The nervous system is the leading physiological system of the body.
Neuropsychic development (NPD) is an improvement, a qualitative change in the intellectual and motor skills of a child. At the time of birth, the nervous system of children has this characteristic:
By the time of birth, a healthy full-term newborn child has a well-developed spinal cord, medulla oblongata, brainstem, and hypothalamus. Life support centers are associated with these formations; they ensure the processes of adaptation and survival.
By birth, the GM is sufficiently developed, the mass of the GM is 1/9 of the body weight. Large grooves and convolutions are very well expressed, but have shallow depth. There are few small furrows; they appear only in the first years. The size of the frontal lobe is smaller, the occipital lobe is larger in relation to adults. The length of the spinal cord increases somewhat more slowly than the growth of the spine.
Brain tissue has a histological immaturity of nerve cells; they are oval in shape, with one axon, the nuclei are granular, and there are no dendrites.
The GM cortex is relatively immature, with incomplete myelination of the pyramidal tracts.
The cerebellum is poorly developed.
2. The first two years of life
Intensive growth and development of GM.
3. First half of the year
The differentiation of the striatal nucleus and pyramidal tracts ends, and therefore the rigidity of the nuchal muscles disappears, spontaneous movements are replaced by voluntary ones.
4. Second half of the year
The cerebellum grows and develops rapidly and is completed by the age of 2 years.
Neuropsychic development of a child under one year of age
Key indicators that are assessed in the first six months of a child’s life:
- 1 month. The baby may not fixate his attention for a long time and follow bright, shiny objects. A clear reaction to loud sounds is visible: he shudders slightly. Parents can see the baby's first smile. You can also record an attempt to hold up your head if the baby is lying on his stomach.
- 2 month. The baby can already continuously follow the toy that moves in front of his face and listens to sharp sounds. The baby can already respond with a smile to the adult’s stories and respond to them. Among the additional acquisitions, you can find that he already holds his head well for several minutes.
- 3 month. The baby can already fix his gaze on any object and examine it well. Additionally, there is also the ability to record hearing. Parents talk to the child, and he answers them with a smile or movements of his legs and arms. The child can fix his head for several minutes if he is in a prone position.
- 4 months. During this period, the baby can already recognize his parents, turn his head in all directions and respond to sounds. From time to time you can hear loud and boisterous laughter. The baby can independently roll over from his stomach to his back. If necessary, he can pick up a toy or rattle. This period is also characterized by the so-called humming.
- 5 months. The baby already recognizes his loved ones well, so he does not go into the hands of strangers. He can stand on his feet, periodically tucking them in, with the help of adults. His grasping reflex and periodic attempts to speak are becoming increasingly evident.
- 6 months. The child can not only roll over from side to side, but also pick up a toy. Syllables appear in speech that parents can clearly recognize. During complementary feeding, he confidently eats from a spoon.
Baby's reaction to sound
A child continues to actively develop in the period from six months to six months. Parents can record obvious mental development and changes in emotional state:
We recommend reading: How to develop a child up to one year old
- 7 month. The baby is already crawling quite well. He begins to gradually play with various objects, periodically moving them from place to place. Parents can already hear clear pronunciation of individual syllables. He can be taught to drink from a special cup and show certain objects that are in his field of vision.
- 8 months. The baby begins to stand up, sit down and move around independently. You can keep him busy for a long time with interesting toys. You can observe how he independently tries to pronounce individual words or syllables. He can be trained to hold small objects and perform certain actions, such as the “goodbye” gesture.
- 9 months. The child is able to walk independently on two legs with the help of additional support. Can arbitrarily perform various actions with interesting objects. In babbling, you can already clearly hear individual syllables and even words. The baby reacts to his name and can show the location and direction to a specific question. He can also drink from a regular cup. Parents only need to hold her lightly.
- 10 months. Children at this age should already be able to climb onto a low surface on their own. They also figured out how to open certain boxes and doors. With their speech, they try to be like adults, so they even parody their timbre. By this time, the baby should already utter his first words, drinks from an ordinary cup and understands all the requirements of an adult.
- 1 year. Most often, during this period, the children already walk on their own and clearly pronounce about ten words. The baby independently takes a cup, drinks from it and fulfills some of the adult’s requirements.
It is important for the baby to establish neuropsychic contact with his mother. Thanks to this, he will be able to become more socialized and adapt to all environmental conditions. As he grows up, his visual and auditory perception of the world will improve. It is important for parents to create a positive set of emotions. They must support him in all endeavors, form correct speech and be a good example.
General table of child development in the first year of life
It is important to regularly check and compare the developmental characteristics of your baby with the normative ones. If necessary, you should help him develop the necessary skills. Overwork should not be allowed, because it negatively affects the baby’s health.
Prenatal period and first days of life
The nervous system is formed in the third or fourth weeks of fetal formation, then goes through four main stages:
- First, the neural plate appears. The edges of the plate then close to form the neural tube.
- The spinal cord develops from part of the neural tube, the other (anterior) part is divided into several brain vesicles.
- Nerve cells move and distribute.
- Myelination of pathways occurring sequentially in the brain, then in the spinal cord.
Three months before birth, the fetal brain is already sufficiently formed, including the cerebral cortex. The nervous system is already capable of normally ensuring the intrauterine existence of the organism. The newborn's brain is well supplied with blood, but its tissue contains a lot of water, which can cause complications in diseases, such as edema. The gray matter of the brain is poorly separated from the white matter, the most immature is the cerebral cortex - it is fully formed only by 5-6 years.
A newborn, barely born, already has innate reflexes that help him tune in to the environment, helping him adapt to it. From the moment of birth, he reacts to stimuli: light, temperature, pain, but these reactions are not coordinated and cause a response in the form of movements of the whole body. This indicates that arousal easily moves from one part of the brain to another.
The reflex reaction to hunger, cold and pain is to scream. This is a mechanism inherent in nature and promotes the survival of the baby. Touching the lips causes the second main reflex - sucking, as a result of which inhibition spreads to areas of the brain, lasting the entire period of satiety. Therefore, after eating, the baby usually falls asleep. In the first days of life, the cortex is not involved in the reaction to stimuli, but its cells can be excited by impulses coming from the underlying parts of the brain. Basically it is the distinction between light and individual colors.
The neuropsychic development of children under one year of age has its own characteristic features. In the first couple of years, the brain grows rapidly, its mass increases due to the formation and branching of axons and dendrites. The cerebellum, which is responsible for the coordination of movements, grows most rapidly, and myelination of nerve fibers occurs - they are covered with a fat-like substance - myelin, which is responsible for insulation. As this process progresses, the conductivity of nerve cells increases and the formation of new neural connections accelerates.
Features of the development of auditory and visual reactions
After the baby is born, his auditory and visual analyzers are well developed. However, he cannot move well or react correctly to certain objects. Until the age of 1 year, he still learns to fix his gaze on a specific object. Parents will be able to notice how every day he begins to follow a certain subject better and better. Immediately after birth, its capabilities are short-term and not stable enough. Over time, the baby will be able to follow any object that is currently in motion.
The possibilities of hearing are becoming greater every day. Three months after birth, the child is already listening and trying to understand where this or that sound wave is coming from. He understands well not only the meaning of words, but also the tone in which they were spoken.
Knowing the world and yourself
Stages and patterns of CPD
Four laws of the formation of mental functions according to Vygotsky:
- The child's psyche develops in its own rhythm, this process is complexly organized in time, its pace can change. The year in infancy and adolescence differ significantly in importance.
- Development is a sequence of qualitative changes. A baby should not be perceived as a small likeness of an adult, simply with less life experience: this is a qualitatively different creature in its mental parameters.
- Different mental functions are formed unevenly, each of them has its own optimal time.
- Higher mental functions initially arise in communication with significant people as a form of group behavior, and only then are “appropriated” by the psyche of the smallest person, becoming his own.
Vygotsky believed that learning is the main factor in mental progress. He discovered the so-called “zone of proximal development”: this is the difference between the level that exists now and where the skill could be improved with the help of correctly selected tasks. This means that good learning involves slightly more complex problems than the child is ready to solve at a given level. It is necessary that he constantly overcome himself a little, do previously impossible things, thus moving forward all the time, without stopping there. The ideas that Vygotsky proposed were then developed by other Russian psychologists, such as B. D. Elkonin, A. N. Leontyev, L. Ya. Galperin and others, who laid the foundations of Russian developmental psychology.
Child development psychology, or age-related, identifies the main stages that the child’s psyche goes through in the process of formation:
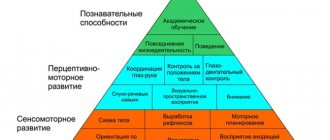
- Mastering fine and gross motor skills. The neuropsychological development of children from birth to 1 year is characterized by the emergence of basic movement skills.
- Sensory perception. A child under three years of age develops skills in responding to the perceived world.
- Thinking. From three to twelve years of age, a child learns to think and think individually.
- The final formation of the psyche, the formation of personality, occurs from twelve to fourteen years.
Each age period has its own leading activity, in which a restructuring of basic mental processes occurs, changing over time under the influence of new emerging motives that encourage children to change their position in the surrounding community of people.
There are certain visible signs that the child’s psychological development is within normal limits; every parent should know them. The mental development of children under one year of age is particularly intense, with new changes occurring every month. However, the given time frames are very approximate: if something happens a little later, this is not a cause for concern. Some skills may be ahead of the curve, while others may be a little behind.
Features of the formation of emotional reactions
It should be noted that in a child in the first months of life, only a negative reaction to a change in circumstances can be recorded. He can express his dissatisfaction through loud crying and screaming. Actions are necessary for the mother as a signal and to attract attention. After this, he waits to return to his previous comfortable conditions. Over time, parents begin to understand that their child requires food and changing diapers.
Over time, over the months, you will be able to notice the baby’s reaction to the parents’ conversation. He can smile, laugh. The baby's reaction will be exactly the same as that of an adult. To further attract attention, he may also throw back his arms and babble happily. In medical practice this is known as revitalization, which occurs in a complex manner.
At five months, orientation in space should already be clearly visible. Thanks to this, he can distinguish mom and dad from other adults. You can notice the manifestation of a certain set of emotions and reactions towards close people. Quite often you can notice resentment if the necessary attention is no longer given to him.
After a certain time, new people also become interesting to him. In relation to them, the baby can show a wide variety of emotions and feelings. They can be both positive and negative. The manifestations become clearer and more intelligible every month.
Interaction with other children is taken into account
Cognitive activity in a baby begins around six months. He begins to regularly manipulate various objects or toys. Parents may notice periodic curiosity that allows the child to explore the world and obtain necessary information about it.
At nine months, the baby’s emotional state should already be fully formed. It becomes more difficult for him to establish a connection with a complete stranger. You may notice occasional timidity and shyness. He must build relationships with people due to his growing curiosity.
Caring for a newborn baby
In the first month of life, special attention is paid to caring for a newborn baby, especially the umbilical wound.
Child care consists of regular hygiene and hardening procedures.
Hygiene procedures consist of regular and timely cleansing of the skin, changing wet diapers and diapers, bathing, and treating the umbilical wound. It is also necessary to keep your ears, eyes and nails clean and healthy.
Hardening activities during the newborn period consist of regular walks in the fresh air and air baths.
You can read about the intricacies of caring for a newborn baby in the article - The basics of caring for a baby: what do you need to know?
Formation of the movement
Immediately after the baby is born, his coordination and ability to move over long distances improve. He will be able to gain full control of his arms and legs by the third month. This will manifest itself in the form of attempts to grab one's nose, touch one's face, or pick up a toy. Parents may notice how periodically he picks up the edge of a blanket or diaper. The child cannot yet grab the toy, so he simply clenches his hand into a fist and pushes it.
If you help him and put the toy in his hand, he will squeeze it very tightly. Thanks to this, pediatricians check the characteristics of the grasping reflex. During this period, he strives to taste any object, so it is important not to let him chew small parts. They can harm the child.
At five months, a child moves almost the same as an adult. However, some of his actions may seem irrational from the outside. For example, to pick up a toy, he can additionally move his legs. That is, actions are not always only necessary. They will be sharpened for up to ten months. After this period ends, the baby will be able to fully control all his movements.
What should a newborn baby be able to do?
Immediately after birth, the organs and systems of a newborn child’s body have an unequal degree of maturity. The nervous system, although ready to function, many of its parts are still poorly developed. For example, visual, auditory, and tactile analyzers are better developed than those that provide coordinated movements.
In the first days of life, many babies can already fix their gaze on the face of an adult, but this is a very unstable reaction. When there is a loud sound or harsh lighting, the child reflexively closes his eyes and shudders. In the second week of life, the baby begins to listen to conversations and can make single, quiet vowel sounds. He recognizes his mother (by her voice, by her smell).
During the first month of life, the baby sleeps most of the day.
The movements of the newborn, at first sharp and convulsive, gradually become smoother, and the physiological hypertonicity of the muscles gradually disappears.
During the newborn period, the baby is in one of three states: sleep, quiet wakefulness, active wakefulness.
On average, a newborn baby sleeps about 18 hours a day. The baby's sleep is intermittent, usually evenly distributed throughout the day. By the end of the first month of life, sleep and eating patterns may begin to develop.
Features of speech development
During the first year of life, the child begins the process of developing speech skills. At the first stage, he can only pronounce individual sounds, which turns into humming. This state is accompanied by a change in the emotional background. Parents will be able to clearly record the manifestation of positive and negative emotions in their baby.
Walking smoothly turns into singing within five months. At the moment, some sounds remain inaccessible to the baby. However, you can record how he carries on a conversation on his own for a long time. Thanks to this, he seeks to attract attention or demonstrate emotions.
By eight months, the child is already learning to distinguish commands and analyzes every word. A connection is observed between visual, auditory, and emotional reactions. Parents can already play with him. Some people manage to teach the baby to wave his arms or clap his hands. At this time, you can already hear baby babble, which is accompanied by an unusual intonation.
Children pronounce their first word before they are one year old. It usually consists of two identical syllables. The child begins to quickly improve his acquired skills, so soon he will have several words in his arsenal.
Newborn nutrition
The best thing for a newborn baby and a child of the first year of life is mother's breast milk. It contains all the necessary nutrients, vitamins and microelements.
The first breastfeeding is carried out a few minutes or hours after birth (if there are no contraindications), but no later than 24 hours after birth.
A newborn's stomach is very small, so he needs to be fed frequently, about 6-7 times a day, which is approximately every 3-3.5 hours. Currently, the free feeding method is widely practiced - this is when the baby suckles at the breast as often and for as long as he wants.
When breastfeeding, the baby usually regulates the required amount of milk himself. To roughly calculate the required amount of breast milk, you can use several methods.
Up to 7-8 days of age:
Formula Tour
Milk volume = n x 70 (with a newborn’s body weight less than 3200 grams)
Milk volume = n x 80 (with a newborn’s body weight over 3200 grams)
n – child’s age in days.
For an older child
Volumetric method
The required daily amount of food for a child aged 7-10 days to 2 months should be 1/5 of body weight.
At the end of pregnancy and in the first days after the birth of the child, colostrum is secreted from the mother's mammary glands. Colostrum is a thick, yellow liquid that is very nutritious and high in calories. Transitional milk appears at 4-5 days of life, and from 2-3 weeks mature milk begins to be released.
The milk that the baby receives during one feeding is divided into: earlier (at the beginning of feeding) and later (at the end of feeding). Earlier milk is more watery and contains a lot of protein and lactose. Late milk is rich in fat.
While breastfeeding, take a comfortable position; proper breastfeeding should not cause discomfort to either the baby or the mother.
Physical development table
The development of various skills is approached comprehensively, taking into account the child’s motor abilities depending on age. Assessment of the physical development of the infant includes several parameters:
- Body length increases faster in boys. Growth slows down after birth and may be more intense in the lower extremities. The first three months it increases by 3 cm in 4 weeks, then up to six months the figure is 2.5 cm, the next three months - 1.5 cm. From 9 months to a year the increase is 1 cm per month.
- Body weight - the first six months increases by 800 g, then up to a year - by 400 g. For each extra cm of height, 300 g of weight is added.
- Head circumference - up to 6 months increases by 1.5 cm, then up to a year - by 0.5 cm.
- The chest circumference increases by 2 cm up to six months, then by 0.5 cm up to 12 months.
- Changes in body proportions can be calculated using the Body Condition Index. To the three shoulder circumferences the thigh and shin circumferences are added. Height is subtracted from the resulting number. For infants, the norm varies between 20-25.
Approximate changes in parameters occur in accordance with the table:
| Age (months) | Body length(cm) | Weight, kg) | Head circumference (cm) | Chest circumference (cm) |
| At birth | 49-54 | 2,6-4 | 33-37 | 31-35,9 |
| 1 | 52-55 | 3-4,3 | 35,8-37,2 | 34-36 |
| 2 | 55-57 | 4,5-5 | 37,5-38,5 | 36-38 |
| 3 | 58-60 | 4-6 | 38-40 | 36-39 |
| 4 | 60-63 | 4,5-6,5 | 38-40 | 36-40 |
| 5 | 63-67 | 6,5-7,5 | 37,5-42,2 | 37-42 |
| 6 | 65-69 | 7,5-7,8 | 42-43,8 | 42-45 |
| 7 | 67-71 | 8-8,8 | 43,8-44,2 | 45-46 |
| 8 | 71-72 | 8,4-9,4 | 44,2-45,2 | 46-47 |
| 9 | 72-73 | 9,4-10 | 45,2-46,3 | 46,5-47,5 |
| 10 | 73-74 | 9,6-10,5 | 46-47 | 47-48 |
| 11 | 74-75 | 10-11 | 46,2-47,2 | 47,5-48,5 |
| 12 | 75-76 | 10,5-11,5 | 47-47,5 | 48-49 |
When assessing the growth of an infant, you need to take into account the time of year: in spring and summer, changes are higher compared to autumn and winter.