Pathogenesis
Bacteria enter the body through contact and household contact. The less the baby pays attention to hand and oral hygiene, the higher the likelihood of spreading a staphylococcal infection. Eating unwashed foods or stale vegetables and fruits can also lead to infection.
The disease will not develop if the immune system is in order. Otherwise, bacteria multiply quickly. The following factors can weaken the immune defense:
- previous colds;
- long-term use of antibiotics, corticosteroids and immunosuppressants;
- avitaminosis;
- physical inactivity;
- unbalanced diet;
- recurrent herpes;
- poor environment and frequent stress.
The infection can be transmitted through airborne droplets and airborne dust. Staphylococcus aureus, also known as aureus, remains active in dust for up to six months. If you neglect the rules of hygiene and do not carry out wet treatment of the room in a timely manner, infection is guaranteed.
There is also a so-called iatrogenic route of infection. It is associated with non-compliance with medical standards when carrying out medical procedures or diagnostic studies. Self-infection is also noted. In this case, the child has pathogenic flora in the throat, but in such an amount that there are no symptoms. The slightest weakening of the immune system leads to the activation of microorganisms and the growth of their colonies.
Methods of infection
Staphylococcal infections are a hospital scourge. Their number exceeds a hundred. The bacterium is very persistent, easily clings to humans, its treatment is quite troublesome due to the high adaptability of the microorganism. Often, Staphylococcus aureus penetrates the respiratory passages due to caries and chronic pathologies of the upper respiratory system. With autoinfection, bacteria penetrate from the surface of the skin inside due to lesions and disruption of the integrity of the epidermis and mucous membrane. The exogenous route involves contact with contaminated objects or products.
You can become infected:
- Through common household items with increased sensitivity of the body.
- Bacteria are also transmitted through the air by inhalation, coughing, and sneezing.
- If germs live in dust and you breathe it in, you can get sick.
- You can also catch the infection through contact with the secretions of an infected carrier.
- The bacteria gets inside with contaminated food due to insufficient hygiene and sanitation.
- There is a danger of infection during medical procedures due to insufficient sterilization of instruments during diagnosis or surgery.
Clinical picture
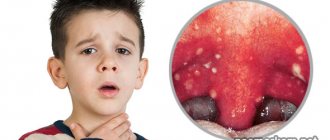
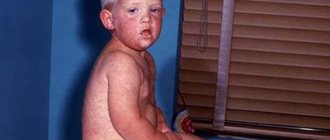
Symptoms vary depending on the form of the disease. The presence of an infection in the throat implies the development of tonsillitis or laryngitis. Sore throat is the most acute. It is accompanied by an increase in body temperature to febrile levels, pain when speaking and swallowing, and swelling. Associated symptoms of staphylococcal sore throat are:
- enlargement and redness of the tonsils;
- pale yellow coating in the throat;
- lacrimation and photophobia;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- joint pain and muscle aches;
- chills and fever.
You need to know what a healthy throat looks like in a child in order to detect the inflammatory process in time. The presence of spots, swollen tonsils and a red throat are characteristic signs of tonsillitis. Normally, the mucous membrane is uniformly colored, there are no spots or plaque.
Pharyngitis is accompanied by a dry cough and sore throat. Staphylococcal laryngitis manifests itself similarly, but it rarely occurs as an independent disease and is usually accompanied by tracheitis. The temperature in this case is kept at a subfebrile level. As sputum is produced, the cough becomes wet.
If a fungus is simultaneously detected in a child’s throat, they speak of a mixed infection. Candidal tonsillitis in symbiosis with pathological staphylococci is more often diagnosed in newborns. The symptoms of fungal tonsillitis are mild, but when Staphylococcus aureus is activated, characteristic manifestations of a bacterial infection occur: general intoxication of the body, weakness, anxiety, sleep disturbance. The child refuses the breast.
Alarm Signals
If the number of bacteria present in the child’s throat does not exceed acceptable values, then no painful symptoms will occur. The infection can only be detected through laboratory analysis. But as soon as S. aureus manages to detect a gap in the immune defense, intensive growth immediately begins, and then the health condition gradually worsens. The very first signs of a sore throat caused by Staphylococcus aureus include:
- constant sore throat, slight pain, feeling of discomfort;
- swelling and redness of the mucous membranes of the throat;
- formation of purulent plaque and purulent plugs;
- elevated temperature.
Painful manifestations can be not only directly in the throat. Thus, staphylococcal infection is often accompanied by the following symptoms:
- abdominal pain, indigestion, upset stomach;
- severe flatulence;
- nausea;
- the appearance of small and large ulcers in various parts of the body;
- Strong headache;
- aches throughout the body, a feeling of weakness, fatigue.
At the same time, young children become capricious, restless, constantly cry, cannot sleep, and do not eat well.
Diagnostics
Smear culture is recognized as an information research method. It identifies the pathogen itself and its sensitivity to various types of antibiotics. If a bacterial infection is detected in an infant, breast milk is additionally taken for analysis.
During laboratory tests, it is possible to detect mushrooms in a child’s throat if they are present. If an inflammatory process of a systemic nature develops, it is necessary to undergo general tests. An experienced doctor will be able to determine the condition of the nasopharynx by its appearance. But if it is easy to examine a child of conscious age, then how to examine the throat of an infant? In this case, use a medical spatula or a small teaspoon with rounded edges. Open the child’s mouth slightly and press the tongue, freeing the throat.
It's good if you have a spotlight at hand. With its help, it is possible to enlighten the tonsils and the root of the tongue. In the presence of inflammation, swelling, hyperemia, and serous plaque will be visible. There is no need to put the spatula deep into the child's mouth. With its help, only the edge of the tongue is held. Parents of the baby can also carry out a similar manipulation at home. If suspicious symptoms are detected, consult a doctor immediately.
Complications
When an infection enters the body, the immune system is further weakened. Against this background, other microorganisms are activated: viruses, fungi. A superinfection develops, which is difficult to treat with antibiotics alone.
Staphylococcus in a child’s throat can cause the following complications:
- meningitis;
- toxic shock syndrome;
- staphylococcal pneumonia;
- endocarditis;
- sepsis.
If general blood poisoning occurs, the prognosis is unfavorable. Children's immunity is not able to cope with total inflammation and decay processes. The child’s body quickly loses water, deep phlegmons and abscesses form. Fortunately, such complications occur in exceptional cases.
Staphylococcus in the throat should not be underestimated, if only because an infection in the mouth causes germs to spread inside when swallowing. Staphylococcus quickly rises up the nasopharynx or down the esophagus. The infection can spread throughout the body along with the bloodstream. Timely and adequate therapy will relieve the unwanted consequences of the disease and prevent relapses. Staphylococcus in early childhood is especially dangerous, which is associated with the imperfection of the child’s immune system.
Sore throat is the most common disease of children caused by staphylococcus
Oddly enough, sore throat is a disease that is provoked by these microorganisms. But we must not forget that it is extremely rare to make such a diagnosis on your own. Without medical education and experience, few people will be able to correctly identify a sore throat, as well as identify its cause, of which there may be several. For example, there are two options for the occurrence of sore throat:
- Staphylococcal - the causative agent staphylococcus, actively affecting the tonsils, causes pain in the throat when swallowing, coughing and fever.
- Streptococcus - the causative agent of streptococcus, has excellent ways of forming colonies, and is also able to adapt to various conditions. It is worth noting that streptococcus is more resistant to the effects of drugs.
One way or another, it is impossible to determine the type of sore throat “by eye,” so in solving this problem it is important to trust a specialist who will select the appropriate effective treatment, identifying streptococcus or staphylococcus as the cause of the illness.
Therapy
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus in the throat in children requires an integrated approach. Therapy is aimed at suppressing the infectious agent, strengthening the immune system, and sanitizing the throat. Children over 5 years old are offered rinses with antiseptic solutions. A solution of chlorhexidine and Miramistin will be beneficial. Chlorophyllipt and Hexoral give good results in local treatment.
The use of throat lozenges is more of an auxiliary measure. Such drugs soothe pain, anesthetize, and make swallowing easier. The lollipops also contain anti-inflammatory components, but in low concentrations.
Antiseptics for the throat are available in the form of sprays, lozenges and solutions for spot treatment of the tonsils. When purchasing a drug, pay attention to age restrictions. Many products are not suitable for use by children under 7-8 years of age. When using the drug, carefully study the instructions. Side effects of local antiseptics include drying of the mucous membrane and disturbance of taste.
The basis of treatment is antimicrobial drugs. Only the pediatrician decides how to treat an infection in early childhood. He will select the optimal medications based on the clinical picture and age of the patient.
Antibacterial treatment of staphylococcus
It is possible to destroy streptococcus in a child’s throat with the help of penicillin antibiotics, macrolides and the latest generation cephalosporins. The first category of effective drugs used in childhood includes Flemoklav Solutab, Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav. Effective macrolides include Sumamed and Azithromycin. Zinnat and Ceftriaxone are considered safe and effective cephalosporin drugs.
The minimum course duration is 5 days. On average, it takes 10-12 days to treat staphylococcus with antibiotics. If the child cannot be given antibiotics, staphylococcal bacteriophages are prescribed. Bacteriophages are understood as preparations containing beneficial viruses that destroy bacteria without disturbing the microflora. Uncontrolled use of bacteriophages can cause bacterial imbalance.
Prognosis and prevention
Staph infections can be successfully treated if detected early. It is important not to start the disease and prevent complications. Staphylococcus quickly spreads to neighboring organs and tissues, so treatment is continued even after the main symptoms subside. After recovery, it is necessary to pay attention to strengthening the immune system. The child is accustomed to hardening procedures, the diet is enriched with vitamins, and more fresh vegetables and fruits are introduced. Do not allow spoiled foods to enter your child's food.
They pay attention to hygiene, regularly carry out wet cleaning of the premises, ventilate the rooms, and regulate air humidity. To protect your child from infection, contact with sick children should be avoided.
From an early age, a child is taught to regularly wash his hands, brush his teeth, and prevent dirty objects from getting into his mouth. Do not share utensils or personal hygiene items. As the child grows older, cases of exacerbation of staphylococcal diseases decrease, which is associated with the development of immune defense and the formation of proper hygiene habits.
How dangerous is Staphylococcus aureus and how is it transmitted?
Staphylococcus aureus, or aureus, causes acute inflammatory processes in the children's body, including meningitis and sepsis. The waste products of the microbe lead to severe intoxication. In the absence of timely treatment, there is a risk of developing diseases that cause mental retardation or even death.
There are two ways of infection: exogenous (from the outside) and endogenous. External is the most common, because the main method of transmission is airborne. It also includes the artificial method (through contaminated medical instruments) and the nutritional method (due to non-compliance with personal hygiene rules and consumption of low-quality food). Endogenous infection occurs when aureus is spread by blood and lymph, for example, from infected skin or carious teeth.
Causes of staphylococcus in the throat
The cause of this infection in children is weakened immunity, which is unable to suppress the development of the disease. Since Staphylococcus aureus is usually transmitted by airborne droplets, visiting public places is a common cause of the disease. The bacterium enters the oral cavity and takes hold in the throat, causing infection. The remaining causes of the disease are divided into two groups: external and internal.
The infection is easy to pick up in crowded places; the disease is especially common in kindergarten children
- stress;
- poor quality food and medicine.
- dysbacteriosis;
- avitaminosis;
- chronic diseases.
Staphylococcus aureus is especially often diagnosed in infants. The bacterium is transmitted to them during childbirth or feeding. It is common in children and other age groups.
Bacteriophages and toxoids
If antibiotics are ineffective, special drugs containing viruses that infect only staphylococcal bacteria are prescribed. These medications are administered in different ways: orally, irrigate the oral cavity with compounds, make applications, rinse, drip. For throat staphylococcus, as a rule, rinse the mouth with the product four times a day, seven days.
To prevent recurrence of infection and treat an existing problem, toxoids are used. They are a vaccine that encourages the body to produce certain antibodies. The medicine enters the bloodstream through a course of subcutaneous injections. This method is not acceptable for treating children; it is used only for treating adult patients.
Symptoms that appear in a child with illness
The incubation period occurs without the appearance of symptoms. At the moment of activation of Staphylococcus aureus on the pharynx, the following manifestations are characteristic:
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- cough;
- temperature rise up to 40 degrees;
- painful difficulty swallowing;
- purulent plaque on the tonsils;
- weakness, dizziness;
- digestive disorders.
These symptoms are common to many infections. If one or more signs are present, you should immediately contact your pediatrician to clarify the diagnosis and choose treatment. If the temperature rises sharply, an ambulance is called.
Symptoms of staph infection
Staphylococcal infection manifests itself in the throat:
- Pain and burning;
- Soreness;
- The need for frequent swallowing;
- Constant coughing.
Mild symptoms of the disease can increase for up to 2-3 days, and then turn into a more pronounced severe form, which is characterized by:
- Suppuration. Staphylococcus is a common purulent infection. Having established themselves on the mucous membrane, bacteria secrete enzymes that destroy cells. Microbes feed on the products of cellular decay and through them move further into the depths of the tissues. When bacteria are deactivated by immune cells, pus is produced. Therefore, boils and ulcers in the throat, as well as inflamed tonsils are clear symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus infection.
- Elevated temperature necessarily accompanies the ongoing pathological process.
- Signs of general intoxication necessarily accompany the disease: weakness, nausea, dizziness, lack of appetite.
- Cough with staphylococcus is a constant companion to a throat infection.
Interpretation of analysis indicators in the presence of staphylococcus
To identify Staphylococcus aureus, a general blood test and a description of the symptoms are not enough. When diagnosing the disease, the following tests are prescribed:
- blood test using PCR method;
- swab from the affected area;
- bacterial culture of urine or feces.
Swab from the throat and nose for staphylococcus.
Various types of staphylococci are often found in smears, incl. golden. An indicator of 10 to the 3rd degree is considered normal - if the permissible values are not exceeded, this is not considered a pathology. The upper limit of normal for Staphylococcus aureus is 10 to 6 degrees. The doctor assesses the threat of infection development individually according to four degrees of growth in the number of microorganisms:
- norm;
- borderline normal;
- moderate pathology;
- pronounced pathology.
It follows from this that if the value of Staphylococcus aureus 10 is 4 or 5 degrees, there is no need to panic. Timely diagnosis and selection of medications guarantee a favorable outcome of therapy.
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus in the throat
For diagnosis, you should contact a pediatrician, who can redirect the little patient to an otolaryngologist or infectious disease specialist. Sometimes a consultation with an immunologist is required, as well as sugar testing.
Treatment for staphylococcal infection in children differs from that in adults. At a young age, special care is needed in selecting antibacterial treatment. Some pediatricians, in a number of simple cases, try to exclude it altogether. If, despite the detected staphylococcus, the child feels healthy, then you can get by with drugs to strengthen the immune system. In general, the duration of therapy is individual. Decisions regarding treatment methods are made solely by the attending physician.
Use of antibiotics
Over time, staphylococcus in a child’s throat began to show resistance to old antibiotics, so new generation drugs are now being used. The specifics of antibacterial treatment and the possibility of individual intolerance should be taken into account. Drugs, doses, frequency and duration of administration are prescribed by a specialist.
For the treatment of children, the least toxic drugs are selected. Etiotropic treatment is carried out for at least a week, because an insufficient course of antibiotics can harm the body. The selection of medications occurs only after an antibiogram. If the microbe does not have time to enter the blood, then antibiotic therapy can be avoided. If antibiotics are ineffective, special bacteriophages are prescribed.
The most common doctor's recommendation is inhibitor-protected semisynthetic penicillins (for example, Amoxiclav). For young children, it is advisable to use a drug of the same group, but in a dispersible form - Flemoklav solutab. The doctor calculates the substances and their doses depending on individual factors. Antibiotics of the following groups are also used:
- cephalosporins;
- aminoglycosides;
- macrolides;
- lincosamides.
Antistaphylococcal immunoglobulin
Antistaphylococcal immunoglobulin is an injectable drug that contains antibodies to most strains of pathogenic gram-positive microbes. The medicinal solution is obtained from donor blood or serum. The dosage and duration of use of intramuscular injections depends on the child’s age and weight.
Direct indications for the use of the drug are any staphylococcal infections in patients over 6 months of age. As a rule, antistaphylococcal immunoglobulin is used together with antibiotics to enhance the effect of antimicrobial components. With the help of the medicine, it is possible to eliminate even generalized forms of inflammation, including sepsis.
Advanced forms of purulent tonsillitis and laryngitis are treated with hyperimmune antistaphylococcal plasma. It contains specific antibodies that destroy almost any strain of gram-positive bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus. The medicinal solution is administered intravenously to children for 2-3 days, after which the symptoms of the disease are smoothed out.
Staphylococcus aureus in the throat - treatment in children: 16 means to fight bacteria
Staphylococci in the throat are bacteria belonging to the group of gram-positive non-motile cocci. They are a segment of opportunistic human microflora. However, there is also a pathogenic form of this microorganism (golden), which, under favorable conditions, is activated and causes inflammation of the organs. The danger of bacteria lies in the production of harmful enzymes and toxins that disrupt the functioning of human cells.
The result of infection is purulent skin lesions, sepsis, and severe intoxication. It is very important to identify the pest in a timely manner, especially in children, so as not to provoke dangerous complications. Timely detection of staphylococcus and its treatment will protect the child from further complications.
Results
- The danger of staphylococci lies in the production of harmful enzymes and toxins that disrupt the functioning of human cells.
- The presence of staphylococcus in the throat leads to the appearance of laryngitis or tonsillitis, sore throat.
- Therapy for Staphylococcus aureus in the throat in children involves the use of comprehensive health measures.
- Antibacterial agents, rinses, immunomodulators, and folk remedies will help destroy harmful microorganisms in a child’s throat. We also recommend that you familiarize yourself with the sore throat spray for children in this material.
Causes and symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus in the throat in children
Staphylococci enter the human body through contact and household contact. Other factors can also cause a child to become infected:
- lack or poor hand and oral hygiene;
- eating dirty, stale foods.
The pathogenic bacteria in the throat is not activated if the baby has a strong immune system, but if the defense is weakened, it spreads quickly. The defense mechanism can be weakened by:
- avitaminosis;
- previous acute respiratory viral infections;
- long-term therapy with antibiotics, immunosuppressants;
- recurrent herpes sore throat;
- physical inactivity;
- poor nutrition;
- nervous disorders.
The presence of staphylococcus in the throat leads to laryngitis or tonsillitis. Often, a sore throat occurs in a more acute form, which is accompanied by symptoms such as swelling, increased body temperature, and pain when swallowing. Associated manifestations of staphylococcal lesions are:
- enlargement and redness of the tonsils;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- the presence of a pale yellow coating in the throat;
- lacrimation;
- chills;
- joint pain or muscle aches.
How is staphylococcus transmitted? Causes of infection
All diseases caused by bacteria can occur as a result of the fact that the infection enters the body due to a violation of the integrity of the skin or mucous membranes, because it is a permanent inhabitant of the human microflora.
In addition, infection can occur exogenously, that is, through food or through close contact. At the same time, we should not forget that some people are permanent or temporary carriers of this bacterium, which also has a significant role in the possibility of transmission. At the same time, pathogenic bacteria do not manifest themselves in any way, and such people pose a particular danger to those around them.
The following possible routes of transmission of infection are distinguished:
- Contact and household path. When bacteria enter the body through various household items or through direct contact with the skin. Sometimes it is enough to use someone else's towel or bedding for infection to occur. In this case, the bacterium can cause either an inflammatory process or simply invade the body and lead to carriage;
- Airborne path. That is, a person inhales air in which bacteria are present. Most often, the source of infection is sick people who release bacteria when they cough, sneeze, or simply breathe;
- Dust. Bacteria tend to exist for a long time in the surrounding dust. When it enters the respiratory tract, infection occurs. This path is called “air-dust”;
- The fecal-oral route, which is also called the nutritional route. In this case, the bacteria are released when an infected organism vomits or defecates. An uninfected person eats foods that contain staphylococcus and becomes ill. This often happens due to insufficient hygiene, namely through dirty hands;
- Medical instruments. The bacterium can penetrate into a healthy body through poorly processed medical instruments; this is the so-called artificial method of infection. Infection occurs during diagnostic procedures, for example, during bronchoscopy, as well as during surgery. An additional danger is that instruments may be disinfected in the usual way, but they contain bacteria that have developed resistance to specific sanitization methods.
In addition to the listed routes of infection, there are also indirect reasons that provoke human infection with staphylococcus:
- Any disease that causes a decrease in immune strength. This also includes frequent and severe stress and irregular sleep;
- General hypothermia of the body. This reason plays a leading role in the development of the inflammatory process in the upper respiratory tract. At low body temperatures, the work of the cilia of the ciliated epithelium, which line the nasal mucosa, slows down. Thus, it is much easier for staphylococcus to enter the body and provoke an inflammatory process;
- Existing diabetes mellitus and other disruptions in the endocrine system;
- Bad habits such as smoking and frequent drinking of alcoholic beverages.
- The presence of the immunodeficiency virus or AIDS;
- Any chronic diseases;
- Age. According to statistics, newborns, early preschool children and the elderly are most susceptible to infection;
- Viral infections often precede the disease becoming bacterial. In most cases, this is observed with influenza and ARVI, when, against the background of decreased immunity, the staphylococci existing in the body begin to exhibit pathological activity;
- Long-term use of vasoconstrictor drops, which disrupt the integrity of the nasal mucosa and promote infection;
- Inhalation of allergens and toxic substances leads to trauma to the bronchi, which can become a provoking factor in the development of bacterial inflammation;
- Insufficient hygiene;
- Eating contaminated foods;
- Violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes or skin.
Treatment of staphylococcal infection in the throat of a child
During the examination of the child, the specialist will prescribe a bacterial culture of the smear; if the baby has a problem, he will also check the mother’s milk for pathogenic microflora. Therapy for Staphylococcus aureus in the throat in children involves the use of comprehensive health measures. Treatment is aimed at blocking the infectious agent, strengthening the body's defense mechanisms, and sanitizing the throat.
How to treat with antibiotics
Antibacterial agents will help destroy harmful microorganisms in a child’s throat. The least toxic substances are used to treat children. Etiotropic treatment is carried out for about a week. The selection of medications in this group is carried out after an antibiogram.
Amoxiclav
The drug is presented in the form of powder and suspension. The substance is prescribed to children from the age of two months.
The effect of the antibacterial drug depends on the dosage. In small quantities, it has a detrimental effect on the growth of staphylococcal microorganisms. If the dose is large, it completely destroys bacteria. Oral administration is allowed for patients over 6 years of age. The daily dose is set by the pediatrician depending on the child’s body weight and is 45 mg/kg body weight. The minimum course of treatment is 5 days. In severe cases, therapy is extended to 10 days.
Flemoklav
Amoxicillin is the main component of Flemoklav. It belongs to the penicillin group. An additional ingredient is clavulanic acid. The substance has an extensive bactericidal effect against staphylococci, enterococci, streptococci and other pathogenic microorganisms. The tablets are approved for use from three months of age. For children under 12 years of age weighing up to 40 kg, the dosage is 30 mg/kg per day. Price from 260 rub.
Kanamycin
An antibiotic of the aminoglycoside class, it has broad bactericidal properties. The drug is active against many gram-positive pathogenic microorganisms. Children are given it intramuscularly. The daily dose is 15 mg/kg, up to 3 times a day. The treatment regimen may vary depending on the severity of the disease and the effect of drug therapy. Price from 540 rub.
Rifaximin
An antibiotic with a broad spectrum of action, belonging to the group of ansamycins. Prescribed from the age of two. For children under 12 years of age, the dosage is from 0.4 to 0.8 g per day in the form of a suspension. The daily volume of the substance is distributed into several doses. For the younger children's group (2–6 years), it is recommended to take 0.2–0.6 g of the drug in 2–3 procedures. The duration of the course is a week.
Use of antistaphylococcal immunoglobulin
This drug is sold as a solution for intramuscular administration. It is recommended in complex treatment with simultaneous administration of an antibiotic. The product is effective in severe forms of staphylococcus infection and its manifestations. The medication strengthens immunity to the harmful effects of staphylococcal strains. The treatment regimen is selected by the doctor, it depends on the diagnosis and the age of the child. For generalized staphylococcal lesions, a single dose per 1 kg of body weight in children under 5 years of age is 100 IU. The course will require 3-5 injections every other day or daily. Price for 10 ampoules - 9600 rubles.
Antistaphylococcal bacteriophage
A powerful immunostimulating substance that can specifically act on staphylococcal bacteria. The product is used for oral administration, irrigation and administration into the cavity of ENT organs. Recommended dosages for children:
For purulent-inflammatory pathologies of the throat, the drug is administered in a dose of 2–10 ml up to 3 times a day. Bacteriophage is also used for rinsing and washing. Price - from 550 rub.
Staphylococcal toxoids
The drug is available in liquid form and is a vaccine. The substance consists of staphylococcal toxoid, sorbent and other additives. When administered, it promotes the formation of specific antibodies to the exotoxin of the pathogenic microorganism. The course of immunization for infections in children over one year old consists of two injections of the drug, performed every other month.
Can it be cured by rinsing?
Rinsing is recommended for children along with antibiotics. These procedures relieve pain, destroy infection, and restore strength.
Chlorophyllipt
The product provides antiseptic and antimicrobial effects. The solution contains chlorophylls, minerals, essential oils, phytoncides, and other compounds that destroy pathogenic microorganisms. The extract is effective against staphylococci, since it affects strains that do not die even after an attack by antibiotics. Treating the throat reduces pain, eliminates redness, reduces cough and other symptoms.
For children, Chlorophyllipt is prescribed in a diluted form for farengitis. To prepare, 10 ml of the product must be dissolved in a glass of slightly warm water. Gargle at least three times a day. Price - 300 rub.
Chlorhexidine
To rinse, 20 ml of solution must be held in the mouth for 45 seconds. Perform the procedure half an hour before meals three times a day. The duration of therapy is 10 days. Treatment with Chlorhexidine is effective, economical and safe. For children under three years of age, the product is allowed only in the form of a spray or gauze swabs moistened with an antiseptic. Price - 12 rubles.
Furacillin
The medicine is often included in the treatment of chronic tonsillitis and tonsillitis along with antibiotics. The solution removes pathogenic bacteria and purulent fluid from the mucous membranes, and blocks the progression of inflammation. The drug is used for local action, so it is recommended for infants.
To rinse, you need a solution prepared from a tablet, which needs to be filled with 100 ml of warm boiled water. Before use, be sure to strain the liquid so as not to injure the mucous membrane with undissolved crystals. The throat should be gargled with a warm mixture at intervals of 2 hours, only after eating.
Other antibiotics for staphylococcus
In some cases, a person is prescribed other antibiotics, because many people have allergic reactions to penicillins. The following medications may be recommended:
- Sumamed
(520 rubles). Refers to macrolides, unlike penicillins, has little effect on the normal intestinal microflora, causes fewer side effects. Suppresses the synthesis of microbial cells, inhibits their development. Microbes easily become resistant to the active substance (azithromycin), so the drug is usually used no more than once every 1-2 years.
- Vancomycin
(170 rubles). Antibiotic of the glycopeptide group, inhibits the biosynthesis of microbial cell walls. It affects most types of staphylococcus, is very powerful, bacteria practically do not develop resistance to it.
- Kanamycin
(450 rubles). Belongs to aminoglycosides, penetrates microbial cells, disrupting the production of proteins for RNA. Allowed for children from a month, but contraindicated during lactation and pregnancy.
In case of severe staphylococcal tonsillitis, the patient may be prescribed cephalosporin antibiotics (Cefalexin, Pancef), but such drugs are not used unless absolutely necessary.
Staphylococcus aureus in a child’s throat is always a problem, but not always a disease
Author: Alexey Shevchenko July 03, 2021 23:17 Category: Nature and people
Good day, dear friends of Alexey Shevchenko’s blog “Healthy Lifestyle”. A huge number of bacteria are constantly present in the human body. Some of them, such as Staphylococcus aureus or S. aureus, are especially well adapted to colonize literally all areas of the body. Most often, these uninvited guests settle in the nasopharynx, groin, perineum and intestines.
In this article I want to talk a little about the topic of Staphylococcus aureus in a child’s throat.
Dangerous roommate
Human life is unthinkable and even impossible without bacteria. Some of them are an essential part of the digestive system, others by their presence protect us from the attack of pathogenic microflora, but there are also those that behave like a sleeping cell of terrorists.
In fact, they are capable of causing severe or fatal diseases, but for the time being they do not cause the slightest harm and do not show their presence in any way. This is exactly how the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus behaves when it colonizes the human body. (The features of this bacterium are also described here).
Throughout peaceful coexistence, the human body receives neither harm nor benefit from S. aureus, while the bacterium derives some benefit. This cohabitation is called commensalism.
At the same time, the bacterium behaves very cunningly: it multiplies exactly in those quantities that do not cause an immune response from the host body. The microbe subtly senses the state of the immune system, and as soon as the protective forces are sufficiently weakened, it goes on the attack and begins mass reproduction.
It should be noted that the asymptomatic presence of S. aureus in the nose and throat is extremely common. A number of international studies provide the following data:
- in Western European countries, 25% of the population are carriers of S. aureus;
- in Norway – 27.6%;
- in Switzerland – 36.4%;
- in the USA - 30.4%;
- in Japan 35.7%;
- in China – 23.1%;
- in African countries – 13–18%;
- in Mexico - 37.1%.
S. aureus is most widespread among tribes living in the Amazon rainforest. There, 57.8% of the population are carriers of nasal S. aureus.
Determination of pathogen
Staphylococcus is a representative of immobile gram-positive microorganisms that have the shape of a ball or sphere, reaching a size of one and a half microns. This microbe provokes inflammatory processes in the human body. There are about twenty forms of this single-celled organism. Most of them are an integral part of the human microenvironment. And with a fully functioning immune system, these organisms do not cause any problems, being opportunistic.
The causative agent of infections in the vast majority of cases is Staphylococcus aureus. It is a representative of bacteria that produce an enzyme that clots blood. Among those that do not produce this enzyme (coagulase), only epidermal and saprophytic staphylococci are considered pathogenic. The hemolytic subtype, leading to systemic inflammation, is also considered pathogenic.
Staphylococcus is localized in children, mainly on the surface of the mucous membrane in the nose and pharynx, occasionally in the genitals, in the gastrointestinal tract, on the epidermis of the armpits, and in the groin. Staphylococcal infection refers to certain ailments with typical manifestations of poisoning by bacterial secretion products and purulent-inflammatory localizations.
The class of microbes under consideration is quite resistant to dryness, high temperature, pure alcohol, and sweat. The acidity for their beneficial growth is approximately seven and a half pH. Parasites can exist in oxygen and oxygen-free environments. These organisms often mutate to become resistant to antibacterial drugs. Bacteria contain more than fifty antigens that provoke an allergic response, autoimmune pathologies that affect blood components, epidermis, and excretory organs. Half an hour of heating to seventy to eighty degrees Celsius destroys them. At one hundred and fifty degrees they are neutralized immediately.