papule diameter is 7 mm. The doctor prescribes a repeat test for the patient to confirm infection with Koch's bacillus.
The child undergoes blood and urine tests and undergoes X-ray diagnostics. The phthisiatrician prescribes a course of treatment for the patient if Mantoux reaches 8 mm. In some cases, the size of the papule is a reaction to a low-quality vaccine. For treatment, the doctor recommends that the child take anti-tuberculosis drugs if the size of the papule exceeds 7 mm.
A serious cause for concern among parents is the size of the Mantoux test of 12 mm. The patient is recommended to undergo Diaskintest and take a repeat x-ray. Sometimes the doctor asks to provide the results of fluorography of relatives.
A 12 mm papule is recorded in children suffering from allergies.
A child vaccinated with BCG may have a Mantoux measurement of 13 mm at age 5, but by age 6 it becomes negative. An enlarged papule with a diameter of 14 mm appears if a child accidentally wets it or eats highly allergenic foods, such as chocolate.
A Mantoux diameter of 15 mm indicates the development of the primary tuberculosis process. The patient is recommended to undergo treatment in a hospital.