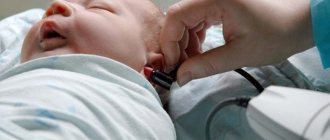
Vaccination has become part of mandatory medical procedures. This won't surprise you anymore. But it happens that the child gets sick after Mantoux. Parents in such a situation begin to panic. The main thing is to calm down and consult a doctor, he will explain everything and determine whether it is a disease or just the body’s reaction to the vaccine.
There is a danger of contracting tuberculosis from the Mantoux test test. And this is already a very serious problem for parents! Complications after vaccination are possible. The mechanism of its action is precisely based on causing a response from the body. This entails an increase in temperature and fever, which is perceived as the first symptoms of infection.
Illness or reaction to the test
In order to strengthen the stability of the immune system, a person is given an injection.
Cells become acquainted with a new antigen, a substance that under normal conditions is perceived as foreign to the body and is not found in its internal environment under normal conditions. When an antigen enters the human body, antibodies begin to be produced by body cells that are released when the antigen appears.
Then an interesting complex AGATE (ANTIGEN + ANTIBODY) is formed and eliminated, that is, released into the environment. Thus, the process of differentiation of cells into friendly and foreign occurs and protection from a hostile environment is provided.
After becoming familiar with the antigen, memory cells form stable immunity. And these days the Mantoux reaction occurs, symptoms similar to those of the disease appear. But don't panic. This is a normal defense mechanism that worked in time. Everything will be fine with the child, his body functions normally and takes care of him.
Mantoux after illness
Is it possible to get vaccinated after the baby has had, for example, a sore throat or bronchitis? Many parents know that performing the Mantoux test immediately after an illness is not recommended. Being sick before vaccination means postponing it for several weeks. This rule is due to the fact that the body is weakened, and the introduction of a sample can have a negative effect. The body has not yet fully restored its reserve of strength, and it will not be difficult for an infection to penetrate it and gain a foothold.
Another reason is that a recent infection may affect the test results, making them incorrect or inaccurate. And in this case, the very meaning of the event disappears.
Any decision related to the child’s health primarily depends on the parent. A parent may find it necessary to carry out a reaction immediately after an illness, without fully understanding the situation, and then the baby’s health may be in danger. Here, as in many other cases, a preliminary consultation with a doctor will not hurt.
Doctors recommend carrying out the reaction only a month after the child’s recovery, so that his immunity has time to fully recover.
In addition to a recent illness, the results can also be affected by:
- allergy;
- menstruation;
- quarantine period.
When carrying out a reaction, it is better to take into account all possible factors that could distort the result and try to get rid of them.
Antihistamines after Mantoux
Antihistamines are substances that suppress the action of histamine. There has been debate for quite some time about whether it is necessary to take them before and after the Mantoux vaccination or, on the contrary, this should not be done under any circumstances.
Most are inclined to believe that it is necessary to take antihistamines. Their action is aimed at suppressing a possible allergic reaction, which, in turn, helps to obtain the most accurate Mantoux results. It is important to always read reviews about the medicine.
Reasons for feeling unwell after Mantoux
Recently Mantoux was placed and the child fell ill due to the administration of tuberculin. All symptoms point to this.
The reasons may be of different nature, however, everything is normal if the following conditions are met:
- Fever occurs only 2-3 days later, and not immediately after vaccination.
- Itching and redness appear after the injection.
- The size of the halo around the injection site reaches 1.5 centimeters.
If the injection is done incorrectly, contamination and infection can occur. There is no guarantee that a child will not get tuberculosis from Mantoux.
Usually this is very similar to acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections, which is a cause for concern:
- Unbearable headaches.
- Unreasonable nausea and vomiting.
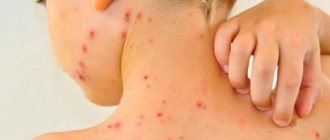
- Various types of skin rashes.
- Significant decrease in blood pressure.
- Hyperthermia (increased body temperature).
- Lethargy and fatigue even with minor exertion.
- Runny nose, nasal congestion.
Among the reasons for poor health, there are a number of factors that provoked a deterioration in the condition. These include periods of exacerbation of diseases.
Effect on sample results
Mantoux is not a vaccine, so it rarely causes side effects. Among the negative consequences, a child may experience an allergic reaction to tuberculin. But children who suffer from severe allergies or have recently had an infectious disease are usually at risk.
Although doctors believe that if the child is healthy at the time of the test, then it can be done no matter how much time has passed after the illness, but pediatrician Komarovsky has the opposite opinion. He is sure that you need to wait a certain amount of time after the illness, and only then do Mantoux. Moreover, this should not be done at the time of exacerbation of the disease.
In this condition, the body may not respond adequately to tuberculin, and then thickening and redness appear at the injection site, indicating an infection that actually does not exist.
There are also opposite situations when the immune system is so weakened that it cannot give an adequate response to the presence of mycobacteria.
Opinions on this issue are divided, so it is better to let the body fully recover and get stronger.
What to do when a child gets sick after a Mantoux test
To avoid getting sick, prevention is necessary. Yes, it is much easier to prevent an infection than to cure it.
Precautionary measures are very simple and consist of preventing the risk of infection. It consists of two factors: the environment and pathogenic microorganisms in it. If nothing can be done from the second point naturally (in such cases only artificial vaccinations help: for example, Mantoux against tuberculosis), then we can still fight the first.
Precautionary measures:
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Sunbathing, contrast showers, sports: all this will only be beneficial.
- Do not walk in crowded places (the likelihood of infection is much higher).
- Avoid contact with sick people.
- Boost your immunity with fruits.
If your child is sick, look at the temperature! Low-grade fever means that everything will go away on its own after a few days. Above 37.5°C makes one think about a serious illness due to an additional infection (the cause is not tuberculosis).
In this case, consult a doctor to avoid consequences!
Actions that are unacceptable:
- Do not give your baby antipyretics after vaccination.
- Treating it with other drugs is a bad idea.
- Do not give Cytovir, which would do a great job against flu and colds. Everything will happen without your intervention.
They made Mantoux and the child fell ill: after vaccination, is it possible, what to do, with tuberculosis, diagnosed
The Mantoux test or reaction is a diagnostic procedure that is performed in children for the early detection of tuberculosis. If Mantoux was done in the hospital and the child became ill, then parents should take appropriate measures aimed at identifying the cause of the development of the pathological process. Such a reaction is not always an indicator that the body has tuberculosis.
Causes
Before administering a tuberculin drug, the child should be examined by a pediatrician and make sure that the patient is healthy at the time of the diagnostic procedure.
The Mantoux test is not recommended if the body is weakened by illness.
Under these circumstances, the results of the study may be unreliable, and due to the fact that the immune system is weakened, the patient’s health condition may worsen.
If the child has recently suffered from a viral or other disease, the test is not recommended. In order for the body to get stronger after an illness, you need to wait 2-4 weeks. If you do not adhere to these rules, you can get sick from Mantoux. The child may develop a fever, cough, runny nose, etc.
Such symptoms indicate that the weakened body was unable to resist other viruses and infections, but it is impossible to get tuberculosis.
During the Mantoux test, the patient is injected with a drug that contains non-living tuberculosis mycobacteria that have undergone special treatment.
The cause of deterioration in well-being after a tuberculin injection may be:
- at the time of the test the child was not healthy;
- inadequate quality of tuberculin;
- improper storage of injectable drugs;
- teething;
- injection site infection;
- allergic reaction to a sample, etc.
Parents' actions
When, after Mantoux, there is an increase in body temperature, the site of the tuberculin test increases (more than 15 mm) or it itches, you need to contact a phthisiatrician. In rare cases, Mantoux can cause an increase in temperature (not more than 37.5°C) in children, even if the patient was healthy at the time of the procedure. This complication goes away on its own without medical intervention.
If a child gets sick or parents have any doubts about his health, you should consult a pediatrician.
What do you think are the most important factors when choosing a medical facility?
- Trust in the doctor 74%, 548 548 – 74% of all
- Modern equipment 14%, 104 votes104 votes – 14% of all
- Advice from friends 4%, 33 votes33 votes – 4% of all
- Cost of services 4%, 28 28 – 4% of all
- Close location to home 3%, 24 votes24 votes – 3% of all
- 8 – 1% of all
How to treat
When, after a Mantoux vaccination, a child develops symptoms of the disease, antipyretics or other drugs should not be given independently. Before treatment, it is necessary for the doctor to conduct an examination, order an examination (if necessary) and make a final diagnosis.
If the temperature rises to a critical level, you must call an ambulance. If it is impossible for doctors to arrive in the near future, parents will be given recommendations over the phone on how to provide first aid.
When the diagnostic results confirm that the child fell ill after Mantoux due to a weakened immune system or an allergic reaction, he is prescribed symptomatic treatment.
If tuberculosis is suspected, additional tests must be performed. X-ray examination may be required.
If tuberculosis is diagnosed, the patient will have to undergo treatment at a tuberculosis clinic.
How to avoid
To prevent complications that may arise after a tuberculin test, parents are advised to closely monitor their health. At the time of the diagnostic procedure, the child must be healthy, and he must also have no other contraindications to Mantoux.
After vaccination, you should limit your time spent outside. In unsatisfactory weather conditions, it is better to stay home. You should not walk in public places where your child could become infected with an airborne disease.
The room must be regularly ventilated and wet cleaned. The child must eat well and maintain a sleep-wake schedule.
The papule that forms on the arm after tuberculin injection should not be combed, bandaged or rubbed with a washcloth.
Contact with water does not affect the test results, so Manta can be wetted.
Source: https://Ukol.expert/privivki/sdelali-mantu-i-rebenok-zabolel
Contraindications for Mantoux
To ensure that the manipulation is beneficial and, most importantly, does not harm the baby, follow the rules and precautions.
There have been cases when Mantoux was administered and the child became suddenly ill due to associated complications. As it turned out, there are contraindications to the test, under which it should be abandoned:
- Skin diseases of any nature (in this case, a hyperergic reaction, that is, AGAT, which was discussed above, will deviate from the normal course and lead to undesirable effects).
- Infectious diseases, both acute and chronic: sore throat, acute respiratory infections, influenza.
- Quarantine among children: a common consequence of a chickenpox outbreak.
In the above cases, the test is either canceled or carried out after a certain period, when there are no reasons for refusal.
Why do a Mantoux test every year?
The Mantoux test is used throughout the world, including in Europe and North America, as a screening test to detect tuberculosis infection. In domestic practice, annual testing using the Mantoux test has been introduced since 1975. Screening is the examination of large groups of the population in the simplest and most cost-effective way to identify patients in need of medical examination and care.
The purpose of these tests is to evaluate the immune system's response to tuberculin entering the body. Tuberculin is a substance containing fragments of the wall of killed tuberculosis bacteria and substances from the nutrient medium on which the mycobacteria were grown. The Mantoux test is a small intradermal injection, the injected drug remains under the top layer of the skin. It should not be confused with vaccination.
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
An ardent supporter of flu vaccination and Mantoux tests is Dr. Evgeniy Komarovsky. And there is logic in his zeal, because thanks to vaccination and inoculation, the increase in morbidity and mortality has decreased by 80%, and life expectancy has increased.
Komarovsky clearly believes that the Mantoux reaction is worth doing. According to him, this makes it possible to diagnose whether a child has tuberculosis or not. In case of a positive response to the administration of tuberculin, hyperemia will occur against the background of allergies and an increase in temperature. The body will show a defensive response. And, conversely, in the absence of contact with viruses, it will “keep silent”, and the effect of the vaccination will not appear outwardly.
How to evaluate the results of the Mantoux reaction?
Starting from the age of one year, the child is given a tuberculin test annually. The doctor measures the transverse size of the “button” three days after the administration of tuberculin and sums up the results. The “verdict” can be: the reaction is questionable, the reaction is negative, or the reaction is positive. In turn, a positive test can range from “weakly positive” to “strongly expressed”. Based on the results of the Mantoux reaction, doctors identify children who are infected (not sick!) and not infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Many of you have heard the word “turn” from doctors, what is it?
The Mantoux test is a positive reaction that occurs for the first time (the diameter of the “button” is 5 millimeters or more). Virus occurs in children infected with Koch's bacillus.
If, based on the results of the Mantoux test, the doctor suspects infection with tuberculosis, the child is sent to an anti-tuberculosis dispensary for consultation with a phthisiatrician and additional research.
What to do and how to treat correctly
Sometimes after performing Mantoux, a child can experience a significant increase in body temperature. This usually indicates a hyperergic reaction. Then the following symptoms will be added to hyperthermia:
- button size – more than 15 mm;
- severe itching at the injection site;
- redness.
In this case, you should immediately contact a phthisiatrician.
If the temperature rises, but nothing happens at the injection site, then there is no need to bring the temperature down to 37.5 degrees. After a couple of days she will return to normal on her own.
A temperature above 38 degrees signals the onset of a cold. It needs to be brought down using an antipyretic. If redness and itching appear at the injection site, the sick child should be given an antihistamine.