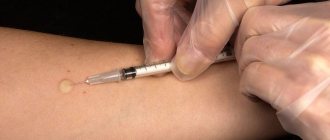
One of the ways to detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the human body is the Pirquet test. An extract based on dry purified tuberculin helps determine the causes of increased Mantoux, made before the test. With its help, it is possible to recognize why the papule arose, due to infection or as a reaction to BCG. The study also allows us to determine how strong a person’s anti-tuberculosis immunity is.
How to measure Mantoux: how the doctor will do it and why
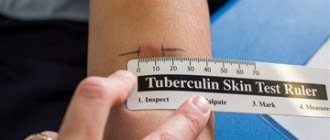
To measure Mantoux, a doctor or nurse uses a tuberculin ruler. It is a flexible strip of completely transparent plastic with clearly marked millimeter divisions. If you take a regular one, it gives a measurement error of 1-2 mm. Such a deviation can be decisive when the result is questionable. It is strictly forbidden to use homemade devices for measuring in the clinic.
Mantoux measurements are needed in order to identify the individual reaction of the body to the introduction of tuberculin. It is called specific allergic, as it involves the movement of special cells of the immune system to the injection site. They have had contact with the tuberculosis bacillus in the past. The more of them there are in the body, the wider the papule will be - a transparent elevation of the skin.
What is a tuberculin test
Important! A tuberculin test is a specific immunological test that determines the presence of tuberculosis infection in the body.
The main method of tuberculin diagnostics in our country is the Mantoux test, although currently some parents and doctors prefer another method, which is called Diaskintest. Its advantage is greater accuracy and specificity. While a positive Mantoux reaction can be associated both with infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis and with BCG vaccination, Diaskintest reacts only to pathogenic microorganisms. However, this method of diagnosing tuberculosis is just beginning to be introduced into Russian medical practice.
Many parents mistakenly believe that the Mantoux test is a vaccination. Mantoux is a diagnostic test named after the French scientist Charles Mantoux who first proposed it. And the vaccine against tuberculosis infection is BCG (an abbreviation for “Bacillus Calmette-Guerin” in French transcription), which, in the absence of contraindications, is given to the child in the first days after birth.
How to correctly measure Mantoux using the ruler itself
If parents try to measure Mantoux themselves with a ruler, then they need to take into account the high probability of an incorrect result. Therefore, even nurses, when allowed to evaluate samples, undergo special courses.
To bring the result as close as possible to the true one, it is important:
- have a flexible ruler with clearly marked divisions; you can use a strip of graph paper glued to tape or adhesive tape at home;
- place your hand on a hard surface;
- provide bright lighting;
- take the measurement strictly across the forearm, that is, parallel to the bend of the elbow, and the ruler passes through the injection point.
If the papule is not visible, there is no elevation of the skin, then there is a possibility that the lump is located in the skin. Then you need to feel it very carefully and make marks on the borders with a ballpoint pen. With independent measurements, it is not possible to correctly assess the result, since the doctor also focuses on the size of the scar after the injection of the BCG vaccine on the shoulder, last year’s diameter of the papule, and the presence of signs of infection in the child.
What is not recommended after the test
When performing Mantoux, it is important to remember that the reaction can be either false positive or false negative if a number of simple rules are not followed:
- Do not rub or scratch the sample site;
- It is forbidden to apply adhesive plaster and bandage;
- Do not lubricate the injection site with creams, ointments, brilliant green, iodine, or antiseptics;
- You can’t sweat – that is, dress too warmly.
We recommend reading! Follow the link: What will be the result if you wet the Mantoux sample with water?
Despite the fact that previously children were forbidden to wet Mantu, now an adjustment has been made to this recommendation: you can wet it, but you cannot rub the papule with a washcloth when washing. You also do not need to follow any special diet. If a child is allergic to a product, then during the test it must be excluded from the diet.
How to measure Mantoux for a year old child
To measure Mantoux for a one-year-old child, he needs to be in a calm state and not move his hand. To do this, it is better to distract him, switch his attention to a toy or cartoon. It is more convenient to take measurements together. The doctor must take into account the size of the scar on the shoulder of a one-year-old child if vaccination was carried out in the maternity hospital. Therefore, you need to measure its thickness.
With a post-vaccination scar up to 2 mm, the papule on the forearm should not exceed 5 mm. If the graft mark is 2-5 mm, then the diameter of the “button” is allowed from 5 to 11 mm. A child per year with a scar of 6-10 mm may have papules ranging in size from 5 to 15 mm.
How are the analysis results interpreted?
The result of the research is determined by a phthisiatrician after 48 hours. The state of the human body and the presence or absence of infection are determined by the nature of the redness and the size of the papules:
- if there is no allergic reaction, this is normal, which means the person is healthy;
- a papule up to 3 mm in diameter indicates a questionable result, requiring re-vaccination and re-evaluation of the result;
- a papule of 4-10 mm means that the patient is at risk and can become infected, but subject to constant contact with a patient with tuberculosis;
- a papule of 10-15 mm, especially with the presence of ulcers at the vaccination site, indicates a sharply positive result and a high probability of developing tuberculosis.
What is a graduated sample
Since the development and first research by Pirquet, the sample has been improved and refined. This is how a modified or graduated tuberculin test arose, which is taken mainly for infected children. The goal is to determine individual sensitivity to the causative agent of tuberculosis.
To carry out analysis in children, AT solutions of concentrations of 100%, 25%, 5% and 1% are used. The substances are applied in drops to the skin of the forearm, then with special tweezers an incision or scratch is made on the skin epithelium through the drop. A positive reaction to tuberculin of all concentrations confirms the diagnosis: primary tuberculosis in the active phase.
What can distort the Mantoux reaction and enlarge the papule?
The Mantoux reaction will be incorrectly assessed, and the size of the papule will be larger than the true size if there is:
- previous infection in the current month;
- vaccination or administration of immunoglobulins, serums, immune stimulants;
- diseases of internal organs in the acute stage;
- worsening of allergic and skin diseases;
- mid-menstrual cycle in girls;
- helminthic infestation;
- insect bite;
- frequent contacts with tuberculosis patients;
- tuberculin diagnosis more than once a year;
- thyrotoxicosis (excess of thyroid hormones);
- scratching, lubricating or covering the papules with an adhesive plaster.
Errors in performing the Mantoux test (for example, violation of the injection technique) cannot be completely excluded. Therefore, in all cases of a reaction unusual for a child, a diagnosis is not immediately made; to confirm it, blood tests, Diaskintest, and chest x-ray are performed.
If you are aware of a tendency to allergies, the doctor recommends taking medications with an antiallergic effect (for example, Suprastin, Claritin) 3 days before and 3 days after the test.
It is also important to exclude from the diet during this period all foods that cause food allergic reactions: honey, chocolate, eggs, fish, nuts, strawberries, and reduce the amount of sweets and flour in the diet.
What to do next if the result is positive
If the Mantoux test result is positive, then you will need to contact a phthisiatrician and undergo additional examinations - fluoroscopy, radiography, bronchoscopy, laboratory tests of blood and sputum. Parents can contact private clinics for alternative diagnostic methods.
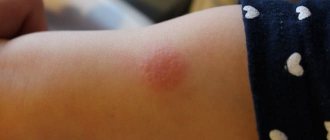
Mantoux papule is a neoplasm that forms in the first 2 days after the test and disappears on its own after 2-10 days. Doctors determine the body’s reaction by the size of the “button,” and it can be negative, positive, or questionable. The absence of a papule in certain cases does not indicate the presence of tuberculosis, but is perceived by specialists as a negative reaction.
Reference materials (download)
| # | File | file size |
| 1 | All about the Mantoux test | 169 KB |
| 2 | If you refuse to perform a Mantoux test, clarifications of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated July 13, 2016 | 79 KB |
| 3 | Instructions for use DIASKINTEST. Recombinant tuberculosis allergen in standard dilution, solution for intradermal administration | 134 KB |
| 4 | Article. Impact of application in diagnosis. algorithm of the PCR method in real. time for the effectiveness of treatment of tuberculosis with MDR pathogen. 2019 | 316 KB |
| 5 | Algorithm laboratory. diagnosis and monitoring of treatment of drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis using rapid molecular methods. WHO. 2017 | 2 MB |
| 6 | Federal clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of latent tuberculosis infection in children. ROF.2015 | 374 KB |
| 7 | Federal clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of tuberculous pleurisy. ROF. 2014 | 361 KB |
Difficulties in diagnosing breakdown
A positive tuberculin test in itself is not a sign of tuberculosis. As we wrote above, it can be observed after BCG vaccination. If an allergy to tuberculin develops, which manifests itself as a positive reaction to the Mantoux test, doctors say that immunity to the pathogens is formed.
When is it necessary to sound the alarm? In a situation where the child's reaction has always been negative, but suddenly becomes positive. This is called a “tuberculin test turn” and requires mandatory consultation with a phthisiatrician, as it may be a sign of infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A pronounced positive reaction (papule with a diameter of more than 12 mm) that persists for several years should also be alarming.
The tuberculin test is only the first step necessary to diagnose tuberculosis. If there is a suspicion of infection with Koch's bacillus, the child will in any case be prescribed additional examinations: x-rays of the lungs, urine, blood, and sputum tests. Therefore, you should never be afraid of a visit to a TB doctor - this is a necessary precaution for timely detection or prevention of the development of a dangerous disease.
Side effects and complications
After the Pirquet reaction, the development of local and general negative reactions cannot be ruled out:
- a feeling of discomfort (pain, burning) in the area where tuberculin was applied;
- headache of varying severity;
- general weakness, poor health;
- increased body temperature;
- various allergic reactions (rash and itching of the skin, urticaria, angioedema).
If such reactions occur, you should consult a doctor who, if necessary, will prescribe treatment aimed at reducing unpleasant symptoms.
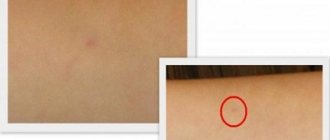
Example of an allergic reaction
Often, side effects can be confused with a hyperergic (excessive) immune response to an antigen. In particular, the student underwent a Pirquet skin test - swelling of the skin with a diameter of more than 30 mm was observed, and the size of the hyperemia did not exceed 10 mm. In such cases, additional research is required; for example, the doctor may recommend Diaskintest.
When is vaccination contraindicated?
The key to a reliable result of a tuberculin test is proper care of the papule. Incorrect treatment leads to distortion of the result and referral to a phthisiatrician. The basic rules are as follows:
The resulting seal should not be wetted, rubbed, sealed with a band-aid or smeared with brilliant green. The same applies to iodine, peroxide, and any liquid in general. On the second or third day, the papule may begin to itch
It is important to ensure that the child does not scratch the injection site. By scratching the tumor, the baby can introduce germs, which often leads to an unfavorable outcome.
Every year in schools, students are given the Mantoux reaction. It is a diagnostic test that helps determine the presence of tuberculosis infection or the quality of vaccination against this disease.
Restrictions
To obtain a reliable result after a test (not vaccination!) Pirke for 48 hours, you should adhere to some restrictions. At this time you cannot :
- moisten the skin in the area where the tuberculin solution is applied with water;
- cover the papule with a bandage and apply bandages;
- exert a mechanical effect on the skin (combing, tearing);
- apply various medications.
Expert opinion
Lyudmila Sokolova
Pediatrician, doctor of the highest category
Ask a Question
If a child is taking any medications, then before performing the Pirquet test, you must warn the doctor about this.
Manifestation of reaction
The test is performed to determine the resistance of the child’s immune system to the tuberculosis bacillus. If lymphocytes have already encountered the causative agent of the disease, they begin to actively move towards the site of drug administration. Therefore, a slight lump should appear at the injection site.
The doctor evaluates the result on the third day after the injection. The characteristics of the manifestations are individual; with an infiltrate larger than 5 mm, a positive result is recorded. In some cases, redness without a papule is allowed. The absence of an immune response indicates a negative result. In some cases, the doctor concludes that re-vaccination with BCG is necessary. An alarming signal is an increasing size of the infiltrate compared to the result of the previous test.
The presence of intense immunity is characterized by a pronounced reaction due to active interaction with the pathogen. Signs of the development of a hyperergic Mantoux reaction are:
- increased seal size (more than 17 mm);
- ulcers, suppuration in the area of infiltration;
- severe Mantoux hyperemia;
- dark spot after a week;
- the appearance of a red mark to the elbow;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes.
Such symptoms indicate an excessively expressed immune response of the body.