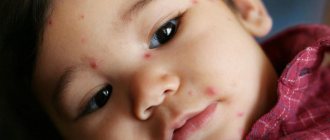
Causes
A common cause of allergies for all age groups of people is excessive sugar consumption.
But this carbohydrate does not act as a direct allergen. Sucrose only contributes to the manifestation of allergic reactions due to human consumption of proteins and fats, as well as flavors and dyes contained in confectionery products. In children, adults and pregnant women, allergies can be caused by different factors.
Features in children
Children's bodies are especially sensitive to allergens. The reasons for them are the following factors:
- disruption of the food processing process;
- low immune defense;
- lactose intolerance;
- lack of the enzyme sucrose in the body;
- the presence of carcinogenic additives and dyes in food;
- the child's use of artificial milk formulas;
- excessive consumption of sweets by the child;
- the presence of parasites in the body;
- hereditary predisposition.
In children, sugar itself is not an allergen. It only accelerates the fermentation processes in their body, irritating the stomach and intestines.
A common cause of allergies in them is poor-quality food with a large number of protein allergens.
Features in adults
The causes of allergic reactions in adults and children are similar. But the former are less susceptible to this disease due to their developed immunity.
Among the specific causes of sweet allergies in adults are:
- smoking;
- age-related hormonal changes in the form of menopause, menstruation;
- consumption of foods with a large number of allergens (citrus fruits, chocolate, honey).
During pregnancy
Pregnant women are allergic to sweets due to hormonal changes in their body. When allergens enter it, it causes an immune response. Special causes of allergic reactions in women during pregnancy are:
- excessive consumption of a certain product against the background of the pregnant woman’s constant need for it;
- weakened immunity due to a lack of the hormone cortisol, which suppresses allergies in pregnant women;
- high blood pressure;
- frequent swelling.
Allergies in pregnant women are less dangerous for the mother herself, but pose a threat to the fetus.
In the future, the disease can be inherited by the child.
Mechanism and features of “sweet” allergies
It is mistakenly believed that the cause of this phenomenon is sugar. This substance belongs to carbohydrates (disaccharides) and serves as the most important source of energy for the body. Sugar itself cannot be rejected by the body - the allergic mechanism has another reason, which is discussed below. Numerous photos of sweet allergies in children clearly demonstrate the different course of the disease - from barely noticeable spots to serious tissue swelling. The strongest intoxication of the child’s body is caused not by sugar, but by the following substances:
- products of the breakdown of sugars in the intestines, which enter the blood and are distributed throughout the body;
- components in sweet desserts - cocoa, whey, nuts, casein, chicken eggs;
- impurities – flavorings, stabilizers, preservatives, food colorings;
- pieces of fruit in desserts - zest and pulp of citrus fruits, dried berries (strawberries, raspberries);
- components of creams, jellies and fillings - cream, milk powder, egg white, vanilla, ginger, cinnamon.
Sweets in reasonable quantities provide not only emotional pleasure, but also practical benefits. Proteins and fats cannot replace the energy value of carbohydrates. Therefore, complete exclusion of sugars from a child’s diet is unacceptable.
To ensure a balanced diet for allergies, it is allowed to feed your baby foods with simple carbohydrates (monosaccharides) - diet cookies, jams with fructose, fruits with easily digestible glucose (grapes). It is prohibited to replace sugar with honey and products containing it. It contains natural plant pollen - a strong allergen.
After a foreign substance enters the human body, the defense system begins to secrete antibodies. If adults and children are predisposed to allergies to sweets, the fermentation process of the undigested product begins, the intensity of which increases many times with sucrose. Thus, compounds designed to prevent the unwanted reaction from occurring do not work.
As a result, toxic substances are released, which begin to be absorbed into the blood. After some time, the first symptoms of a sweet allergy appear. In adults it is very rare, but it happens that some fruits are the source of the foreign compound.
Causes of allergies
If you are allergic to sweets, parents assume that it is sugar that causes the body to react in the form of a rash and redness, but this is not entirely true.
Sugar itself is not an allergen, but the glucose it contains provokes fermentation in the stomach, mainly of protein products. As a result of these processes, toxins are released, which cause allergic reactions. It must be borne in mind that glucose is present in most foods, including vegetables and fruits, and flour products. But most often allergies are provoked by the following sweets:
- caramel;
- Dessert;
- candies with dyes;
- cakes, especially protein ones;
- bars and chocolate;
- baking;
- marshmallows;
- marmalade
The reaction is due to the rich composition and addition of ingredients with a high risk of causing allergies. The following are usually added to products: honey, citrus fruits and berries, eggs, cocoa, wheat flour, nuts and dry cream. In addition, various artificial flavors, dyes, and carcinogens, which many manufacturers add to products, can serve as “provokers” for allergies.
Try to pay attention to the ingredients of products, even if you buy products for yourself. The Valio Clean Label line contains only natural and traditional ingredients, completely free of E-additives and artificial components.
Symptoms of a sweet allergy
Allergic reactions in humans to sweets can manifest themselves in various forms. The most common symptoms are:
- rashes on different parts of the body;
- itching;
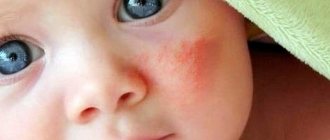
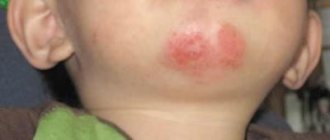
- swelling of the skin on the face and other parts of the body;
- hives;
- eczema;
- dermatitis;
- suffocation;
- sneezing;
- nasal congestion;
- cough;
- severe itching in the nose;
- wheezing;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- flatulence;
- nausea;
- vomit.
The most susceptible to reactions to sweets are the human skin, respiratory system and digestive organs. The most dangerous symptom of a sweet allergy is anaphylactic shock, which leads to severe swelling of the larynx and a drop in blood pressure to life-threatening levels.
Quincke's edema is dangerous as one of the possible symptoms of an allergic reaction. With it, a person experiences severe swelling of the skin.
Symptoms can appear quickly (a couple of hours after eating food with an allergen) or slowly (after 3-4 days). In the second case, it is more difficult to tolerate.
Symptoms: description and photo
Signs of allergy development manifest themselves in different ways. They mainly affect:
- breath;
- skin;
- digestion;
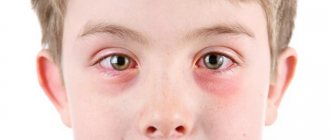
- mucous membranes of the eyes.
In a baby on breastfeeding
Dangerous components of chocolate can enter the baby's body along with mother's milk. During the period of breastfeeding, women should stop eating treats. Signs of allergies:
- Changes in the skin - a rash appears, peeling on the cheeks and neck, scales form under the hairs, diaper rash and sweating, severe itching.
- Diathesis is observed in young children.
The baby often spits up, cries and screams. He has constipation, bloating, colic, and vomiting.
In older children
The consequences of allergies are as follows:
- The appearance of urticaria, which is accompanied by swelling, burning, and itching.
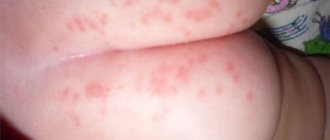
- Skin rash - small spots or merged areas.
- Anaphylactic shock. Blood pressure drops sharply, fainting.
- Quincke's edema. In this case, there may not be a rash. Severe swelling appears not only of the skin, but also of the internal organs.
To all of the above you can add:
- bloating;
- stomach ache;
- diarrhea;
- constipation;
- vomit;
- choking cough;
- dyspnea;
- runny nose and nasal congestion.
The severity of the problem varies from person to person. It depends on the amount of allergen in the child’s body and on the state of the baby’s immune system.
Allergy symptoms in adults
Symptoms of a sweet allergy appear the same in adults and children. The most common symptom is the appearance of skin rashes after consumption. Most often they are localized on the face and torso. What does a sweet allergy look like? The rash is similar in appearance to urticaria, the size of the rash varies from 1 to 2 mm. In some cases, adults develop extensive red spots. The picture is accompanied by severe itching.
In medical practice, there are two types of allergic reactions:
Instructions for the use of Chloropyramine injections for psoriasis and analogues
- Pathology of immediate type. It develops instantly, acutely and violently - literally 1-2 minutes after contact with the provocateur product. Often such reactions lead to swelling of the larynx and subsequent suffocation.
- Delayed reaction. Usually occurs 1-2 days after consuming the product. Often transforms into a chronic form.
How does a sweet allergy manifest itself? The severity of clinical manifestations is determined by the intensity of the immune response and the general condition of the body.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction to sweets:
- Skin rash similar to urticaria. Affects arms, neck, legs, torso, legs, buttocks; if the rash is on the face, it is often confused with diathesis in children or dermatitis. The rashes can be single or multiple, merging into massive conglomerates;
- The skin becomes swollen, red, and itchy. When scratching, wetness is revealed, after which the rash dries out and becomes crusty;
- Scaly spots appear on the legs, similar in appearance to eczema.
With severe allergies, some patients experience not only itching, but also a burning sensation. In addition, skin manifestations are accompanied by a runny nose, sneezing, watery eyes and headaches. When the mucous membrane in the oral cavity is damaged, stomatitis occurs.
Important: the most dangerous complications of allergies are angioedema, anaphylactic shock, and an attack of suffocation. They are life-threatening, so medical help is required at the first sign.
An allergy to sweets does not require a complete abstinence from confectionery products. It is enough to exclude exactly the product that provokes the pathological reaction. This is difficult to do, but possible. Glucose is necessary for the body for the normal functioning of all internal organs and systems. If you give up sweets, you will experience a constant feeling of fatigue, irritability, and insomnia.
What to do if acne appears from sweets?
There is no panacea, but if you follow some rules, you can reduce the number of boils on your face and body.
Here are some tips:
- Make sure the cause of the abscess is correctly identified;
- Use a special diet, which is prescribed by dermatologists in case of dermodicosis. You will have to get rid of everything fatty, fried, spicy and sugar-containing. Refusal of these products will significantly reduce the load on the liver and digestive tract and will help better absorption of nutrients and components;
- Beware of stress associated with increased hormone release;
- It is completely impossible and even harmful to get rid of sugar; the body needs glucose for the functioning of the brain and muscles. Do not give up natural juices without preservatives, fruits and drying.
Diversify your diet with protein and carbohydrate foods.
Create a special menu for yourself for the day:
- In the morning, be sure to eat fresh fruit (bananas, strawberries, apples);
- During lunch, be sure to refresh yourself with liquid soup or borscht. This is important for normalizing the absorption of nutrients in the intestines. To satisfy your hunger, eat buckwheat, corn or rice side dish;
- After lunch, drink a fruit smoothie or vegetable juice;
- In the evening, treat yourself to a sandwich with cheese and butter, tea without sugar;
- When going to bed, drink a glass of dietary kefir to normalize the microflora.
Pseudoallergy
The appearance of certain symptoms after a person eats sweets may not always indicate the development of an allergy. There are true and false allergies.
False allergies are characterized by:
- active release of histamine into the blood after a person consumes proteins, berries, cocoa beans and other allergens;
- active formation of peptides in the body;
- metabolic disorder in the body.
The symptoms of real allergies and pseudo-allergies are largely similar, but there are a number of differences:
| Signs | True allergy | Pseudoallergy |
| Manifestation | After the second meal containing the allergen | After the first meal |
| Eosinophil blood cell count | Increased number | Normal indicator |
| Influence of hereditary factor | Available | Not available |
| Detection of an allergen when it is exposed to a skin area (diagnosis using a scratch test) | Positive test | Negative test |
| The amount of allergen required for an allergy to occur | A small amount is enough | Requires a large dose of allergen |
| Immunoglobulin E level in the blood | High | Normal |
| There is a connection between the amount of allergen and the nature of the allergy manifestation | No connection available | There is a direct connection |
In some patients, true allergy and pseudoallergy can occur simultaneously. In this case, the symptoms of the disease intensify.
Ingredients in sweets that cause itching
It is wrong to think that sugar is the reason why you itch for sweets. Sugar is a natural product, and a priori it cannot be an allergen.
Milk
So why am I itching then, you think. From the following products:
- Milk. Nowadays, a child without an allergy to dairy products is very rare, and milk, as you know, is added to almost every cake, pastry and other sweets.
- Eggs. This is a strong allergen; whites are added to marshmallows, whites and yolks are added to baked goods.
- Nuts. Any nut is a potential allergen for any person; they are often added to sweets.
- Honey. All bee products contain pollen and cane sugar,
Honeyto which the body may have a negative reaction.
- Fruits and berries. Citrus fruits and berries can become individually intolerable foods for each person from a very early age.
- Chocolate. The allergy is caused by the protein contained in cocoa beans and chocolate.
- Gluten. Every mother whose child suffers from food allergies knows what gluten is and where it is found. Gluten is a component of every cereal plant, and grains (flour) are a component of every baking dough.
- Chemical substances. Dyes, sweeteners and flavor enhancers contain a good half of the periodic table, and allergies are the easiest result of consuming such products.
Diagnostics
Detection of allergies to sweets is carried out using the following methods:
- Blood test for immunoglobulin levels. It involves collecting venous blood from the patient. The allergen is introduced into the sample taken. Based on the reaction, the allergist is able to determine the presence or absence of a false allergy in a person.
- Conducting skin tests by applying an allergic substance to or under the skin.
- Conducting provocative tests through the patient's consumption of products containing allergens. If a reaction appears after half an hour or an hour, a diagnosis is made. The method is rarely used due to its danger and unpredictability for the health of patients. After the test, the person must be under the supervision of allergists for 24 hours.
Allergen test
Skin testing for allergens is often used. One of the common forms of diagnosis is a prick test by applying an allergen to various areas of the patient’s skin. A change in the color of the reagent will indicate the development of an allergy in a person.
In some cases, the allergen is injected under the patient's skin. After a couple of hours, the sample result is examined.
Allergen tests are not performed on small children under 3 years of age. For them, the only possible diagnostic method is a safe blood test.
First signs and symptoms
The main difference from the signs of food allergies in adults is the rare manifestation of reactions in the nasal passages, in the eyes, and in the bronchi. The action of irritants inside the body is clearly visible on the surface of the epidermis.
Main symptoms:
- characteristic rashes on certain parts of the body. Locations: cheeks, face, knees, elbows;
- At first, the rash resembles small blisters, later the rash transforms into islands, individual elements merge into a common red-orange surface;
- gradually the rashes become covered with a rather dense crust, peeling of the skin often develops;
- An unpleasant sign is severe itching of the affected areas. Toddlers and older children do not understand how dangerous it is to scratch itchy areas; sometimes they scratch their cheeks, face or elbows until they bleed, which threatens the development of secondary infection;
- with a true allergy, a large volume of a highly allergenic product can develop a severe, life-threatening form - angioedema; in younger patients, anaphylactic shock is possible. If characteristic symptoms appear (swelling of the face, hoarse breathing, large red blisters on different parts of the body), urgent medical attention is needed, otherwise the consequences may be irreversible.
False alarm
Very often, an allergy to sweets in children is confused with a reaction to other allergens present in dessert. First of all, chocolate, honey and citrus fruits. Such symptoms greatly distort the picture of the disease, so identifying the culprit allergens is best done in a clinical setting.
Don’t forget about “pseudo-allergy”. This is the name for the situation when the release of biologically active substances occurs without the production of immunoglobulin E. The symptoms are identical to an allergic reaction.
A similar situation occurs when overeating potentially allergenic foods. Moreover, what is decisive is not whether a person is allergic to a specific food, but the amount of food eaten. A couple of tiny tangerines won’t do any harm, but a kilogram or two at a time is a completely different story.
Particular attention should be paid to diet. The body is not able to cope with large volumes of food, and any large feast can provoke pseudoallergy.
Diagnostic measures
My child is allergic to sweets, what should I do?
If you find signs of allergies, your baby should definitely be shown to a pediatrician and an allergist. The doctor will take the necessary tests and give nutritional recommendations.
Diagnostic measures include:
- clinical picture and survey
- blood tests (general analysis and biochemical);
- skin allergy tests: the main groups of allergens are applied to small skin scratches and the body’s reaction is recorded. This study is usually not carried out for children under the age of 3 - 5 years due to its specificity.
If a child is diagnosed with a sweet allergy, treatment should only be prescribed by a doctor. At the first signs of a reaction, you should avoid consuming the allergenic product and seek advice from a specialist.
Treatment of allergy to sweets
Allergic reactions to sweet foods are treated in several ways:
- hormonal injections and droppers in severe cases;
- taking medications of various groups;
- folk remedies for weak manifestations.
Relieving severe symptoms of sweet allergy
Severe allergy symptoms manifest themselves in the form of angioedema and anaphylactic shock. With such symptoms, a person needs immediate administration of anti-edema and antihistamines. Patients need:
- anti-edema agents in the form of injections (“Prednisolone”, “Hydrocortisone”);
- drugs that eliminate seizures (Suprastin, Diphenhydramine, Tavegil);
- sorbents (activated carbon, Polysorb).
In case of severe symptoms, it is necessary to immediately administer intramuscularly one ampoule of an anti-edema agent and an antihistamine.
Further treatment of the patient is carried out in a hospital.
Drug treatment
Drug treatment of allergic reactions to sweets involves the patient taking the following medications:
- antihistamines in tablet form (Claritin, Zirtek, Tavegil, Loratadine, Suprastin);
- non-hormonal ointments (Gistan, Fenistil, Pantoderm);
- hormonal ointments for severe skin manifestations (Flucinar, Hydrocortisone).
When treating allergies, it is not recommended to take medications to enhance immunity.
Children are recommended to use emollient ointments that soften the skin.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are effective for treating sweet allergies. Among them are:
- infusions of celandine for oral administration, as lotions (2 tsp herbs are poured with boiling water and infused for several hours);
- infusions based on plantain, string, dandelion, aloe as lotions for allergic skin areas;
- infusions of sage, chamomile, mint for oral administration as a means to enhance immunity and in the form of lotions.
Herbal infusions must be drunk for several weeks and maintained throughout the course even when allergy symptoms disappear.
When preparing infusions, you can mix herbs and consume them before meals 4 times a day.
Treatment
How and how to treat sweet allergies? Treatment should begin with a strict diet. Be sure to exclude all types of allergens from the menu. Thanks to a strict diet, the body will autonomously cope with dangerous products, neutralize them and remove them naturally.
Drugs
A signal to consult a doctor and prescribe medication is the persistence or worsening of any of the symptoms. To relieve itching, swelling and skin rash, symptomatic measures are first prescribed:
- Antihistamines - Cetrin, Claritin, Loratadine, Diazolin, Suprastin;
- Enterosorbents – activated carbon, Polysorb, Smecta;
- Ointments and creams - Bepanten, Fenistil, Advantan, Sinaflan, Skincap.
In the case of a severe course of the disease, the attending physician prescribes a desensitization method - a minimal amount of allergen is injected subcutaneously into the patient’s body. The procedure is carried out cyclically, as a result of which the body “gets used to it” and develops the correct response pattern to the product in the future.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is widely used to treat sweet allergies in children. But remember that folk recipes are a complement to the main method of therapy. Traditional methods of treatment alleviate the patient's condition in a short time.
Important! Use traditional medicine methods only after consulting an allergist!
- Please note: Akriderm against allergic rashes
To treat the disease, it is recommended to use rubdowns and herbal baths (chamomile, string, celandine, sage, valerian), nettle tinctures, celery juice, dill infusions, mumiyo solution, dandelion juice.
Traditional medicine should be administered in small doses. If a reaction develops, immediately stop home treatment. It is contraindicated to use alcohol tinctures or medicinal herbs containing poison in the treatment of children).
Important! For children under 1 year of age, taking traditional medicines orally is contraindicated. In the treatment of infants, rubdowns and herbal baths are used.
- Be sure to read: food allergies in children
Traditional recipes for fighting allergies
There are many folk recipes that can relieve allergies. Many of them are based on medicinal herbal collections. For example, doctors often advise people who often suffer from this disease to constantly drink chamomile tea or a decoction of the chamomile.
It will be good if these herbs completely replace coffee and black tea, which are also not harmless for allergy sufferers.
Take mumiyo diluted in warm water . One gram of mumiyo is enough to prepare a liter drink. The solution is drunk half a glass once a day. This remedy significantly reduces the number of skin rashes and their intensity. And also rub red spots with mumiyo solution.
Nettle not only has a pronounced healing effect, but it is also a source of vitamin A, which is very necessary for allergy sufferers for tissue regeneration. Drink a nettle decoction of one hundred grams twice a day.
Celery has proven itself to be excellent in the fight against allergies. A decoction from the root of the plant is drunk three times a day. You can prepare fresh juice, which you take one tablespoon four times a day.
Drink one glass of freshly squeezed juice from carrots, apples and cabbage For that. To ensure that the vitamins are absorbed as best as possible, add a teaspoon of olive oil to the juice.
With the help of this drink, toxins are eliminated after allergies and the body is cleansed. The treatment process takes place very quickly over several days. To prevent itching, skin spots are lubricated with dill juice diluted with water.
How to get rid of itching with a sweet allergy
The most unpleasant thing about allergies is the rash and itching that accompanies it. While a runny nose or red eyes can still be tolerated, the rash is very severe. But there is practically no allergy to sweets without a rash. It is recommended to carry out the following procedures at home:
- Prepare a decoction of the string. Compresses are made from the prepared strong decoction twice a day. Seedling is a plant that has powerful anti-inflammatory properties. It also perfectly relieves any irritation and heals wounds.
- You can try to relieve itching with sea salt. It is enough to dissolve one tablespoon of salt in a liter of warm water and wash the redness with it. For best effect, apply compresses.
- Like salt, ordinary baking soda perfectly relieves itching. It is dissolved in warm water and also applied as a moistened compress to sore spots.
Baking soda and salt can be combined in one solution .
Treatment methods
There are several treatment methods.
Diet
In most cases, treatment of acne from overeating sweets begins with a diet that includes proper nutrition.
On this topic
- Pimples
5 ways to get rid of acne right now
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- March 29, 2021
Preference should be given to foods with a low helicemic index that are slowly absorbed. And sugar consumption should be reduced, but this should be done gradually so as not to cause a stress reaction in the body.
Doctors categorically prohibit completely abstaining from consuming sugar and sweet foods. This will lead to disruption of insulin production. Such drastic measures have a negative impact on well-being and cause:
- drowsiness;
- headache;
- irritability;
- depressed mood;
- weakness.
After a break in consuming sugar-containing foods, the body needs to replenish its glucose reserves and craves even more sweets.
Skin care recommendations
To prevent and treat rashes that appear as a result of eating sugary foods, dermatologists recommend following certain skin care rules:
- Wash your face morning and evening using warm water (it opens the pores) and tar or antibacterial soap.
- If acne appears in the forehead area, you need to keep clean . They quickly become dirty, touch the rashes and spread them to other areas of the face.
- For rapid healing, acne must be treated with salicylic or boric acid.
- Periodically cleanse the skin with 3% hydrogen peroxide.
- After removing makeup and washing your face, wipe the inflamed areas with decoctions of medicinal herbs (calendula, string, chamomile, St. John's wort).
You need to refrain from:
- independent mechanical removal of acne;
- using powder, foundation or other decorative cosmetics that clog pores on inflamed areas;
- treating pimples with astringents (film-forming) agents, as they aggravate inflammation;
- long (more than 15 minutes) use of warm compresses;
- carrying out cosmetic procedures, using scrubs and peeling.
When the sebaceous glands are active, caused by the consumption of sweets, cosmetologists do not recommend using alcohol-containing products and washing your face more than twice a day. If you artificially dry the skin, the sebaceous glands will produce sebum with greater intensity.
Drug treatment
You can get rid of rashes caused by overeating sweets on your own (with the help of diet and proper care) only if you have a small amount of acne. In other cases, consultation with a dermatologist is necessary. He analyzes the causes of the rash and prescribes medication.
Women whose excess carbohydrates have led to an increase in androgen levels are prescribed medications containing estradiol, the female sex hormone.
If acne is caused by an allergic reaction of the body, the doctor will prescribe a course of antihistamines.
Allergens
The most powerful allergens include:
- sugar;
- chocolate;
- honey.
The allergic properties of these products manifest themselves in different ways and depend on the components they contain.
Sugar
Allergies to sugar most often occur in children under 4 years of age. Moreover, the product itself does not cause allergies. The sucrose contained in it can provoke a reaction. Sucrose acts as a catalyst for fermentation in the body and provokes the body's immune response to other allergens.
In adults, allergies to sugar components are less common. A common cause is additives in the product.
Chocolate
Chocolate has strong allergic properties. This is due to the presence of protein in its composition, which in itself is a strong allergen. For this reason, chocolate and sweets are not recommended for children under 2.5 years of age due to the high risk of developing complications in them such as asthma, psoriasis, and eczema.
Honey
An allergy to honey often manifests itself immediately.
If there is an excess of the product, a person may experience anaphylactic shock.
The allergic properties of honey are associated with the high content of a whole group of allergens in it: protein components, wax, fructose.
Varieties
Depending on what exactly the allergic reaction has developed to, there are three main types of allergies to sweets.
- For chocolate. The most common type. Develops immediately after the baby eats chocolate candy or chocolate, a rash and itching appears. It is most often observed in children aged two to eight years. Such an allergy can persist for a whole week, and can disappear as suddenly as it appeared.
- An allergy to sugar in children can occur not only to the sweet sand itself, but also to foods containing sucrose, for example, sweet vegetables and fruits. In this case, there is a mild form of allergy. Hyperemia of the skin is typical; the tongue and lips may swell. The reaction will disappear in three days, maximum five.
- On honey It is one of the body's most dangerous responses to sweets. May provoke the development of Quincke's edema and cause suffocation. The allergic reaction may persist for two weeks.
At-risk groups
- As with other types of food allergies, children under the age of 15 are most susceptible to this disease. The reason for this is the immature digestive and immune systems. The good news is that most symptoms disappear or improve by age 18.
- Another group includes people with disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Here, an allergic reaction is a concomitant factor that disappears after healing from the underlying disease.
- The last factor influencing the occurrence of a sweet allergy is pregnancy. Moreover, in this case, the disease poses a danger not only to the mother, but also to her unborn child. So be careful.
Possible complications
As a result of an allergy to sweets, bronchospasm may occur.
One of the most common consequences is the transition to a chronic form. In addition, more serious complications may be present, such as:
- Quincke's edema;
- attack of suffocation;
- bronchospasm;
- anaphylactic shock;
- high grade skin lesions.
Diet for allergies
If a person is prone to allergies, he must follow a diet that includes:
- vegetables, cereals, broths;
- bread with grains, baked goods without sugar;
- herbal teas.
You should avoid allergy trigger foods or significantly reduce their consumption:
- eggs;
- smoked meats;
- fish;
- canned food;
- spicy seasonings;
- fatty foods;
- garlic with onions, horseradish;
- sausages;
- mayonnaise;
- tomato juice.
Allergy sufferers are advised to replace sweets with alternative desserts:
- berries;
- jelly;
- dried fruits;
- jelly;
- unsweetened fruits;
- homemade cakes and desserts with a minimum amount of sugar.
Sugar replacement
To reduce the risk of allergies, patients are recommended to use sweeteners.
These include both natural analogues of sugar (stevia) and synthetic ones (sorbitol, xylitol). Sweeteners are no different from sugar in sweetness, but have much lower calorie content.
Prevention
Prevention of sweet allergies includes:
- following a diet excluding foods containing allergens;
- strengthening the immune system through exercise;
- maintaining psychological balance, avoiding stress and strong feelings;
- varied diet;
- moderate consumption of sweets.
Cleansing the body
If a person is allergic to sweet foods, it is recommended to cleanse the body. To do this he needs:
- reduce consumption of allergic foods;
- exclude fried, fatty and smoked foods, spicy foods, baked goods, soda, alcohol and processed foods from your diet for several months;
- replace allergenic foods with fermented milk products, vegetables, cereals and broths.
People of all ages are susceptible to allergic reactions to sweets. They are especially typical for children. The disease requires complex treatment in the form of diet and medication. The most reliable preventive method against allergies is moderate consumption of sweets.
What to do if your child has allergies
The symptoms of a child's allergy to sweets are known, as well as the reasons, so what to do if your baby's cheeks still turn red. You can look at the photo, you can also watch Komarovsky’s video, but the correct decision is completely different.
At the first signs, you shouldn’t turn a blind eye. Even small redness can cause harm to a child’s body. It often happens that a childhood allergy develops into an adult and a person suffers from it all his life.
After all, sweets mean not only sugar and cakes, but also fruits, ordinary baked goods, honey and much more. Therefore, it is worthwhile to initially take care of the future life of your children.
If you notice redness on your child’s body and are not sure whether it is from sweets, you should still call a pediatrician or go to a medical facility yourself. Remember everything your child ate, what they washed their clothes with and bathed him. And if you have no doubts, you should begin treatment immediately.
Diagnosis of sweet allergies in adults and children
The manifestations of an allergic reaction to sweets are usually the same as allergies to many other foods. Therefore, in order to accurately determine the irritating substance, you need to contact a specialist who will conduct an examination and possibly prescribe tests.
The main task in blood testing is to determine the level of IgE immunoglobulins, which play an important role in the functioning of the immune system. A complete blood count helps determine the number of eosinophils. If the level of these cells is elevated (which is precisely what a general blood test determines), it can be assumed that an allergy is occurring.
Why do sweets cause acne?
The thing is that sweets contain the simple sugar glucose, which significantly affects the speed and intensity of hormonal reactions in the body.
- A particularly important role in this process is played by the release of androgens, which stimulate the production of subcutaneous sebum. Without proper body care and exercise, pores become clogged and sweet acne appears.
- In addition, glucose promotes the production of insulin, which stimulates the release of sex hormones into the blood. The body needs insulin to process glucose; it is a very useful and necessary substance.
But an excess of this carbohydrate in the blood is accompanied by increased work of the pancreas and sebaceous centers. After subcutaneous fat reaches its target - the epidermis, it interacts with rapidly multiplying bacteria, creating a focus of infection.