Hypertonicity in children
The child's tense muscle tone causes a limitation in the infant's spontaneous and voluntary motor activity. Nine out of ten children are born with a similar pathology, because their body has not “rebuilt itself for an autonomous existence.”
Causes of tone disturbance
Deviation of muscle tone from the norm in infants is due to the fact that the child, while in the mother’s tummy, did not receive enough oxygen or B vitamins. Reasons also include:
- illnesses of a woman during pregnancy, stress and toxicosis;
- complicated, protracted or rapid labor, its stimulation or caesarean section;
- birth injuries;
- influence of toxins;
- bad ecology;
- blood incompatibility, etc.
Symptoms and signs
Violation of the infant’s weight gain is noticeable due to external indicators. The first signs of hypertension are:
- restless behavior (crying with a trembling chin);
- poor sleep;
- a sharp and irritated reaction to dull sounds and dim light;
- constant regurgitation after breastfeeding;
Arching and throwing back the head indicate hypertonicity
- arching, throwing back the head;
Hypertonicity is observed in the first six months of life in a healthy child.
- constantly bent (even in sleep) legs and arms;
- torticollis and uneven folds of the buttocks are noticeable.
Method for detecting hypertonicity: take the child under the armpits and place him on a flat surface. A healthy child will stand on his entire foot, but if the baby walks “on tiptoes” - this is a sign of hypertonicity
While your baby is awake, it is also easy to notice symptoms of muscle dysfunction. Take the child under the armpits and place him on a flat surface. The baby's gait reflex should work. A healthy child will stand on his entire foot, but if the baby walks “on tiptoe”, this is a sign of hypertonicity.
Signs of hypertension:
- sleep disorders: the child sleeps restlessly and often wakes up;
- in a lying position: the child’s head is thrown back, arms and legs are tucked, the child’s whole body is arched back, arms, legs and chin are shaking;
- the hands are clenched into a fist, with the thumb inside the fist;
- even weak light and quiet sounds irritate the child;
- frequent regurgitation after eating;
- walking “on tiptoes”: when the child is lifted, holding him by the armpits, and placed on his feet on a flat surface, he does not stand on his entire foot, but only on his toes.
- During sleep, the head is tilted back, arms and legs are tucked. If you try to separate them, you will feel resistance; when you try again, the baby will start crying a lot;
- the head is most often turned to the side;
If you notice any of these signs, consult your doctor. The sooner you take treatment, the more effective it will be.
Pathology or normal?
You need to know that until 3 months of life, the baby has obvious physiological hypertonicity. After birth, the baby maintains the fetal position, which causes this disorder. If the muscles are not very tense, it means that hypertonicity is within normal limits. The legs and arms can be easily straightened and the fists unclenched. Muscle tone decreases over time. This adaptation process takes place by the age of six months.
Pathological hypertonicity manifests itself in the fact that the nervous and muscular systems of the newborn develop incorrectly.
Let's take a closer look at some treatment methods
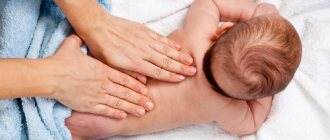
Massage
Conditions required for massage to a newborn:
- the room should be well ventilated and free from drafts;
- air temperature from 20 to 23 C˚;
- comfortable, strong table;
- Before the massage, you must thoroughly wash your hands and remove jewelry from them.
Massage should be carried out when the child is calm. If he cries and is capricious, calm him down and wait until he returns to normal.
- Do not perform exercises immediately after the baby has eaten or just woke up;
- Avoid patting and chopping movements;
- use baby massage oil.
The duration of the procedure for infants up to 3 months of age is 5 minutes, for those older - 10 minutes. During the first year of life, massage is performed once every 4-5 days.
Massage techniques:
- Using rubbing movements, massage the child’s arms from the shoulder to the toes, and the legs from the foot to the groin.
- "Lulechka." Place your baby on his back and your palms under his head and back. Smoothly and gently rock the baby to the right and left, forward and backward. Now place your palms under your baby's buttocks and legs and repeat the movements.
- "Rock." Take the child under the armpits and gently rock him to the right and left.
- When massaging your arms and legs, make movements “away from you” with the back of the hand, and “towards you” with the inside.
- Massage the baby's hands by holding his hand in your hand so that the hand is parallel to the baby's body.
- The following exercise for the baby's arms and legs helps a lot: take the baby's limb between your palms and gently make rubbing movements back and forth.
- Grasp the child's limb with your palm and make several squeezing movements.
- The limb massage should be completed with light shaking movements and stroking.
Gymnastics
During the first year of a child’s life, physical therapy is carried out in courses of 15-20 days in a row with breaks of 1-1.5 months. Gymnastics should be carried out smoothly, do not use active exercises, since they stimulate the muscles, and our goal is to reduce muscle tone. When performing exercises with passive movements, do not perform the exercises “through force”.
Types of muscle hypertonicity
The most noticeable MT disturbances in a child are in the legs and arms.
For children with hypertonicity of the legs, walkers and jumpers are contraindicated
- Hypertonicity of the legs affects the speed of development of motor activity in general. Newborns with this pathology crawl and take their first steps later. Walkers and jumpers are contraindicated for these children, as they, on the contrary, increase stress.
- Hypertonicity of the arms is expressed in muscle resistance when the arms are moved away from the chest, but the fingers are tightly clenched into a fist.
- Increased tone of the neck muscles is caused by the general tension of the muscles of the infant. Usually the cub holds its head tilted to the side, but not if there is a problem in the ligaments or muscles.
It is important to know! Hypertonicity in an infant goes away within six months, otherwise the help of a doctor is necessary.
Why is hypertension dangerous in infants?
- Speech pathologies;
- Incorrect posture;
- Disturbances in the respiratory system;
- Slowing down the overall development of the body;
- Incorrect formation of gait;
- Motor skills disorders;
- Possible cerebral palsy;
- Brain development disorders.
Hypertonicity of the legs:
Babies with this disease begin to walk and crawl later. Such increased muscle tone in infants is especially dangerous for the development of the motor system. For children with this diagnosis, walkers and jumpers are contraindicated, since the load will be distributed on the pelvic muscles and spine .
Hypertonicity of the hands:
Signs: hands are tightly clenched at the chest, when you try to unclench them, strong resistance arises. If this muscle tension persists for a long time, consult a doctor.
Treatment
Which treatment method is preferred depends on the age of the baby and the degree of the disorder. The doctor may prescribe:
- massage;
- gymnastic exercises;
- healing baths;
- swimming;
- electrophoresis.
Massage
Performed by a professional children's massage therapist. The specialist knows where to use a relaxing massage and when to apply an intense massage. In 10 standard sessions, the baby’s muscles should return to normal.
Massage has a beneficial effect on the baby's health
After the massage, a caring mother can continue the treatment with gentle, calm stroking and touching. A soothing voice will relax the baby.
Massage technique
Gymnastic exercises
Set of exercises
- Use your palm to stroke the arms, legs and back.
- Place the baby on his tummy and rub the skin in a circular motion. Then do the same with the limbs, placing it on the back.
- Take the child’s brush and shake it lightly. The hand needs to be supported in the forearm area. Do this exercise with all limbs.
- Grasp the legs by the shins and rock the baby.
- You need to finish the massage by smoothly stroking the limbs.
Exercises on a fitball will also help relieve tension.
Exercises on a smooth fitball will also help relieve tension. The baby is placed on the ball with his tummy and begins to rock slightly in different directions. A good way would be to stomp or pat the ball with your baby's hands or feet; this will relieve tension and lift his spirits.
Ball exercises for kids (video)
Healing baths
Try to normalize your muscles by taking a bath every few days. Warm water relaxes muscles and removes tightness. It is advisable to add oregano, lavender, motherwort or eucalyptus to it.
The main thing is that the child does not dive, because this will cause stress, which will lead to an increase in the symptoms of hypertonicity.
Methods for determining muscle tone
There are several ways to understand what muscle tone a newborn has.
Pulling on Handles
Place the child on a hard, flat surface, grasp his hands and gently pull them towards you. If his elbows are calmly straightened and his stomach sticks out when sitting, it means he has low muscle tone (hypotonicity). If the elbows still do not straighten, then this is increased muscle tone (hypertonicity).
Tonic reflex
The tonic reflex is a natural reaction of the flexor and extensor muscles to changes in body position. For example, if you place a child on a hard, flat surface, he will begin to “open up,” i.e. try to straighten his limbs, and when you turn him over on his tummy, then, on the contrary, he will begin to “close up”. If there is no reaction to such positions, then this is hypotonicity. If such a reaction persists in a child older than 3 months, then this is hypertonicity.
Symmetrical and asymmetrical reflex
A symmetrical and asymmetrical reflex should normally persist in a newborn for up to 3 months. Place the baby on his back, and your palm on the back of his head and slightly tilt his head towards his chest - the baby should straighten his legs and bend his arms. Now turn your head to your right shoulder - the baby should extend his right arm forward, straighten his right leg, and bend his left. Now turn your head to your left shoulder - the baby should repeat the same thing in a “mirror” version. Absence of the reflex - hypotonicity, persistence of the reflex after 3 months - hypertonicity.
Support reflex
Take the baby under the arms and try to put him on his feet on the changing table, slightly tilting him forward, as if pushing him to take a step forward. Normally, the baby should rest on a flat foot with straightened toes. If the baby refuses to walk or instead of standing, he crouches, it means he has hypotension. If the baby rests only on his toes instead of a straight foot, it means he has hypertonicity.