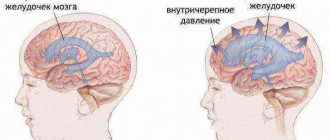
Serous meningitis is a very dangerous and serious disease, the same for children and adults. When this disease occurs, inflammation occurs in the membranes of the brain.
According to etiology, the following types of serous meningitis are distinguished: fungal, viral and bacterial (syphilitic, tuberculous, etc.) meningitis. In addition, primary and secondary forms are distinguished.
Primary meningitis occurs due to primary damage to the meninges, which is not preceded by any infectious agents. Secondary damage to the meninges occurs after an infection, as a complication.
The mildest form of meningitis is considered to be that caused by viral infections. The disease occurs without serious complications, and with timely treatment by highly qualified specialists, it goes away without a trace. If treatment is late or not entirely adequate, then in the case of viral meningitis, the consequences for an adult or child can be very sad.
Origin of nervous system disease
Meningitis can be primary, when the inflammatory process develops as an independent pathology, and secondary, when it is a complication of another bacterial or viral disease.
The main causes of serous infection in babies:
- enteroviral bacteria;
- sepsis and brain and skull injuries;
- the presence of fungi, viruses or bacteria in the child’s body that contribute to the development of inflammation.
In the secondary form of the pathological condition, serous meningitis can form as a complication of any bacterial, various viral or fungal infections.
Methods of transmission of the disease and what it is
Meningitis is a lesion of the inner lining of the brain, characterized by serous inflammation, which can be provoked by fungi, bacteria or viruses. The pathological process develops quite quickly. The main cause of the disease is enteroviruses. You can become a spreader of the virus or become infected with it in the following ways:
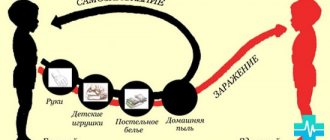
- Infection through contact. Microorganisms and bacteria enter the child’s body through food, drinking contaminated water, or neglecting basic hygiene.
- The virus is transmitted through airborne droplets during sneezing and coughing as a pathogen and settles on the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract.
- Meningitis is easy to catch when visiting a swimming pool or in open water; children with weakened immune systems are most susceptible to infection.
Serous pathology is especially dangerous for infants - during this period of time, the influence of pathogenic microorganisms has a detrimental effect on the nervous system and the cells of the “gray matter”. Meningitis in babies under one year of age can cause serious consequences in the development of the psyche, hearing and vision.
Spread of the virus by airborne droplets
Symptoms of the pathological condition in children
Serous pathology is characterized by an acute, rapid course. The temperature rises to 40 degrees. The patient is worried about migraine attacks, which are accompanied by diarrhea and severe vomiting. Frequent manifestations of the pathological condition are pain in the stomach, anxiety, delirium, and severe cramps.
A week later, the acute period subsides, the temperature returns to normal, and the symptoms disappear. But it is necessary to carefully monitor the patient’s condition, because after some time a relapse occurs.
In addition, signs may be found indicating an inflammatory process in the peripheral and central nervous systems. Serological and virological examination methods will allow you to accurately determine the type of pathogen.
The pathology proceeds latently for 4 days. At the end of this period, serous meningitis acquires symptoms in children such as:
- sudden increase in temperature to 38-40 degrees;
- spasms in the temporal part of the head, which increases with extraneous sounds, eye movements, and bright light;
- seizures;
- tearfulness, nervousness;
- pain in the legs, arms, joints, general malaise;
- lack of appetite, attacks of vomiting, nausea;
- diarrhea and pain in the abdominal area;
- signs of ARVI.
In infants, the fontanelle swells, Lesage's symptoms are observed - when lifting the child up by the armpits, he begins to intuitively pull his legs towards his stomach. The sensitivity of hearing and eyes increases. The child cannot press his chin to his chest.
There are also standard symptoms of serous meningitis - Kernig's sign - the baby is unable to straighten his leg, Brudzinski's sign - when bending the head, the lower limbs bend.
Brudzinski's sign
Specific symptoms
When examining a person with serous meningitis, the symptoms are expressed in excessive tension of the neck muscle group, their rigidity, that is, the inability to bring the chin to the chest.
There are also several meningeal symptoms such as:
- Kernig's sign is the inability to straighten a leg bent at a right angle.
- Brudzinski's symptom: lower - if one bent leg is straightened, this leads to reflex flexion of the second leg, upper - if the head is bent, the legs involuntarily bend.
All these symptoms of serous meningitis can be expressed to varying degrees, to a lesser or greater extent; in very rare cases, these signs can be combined with generalized damage to other organs.
Methods for diagnosing a pathological condition
Before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to establish a diagnosis of the disease and determine the type of pathogen. The main methods for diagnosing serous pathology include:
- Analysis of cerebrospinal substance. The fluid can be obtained through a puncture in the lumbar region. When diagnosing pathology, various characteristics of a substance are studied (transparency and shade, composition and number of cells, glucose, protein, as well as the state of the microflora). This allows us to determine disorders characteristic of inflammation of the inner membranes of the brain.
- Eye examination, skull x-ray.
- QCT and MRI - determines the presence of inflammation and its nature.
- Electroencephalography.
An accurate diagnosis is made based on a combination of several signs: the presence of symptoms of serous lesions, infection, as well as pathogenic processes in the cerebrospinal substance. In the absence of adequate therapy, the consequences of meningitis in a child may be irreversible.
Complex therapy of serous inflammation in children
If you suspect a disease, you must urgently seek help from a doctor and ensure that the baby is hospitalized. Most often, the causative agent of this type of meningitis is a virus, so antibiotics are not used. Drugs in this group are prescribed only for unidentified diagnoses.
Complex therapy of the disease includes:
- When treating a pathological condition caused by a viral infection, antiviral drugs – interferon – are indicated. To treat diseases caused by herpes or the Epstein-Barr virus, Acyclovir is used;
- Patients with weak protective functions of the body, as well as infants, require specific or nonspecific antiviral treatment: intravenous administration of immunoglobulin;
- dehydration - used to lower blood pressure, Acetazolamide, Furosemide, Lasix are indicated. Colloids are not recommended due to the risk of heart failure;
- antispasmodics will help reduce the painful syndrome - “No-shpa”, “Drotaverine”. Manifestations of intoxication can be eliminated by intravenous administration of an isotonic saline solution (saline, ascorbic acid, Prednisolone);
- At high temperatures, antipyretic drugs are used - Ibuprofen, Paracetamol. Convulsions in children can be eliminated with Domosedan or Seduxen;
- patients are prescribed bed rest, rest, it is advisable to darken the room;
- timely antibiotic therapy (for unidentified forms) helps prevent the severe consequences of meningitis (hemorrhage, cerebral edema);
- complex therapy includes: cocarboxylase, vitamin C, B6/2. As an additional treatment for serous pathology, oxygen therapy is recommended - the use of oxygen;
- nootropic medications – “Piracetam”, medicine “Glycine”. Other drugs for the treatment of pathologies of the nervous system: “Nicotinamide”, the drug “Inosine”, “Succinic acid”, “Riboflavin”.
With adequate treatment, serous types of meningitis in children, unlike purulent diseases, are benign, short-term in nature and rarely provoke complications.
Succinic acid is good for the brain
Treatment
If there is any suspicion of meningitis, you should immediately call an ambulance and hospitalize the child or adult in a hospital.
Due to the viral etiology of the disease, the use of antibiotics is inappropriate. Antiviral drugs - arpetol, interferon, acyclovir - can play a significant role in the treatment of serous meningitis in children and adults.
In case of immunodeficiency, the patient is prescribed a course of normal human immunoglobulin, donor and placental gamma globulin. If serous meningitis is provoked by measles, then anti-measles immunoglobulin is used; for influenza, anti-influenza immunoglobulin is used.
Dehydration is essential for reducing intracranial pressure, so diuretics are prescribed - Lasix, Furosemide. At temperatures above 38C, antipyretics are used - paracetamol, ibuprofen. Also, each patient is prescribed antihistamines that relieve fever and the main signs of meningeal syndrome. Such drugs include suprastin, tavegil and the well-known diphenhydramine.
With timely and adequate treatment, serous meningitis in children, unlike purulent ones, is benign, short in duration and rarely causes complications.
Rehabilitation after treatment
All children who have had the serous form of meningitis need a full recovery. For maximum effectiveness of the treatment, it is necessary to carry out some rehabilitation procedures under the supervision of a doctor.
If there is no threat to life, rehabilitation therapy is started during the recovery period. Such activities begin to be carried out in a hospital at an infectious diseases hospital and continue in a sanatorium-type institution.
Rehabilitation includes:
- Following a special diet.
- Physiotherapy.
- Various techniques with the participation of doctors of narrow specialties.
A baby who has suffered a serous form of pathology is registered at the clinic’s dispensary for 2 years. For 60 days, a neurologist examines the child every month. Then the frequency of visits to the clinic is reduced to once every three months, after which once every six months.
In severe forms of inflammation of the inner membranes of the brain, the duration of clinical examination may extend beyond 2 years. The effectiveness of treatment of the disease depends on timely diagnosis and correct complex therapy.
Rehabilitation
Possible complications of the disease in a child
Parents are most interested in what consequences a pathological condition can provoke in a baby. With the capabilities of modern medicine and timely diagnosis, the risk of complications is minimized.
Specialists sometimes have to deal with situations where the signs of serous meningitis in children begin to bother parents quite late. In this case, the consequences of the disease in the child may manifest themselves in the form of:
- attacks of headaches;
- restlessness during sleep or insomnia;
- difficult memorization, perception of information;
- uncontrolled contraction of a particular muscle group.
Doctors have to deal with similar consequences of meningitis most often. Residual signs of the disease can bother children about 5 years old, but provided that the inflammatory process is of moderate severity. After some time, such manifestations go away on their own.
Severe complications include:
- Loss of vision, hearing.
- Deviations in mental and mental development.
- Impaired conversational speech.
- Failures in coordination of movements.
- Paralysis of limbs.
- Paresis of legs, arms.
- Epileptic seizures.
But such consequences are not observed often, and they can be neutralized with the help of a specialist and complex, long-term therapy. Therefore, timely consultation with a doctor is the key to good health of the child in the future.
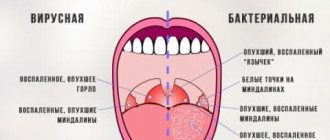
Serous meningitis in adults: symptoms
With this type of meningitis, the first symptoms in adults are mild. These may be: general weakness, fatigue, mild headache, sore and sore throat, cough, runny nose.
Such symptoms are characteristic of various acute respiratory viral infections, which are easily treatable, so most patients do not pay much attention to them; in extreme cases, they begin to take various medications aimed at improving their well-being.
The obvious symptoms of serous meningitis in adults are:
- high body temperature;
- migraine-type headache that does not stop even after taking painkillers;
- vomiting without nausea, regardless of food intake;
- chills, fever, clouding of consciousness;
- state of delirium, hallucinations;
- abdominal pain, indigestion, diarrhea;
- irritability;
- lack of appetite;
- convulsions, loss of consciousness (in severe cases).
There is an increased level of lymphocytes in the patient's cerebrospinal fluid. Diagnosis is based on data from lumbar puncture, laboratory diagnostics of blood and urine.
Basic preventive measures
Precautions
To prevent inflammation of the membranes of the brain, you should protect your baby from exposure to fungi, bacteria, and various viruses. As a preventative measure, it is recommended to follow some rules:
- do not swim in dirty waters;
- drinking water must be boiled and pre-purified;
- all products must be processed;
- constantly wash your hands after going outside and before eating;
- healthy eating;
- correct daily routine;
- multivitamin complexes to boost immunity;
- during epidemics, you should avoid visiting crowded places;
- carry out wet cleaning of the premises;
- keep all toys clean;
- carry out timely treatment of fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases;
- limit the baby’s contact with carriers of infection.
Serous meningitis is a serious disease transmitted by airborne droplets and contact. The pathology can be secondary or primary in nature; depending on the form and type of pathogen, appropriate treatment is selected. At the first signs of inflammation of the meninges, you should immediately consult a doctor and undergo an examination.
Consequences of serous meningitis
According to doctors, half of the patients cured of meningitis continue to experience health problems for many years. After meningitis, patients complain of difficulties with remembering information, spontaneous muscle contractions, and mild migraine-like pain.
But these complications are typical for mild forms of the disease. If the disease is complicated, the person may even lose hearing or vision. In addition, some forms of this disease can provoke disruption of the brain and difficulties with mental activity.
In fairness, it must be said that, fortunately, such consequences of the disease occur only in one and a half percent of all those who have suffered this disease. But in very rare and difficult cases, this disease can even lead to death.
(Visited 3,637 times, 1 visits today)