Prevention
The baby should receive all the necessary substances with food appropriate for his age.
At the same time, it is undesirable to give a child sweets under three years of age (except for marshmallows and marshmallows), and also carefully introduce highly allergenic foods into his diet, monitoring the reaction
If a child has a complicated heredity, then to prevent scrofula it is necessary to include in the child’s diet as often as possible nettle soups, strawberries, coffee made from acorns or chicory based, and oatmeal. To prevent the disease, you can also periodically give your child herbal decoctions used in treatment, in particular, an infusion of plantain or black currant leaves.
With proper treatment, scrofula cannot be called a dangerous disease. But so that its appearance does not bring discomfort to either the child or the mother, you should adhere to a few simple rules:
- ensure that the premises are ventilated and there are no allergy-causing factors in the home;
- the child should often be outside;
- The child’s diet should be rich in vitamins and microelements (vitamins A, B, C, D);
- if the mother of a baby discovers symptoms of diathesis, she should exclude sweets from her menu (especially foods such as chocolate and cocoa), red fruits and vegetables and other allergens, reduce the consumption of dairy products and eggs, poultry;
- It is not recommended to give infants plant foods in order to protect them from the appearance of scrofula.
By following these simple steps, you can ensure the safety of your child and save yourself from unnecessary worry. And remember that scrofula is not terrible, you just need to start treatment immediately when it is detected, and everything will be fine.
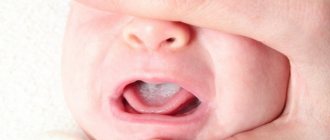
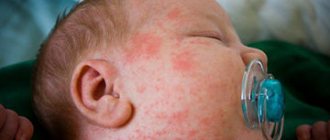
It gets wet behind the ears of a baby (scrofula)
Carefully examining the skin of their babies, parents often notice small spots or yellow crusts behind their ears. They can cause discomfort and itch for children. Such manifestations are called scrofula.
What is scrofula?
Doctors explain the origin of this disease in different ways. Sometimes we are talking about disorders in the immune system. There is also an opinion about a mild form of tuberculosis caused by the tuberculosis bacillus. However, the most reasonable and widespread point of view is that scrofula is a form of atopic dermatitis.
This unpleasant phenomenon is expressed by small spots or golden crusts behind the ears. Over time, these crusts begin to peel off, revealing wet, pink or reddened areas of the baby’s skin.
Causes of scrofulous crusts
- An abundance of fatty, fried and floury foods in the diet of a nursing mother.
- An unbalanced diet for the child, a large amount of sweets.
- Incorrect mixture.
- Alcoholism, which affects the mother of the child.
- Chronic malnutrition of the baby.
- Lack of fresh air and light.
- Hereditary factors - cancer, syphilis or tuberculosis in the father or mother.
- The child's parents are not young.
- Distressed family conditions.
It is quite possible to cure scrofula if it is not neglected. But the longer the disease is left unattended, the more difficult it becomes for therapy.
If scrofula is detected in time, it goes away without a trace; you just need to contact a pediatrician, who will prescribe treatment.
Treatment of scrofula
Diet . This requirement applies to both the child and the mother if she is breastfeeding.
By excluding sweet, fatty, flour, smoked and fried foods, we will achieve a significant effect in eliminating itchy crusts.
Sometimes this is enough to extinguish the manifestations of the disease, since for children living in satisfactory sanitary and hygienic conditions, it is diet that becomes the decisive factor in recovery.
Cleansing the body . The doctor may prescribe enterosorbents, for example Enterosgel. They remove allergens and help your baby get rid of unpleasant symptoms.
Strengthening the immune system . It is better not to use synthetic vitamins, eat more vegetables and fruits, and whole grain cereals. Regular consumption of carrot juice and a decoction of black currant leaves is effective against scrofula. It would be good to include foods containing vitamins A and D in your daily diet.
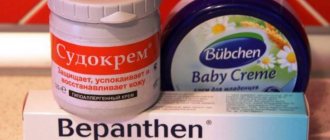
Quite often, doctors prescribe ointments for children to relieve itching and heal the skin. Zinc ointment or Bepanten effectively fights the external manifestations of scrofula.
If the disease is advanced, you have to resort to more radical measures, such as cauterizing the affected areas of the skin with fucorcin.
Scrofula in children behind the ears: photo and treatment of cracked, weeping and flaky skin
In the process of carrying out hygienic manipulations, it is necessary to pay attention not only to the ears, but also to the space behind them. When taking a bath, you need to lower the baby's head into the water so that only the face remains on the surface, this will soften the crusts and remove them without any problems.
Immediately after water procedures, you need to take a piece of bandage, wrap it around your finger, moisten the material in vegetable or medicinal pharmaceutical oil (for example, sea buckthorn) and treat the clean and dry skin behind the baby’s ears. Tip: Increased attention to the area behind the child’s ears should be paid in summer months
If sweat constantly accumulates in the hidden area, the baby will suffer from diaper rash, irritation and inflammatory processes. In some cases, you can even use powder to prevent moisture buildup.
Tip: Increased attention should be paid to the area behind the baby's ears during the summer months. If sweat constantly accumulates in the hidden area, the baby will suffer from diaper rash, irritation and inflammatory processes
In some cases, you can even use powder to prevent moisture buildup.
After a few minutes, carefully wipe the treated areas, removing any remaining plaque and medication.
Such manipulations are also good for preventing the condition. As a last resort, it is recommended to wipe the problem area every day with a cotton swab dipped in warm water. Twice a week we apply moisturizing cream or a little vegetable oil to the skin to soften the tissues.
Scrofula in children behind the ears
Scrofula is the name of exudative diathesis, known since the time of our grandparents, which is considered a manifestation of dermatitis at an early stage. Basically, this disease affects the area behind the ears and most often affects children from two to ten years old. Scrofula behind the ears in infants is much less common.
Scrofula behind the ears - causes of occurrence
- In most cases, the main causes are hereditary predisposition. Children whose parents suffered from syphilis, tuberculosis and various cancers have a high risk of developing scrofula.
How to treat such unpleasant scrofula behind the ears?
For topical use, sudocrem, zinc ointment, bepanthen or fucorcin are recommended. Traditional medicine recommends bathing the baby every evening in decoctions of medicinal plants (oak bark, tricolor violet, etc.) to relieve itching and inflammation. Infusions and decoctions are also used internally (for example, coltsfoot).
womanadvice.ru
- Scrofula in adults
- Gneiss in adults
If an adult gets wet behind the ears, it can be a symptom of various diseases. First of all, weeping skin indicates the presence of some kind of skin disease, so treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
Often, constant moisture behind the ears can be accompanied by itching, peeling of the skin, irritation and burning. The causes of a constantly weeping area behind the ear are determined using secondary symptoms.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
Scrofula in adults
Scrofula most often occurs in children, but any adult is not immune from this disease. Why is it necessary to promptly treat scrofula? Although the disease itself is not terrible, tuberculosis can become a complication, and the infection easily spreads to the brain and causes life-threatening inflammation there.
Scrofula is a disease of the circulatory system, affecting joints and bone tissue, as well as the lymphatic system. Its symptoms appear on the skin: behind the ears in adults most often.
If left untreated, scrofula on the skin can spread to other areas of the body. The skin affected by the symptom of scrofula is very itchy and becomes golden in color, a crust forms on it, which may come off over time.
The skin at the site where the crusts form is very flaky, and after they disappear, it turns pink and constantly gets wet.
Cracks behind the ears in the area of weeping ulcers are quite dangerous: the infection can not only penetrate the blood, but also spread to the internal organs of the ear, and then through the nasopharynx to the brain, which is deadly. The danger of scrofula in an adult is that the disease may not appear immediately.
Scrofula is not an infectious disease and is not transmitted from person to person through skin-to-skin contact or airborne transmission. Main causes of the disease:
- improper diet with a lack of vitamins;
- low immunity due to lack of physical activity;
- insufficient skin care, especially in the area of the ears and ear canal.
Features of treatment for children of different ages
As a rule, therapy for this disease does not depend on the patient’s age. If you suspect scrofula or diathesis, the skin is dry, cracking, or wet wounds appear behind the ears, you should contact your pediatrician as soon as possible (see also: dry skin on the legs and arms of a child). He will refer you for consultation to a pediatric dermatologist and allergist.
Experts will determine the cause of the sores and cracks. A special diet will be developed.
The next stage is the prescription of medications to relieve itching and remove crusts. If left untreated, a secondary infection may develop due to constant trauma to the skin when scratching; the wound behind the ears rots and enlarges. With timely treatment, scrofula can be cured in a short time.
It is important to strengthen the child's immunity. The defenses of a healthy baby’s body are able to cope with scrofula on their own.
Drug therapy
- Ointments. For the treatment of scrofula, Sudocrem, Tsindol, zinc ointment, Topicrem, Drapolene are used. They dry the wet crusts well, which then come off easily. Typically, these products are applied 2-4 times a day to clean skin, without washing off for several hours.
- To moisturize the skin with cracks and dryness, Bepanten is used.
- Cauterization with Fukortsin. This is a crimson-colored drug that effectively disinfects and cauterizes disease-affected skin. The child may complain of a burning sensation in the areas treated with Fukortsin. It is used if there is no improvement after 3-4 days of treatment with ointments.
- Enterosgel and other sorbents are used to remove toxins and cleanse the body. They also remove allergens.
Hygiene procedures
When scrofula does not cause symptoms other than crusts on the scalp and does not progress, it may not be treated. In this case, they get by by simply combing out the scab, that is, the crusts. Before this, the skin is generously lubricated with nourishing baby cream or Vaseline oil, and they are combed out with a regular comb. When removing crusts from a child under one year old, you need to be careful not to damage the fontanel.
Conspiracies for scrofula
Some tried to cure scrofula through magic, reading spells. In the old days, it was important to resort to magical help for all issues, not only for the treatment of scrofula.
This plot is read at sunset over a patient with scrofula:
So that the eyes look, the ears do not hurt The servant of God (name), rolled away, fell off to foreign shores, into dirty water, into damp bad weather. Zolotukha is an evil old woman, leave behind God’s servant (name). Amen.
On the sea-ocean, on the island of Buyan, there lies a stone forty fathoms, and on this stone a girl sits, inventing scrofula. Scrofula-rubella, you should not be here, you should not live here, you should not break bones, you should not rot your joints. Amen
Nowadays it is foolish to believe that wearing earrings or touching the hand of a healer will get rid of scrofula. Resorting to conspiracies is also illogical. Medicine has long proven its ability to quickly and reliably get rid of scrofula. Treatment of scrofula is simple, but you should carefully and strictly follow your doctor’s recommendations.
Symptoms
To establish the cause of changes in the skin behind the ears, you should first pay attention to the symptoms. After all, every disease has certain signs by which one can draw a conclusion about the existing diagnosis.
First, the doctor interviews the parents or the child who is already quite old. This is necessary to identify provoking factors, information about the onset of the disease and its course, as well as subjective signs (complaints). A physical examination is then performed with local and general examination.
Diaper rash
Overweight babies often have diaper rash. They appear in areas of the skin subject to constant friction, where there is increased humidity, including behind the ears. At first there is simply redness, then small cracks appear. In this place, weeping develops, crusts form, and later an infection (pustules) may develop. The baby becomes restless because it brings him discomfort.
Exudative diathesis
Exudative diathesis is understood as a pathologically altered reaction of the child’s body to unfavorable environmental factors: food, microbes, chemicals, medications. This is manifested by an increased tendency to allergic or inflammatory damage to the skin and mucous membranes. Symptoms of diathesis are usually caused by sensitization to food products (cow's milk, eggs, citrus fruits, strawberries, chocolate, etc.). In the area of the scalp, on the cheeks, behind the ears, first redness appears, then itchy blisters with clear liquid. Over time, they burst, and in their place yellowish crusts with small cracks and peeling form. Due to the desquamation of the surface layer of the epidermis, the tongue becomes “geographical”. And various spots and papules may appear on the body.
The clinical picture in children with exudative diathesis often includes disorders of other organs and systems:
- Stool instability (alternating constipation and diarrhea).
- Poor weight gain.
- Frequent colds.
- Anemia.
- Rickets.
Therefore, even such a symptom as a rash on the cheeks or behind the ears requires careful attention. You should not think that this will go away on its own - you need to see a doctor for an examination before the situation goes even further.
Dermatitis and eczema
It should be noted that skin lesions are often inflammatory in nature. Infants and adolescents may experience what is called seborrheic dermatitis. It develops on the scalp, eyebrows, behind the ear and in the external auditory canal. Dry seborrhea is accompanied by skin hyperemia, the formation of scales and cracks. Sometimes papules form, merging with each other. The skin thickens, the child feels itchy and tries to scratch the area. When the external auditory canal is affected, a feeling of fullness in the ear may be noticed.
Microbial eczema is characterized by the appearance of blisters, which, after opening, form a weeping surface. The cracks are covered with yellowish-gray crusts. In the future, otitis externa may develop with corresponding symptoms: itching and burning in the ear, discharge from the ear canal, and hearing loss. Eczema from an acute form often becomes chronic.
Fungal infection
The appearance of cracks behind the ears in a child can also be associated with a fungal infection. It is in the nature of dermatitis or otomycosis. The latter is caused by the spread of microbial inflammation from the parotid region to the ear canal. Then you should expect the following symptoms:
- Itching and pain in the ear.
- Noise and feeling of congestion.
- Discharge from the ear.
- Skin redness.
The nature of the discharge is determined by the type of fungus. When examined in the external auditory canal, caseous masses of brown or black color, similar to blotting paper (in case of mold infection), yellowish crusts with cheesy layers or a white film (in case of candidiasis), may be detected. The spread of the process to the tympanic cavity leads to the appearance of otitis media. Then the clinical symptoms will become more pronounced.
Your child’s ear gets wet: why and what to do
Children are the joy and meaning of our lives, which is why we worry so much when children have health problems. In this article we will look at such ailment as weeping rashes behind the ears, their causes and methods of treatment.
Why does a child get wet behind the ear?
This problem is only a symptom of a disease such as weeping diathesis, but not the disease itself. Violation of the skin behind the ears in a child usually occurs at a very young age. This connection between weeping diathesis and early age is explained by a weak immune system, as a result of which children are more susceptible to such diseases than adults.
As soon as you notice a weeping rash behind your child's ears, immediately contact a qualified specialist: a dermatologist or pediatrician.
The reason for the formation of diathesis and the formation of weeping rashes behind the ears in newborns and children under one year old is an incompletely formed digestive system. There are two factors that overload the esophagus:
- Overfeeding. As mentioned above, in the first year of life a child’s digestive system is still developing. When large amounts of food are received, the gastric mucosa cannot cope, producing an insufficient amount of enzymes that break down food. Because of this, the baby’s intestines begin to suffer, releasing harmful toxins into the body. The body's response manifests itself in the form of rashes on the face, near the ear, and especially in the bends of the limbs and folds of the skin, which is a signal that the esophagus is not functioning properly.
- Accumulation of allergic reagent. Here, it is not the quantity, but the quality of food consumed by the baby, and, during breastfeeding, by his mother that is highlighted. When breastfeeding a baby naturally, a woman must adhere to a strict diet, which means eliminating preservatives, large amounts of sweets and starchy foods, and eating foods in small doses that often cause allergies, for example, strawberries, honey, nuts, etc. The mother needs to carefully monitor the baby’s reaction to the introduction of new foods. If you do not follow a diet, a cumulative effect begins to work in the child’s body, which leads to a persistent allergic reaction.
Up to a year, the baby’s immune system is formed, and if the diet is adjusted in a timely manner and the problem that has arisen is treated, then such rashes will remain just a signal and will not develop into an allergic pathology. The appearance of a situation where a child’s skin gets wet and bubbles near the ear does not always indicate the presence of an allergic factor.
Other symptoms of weeping diathesis
Weeping diathesis begins with the appearance of hyperemic rashes near the ear and on other parts of the child’s skin. Redness can be of different sizes: sometimes the size of the hyperemic area is smaller than a coin, sometimes it covers the entire parotid area along with the earlobe.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-Z3O2P6k0l4
The peculiarity of such rashes is that in the area of hyperemia one can observe the appearance of small bubbles filled with colorless liquid.
After some time, these bubbles burst and leave wet patches of skin in their place. With timely treatment, the damaged area becomes covered with a crust and soon disappears.
In an advanced stage and without proper care, microbes and bacteria take root well on the weeping surface of the skin, causing the appearance of a purulent focus.
Advanced areas of weeping diathesis can swell and cause severe itching. Children scratch their ears, not allowing the wounds to heal, bringing in dirt and thereby aggravating the course of the diathesis.
Also, due to itching, babies' sleep is disturbed. If the situation requires, after treating the damaged areas of the skin, you can put a thin cotton cap on the child.
The cap cannot be worn constantly; the child’s skin must breathe and the wounds must dry out.
To reduce the likelihood of weeping diathesis, it is necessary to exclude the following risk factors:
- improper nutrition of the mother during the lactation period;
- unbalanced diet for the baby;
- neglect of the rules for introducing complementary foods;
- taking certain groups of medications during breastfeeding;
- preference for synthetic materials in clothing, non-certified baby care products, which cause skin irritation and allergic rashes.
Treatment
If you notice a rash behind your child’s ear, don’t hesitate, make an appointment with a dermatologist. The doctor will quickly make a diagnosis and prescribe medications that will be intended to treat a specific disease and match the age of your child.
Treatment of weeping diathesis first begins with searching for the cause of the rash: in addition to a visual examination, the dermatologist will ask questions about the child’s diet and any allergies he has. At the stage of searching for the cause, a dermatologist may recommend visiting an allergist and immunologist. These specialists will identify the allergen that causes diathesis in your child.
By eliminating histamine and leveling the allergic background, treatment will quickly give positive results.
Since the treatment of weeping diathesis is complex, your child will be prescribed ointments or creams for external use. These medications are prescribed purely individually and only by a doctor.
If you need to slightly alleviate the symptoms of weeping rashes behind the ears in a child before you see a dermatologist, you can wipe the damaged areas with an antiseptic, for example, Miramistin, and then lubricate the entire area with Bepanten cream.
Do not cover wounds with adhesive tape under any circumstances; the skin must breathe.
In folk medicine, there are a huge number of recipes that can ease the course of diathesis. Some of them are approved by pediatricians. For example, it is quite possible that a dermatologist or pediatrician can agree on the use of baths with a decoction of nettle or chamomile leaves.
A bath with a decoction of pine needles has also proven to be an excellent recipe for skin diseases. Pine needles have antiseptic and soothing properties. Adjust your child’s diet by enriching it with vitamins and macroelements. If diathesis develops in the autumn-winter period of the year, vitamin D supplementation is necessary.
The doctor will calculate the dosage based on the child’s age and state of health.
In conclusion, here are a few recommendations that you can follow to reduce the likelihood of weeping rashes on your child’s body and behind the ears or prevent a recurrence:
- Complementary feeding should be started in strict accordance with age and according to the list of permitted products.
- Keep a food diary where you need to note every reaction that occurs after eating. For example, the earlobe turned red 12 hours after taking an apple.
- Avoid overfeeding your baby.
- Get regular checkups with your pediatrician.
- During lactation, limit the consumption of foods containing a high percentage of histamine.
Do not forget about general strengthening procedures: the child needs fresh air, sun and good sleep.
Source: https://bezotita.ru/simptomy/moknet-za-ushami-u-rebenka.html
Symptoms
The onset of the disease in its general clinical picture is similar to the symptoms of a number of other skin problems, especially atopic dermatitis, which is why it is called exudative (exudative-catarrhal, allergic) diathesis. Itching of the skin in the affected area (mainly behind the ears) and redness of a small area are the first signs of the disease. A small area itches, which gradually grows in area. Less commonly, itching affects:
- scalp;
- limbs;
- face.
Gradually, peeling in the affected areas is added to the itching; the scratched areas are covered with thin crusts that have a golden-white, honey, or yellow hue. As the disease progresses, the itching becomes more and more uncomfortable, so children and adults scratch the affected area, which leads to a worsening of the situation. Cracks of small depth form in this area and regenerate very slowly.
In children
According to official statistics, children, especially those under 6 years of age, are affected by scrofula more often than adults, due to which it is associated with exudative-catarrhal diathesis affecting infants. The main diagnostic sign for people of all ages is the same: the formation of crusts behind the ears. Afterwards, the clinical picture is complemented by the following symptoms of scrofula:
- On flaky, inflamed red spots, where an active inflammatory process occurs, serous fluid begins to secrete, which, when dried, forms dense crusts of a pale yellow color.
- Peeling and inflammation spread to the scalp, but the follicles are not affected. The baby constantly scratches areas that cause discomfort, and rubs his head on the pillow in his sleep.
- Due to the inflammatory process, the cervical lymph nodes begin to grow: they are easily palpable, gradually become visible (stand out against the background of the neck muscles), and respond with pain on palpation.
- The affected areas are accompanied by a rash.
Local symptoms are not the only manifestation of scrofula in children: it may be accompanied by signs of a general deterioration in health. Due to constant discomfort in a specific area, the child becomes lethargic, irritable, and tearful (applies mainly to infants). He has:
- redness of the eyes and increased tearing;
- discharge of pus or mucus from the ears (less often from the nose);
- hearing impairment.
The baby may lose appetite and have trouble sleeping. Older children complain of discomfort in the muscles (stiffness), experience cramps, and joint pain. A negative effect on the digestive process is possible, frequent bloating is possible, but the clinical picture (in terms of general health - local signs do not change) also depends on the form that the disease has taken:
- Torpid - characterized by increased lethargy of the baby, severe pallor of the face, swelling of the lips, weakening of the muscles, which affects his actions. Due to digestive problems, the child constantly suffers from flatulence (bloating) and diarrhea.
- Eretic - due to lack of appetite and digestive problems, the child loses weight, the skin turns pale, may have a blue tint, and with thin skin all the veins are visible. Children with this type of scrofula are highly sensitive (react sharply to pain and other discomfort) and are very mobile.
In adults
Even children aged 12-14 years suffer from scrofula less often than preschool children, and adults are almost never given this diagnosis - much more often doctors talk about cutaneous tuberculosis. This is a whole group of dermatoses that arise mainly against the background of previous or chronic tuberculosis of internal organs, or are the result of the activity of the tuberculosis bacillus. Scrofula in adults manifests itself in almost the same way as in children, starting with mild itching and redness of the skin in the area of the ear folds. Afterwards the following are observed:
- general deterioration of health, characterized by increased temperature (up to subfebrile values - 37.1-38 degrees), muscle weakness, lethargy;
- dense yellow crusts that form at the site of peeling and inflammation, hiding the purple, smooth dermis;
- discharge mixed with pus in the affected areas (if you scratch them), caused by infection of the wound;
- deep cracks next to scabs, healing very slowly and giving off pain when touched;
- large wounds on the affected area in which pus accumulates;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes of the cervical region, which in the absence of timely treatment entails sinusitis, otitis media;
- weight loss;
- chills, fever (as the disease progresses);
- transition of areas of irritation and inflammation from the ear folds to the face;
- arthralgia (joint pain).
Scrofula: what kind of disease is it?
The appearance of this type of scrofula is preceded by the presence of Koch's bacillus, a microbe that is a type of tubercle.
Attention! The infection enters the body primarily through inhalation of contaminated air. Bacteria are not localized in any place, but spread to all cells of the body
A clear indication of the presence of scrofula in a child’s body is an enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes. Untimely treatment leads to the formation of ulcers, which gradually merge with each other.
Symptoms of the disease
The symptoms of scrofula caused by tuberculosis are somewhat different from exudative scrofula. In addition to skin manifestations, a scrofulous child is very restless and nervous, he is weak not only physically, but also psychologically.
- In very young children, the head size is larger than normal, the fontanel is slightly open, and there is a tendency to scoliosis and rickets.
- With scrofulous scrofula, children often have increased appetite, the child constantly feels hungry, although he looks quite exhausted.
- The skin of patients with scrofula is wrinkled and flabby, with the presence of open ulcers and other skin manifestations.
- Patients sometimes experience cramps, painful joints, with obvious swelling.
- Body temperature rises to 39 degrees.
- With minimal loads and activity, rapid fatigue appears.
Causes of the disease in infants
Many factors can trigger the appearance, for example:
- maternal use of alcohol during pregnancy;
- alcohol intoxication during conception;
- metabolic disease;
- rare walks in the fresh air;
- malnutrition and unsanitary conditions;
- bad heredity.
There is an opinion that children born prematurely, whose parents abuse alcohol, and also if they have had or are suffering from any form of tuberculosis, syphilis and cancer have a greater risk of developing scrofula. Scrofula can be contracted in the mother's womb. If the tubercle bacillus has entered the body of a pregnant woman, the fetus will also be infected.
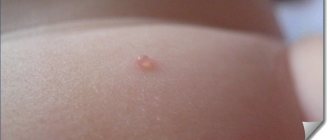
In children, the disease begins with the formation of a mobile painful node, quite dense and located in the area of the ears, lymph nodes or collarbones.
At first it is not large and has a diameter of about a centimeter. Fusing with tissues, it loses its density, liquefies, and becomes loose.
Its size gradually increases and reaches three to four centimeters. Due to this, the node forms into ulcers with the release of caseous masses and pus.
Diagnosis
There are several methods by which the disease can be identified:
- tuberculosis test;
- blood tests for HIV;
- Diaskintest (Mantoux test);
- CT scan of the neck;
- biopsy of affected areas.
Treatment of scrofula of the scrofulous type
Treatment of this type of scrofula involves taking anti-tuberculosis drugs, which have a detrimental effect on the pathogen. For the treatment of scrofula, the drugs Rifampicin, Isoniazid, Streptomycin, etc. are used. The course of treatment is quite long and lasts about a year, and sometimes more.
Photo 2. In addition to the main treatment, it is necessary to rub in ointments to alleviate the symptoms of the disease.
In parallel with therapy, it is important to use external agents - ointments, creams or lotions. The most common prescriptions are Dermatol ointment, Ethacridine lactate lotions, etc.
It happens that surgical intervention is required to remove nodes.
Late treatment may not produce positive results. A small patient may have complications in the form of corneal opacities, cyclitis, keratoconjunctivitis, hearing loss and hearing loss.
Contraindications during treatment:
- swimming in high temperature water;
- bathing too long;
- soaps and detergents that cause dry skin;
- woolen and fleece clothing;
- excessive passion for folk remedies.
Scrofula
What kind of disease is this? Many people really don’t know what this disease is, because it most often occurs in children. Although it can also appear in an adult. This is an infectious disease that can be caused by non-tuberculosis and tuberculosis bacteria. Most often, this condition occurs against the background of poor nutrition and metabolic disorders. Heredity plays an important role in this case, and there are also unfavorable living conditions.
What kind of disease is scrofula? It is a rather complex disease, and rashes can appear not only on the skin, but also on the mucous membranes, lymph nodes, joints, and bones. The main thing is to consult a doctor in time, especially if the causative agent of the disease is Koch’s bacillus, but this can only be determined after a series of examinations, and only after that can adequate treatment be prescribed.
Prevention
There is no specific prevention for any of the varieties of scrofula. There are general recommendations that can reduce the risk of developing pathologies:
The child must be kept in good sanitary conditions, sleep on clean linen and breathe fresh air. You should not overfeed your baby, as this increases the risk of developing allergic scrofula in the form of diathesis. The child’s diet should contain all the necessary vitamins and microelements
It is very important that the baby has enough B vitamins, vitamin E, C, A. If a child is diagnosed with diathesis, then this condition is not contagious, which cannot be said about scrofulosis
In the second case, it is necessary to provide the child with isolated treatment, excluding contact with other children in order to avoid the spread of the disease. You cannot refuse to carry out the Mantoux test; it almost always allows you to determine the presence of scrofula at the very initial stages and begin treatment on time. The child should visit the pediatrician regularly. All complaints about behind-the-ear formations or cracks should be immediately addressed to a specialist when going for an unscheduled appointment.
All about proper ear care and prevention of ear diseases in the next episode of Dr. Komarovsky’s program.
To prevent scrofula it is necessary:
- observe the rules of hygiene - bathe and wipe all folds of a newborn baby on time;
- keep the home and children's room clean, do wet cleaning;
- spend more time outdoors, sunbathe according to the season;
- get enough sleep; children must have a quiet hour during the day;
- eat properly and balanced, take vitamin complexes (VitaMishki, Pikovit);
- up to 3 years of age, completely limit the consumption of sweets - sweets, chocolate, marshmallows, etc.;
- maintain immunity (harden yourself, play sports, walk in the fresh air).
The most important preventive measure to prevent the development of the disease is to monitor the child’s hygiene
To prevent cracks behind the ears in a child and the possible consequences of this symptom, follow these rules:
pay attention to any allergic manifestations after your child consumes a new product; walk in hot weather for no more than 1 hour in the shade; carry out timely wet cleaning of the room and ventilation; strengthen the child's immune system; carry out careful hygiene in the area behind the ears; select anti-allergenic detergents and hygiene products; moisturize the skin with special baby creams; carry out timely treatment of the parotid area in the presence of scratches, cuts and other microtraumas; During pregnancy and lactation, monitor your diet and do not abuse allergenic foods
The most important preventive measure to prevent the development of the disease is to monitor the child’s hygiene
Causes of cracks behind the ears
The cause of cracks behind the ears in a child may be too hard water.
Often parents are faced with the problem of cracks behind their child’s ears. The main factors that provoke their appearance include:
- Sudden changes in ambient temperature and insufficient humidity.
- Swimming in hard water.
- Genetic predisposition to allergic reactions.
- A diet that includes frequent consumption of a variety of sweets and rich foods. If a woman during pregnancy or breastfeeding is addicted to allergenic foods, this can negatively affect the baby.
- Weakened immune system of the child's body.
- Functional disruptions of the digestive system and metabolism.
- Mechanical damage in the area behind the ear, accompanied by the penetration of a fungal infection.
- Hygiene products and synthetic detergents, the composition of which can cause an allergic reaction (shampoo, soap, gel, powder).
- A baby's delicate skin and excess weight can cause diaper rash behind the ears due to constant rubbing.
Such negative factors can affect the occurrence of the following diseases characterized by the presence of this symptom:
- exudative diathesis;
- scrofula;
- eczema;
- dermatitis;
- otomycosis.
How to treat scrofula
The fight against the disease begins through the elimination of provoking factors (mainly allergens), which are some food products - chicken eggs, chocolate, white bread, citrus fruits, whole milk and its derivatives. The apartment should be ventilated and wet cleaned daily. Treatment has 3 goals:
- eliminate the cause of the rash;
- normalize the general condition of the patient;
- restore the skin.
The disease scrofula, according to doctors, is closely related to the state of immunity and metabolism, so taking vitamin complexes (according to indications) will not be superfluous. The patient should drink plenty of clean water and regularly go out into the fresh air. The skin is systematically treated with oil compositions that stimulate healing.
Drug therapy
All medications that a doctor selects for a therapeutic regimen are not aimed at treating scrofula, but at eliminating its symptoms, since there is no specific drug for this disease. Antiseptic solutions (Miramistin) and ointments that block the inflammatory process (zinc, ichthyol) must be used locally. Additionally assigned:
- Antihistamines (Suprastin, Fenkarol, Parlazin) for the allergic etiology of scrofula have an antipruritic effect and relieve other manifestations of allergies. Taken orally in a weekly course.
- Regenerating agents (Bepanten, Panthenol, Actovegin) help speed up the healing of affected areas and are used for a long time - up to 3 weeks.
- Hormonal drugs with a local antipruritic effect (Fucidin, Advantan, Comfoderm) in the form of ointments are used for a short course only if there is no effect from other drugs.
- Enterosorbents (Smecta, Enterosgel), which help remove toxins from the body and cope with the symptoms of general intoxication.
If the doctor, based on the test results, sees the activity of Staphylococcus aureus and tubercle bacillus, the therapeutic regimen can be supplemented with antibacterial drugs for systemic treatment. Streptomycin, Ciprofloxacin, Rifampicin are often prescribed, but the doctor must name the specific names. Mainly used in the treatment of scrofula:
- Baneocin is an ointment or powder based on a mixture of bacitracin and neomycin, a broad-spectrum antibacterial agent. Has a bactericidal effect, inhibits protein synthesis of bacteria. It is prescribed for infectious and inflammatory skin diseases, for local use. The powder is applied locally up to 4 times a day, the ointment up to 3 times a day, no more than 200 g per day. The duration of treatment is a week. The medicine is well tolerated; topically it can cause allergic reactions. Not prescribed for intolerance to aminoglycosides.
- Fukortsin is an antiseptic drug in the form of a solution, prescribed for the treatment of abrasions, cracks, erosions, and pustular skin diseases. It is created on boric acid, resorcinol and phenol. The solution stops inflammation, dries, is not used on open wounds, applied locally with a cotton swab (do not pass over a large area) up to 4 times a day. Adverse reactions are local only: itching, burning. Pregnancy is a contraindication.
- Fenkarol - on hifenadine, a blocker of H1-histamine receptors, has an antiallergic and antipruritic effect. The medication is prescribed for any skin manifestations of allergic reactions, but is prohibited during pregnancy. Tablets are taken after meals, 50 mg up to 4 times a day, washed down with warm water. The duration of treatment can be up to 3 weeks. Adverse reactions – drowsiness, nausea.
Folk remedies
Treatment with alternative medicine recipes involves local and systemic effects on the body: for scrofula, it is useful to take baths with herbal decoctions - currant leaves, nettles. For 200 g of raw material, take 5 liters of water and boil the mixture for half an hour, and then pour it into the bath and dilute with warm water. The procedure lasts 15-20 minutes and is repeated daily. A few more effective recipes:
- Tea with calendula flowers (1 teaspoon of raw material per glass of boiling water, leave for 10 minutes) is drunk daily, 1-2 glasses, if there are no kidney pathologies.
- Cabbage lotions are made in the morning and evening, applied to sore spots for 30 minutes. They are made from 2 tbsp. l. chopped white cabbage, which is boiled for 5 minutes. in a glass of milk.
- A fabric soaked in a decoction of calamus root (any natural) can also be applied for 15-20 minutes, but with a frequency of up to 5 r/day. The decoction is prepared as follows: 1 tbsp. l. pour 500 ml of boiling water over the raw material and leave for 2 hours.
Causes and treatment of diaper rash behind the ear in newborns
The skin is one of the most vulnerable organs in children: it is thin, delicate and permeable to pathological processes. Diaper rash behind the ear in newborns is a common condition that requires immediate treatment. Diaper rash is an inflammatory process of areas of the body that have been exposed to moisture for a long time. This condition is observed in both children and adults.
Diaper rash behind the ear can be accompanied by itching, burning and pain
Common places for diaper rash to appear in adults and babies and their causes
In adults:
- the area of the inguinal folds is a specific area of the skin prone to the formation of a large number of microorganisms and irritations. While walking, this area is subject to the greatest friction and often various types of skin inflammation and skin diseases occur in these places;
- between the toes - occurs in people with excessive sweating of the feet and when using low-quality shoes;
- on the buttocks;
- in the armpits.
In children:
- behind the ears;
- on the neck;
- in the inguinal and intergluteal areas;
- in the armpits;
- in the area between the fingers, in these places the skin is easily vulnerable.
With prolonged overheating of the body, increased evaporation of moisture occurs, which collects in the skin folds. This mechanism disrupts the protective barrier of the skin and diaper rash appears.
Causes of diaper rash in infants:
- warm, synthetic clothing or bedding;
- hyperdynamia - increased physical activity;
- excessive sweating;
- high room temperature, insufficient air circulation;
- improper hygiene procedures;
- allergic reactions;
- overheating;
- friction;
- errors in nutrition;
- hereditary dermatological diseases.
Degrees of development of diaper rash:
- 1 (mild) – hyperemia of the skin;
- 2 (medium) – microcracks and erosion, the appearance of bubbles;
- 3 (severe) – the appearance of ulcers followed by suppuration, an unpleasant odor.
Depending on the severity, diaper rash behind the ear may be accompanied by general malaise, itching, burning and pain in the affected area. If bubbles appear, then the release of serous exudate is possible in the future. When a bacterial infection occurs, the child develops headaches and fever.
The correct selection of care procedures will help eliminate diaper rash already at the first stage. To identify diseases of skin areas, correct diagnosis is necessary. This can only be done by a pediatrician or pediatric dermatologist.
The priority direction in diagnosis is visual examination. Next, you need to conduct a microscopic examination of the skin scraping for fungal contents and culture for microflora.
If the pathology has an allergic etiology, consultation with an allergist is required.
Treatment for diaper rash behind the ears
When bathing or washing your face, it is recommended to add chamomile decoction to warm water.
It is necessary to take timely treatment measures, otherwise diaper rash behind the ears can spread widely, especially when the skin is tender and thin. Additionally, a secondary infection may occur.
The first stage of the disease does not require special treatment. It is enough to monitor the child’s hygiene and ensure comfort. It is also worth considering the use of special protective equipment to cure the auricle.
To eliminate redness that appears suddenly, ointment with Panthenol is well suited - it is hypoallergenic and odorless.
When carrying out water procedures, it is a good idea to add chamomile decoction to warm water.
A positive effect on redness of the skin behind the ears can be achieved by using sanitary baby wipes. At the same time, you should not neglect full water procedures in their favor.
How to treat and what to do for second degree diaper rash behind the ears? In addition to basic hygiene measures, the following is required:
- treat the skin with “talk” based on talc and zinc oxide. They dry the skin behind the ears well without drying out;
- lubricate the skin behind the ears with Methyluracil ointment;
- use ultraviolet light when caring for your baby;
- if pustules occur, it is possible to treat the skin with a solution of brilliant green;
- in case of an allergic form, it is better to add hydrocortisone ointment or desensitizing drugs.
To eliminate serous discharge from the bubbles that appear, it is also rational to use drying agents. Do not apply oily ointments. They create a protective barrier in the form of a film that interferes with tissue regeneration.
Caring for babies' ears requires care. When a baby is urinating, only the outer auricle should be cleaned, since the external auditory canal is very sensitive. For cleansing, it is better to use cotton pads or swabs soaked in a medicinal product.
Third degree diaper rash behind the ears is less susceptible to treatment. Compresses with solutions of tannin and silver nitrate should be added to standard hygienic procedures. After the serous exudate disappears, zinc paste, synthomycin or other antibacterial emulsions are applied to the skin.
In addition to drug treatment, it is worth thinking about traditional medicine. This measure is applicable to eliminate diaper rash of the first and second degrees.
Common and effective treatments
Tea tree oil is considered an effective treatment
- Sea buckthorn juice has restorative, wound-healing and anti-inflammatory effects. Very easy to use.
- Potassium permanganate, or potassium permanganate , is an old but effective remedy. It has good drying, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. There are several ways to use - add to a bath of warm water while bathing or apply to the affected area using a cotton swab.
- Tea tree oil. It has pronounced antifungal, anti-inflammatory and regenerating properties. It is necessary to apply it to the required areas 2 times a day.
- Dentifrice. Well suited as a drying agent. It must be diluted in warm boiled water and lubricated on diaper rash behind the ear. After the mixture has dried, it should be removed with a decoction of chamomile or oak bark.
- Plantain juice has a good effect. It is applied to gauze bandages and applied to the affected areas.
These folk remedies are well suited to prevent relapse. Before use, you should consult a specialist.
Preventive measures effective for eliminating diaper rash
It is recommended to ventilate the room often
To prevent diaper rash, you should follow these simple recommendations:
- observe daily hygiene procedures;
- ventilate the room;
- carry out air baths for the child, lasting 5-10 minutes;
- use special products for washing and rinsing diapers;
- cut the baby's hair short so that the area behind the ears is always open;
- iron children's clothes on both sides;
- dry clothes in the sun (in summer);
- use high quality hygiene products.
Causes and treatment of diaper rash behind the ear in newborns Link to main publication
Source: https://vpotu.ru/oprelosti/za-ushkom
Treatment of exudative diathesis
Scrofula is a disease whose treatment must be prescribed by a doctor. His instructions must be followed strictly. There are a number of restrictions that apply to all children with diathesis:
It is forbidden to bathe a child in hot water. You should not allow your baby to stay in the bathroom for a long time. It is important to choose baby detergents carefully. Preferred are those that are not able to dry out the skin. It is necessary to avoid clothing made of wool and fleece. You can treat scrofula yourself
Without giving up medical therapy, you can follow the rules of home treatment:
You can treat scrofula yourself. Without giving up medical therapy, you can follow the rules of home treatment:
- The child's diet should be balanced. Fried and fatty foods, sweets and smoked foods should be completely removed from the menu. In return, the diet can be enriched with lean meat and fish, vegetables and cereals cooked in water.
- Excessive exposure to a TV, computer or tablet screen is no less harmful than poor nutrition. The child should spend more time outdoors. The baby's sleep should be complete and at least 8 hours a day. A quiet time during the day won't hurt either.
- After talking with your doctor, you can buy natural oil with anti-inflammatory properties at the pharmacy. They need to lubricate problem areas on the child's skin.
- A child's body needs vitamins. If the time of year allows, it is better to give preference to fruits and vegetables. If the disease develops in winter, you need to work with your doctor to select good pharmacy vitamins.
A disease like scrofula does not go away quickly
Therefore, it is advisable to take precautions at all times.
Scrofula in adults of this nature is extremely rare and requires similar therapy. Most often, adults suffer from a more severe type of pathology - scrofulosis.
Introduction of complementary foods
Of course, in addition to using medications and following a certain diet, it is important to remember some recommendations from doctors. This will prevent the development of weeping rashes or reduce the risk of recurrence of the disease.
All complementary foods should be introduced exclusively in accordance with the recommended age. It is prohibited to go beyond the list of acceptable products.
It is best to keep a special diary, which will indicate the food product and the further reaction of the child’s body to its use. For example, 12 hours after taking the apple for the first time, redness became noticeable on the earlobe. You can't overfeed your baby.
Types of scrofula and their differences
With scrofula, the situation is worsened by the formation of lumps in the area of the lymph nodes. Over time they increase in size; in the absence of proper treatment, a fistula or ulcer appears in their place. This condition is very dangerous for humans.
The tuberculous form of scrofula is eliminated as part of inpatient treatment. The treatment process is quite long. Therapy aimed at combating diathesis is carried out on an outpatient basis.
The treatment regimen for diseases also differs. Diathesis is eliminated with antihistamines or hormonal drugs. The diet is also adjusted. Foods that provoke an allergic reaction are excluded from the diet.
Active substances penetrate bacterial cells, preventing their development. The severity of the symptoms of the disease decreases as the course of treatment progresses. Eliminating scrofula is much more difficult than treating diathesis.
A month after the start of therapy against tuberculosis, additional diagnostic procedures are prescribed. They help determine the effectiveness of treatment. The following stages of the tuberculous form of scrofula are distinguished:
- Pre-allergic. Continues for two weeks after infection. During this period, antibodies to infection are formed in the body.
- Allergic. Bacterial cells grow and multiply, and the first signs of the disease appear.
- Proliferation. The body's immune system is activated.
- Necrosis. The body's cells begin to break down, intoxication occurs, and the patient's condition becomes critical.
- Local form. Symptoms of intoxication intensify. The state of health deteriorates significantly.
- Ignoring the situation leads to the development of cirrhosis, severe intoxication of the body is possible, and the functioning of many life support systems deteriorates.
Allergic scrofula does not develop into tuberculosis, but the lack of proper treatment leads to a decrease in a person’s performance and deterioration of health. In especially severe cases, an allergic reaction leads to Quincke's edema - this phenomenon is extremely life-threatening.
You should not deviate from the treatment regimen developed by your doctor. It is assigned on an individual basis. Lowering standards does not lead to the desired effect; increasing the dosage will cause complications in the form of worsening side effects.
Symptoms of the disease
The development of the disease begins with the occurrence of painful itching of the skin and its peeling. At the same time, initially the size of the lesions is small, but scrofulous crusts, primarily affecting the ear, eventually spread to the main part of the head. The areas under the hair are mainly affected without affecting them. You may also experience:
- The appearance of rashes, lichens, lupus.
- There is an increase in lymph nodes in the neck area.
- Mucus or pus is released from the ear and nasal passages.
- The digestive process is disrupted and bloating is observed.
- Hearing deterioration occurs.
- The eyes become red and watery.
- The patient complains of discomfort in the muscles and joints.
- Convulsions may occur.
With scrofula in adults, the symptoms are not much different from the signs observed in children - crusts also appear, and if the form of the disease is tuberculous, then weakness appears and general health deteriorates, the temperature rises, sometimes otitis media develops, a runny nose with purulent discharge, and the lymph nodes are inflamed. There is pain in the back and aches in the limbs.