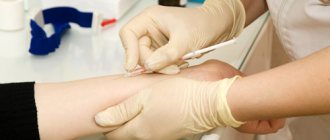
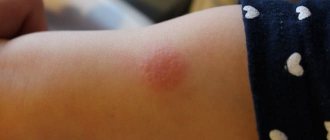
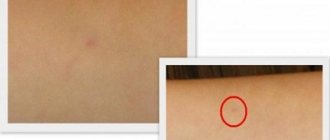
Mantoux is a test that is performed before BCG revaccination. It shows the strength of residual immunity and probable infection with Koch's mycobacteria.
The essence of the test is the introduction of a small amount of tuberculin. After 48-72 hours, the result is assessed. It can be negative, positive or doubtful.
The first option is regarded as the norm. Many parents are interested in what a negative Mantoux reaction means.
To represent the Mantoux test
Tuberculosis is rightfully considered one of the most common and dangerous diseases, which most often affects fragile children's bodies. For this reason, vaccination against the disease is done in the maternity hospital, a few days after the birth of the baby. Thanks to BCG vaccination, the baby's immune system is activated and antibodies against infection are produced.
A year later, the first Mantoux test is performed in order to find out whether the child has developed immunity to the infection and whether the BCG vaccination was effective.
This method is based on the introduction under the skin of tuberculin - a drug of artificial origin, which contains highly purified waste products of the virus. It works on the principle of litmus paper - either a pronounced reaction appears at the site of vaccine administration, or the Mantoux test for tuberculosis gives a negative value.
Tuberculin diagnostics are carried out annually to find out whether Mantoux will be negative for tuberculosis, and whether the corresponding antibodies have been developed.
Factors influencing the tuberculin test
The main factor that can distort test results is an allergic reaction. Often a hyperactive Mantoux reaction occurs due to:
- taking medications;
- eating a specific type of food;
- contact with certain external pathogens;
- parasitic microorganisms on the human body;
- infectious diseases;
- unfavorable environmental living conditions;
- chronic diseases;
- poor nutrition and vitamin deficiency;
- poor quality solution;
- individual characteristics of the skin.
There is an opinion that the injection site should not be wet for three days. This is a myth caused by a different testing method. Previously, a similar test was carried out by scratching the skin and sprinkling the wound with tuberculin. In that case, water entering the affected area was unacceptable. The test is carried out by subcutaneous injection, which is not associated with the risk of distorting the results due to moisture after Mantoux.
Is it necessary to take antihistamines before performing the Mantoux test? As Dr. Komarovsky describes in one of his programs, the tuberculin test is a test for an allergic reaction. It shows how the body perceives foreign cells. Taking antihistamines will distort the results of the procedure, leading to the risk of losing time and information.
How is a tuberculin test performed?
Tuberculin diagnostics are carried out in a clinic, or, if we are talking about organized groups of children (kindergarten, school), in a separate office by a nurse who has undergone appropriate training.
It is very important to conduct research before any vaccinations, otherwise the result may be distorted. If at this moment the child is sick, the sample is taken a month after treatment and complete recovery. Diagnosis is carried out annually, starting from the first year of life.
- For the Mantoux test, disposable special tuberculin syringes are used.
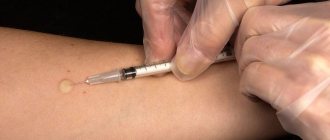
- Tuberculin injection is administered into the middle third of the forearm, subcutaneously
- An infiltrate or papule should form at the injection site, resembling a light-colored lemon peel, up to 1 cm in diameter. After 20-30 minutes it disappears from the surface of the skin
- The body’s response is formed after 72 hours, from which the specialist draws a conclusion about the state of immunity. Measurements of the papule are carried out with a transparent ruler, positioning it perpendicular to the axis of the forearm, and the data must be entered into the child’s medical record or vaccination card.
What does a positive test result mean?
If the body’s response to the test is positive, before proceeding with the procedures, it is necessary to find out several comparable factors. The time from the previous test and BCG vaccination plays an important role. It is likely that antigen cells still exist in the human body, and they give a similar result. The human factor should not be ignored. When exposed to a variety of external irritants, the Mantoux papule may increase in size and give a false test result. The child may scratch the injection site.
We recommend reading:
- How to get rid of condylomas on the head of the penis
- What is the danger of piezogenic papules
- How to get rid of wen on the eyelid
A large papule and a positive response may be the result of an allergic reaction to the first BCG. This is considered normal. Most vaccinated children experience a similar reaction by 12–18 months. In less than 40%, a questionable or negative reaction can be seen. The allergy develops after 45-60 days, and reaches its peak in the first or second year of life. Young children are often diagnosed with a papule measuring 16 mm.
After detecting a large papule, the pediatrician refers the child to a highly specialized specialist - a phthisiatrician. The doctor conducts an additional diagnostic examination to clarify the circumstances of the phenomenon.
If there is a positive result, information about:
- previous BCG vaccination;
- previously suffered infectious diseases;
- individual intolerance to the components of the test preparations.
Experts distinguish positive test results that occur after vaccination from those that indicate the presence of a dangerous infection, due to the appearance of the papule. After vaccination, it has a faint pink color and disappears after 1.5-2 weeks. The indicator of tuberculosis appears as a dark, intensely colored papule. Education does not disappear for a long time.
Test results
In fact, the Mantoux test is a test that has much in common with an allergy test. The reaction to it can be of several types:
- Positive: the diameter of the infiltrate is within 5-16 mm. This indicates the presence of immunity against the pathogen. If the indicators change over several years, conclusions can be drawn about possible infection
- Hyperergic: the size of the papule is more than 17 mm in children and more than 21 mm in adults. It is also possible for small ulcers and ulcers to form at the injection site. This indicates that there are too many pathogenic bacteria in the body and an infection has occurred. And a healthy person can react in a similar way to Mantoux if they have recently suffered an infectious disease or are susceptible to allergic manifestations
- Negative: the absence of any compaction or redness after the injection, or their slight (up to 1 mm) manifestation. This means that the infectious agents have not previously entered the body. However, even with tuberculosis there can be a negative mantoux test: with a very weakened immune system or in case of infection over the past 2.5 months
- Doubtful: the appearance of only redness, or the size of the papule is insignificant (2-4 mm).
If, during the course of the study, the doctor has suspicions about a possible infection, he gives a referral to a specialized anti-tuberculosis dispensary in order to take additional tests on the spot and consult with a specialist - a phthisiatrician.
What does it mean: good or bad?
After intradermal injection of tuberculin, a papule is formed. It has a dense structure and a reddish tint. The doctor assesses the size of the lump that appears. There may also be redness around the papule. The diameter of such a spot varies, but is not taken into account during the assessment.
Many parents think that if the Mantoux test is negative, then the child is absolutely healthy and ready to continue tuberculosis immunoprophylaxis. But we must not forget that the result may be false.
The reliability of the data obtained is influenced by the following factors:
- the quality of the drug used for the test;
- characteristics of the baby’s body, individual sensitivity to tuberculin;
- compliance with the injection technique;
- presence of innate immunity;
- poor nutrition after tuberculin administration;
- allergy condition;
- the presence of chronic diseases of internal organs;
- previously suffered infectious pathologies;
- strength of the immune system;
- recent vaccination.
Typically, a false negative result of a tuberculin test is due to improper administration of the drug or violation of storage conditions of the drug. Inexperienced doctors may misinterpret the result.
There are cases when, after the introduction of tuberculin, a papule does not form. This is also considered a negative result. But we must understand that the absence of a seal is not normal and indicates that the child’s immune system did not respond to the injection.
The complete absence of papule after the Mantoux test may have the following explanation:
- the drug used turned out to be spoiled or counterfeit;
- medical personnel violated the rules for conducting a tuberculin test;
- weakness of the immune system. The body was unable to react with the antigenic material;
- taking antihistamines. The appearance of papule is a response of the immune system to tuberculin. Antihistamine-type medications can suppress it.
In this case, it is necessary to repeat the Mantoux test after a while or perform Diaskintest. The last diagnostic option also involves subcutaneous administration of tuberculin. But the drug used has certain differences. It contains two types of synthetic antigens.
Detects the presence of Koch bacilli in the body. Diaskintest is carried out only as prescribed by a phthisiatrician. If it shows a negative result, this means that the Mantoux test was performed correctly, the baby is healthy and ready for revaccination.
Some people have innate immunity to tuberculosis pathogens. Such children will not have a papule after the Mantoux test either at one year or at 7 or 14 years of age.
If the parents do not have a scar from the BCG vaccination, this indicates innate immunity to tuberculin. With a high degree of probability, the baby’s body will also be resistant to infection.
It is also necessary to take into account that in some children the reaction to tuberculin does not develop after 48-72 hours, but a little later. Therefore, if there are no papules on the second day after the test, it is recommended to wait another couple of days. Thus, it is impossible to say unequivocally whether a negative Mantoux test is good or bad.
Such a reaction may indicate a normal state of health and the need for BCG revaccination in the near future. But it happens that such a result is false. In this case, there is a risk of missing the development of the disease.
Sometimes tuberculosis occurs hidden. If, in the presence of infection, you get a BCG vaccination, the pathology can become acute and cause complications. Therefore, if the test result is questionable, it is better to repeat the Mantoux.
Negative Mantoux test - dangerous or not?
Despite the fact that a negative value is considered within normal limits when the diameter of the papule is less than 1 mm, in practice this result is not always unambiguous, and in case of tuberculosis Mantoux can be negative.
Such a false negative reaction to the vaccine can be caused by the following factors:
- The infection occurred in the last few weeks. In this case, repeated vaccination will be required after 10 weeks.
- Slow reaction of the child’s body, caused by weakened immunity, its instability, vitamin deficiency, general exhaustion
- Serious disorders of the immune system and AIDS weaken the body, which is unable to resist mycobacteria at the proper level. To obtain a reliable picture, additional diagnostics and a test with an increased concentration of tuberculin will be required.
A Mantoux test for tuberculosis with a negative reaction does not cause concern if the child has never been vaccinated with BCG before: the body is not infected, but immunity to tuberculosis is completely absent. Such children may be offered revaccination.
What does a negative reaction look like?
A negative test reaction is manifested by the absence of papules or when there is a small red spot at the site of induration.
A false negative Mantoux test result looks like this:
- no redness;
- no papules;
- seal diameter is less than 1 mm.
To get a reliable result, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- do not use antihistamines. They are capable of distorting the reaction;
- Do not treat the injection area with antiseptic ointments and solutions.
If you receive a false negative Mantoux test result, your doctor may recommend an examination. To get a complete picture of your baby’s health, you will need to undergo urine and blood tests. To assess the condition of the lymph nodes of the chest and lung tissue, it is necessary to perform radiography.
Taking the child's medical history is also important. This will help identify the likelihood of recent infection. It should be taken into account that the response to tuberculin administration in immunized children of different ages may differ. It depends on how long ago the BCG vaccination was given.
The longer this period is, the smaller the papule is formed. According to the plan, BCG is injected for the first time in the maternity hospital. The mother or father can make a preliminary assessment of the result of the Mantoux test in a child on their own. To do this, take a ruler and measure the diameter of the seal.
Options for Mantoux test results for children of different ages are given below:
- when tuberculin is first administered, the reaction to it can be positive in the absence of infection with Koch bacilli;
- at two years the papule can reach 16 mm. At the same time, the child is absolutely healthy;
- at the age of three, the reaction to tuberculin weakens. The majority of children vaccinated according to plan have a negative result;
- at 4-5 years old, the number of children with a negative response to the Mantoux test increases. This is explained by the fact that the specific immunity formed during BCG vaccination weakens;
- six-year-old children often have a questionable tuberculin test result;
- after revaccination, the response to tuberculin remains positive for 5-6 years;
- at 13-14 years of age, a negative Mantoux result is considered normal.
Proper care after the Mantoux test
If you do not properly care for the injection site, you can distort the result. Basic rules of conduct after a tuberculin test:
- Until the doctor assesses the body's reaction, under no circumstances should you treat the injection site with brilliant green, hydrogen peroxide, iodine or any other antiseptic.
- Eliminate contact of the papules with water
- You can’t cover the “button” with a band-aid - the skin underneath will start to sweat
- It is necessary to ensure that the papule is not scratched and touched as little as possible.
After checking the reaction, you can treat the wound or abscess, if any, with a suitable antiseptic.