What to do if you find red spots?
If you accidentally find red spots in your child’s mouth, then do not neglect his health, but take him straight to the doctor to find out the real reason and get laboratory tests.
Your health and the health of your loved ones is priceless, so you should not neglect even such a minor phenomenon as a rash in your mouth. Small pimples can indicate serious problems that a person is not even aware of.
It is worth understanding that the rash is only a symptomatic manifestation of the disease, and not the disease itself.
Timely examination and accurate diagnosis will reduce the risk of complications, especially when it comes to infectious diseases. Remember that proper treatment with appropriate medications can correct the entire situation in a few days.
Chickenpox, or chickenpox
Pathogen: Varicella-Zoster virus (VZV).
Method of transmission: airborne. It is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person by talking, coughing, or sneezing.
Immunity to chickenpox: lifelong. Produced either as a result of illness or after vaccination. In children whose mothers had chickenpox or were vaccinated against it, immunity to chickenpox is transmitted from the mother in utero and persists for the first 6-12 months of life.
Incubation period: from 10 to 23 days.
Infectious period: the entire period of the rash is 5 days after the last rash.
Manifestations: red dots appear simultaneously with a rise in temperature. However, sometimes the temperature may remain normal or rise slightly.
The spots very quickly turn into single vesicles filled with a clear yellowish liquid. Soon they dry out and become crusty.
A distinctive feature of chickenpox is a rash on the head under the hair and on the mucous membranes (in the mouth, on the eyelid, etc.). Very often this rash itches.
Treatment: chicken pox goes away on its own, so treatment can only be symptomatic: lower the temperature, treat the itchy rash with brilliant green (so that by scratching the blisters, the child does not introduce additional infection there), give an antihistamine to make itching less. You can swim if you have chickenpox! But at the same time, you should not rub the affected areas; instead, you need to gently blot them with a towel.
Important: you need to use brilliant green or other dyes (fucorcin, etc.) in order not to miss the next rash, because only old spots will be smeared. It is also easier to track the appearance of the last outbreak of the rash.
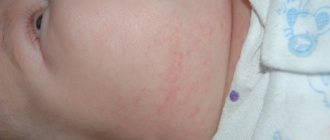
Blisters on a child's body
The appearance of blisters on a baby’s body is a symptom that cannot be ignored. He does not always talk about something alarming, but it is necessary to understand the cause of the rash in order not to miss a situation in which the child needs immediate help. We will tell you what blisters can signal in this article.
We are used to putting a lot of different ideas into the word “blister”. This is a watery rash, an abscess, a formation of unknown nature with or without a head, and a pimple. Medicine answers this question unequivocally. A blister, according to terminology, is a cavityless formation that appears as a result of an acute inflammatory process in one of the outer layers of the skin.
Real blisters (not to be confused with rashes, herpes and other skin manifestations!) have a very short life span - from several minutes to several hours, they rarely last for a day. They appear and disappear very quickly. All blisters are pink and round or oval in shape. The blister protrudes slightly above the surface of the skin and has a dense structure.
The main reason for the appearance of a blister or several similar formations is a point effect on the skin, damage to the papillary layer of the dermis. This is possible due to insect bites or contact with toxic substances of both natural and artificial origin. Quite often, the appearance of such formations on the skin is a sign of an allergic reaction.
Spots with blisters that appear as a result of a burn after intense tanning cannot be considered blisters. Attempts to classify them into this category of entities are a common misconception. All this is true, from the point of view of terminological medical dictionaries. In fact, parents classify any formations as blisters, not only empty, but also filled with watery contents, pus, and blood. And they seek advice specifically about “blisters” in the broad sense of the word, that is, in the layman’s sense.
The location of the skin lesions can tell a lot about the reasons. Let's take a closer look at the most common situations.
Blisters on the hands can be the result of a banal violation of hygiene rules and requirements. If a child rarely washes his hands, then pathogenic organisms can enter microcracks, which cause slight local inflammation. Usually the situation can be easily corrected by establishing regular hygiene procedures and teaching the child how to wash their hands correctly.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to clean your tonsils (tonsils) at home. conditions?
If the blisters are filled with liquid, visually they are similar to those that appear if a child burns his hands with nettles, then we are talking about hives - a local manifestation of an allergic reaction. It can be for both food and medicines. If the urticaria is localized only on the hands, then, most likely, the child had contact with something allergenic through touch (found detergent in the bathroom, reached into the cleaning powder with his hands, etc.).
In this situation, hands should be washed thoroughly and the child should be given an antiallergic drug, for example Suprastin. And, of course, you need to find the source of the allergy and stop the child’s further attempts to put his hands where he shouldn’t. If hives affect not only the hands, but also other parts of the body, it is imperative to show the child to the doctor. Blisters on arms and legs, elbows and shoulders can be signs of insect bites. Fenistil will help relieve itching and discomfort.
In nature, there are practically no infectious diseases that are characterized by a rash only on the arms or only on the legs. However, you still need to show your child to a doctor if the blisters do not disappear after a day.
This is a more dangerous situation. If blisters appear all over the body, then with a high degree of probability the child may have an infectious disease. You should call a doctor immediately. It is better not to take your child to the clinic, since the lion's share of such diseases, accompanied by skin rashes, are contagious.
The following diseases occur with a rash resembling blisters of pink, red, serous color, as well as with watery and other contents:
- chicken pox and other herpetic infections;
- erysipelas;
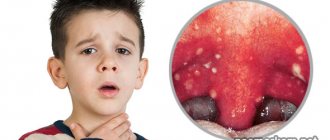
- follicular tonsillitis (in this case, formations resembling blisters are present both on the palate and on the tonsils);
- streptoderma.
There is no need to self-medicate in this situation, especially if there are other symptoms of infection - fever, nausea, diarrhea or vomiting, respiratory signs, which include runny nose, cough, shortness of breath. The younger the child, the more difficult it is for him to fight viral and bacterial infections, and therefore the help of a doctor is a prerequisite for a successful recovery.
Viral infection
Viral infections of the mouth and throat often provoke a small rash on the palate of an adult or child, since the activity of these pathogenic organisms leads to the death of local cells, pinpoint hemorrhages and swelling. Most often the patient is diagnosed with:
- flu;
- herpetic stomatitis (the source of infection is localized in the gums and tonsils);
- herpetic sore throat (the upper parts of the pharynx and tonsils are affected);
- herpetic pharyngitis (infection reaches the middle and lower parts of the larynx, also spreading to the pharynx and tonsils);
- measles or rubella (mostly only in young children);
- ARVI;
- Infectious mononucleosis.
Viral diseases
What can cause the formation of red spots in the oropharynx? Theoretically, the cause of the pathological symptom can be any respiratory disease in which the infection is localized in the throat. Viral diseases are extremely rarely limited to damage to the laryngopharynx mucosa, so patients often complain of inflammation of the nasal mucosa and rhinitis.
Common diseases that cause sore throat in adults include:
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to quickly relieve or relieve toothache Disease Typical manifestations
| flu | high fever, chills, headaches, dry mouth, erythematous rash on the walls of the throat, difficulty nasal breathing, muscle weakness |
| herpangina | febrile fever, vesicular rash in the oropharynx, abdominal pain, difficulty swallowing, hypersalivation, fibrous film on the throat mucosa |
| herpetic stomatitis | red throat, pinpoint rashes on the mucous membrane, burning and sore throat, aphthous formations in the mouth, swollen lymph nodes, painful swallowing |
| measles | high fever, hoarseness of voice, large red spots on the soft and hard palate, redness of the conjunctiva of the eyes, sneezing and photophobia |
| rubella | macular rash on the body, headaches, inflammation of the throat mucosa, red dots on the palatine arches and the back of the pharynx, cervical adenopathy |
| Infectious mononucleosis | fever, inflammation of the pharynx, swollen lymph nodes, pain when swallowing, red rashes in the oropharynx, weakness, migraine, high fever |
| viral pharyngitis | soreness in the laryngopharynx, dry cough, low-grade fever, difficulty breathing, small vesicles on the palatine arches and the back of the pharynx |
It is possible to reliably determine the cause of the appearance of an erythematous rash only after submitting a swab from the throat for virological and microbiological analysis.
If the mucous membrane of the laryngopharynx is strewn with white dots, most likely, the provocateur of inflammatory processes in the ENT organs is a yeast-like or mold fungus (candidal tonsillitis). Untimely treatment of diseases leads to the spread of infection and damage to the lower parts of the respiratory system, which can lead to the development of bronchitis, laryngotracheitis, pneumonia, etc.
Herpes
Many people mistakenly believe that the blistering rash of herpes only affects the lips on the outside. In fact, it can be localized in any part of the oral cavity, skin, and even on the mucous membranes of internal organs.
We suggest you read: Is stomatitis contagious or not when kissing?
The vast majority of people are carriers of the herpes virus, since once they enter the body, viral particles remain in it throughout their lives. When the body's immune defense is weakened, the virus is activated and appears as a red rash on the face and oral mucosa.
When they burst, the blisters become sites of inflammation and secondary infections. Mild herpetic lesions of the mucous membranes can develop into ulcerative-necrotic ones, so careful care is required for inflamed areas of the oral cavity.
Principles of treatment
The success of treatment for red rashes on the throat is determined by the correct diagnosis. During the examination, the therapist will assess the nature of the clinical manifestations of the disease and the location of the rash, after which he will redirect the patient to an otolaryngologist, oncologist or infectious disease specialist.
In the vast majority of cases, red dots and vesicles arise as a result of a viral infection of the respiratory system. Immunostimulating and antiviral drugs will help eliminate pathogenic flora and manifestations of the disease. The following types of medications are most often included in the treatment regimen for ENT diseases:
“Acyclovir” is an antiviral agent, the components of which destroy most of the virions that cause damage to the ciliated epithelium and skin; "Valacyclovir" is an antiviral medicine that inhibits the DNA synthesis of the herpes virus, which prevents the development of infection; “Viferon” is an antiproliferative interferon inducer that increases the activity of immunocompetent cells, which prevents the progression of the disease; "Cycloferon" is an immunostimulant with antiviral action that helps increase the body's resistance.
Solution antiseptics for irrigation of the oropharynx can stop local manifestations of the disease. In pediatric therapy, Faringosept, Hexoral, Orasept, etc. are used to treat hyperemic mucosa.
There are many diseases in which a rash, plaque, and sometimes an abscess appears in a child’s throat. Such diseases include diseases such as influenza, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, acute respiratory viral infections, and the like. All of these diseases can be accompanied by a rash in the child’s throat.
In addition, a rash or plaque on the tonsils in children with these diseases occurs much more often than in adults. Also, an abscess or plug may appear in a child’s throat with such diseases, but if they are detected, one cannot immediately say that it is a purulent sore throat.
First of all, you need to see a doctor for a blood test, and only after that the doctor will be able to make a diagnosis. Naturally, we will not be able to list all the diseases in which plaque, plug or abscess may occur on the tonsils, because there are a lot of them.
Let's consider the main diseases that can cause plaque or rash on the tonsils, as well as an abscess or plug:
Angina. It is in the chronic form of a sore throat that a child may develop an abscess or plug in the throat, and a rash and plaque can also occur in the normal form of a sore throat; Stomatitis. Only with the aphthous form will the child experience symptoms such as rash, plaque and sores; Pharyngomycosis. With this disease, the child’s throat will not only have a rash and plaque, but also many ulcers.
The purulent form of this or that disease is considered almost the most dangerous of all types. In the purulent form, the child’s body temperature can jump to 39⁰C and this is not the worst thing, since the resulting pus can spread throughout the body through the blood.
It is very important not to let this disease progress, since when it becomes chronic, it can lead to complete atrophy of the throat tissue.
Depending on the severity and causes of the disease, symptoms of the disease will appear either separately or all at the same time. Each of the symptoms of the presented throat disease can reach such a degree that it will be necessary to fight exclusively with it.
As soon as the first symptoms of the disease appear, you need to take action, because if you do not carry out proper treatment in the first stages of the disease, the symptoms will reach such a level that your life will be in danger.
The purulent type of the disease develops much faster compared to other forms of the disease, so treatment should not be delayed. What symptoms accompany a rash in a child’s throat? So, the presented throat disease, as a rule, has the following main symptoms:
Severe soreness; Difficulty breathing; Pain when eating; Dry throat; An abscess or plug in the throat is noticeable; Feeling of throat constriction; The appearance of hoarseness; Enlarged lymph nodes; White plaque on the tonsils; Fever; Body temperature can reach 39⁰С; Weakness.
Treatment
The most important thing in treatment is to remove foods from your diet that can irritate your throat. That is, get rid of sour, salty, hot, cold and spicy foods. It is also contraindicated to drink alcoholic beverages and smoke, since tobacco smoke and alcohol also lead to irritation of the mucous membranes.
If you have a sore throat, you need to drink plenty of fluids, and the ideal option would be to drink vitamin drinks, such as rosehip infusions or berry fruit drinks.
Antipyretic drugs are used to reduce body levels. As a rule, the doctor prescribes drugs that include interferon and lysozyme, as well as mineral and vitamin complexes.
Most often, treatment of the purulent form of the disease is carried out with the help of special medications, but if an abscess has formed in the child’s throat, then surgical intervention is necessary, as this may be a sign of the development of acute tonsillitis or pharyngitis. In this case, the abscess must be removed, but before this, a blood test of the child is performed.
Lubricating the inflamed side ridges of the throat may also be prescribed to reduce swelling, which contributes to pain. Removing swelling of the lateral ridges is the most important task in treatment, unless a plug or abscess is discovered, since then the main task will be their removal.
Naturally, it is impossible to lubricate the inflamed side ridges of the throat on your own; only a doctor can carry out such a procedure using special instruments.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of this disease, you need to use the following methods of prevention:
Temper the body; Restore impaired nasal breathing; Strengthen immunity.
Some recommendations for a child who has a rash in the throat:
Do not buy various cough drops as they are a waste of money. They cannot cure the throat, but only ease the discomfort; There is no need to rely only on gargling. In addition, inflammation of the mucous membranes with chronic pharyngitis cannot be treated at all by rinsing with a soda solution, as this greatly dries out and complicates the treatment of the disease; There is no need to use nasal drops very often. Frequent use of nasal drops can cause inflammation and irritation of the throat as the drops flow from the nose into the throat.
Other diseases
Rashes in the throat, causing severe discomfort and pain, signal a change in the morphology of the soft tissues in the areas where the red dots are located. Erythematous spots, localized on the soft palate and tongue, in some cases arise due to the development of complex diseases:
- staphylococcal infection;
- exudative erythema;
- Kawasaki syndrome;
- syphilis;
- roseola;
- meningitis.
Since the list of possible pathologies is quite extensive, if red dots appear in the laryngopharynx, you cannot postpone a visit to the therapist. The principles of treatment depend on the etiological factors in the development of the disease, the localization of the rash and accompanying clinical manifestations. As a rule, antibacterial and antiviral drugs are used to eliminate infectious ENT diseases. Antipyretics, analgesics and antihistamines can make you feel better and eliminate discomfort.
There are a few more diseases that are rare and cause an atypical rash:
- Mononucleosis. Not only the throat, but also the entire mucous membrane in the mouth turns red. The tonsils are enlarged and the throat is sore. It’s difficult to breathe, my nose is stuffy. Bright large spots appear along the sky.
- Pyogenic granule. Places that are often injured turn red.
- Kaposi's sarcoma. Purple spots on the mucous membrane, convex or flat. It happens with HIV infection.
If the doctor notices an atypical rash, he will check to see if the child has something similar. Never self-medicate.
What other diseases can cause the appearance of red spots on the palate in children and adults?
If red spots appear on the palate of yourself or your child, be sure to consult a doctor.
A person can encounter the problem of redness of the palate only once during his life or periodically, which is due to the nature of the disease that has these symptoms. Relapses include herpes, thrush, and enterovirus infections.
Once the body has been affected, it is impossible to get rid of them.
When conditions are favorable for viruses and bacteria, the disease worsens, so it is important to take preventive measures to suppress the pathogen
The characteristic red rash in the mouth is one of the symptoms of other diseases.
- One of the symptoms of tuberculosis is flat red spots on the oral mucosa. Over time, the reddish or red-yellow inclusions merge to form plaques. The surface of the formations is heterogeneous, the color becomes red-bloody.
- ARVI is recognized in particular by red spots on the soft palate and tongue. Associated symptoms are characteristic of acute respiratory diseases.
- Oncology, among a large number of signs, has one more, which is related to the oral mucosa. A small ulcer forms on the palate, increasing in size over time. However, at first it does not cause discomfort, there are no painful sensations. Reaching large volumes, the ulcer begins to interfere, and difficulty is experienced when swallowing.
- Vitamin deficiency is characterized by a deficiency of vitamins and minerals important for all body systems. Their deficiency weakens protective functions and increases vulnerability to bacteria, fungi, viruses and infections. Red spots with vitamin deficiency are located locally on the skin and mucous membranes, without spreading intensively to neighboring areas.
- Herpes is a viral infection that once it enters the body, does not disappear. The disease worsens against the background of weakened immunity. A characteristic sign: small red spots on the mucous membrane, increasing in size, transforming into small bubbles with liquid inside.
- Chickenpox is diagnosed mainly in children under 14 years of age, but this does not exclude the risk of infection in adults. Not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes are covered with spots. In the mouth you can first find small red dots, which turn into bubbles and very soon burst. This results in gray or yellow ulcers with redness around the circumference.
- Measles is characterized by a rash on the skin and mucous membranes, high fever, general physical weakness, and lack of appetite. The affected area even extends to the mucous membrane of the eyes. Initially, white spots form in the mouth behind the cheeks, and as it moves to other areas, the rash acquires a bright red tint.
- Infectious mononucleosis is recognized by its extensive affected area; spots cover not only the palate, but the entire oral mucosa. There is a soreness in the larynx, and the tonsils increase in size. Breathing becomes difficult due to nasal congestion. Characteristics of the spots: the color is bright, the parameters are impressive, they appear more often along the palate, and quickly spread to other areas.
- Scarlet fever is recognized by red spots that are localized on the soft palate. Other signs of the disease: headache, fever, nausea, pain when swallowing. The tongue becomes crimson in color, the mucous membrane is inflamed, and the rash on the skin is very itchy.
A similar mechanism for the appearance of spots in each individual case still has characteristic features and accompanying signs by which the diagnosis is made. But sometimes even the experience and colossal knowledge of a specialist do not make it possible to diagnose the problem without laboratory tests. Therefore, you should not postpone going to the clinic so that the situation does not get out of control.
How to identify a rash caused by an allergy?
An allergic rash in the mouth on the roof of the mouth or the back of the throat usually does not cause discomfort. It can be caused by food, toothpaste, mouthwash or medications. The spots will go away as soon as the allergen wears off.
Symptoms:
- The spots are located symmetrically.
- Between the elements there are light areas on the affected mucosa.
- Elements often merge into a single large spot.
- No itching or burning.
- The rash spreads to the skin.
Despite the seemingly harmless nature of this manifestation, it is still necessary to consult a doctor.
The roof of the mouth hurts: medications and procedures
If you experience pain in the oral cavity, first of all you need to contact your dentist so that he can examine you, establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Important! Before visiting the dentist, do not take untested actions, ointments, or medications to relieve pain. In emergency cases, you can relieve inflammation with chamomile decoction. Effective methods for treating inflammatory processes
Effective methods for treating inflammatory processes
Inflammatory processes in the palate can be treated in several ways, the most effective of which are the following:
When candidiasis appears, the doctor will prescribe certain medications. To get rid of the fungus, Acyclovir or Candide gel is applied to painful areas;
To treat the oral cavity, use furatsilin, or dilute potassium permanganate;
Do not eat irritating foods.
Treatment methods for neuralgia
1. After a thorough examination, you will need a consultation with an oral surgeon, as well as an x-ray. Conventional medications are unlikely to help with such pain, so an injection of ice caine is needed.
2. In order to prevent further spread of inflammatory processes, you need to take antibiotics. But you shouldn’t prescribe them yourself.
Treatment of burns in the oral cavity
1. After receiving burns to the mucous membrane in the oral cavity, it is necessary to rinse your mouth with warm water, and then apply anesthetic gel - Metrogyl Denta.
2. Immediately after eating, rinse your mouth with the following solution: one spoon of calendula diluted in a glass of water.
3. If the mucous membrane has been burned by hot food, then you need to rinse your mouth with warm water until the pain in the palate subsides.
4. If you receive a chemical burn, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. The harmful substance must be removed; to do this, rinse your mouth several times in a row.
Traumatized sky
This is the most common phenomenon that happens to both children and adults, so you need to know what to do in such a situation:
To relieve redness, you can use tinctures of medicinal herbs;
Be sure to visit your dentist and get advice on what solution to buy. If the wound is infected, use Miramistin or Rotokan;
To disinfect the affected area, you can use aloe juice;
Severe pain can be eliminated with painkillers.
Important! If painful sensations occur, you need to contact your dentist in order to avoid improper treatment. Timely contact with a specialist is the key to successful treatment
What infectious diseases are accompanied by a rash in the mouth?
Most often, red spots in the mouth appear due to infection. But the rash will not be the only symptom. The body temperature will rise, the throat will begin to hurt, the person will feel general weakness and pain when swallowing. Associated symptoms determine the type of infection.
These may be influenza, herpes simplex virus, chickenpox, rubella, measles, mononucleosis, erythema infectiosum, roseola, scarlet fever, typhus, syphilis, staphylococcal infection, meningitis. The list of diseases is quite wide, and all of them are very dangerous.
A child's body copes with a viral infection more easily. In case of chickenpox, scarlet fever or rubella, a long quarantine is required, but the child’s condition does not cause concern. After recovery, persistent lifelong immunity is acquired. But measles, rubella and chickenpox are dangerous for adults, they are severe and cause various complications. Treatment is often carried out in a hospital.
In young children, the following diseases, manifested by a rash, are severe:
- Primary infection with the herpes virus.
- Herpetic sore throat.
- Stomatitis.
Important: These diseases develop rapidly and acutely.
Red upper palate of a child | Medical reference
In a child, red dots on the palate or throat are always a signal that unfavorable changes are occurring in the body.
The rash can be found in children at any age. There are two main reasons for the appearance of red spots - an allergic reaction and the development of an infectious disease.
In order not to miss the onset of a serious illness, a child with a rash on the upper palate should be shown to a doctor.
Red spots on the mucous membranes of the mouth, palate and throat in a child: types of rash with photos and explanations
Sometimes a child begins to complain of a sore throat, and parents, looking closely at the baby, notice red dots on the mucous membrane of the palate that resemble pimples. In medical practice, red rashes on the tissues of the throat are called enanthema. What is it, should I be afraid of rashes, and in what cases is the help of a specialist needed?
Treatment for enanthema varies depending on the cause of the rash.
Signs of enanthema - rashes on the oral mucosa
In some cases, malaise may be accompanied by rashes, the nature of which depends on the disease. Most often, enanthema is caused by bacteria or viruses. The baby's condition is characterized by the following symptoms:
- he complains of a sore and itchy throat;
- he has difficulty breathing;
- it hurts for the baby to swallow;
- there is pain and aches in the body;
- In the morning and evening the baby is bothered by a dry cough;
- there is an increase in temperature and signs of intoxication.
Causes of red dots on the throat and palate
There are many causes of enanthema. The most common causes of rashes are:
- fungal infection;
- diseases of a viral nature;
- allergic reactions.
Viral diseases
- One of the common causes of enanthema is the herpes virus. Thus, herpetic sore throat is characterized by high temperature and the appearance of blisters in the mouth - on the tonsils, on the inside of the cheeks, hard and soft palate (more details in the article: treatment of herpetic sore throat in children and photos). The blisters have a transparent or yellow tint and tend to burst, leaving painful erosions.
- Chickenpox can also cause similar symptoms. the causative agent of which is also a subtype of the herpes virus. During the illness, the child develops a rash all over the body, but in rare cases, red spots may also cover the oral mucosa.
- Also, the herpes virus provokes the development of stomatitis (we recommend reading: what stomatitis looks like in a baby and photos). This is a disease that most often affects newborns and children under 3 years of age. Blisters with stomatitis have a cloudy tint and cover the oral mucosa and palatine tonsils. As with herpetic sore throat, with stomatitis the temperature rises. In case of severe intoxication, hospital treatment is indicated.
- Enanthema can accompany ARVI - the throat becomes inflamed, becomes red, a runny nose and cough appear, worsening in the morning and evening. Headache and muscle pain are observed, and the temperature rises.
- Another disease, infectious mononucleosis, is characterized by a sore throat and red spots scattered throughout the throat mucosa. The child has difficulty breathing and enlarged tonsils.
- Red dots can form in the nasopharynx during measles. Recently, thanks to mass vaccination of children, this disease is extremely rare. The baby is at risk of contracting measles only if the parents refuse routine vaccination (we recommend reading: what measles looks like in children and photos). The disease begins with a sore throat, then the temperature rises, a runny nose and cough appear. At this time, several light spots with a red iris may appear on the mucous membrane of the mouth, which gradually spread to the mucous membrane of the throat and oral cavity.
When should you contact a specialist?
Regardless of the nature of the rash in a child (it is present only on the mucous membrane of the throat or distributed throughout the body), you should immediately seek help and explanation from a doctor. Such symptoms may indicate the presence of dangerous viruses or infection in the baby’s body.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Propolis for caries and other folk remedies at home
Without treatment, enanthema of a viral or infectious nature can cause serious complications and spread to internal organs. To determine the exact cause of small rashes, the ENT doctor conducts a thorough examination of the throat mucosa. If necessary, additional tests may be prescribed: general blood and urine tests, allergen identification, etc.
Causes of rashes on the oral mucosa in children and adults
The causes of oral rashes are numerous. Often, the presence of rashes in the mouth indicates dental diseases, dysfunction of organs and systems, and hormonal imbalances. The type of infection can be determined by the nature of the spots and accompanying symptoms. The dentist should make a diagnosis and determine a treatment regimen.
Viral and bacterial infection
Red spots on the palate of a child and a rash on the tonsils are most often caused by viral or bacterial infections. An infectious lesion in a child or adult is accompanied by a febrile state (fever, sore throat, and in some cases chills).
The cause of rashes can be influenza, chickenpox, diphtheria, ARVI, scarlet fever, meningitis and other serious diseases. At a young age, children often encounter stomatitis and herpes sore throat. These diseases are severe, accompanied by acute pain, attacks of nausea and bowel dysfunction.
Fungal infection
Spots that have arisen due to the penetration of fungal agents into the body require special attention. The most common fungal disease of the oral cavity is candidiasis (thrush). Caused by microscopic fungi of the genus Candida. Their activity increases after illness, when the immune system is weakened, when taking certain medications. You can distinguish such a rash in the mouth by a white coating in the oral cavity - on the cheeks, on the mucous membrane, on the tongue. The treatment regimen is chosen by the attending physician after determining the type of pathogen and depending on the patient’s medical indications.
Allergic reactions, poisoning
Enanthema in adults and children is often a consequence of an allergic reaction of the body or intoxication. In both cases, it is presented in the form of small red dots on the palate, tongue, and inner surface of the cheeks. Swelling of the soft tissues is also characteristic, which often leads to bronchospasm and Quincke's edema.
Any rash is a reason for medical examination. For effective treatment and elimination of associated symptoms, it is necessary to identify the allergen that provoked the pathological changes. The most common causes of enanthema of this etiology are:
- material for dental structures and fillings;
- Food;
- toothpastes, mouthwashes, brushes;
- medications;
- teethers, pacifiers.
With an allergic rash, there is no fever or other symptoms of infectious diseases. The rash is located symmetrically throughout the mucous membrane, in some cases it can occur in certain areas of the skin. In case of poisoning, swelling of the soft tissues, an increase in temperature are possible, and sometimes plaque appears on the tongue and the inner surface of the cheeks (on one or both sides).
Rare specific diseases (granuloma, petechiae, sarcoma)
Specks can sometimes indicate the presence of a rare specific disease. In this case, the rash looks like pinpoint red spots or looks like a large spot, located mainly in the throat and palate. The following pathologies are distinguished, characterized by similar symptoms:
- Kaposi's sarcoma. It presents multiple formations on the skin in the form of flat or convex plaques, has a bright purple color with additional shades (red, brown). Quite often it is diagnosed inside the oral cavity (on the palate), on the lymph nodes, and in rare cases - on the internal organs. The disease mainly develops in HIV-infected people.
- Pyogenic granuloma. A benign vascular formation that occurs in areas subject to frequent trauma or affected by staphylococcus. It has a red-cherry hue and looks like a dense rounded nodule. The pathology does not hurt, grows quickly and reaches its maximum size in just a few weeks.
- Palatal petechiae are scattered round spots on the palate or at the top of the oral mucosa (you can see the appearance of the rash in the photo).
Treatment for red spots on the sky
Treatment depends on the identified cause. To determine the cause of the disease, the doctor may ask for a throat swab.
Additionally - blood and urine tests.
It is often necessary to follow a diet - exclude hot, spicy, salty and sour foods, so as not to irritate the oral mucosa.
- If it is a viral infection, then there is no need to treat the rash. The virus itself must be affected. When it disappears, the red spots will also disappear. ARVI is usually treated symptomatically - eliminate cough, nasal discharge, gargle. Plus, they cleanse the body, reducing intoxication. You need to drink more fluid. The influenza virus can be directly affected, so drugs that specifically target it are often prescribed.
- Herpes infection requires drugs that specifically target the herpes virus. After removing it, the rash will disappear on its own. Depending on the severity of the lesion, the doctor prescribes tablets for oral administration or ointments. The former are dangerous because they can suppress the immune system, and viruses become more resistant. The second ones are good when there is already discomfort and tingling, but bubbles have not yet formed.
- For bacterial infections, antibacterial drugs are needed. You should definitely visit a doctor so that he can prescribe the right antibiotic. Bacteria mutate over time, so medications may not work. Then you need to select another drug.
It is likely that the doctor will prescribe inhalation for the child. To carry this out, it is recommended to use specialized children's inhalers. They will help turn an unpleasant procedure into an exciting game!
How is diagnosis carried out?
The main medical measures to identify the causes of a rash or spots in a child’s throat are:
- Visual examination of the throat (in some cases this is already enough to make a diagnosis).
- Study of general anamnesis (medical history).
- General blood test (will show the general condition of the body).
- Nasopharyngeal swabs (used to isolate viruses for various viral infections).
- A throat swab (taken with a sterile swab directly from the affected area of the mucosa, which allows you to accurately identify the pathogen and prescribe appropriate antibiotic therapy).
- Allergy testing (indicated in cases of suspected allergies).
A throat swab must be taken on an empty stomach.
Whatever the reason for the appearance of a rash or spots in a child’s throat, only a qualified specialist can reliably determine it after carrying out certain medical procedures.
Attempts to independently diagnose and treat throat diseases in a child rarely lead to success and can only aggravate the situation. Therefore, you should not risk your child’s health, and at the first symptoms you should immediately seek medical help. Because timely diagnosis has enormous advantages in the treatment of any disease.
We suggest you read How to quickly eliminate the smell of alcohol from your mouth. How to get rid of the smell of fumes and hangovers
Red dots in the throat can be a sign of an allergy or infection. Most often they only accompany the course of the disease. The rash comes in different shapes and can be found on different parts of the throat and palate.
If you find a rash, do not treat it before visiting your doctor. Because of this, the doctor will see the wrong picture. It will be difficult to diagnose and additional laboratory tests will be required. To avoid this, do not delay visiting a specialist.
Mononucleosis
Mononucleosis is an infectious disease in which a spotty rash on the body is sometimes accompanied by a rash in the mouth in the form of pinkish papules on the soft palate and tonsils. They do not cause much discomfort and usually go away on their own within a few days. Complications usually occur only in children under two years of age.
Mostly, mononucleosis affects children aged 3–5 years, but adults who did not have it in childhood are not immune from infection.
Due to the similarity of the symptoms of mononucleosis with tonsillitis and pharyngitis, it can only be diagnosed by a blood test.
Pediatric infectious diseases
Many infectious diseases that manifest as a rash on the palate are known as “childhood” diseases. But this does not mean that adults are not susceptible to infection. Having suffered from such diseases once, a person receives lifelong immunity. But if you do not get the same chickenpox in childhood, there is a risk of contracting this infection in adulthood.
Rubella
With rubella, red spots may first appear on the child's palate, and only then on the face and body. Rubella usually resolves easily and without complications in childhood, with the exception of infants up to one year old. These babies endure the disease very hard, so scarlet specks in the mouth, which quickly merge into specks, should alert parents: this may be the first symptom of rubella. This disease is also dangerous for adults who did not have it in childhood, especially for pregnant women.
Causes
The type of infection determines:
- the nature of the rash, that is, its color and shape, location, time of appearance from the onset of the disease;
- temperature values.
Combinations of these two symptoms can help make the correct diagnosis for treatment. It is radically different for viral, bacterial and fungal infections.
It is worth considering that with some diseases the appearance of rashes is a mandatory sign, while with others, such as influenza, acute respiratory viral infections do not always occur.
Causes of a rash on the throat mucosa in a child with a fever Cause Features of the rash When does the rash appear? What temperature?
| Respiratory infections, flu | Red dots, bubbles on the palatine arches, posterior pharyngeal wall, palate, tongue at the base, tonsils. | On one of the first 3 days of illness. | 37,5-39℃ |
| Herpangina | Reddish dots, also known as papules, 2-3 mm in size, turn into small bubbles with light contents, or vesicles, open themselves in 2 days, merge into painful grayish spots (erosions), after 3-5 days they become covered with crusts and stop hurting . Against the background of solid red mucous membrane of the throat. | 2-3 days from the onset of the disease. | Depending on the characteristics of the child’s immunity 38-40℃ |
| Chicken pox | Painless small transparent single vesicles in a non-inflamed throat, on the arches, palate, back surface, and simultaneously on the mucous membranes of the eyes and oral cavity. | Up to 2 days after the first bubbles appear. | 37-39℃ and higher depending on the shape. |
| Measles | Small reddish spots on the back mucous membrane of the throat, painful, then merge into larger ones. At the same time, on the inside of the cheeks, opposite the 4th and 5th teeth from the middle, there are clusters of white small spots surrounded by red rings. This is a Filatov-Velsky-Koplik symptom specific for measles. | On the 2nd day from the onset of the disease. | 38-41℃, after vaccination the child has 37-37.8℃. |
| Rubella | Small red spots on the back of the sore throat. The child's tonsils are noticeably enlarged. | On the first day, simultaneously with an increase in temperature. | 37-38℃, in severe cases up to 39.5℃. |
| Herpetic stomatitis | The same rashes as herpetic sore throat, but larger - up to 5 mm. First on the mucous membrane of the mouth and lips, then on the root of the tongue, arches of the palate and the anterior parts of the tonsils. Rarely occur in the posterior pharyngeal mucosa. | As a complication 2-3 days after the appearance of papules on the lips. | Initially 37-37.5℃, at the height of the disease up to 40℃. |
| Streptococcal pharyngitis | Gray-white dots on the tonsils are accompanied by acute pain in the throat, which intensifies during swallowing. Then they turn into bagel-shaped red bubbles with yellow spots in the center. | The dots appear in the child on the 1st day and are replaced by bubbles on the 2nd day. | It starts from 38-38.5℃, then it can rise to 39℃. |
| Scarlet fever | Red small dots. The root of the tongue, soft palate, tonsils and arches are bright red, white accumulations of pus may be visible on them, as with a sore throat. The tongue is bright crimson with enlarged papillae. | On the first day. The rash appears on the throat earlier than on the rest of the body. | Up to 38℃ for mild cases, up to 41℃ for severe cases. |
| Pharyngomycosis, or fungal pharyngitis | The child’s throat is inflamed and swollen, it hurts, there is a rash on it like clearly visible grains, cheesy plaques, films, then they tend to merge. The mucous membrane is dry and irritated. Tonsils are enlarged. | From the onset of the disease, gradually growing. | 37-37.5℃, less often higher |
We suggest you read: How many days does diarrhea last during teething and what to do in this situation?
Rashes in the throat of a child: types, manifestations and treatment features | The baby is healthy!
With many infectious and inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx, both viral and bacterial, a rash in the throat may appear. In medical practice, any rash is called enanthem.
For some diseases (for example, ARVI or influenza), pink or red spots on the pharyngeal mucosa are not a characteristic sign of the disease and do not always appear. But for certain diseases, based on the nature of the rash in the throat, a pediatrician or pediatric infectious disease specialist can clarify the diagnosis and determine the tactics of treatment and observation of the child.
By the appearance and characteristic changes of the rash in the throat, it is possible to determine what pathogen is causing the infectious process and prescribe the correct treatment.
There are rashes on the mucous membrane of the throat due to viral (respiratory infections, influenza, measles, rubella, chicken pox, herpes simplex) or bacterial infectious processes.
Rash in the throat due to viral infections
In a child, a rash in the throat due to respiratory viral diseases occurs quite often.
In most cases, the rashes look like red dots and papules on the back of the throat, soft palate, arches and uvula.
Enanthema can appear on the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx in various diseases and has common features:
- localization (location), which corresponds to a specific infectious-inflammatory process that caused the development of these clinical manifestations;
- appearance of the rash and its intensity;
- the stage of appearance of rashes and the chronological sequence of their appearance, which is determined by the number of days that have passed since the first symptoms of the disease appeared.
Rashes due to ARVI and influenza
The rash appears on days 1-3 of illness, most often against the background of an increase in temperature.
Most often, viral enanthema occurs:
- with influenza (red dots or single pinpoint hemorrhages on the back wall of the pharynx and soft palate);
- with parainfluenza (single papular elements on the palatine arches and uvula);
- with adenovirus infection (single pinpoint rashes are often localized on the tonsils against the background of their swelling and bright hyperemia).
Rashes in the nasopharynx due to common respiratory infections and influenza disappear without a trace after the child’s condition improves
Rashes in the throat due to childhood infections
With measles, rubella and chickenpox, in addition to the characteristic rash on the skin, the appearance of enanthema on the nasopharyngeal mucosa is quite often noted
With chickenpox, rashes appear in the throat, on the mucous membranes of the mouth, eyes and genitals in the form of small transparent vesicles 1-2 days after the appearance of the first typical elements of a rash on the skin.
A few hours after their appearance, the vesicles burst and turn into erosions.
With measles, on the second day of illness, small white spots appear on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, surrounded by a bright halo of hyperemia (in the form of a red ring) in the area of 4-5 teeth (premolars); they are called Filatov-Velsky-Koplik spots. This is a specific symptom of measles. In addition to this symptom, the child has a sore throat, and a rash in the nasopharynx appears in the form of small red spots on the back wall of the throat, which can merge with each other.
With rubella, the rash appears mainly on the skin, but with this infectious disease the structures of the throat can become very inflamed, the tonsils become enlarged, and a small red spotty rash appears on the back wall of the throat.
Herpes in the throat
With herpetic stomatitis, the disease begins acutely: the child’s temperature rises and chills appear.
The rash in the throat is similar to the rash with herpes sore throat, but is slightly larger (4-5 mm). Initially they appear on the lips and oral cavity, and then spread to the tonsils in front of the throat, to the uvula and palatine arches.
The posterior wall of the pharynx is extremely rarely affected.
The cause of the spread of a rash to the throat with herpetic stomatitis is considered to be a severe course of the disease and a persistent decrease in immunity
Bacterial diseases
Most often, bacterial infectious and inflammatory diseases, which are accompanied by the appearance of various types of enanthems, are caused by Staphylococcus aureus and beta-hemolytic streptococcus (streptococcal pharyngitis and scarlet fever).
Scarlet fever
Scarlet fever is a childhood bacterial infection with a characteristic rash on the skin and mucous membranes of the mouth and nasopharynx.
With scarlet fever, characteristic rashes appear first on the mucous membranes of the throat (red, pinpoint rash), and then the rash spreads throughout the body.
A characteristic symptom of scarlet fever is a “crimson tongue” with hypertrophied papillae and signs of purulent tonsillitis
Fungal infections of the nasopharynx
Throat candidiasis (pharyngomycosis) belongs to a group of diseases leading to inflammatory fungal infection of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx.
When this pathology occurs, the child has a rash and a sore throat, and the following is also noted:
- dryness in the nasopharynx;
- redness and swelling of the mucous membrane of the throat;
- burning, itching and irritation of the nasopharynx;
- an increase in the size of the tonsils.
A characteristic rash appears on the back wall of the pharynx, tonsils and soft palate in the form of small dots and grains, clearly visible on the inflamed, bright red mucous membrane.
White films or plaques of a cheesy nature are also noted, slightly rising above the surface of the mucous membrane and tending to merge with each other.
How to treat a rash in the throat of a child
A rash in a child’s throat is one of the symptoms of a viral, bacterial or fungal disease.
The dosage and duration of taking the main drugs (antiviral or antifungal drugs and antibiotics) that need to be used to treat the pathology are selected only by a doctor.
Additionally, young patients are prescribed:
- antihistamines (Claritin, Zodak, Zyrtec, Erius);
- immunostimulants (Licopid, Immunorix, Echinacea tincture);
- vitamin and mineral complexes;
- probiotics (Maxilak, Normobakt, Linex);
- restoratives and adaptogens.
Local treatment of inflammation in the throat is also carried out:
- treatment of the nasopharynx with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory solutions (Stomatidin, Miramistin, Rotokan);
- irrigation of the nasopharynx with aerosols with antimicrobial, antifungal and anti-inflammatory effects (Chlorhexidine, Tantum Verde, Hexoral, Bioparox);
- rinsing with a solution of soda or decoctions of anti-inflammatory herbs;
- rinsing with propolis tincture and treatment with sea buckthorn oil or Chlorphyllipt oil solution.
It ogi
- a rash in a child’s throat occurs quite often, but is not always a characteristic sign of the disease;
- self-medication of rashes in the throat often leads to a smoothing of this important symptom of the disease or aggravation of inflammation and swelling of the nasopharynx and/or a change in the nature of the rashes;
- adequate therapy can only be prescribed by a specialist - a pediatrician or pediatric infectious disease specialist.
Treatment of a rash in the throat is an effective fight against the causative agent of the infectious-inflammatory process, reducing local inflammation and stimulating the child’s immune system.
pediatrician Sazonova Olga Ivanovna
Source: https://www.malyshzdorov.ru/vyisyipaniya-v-gorle-u-rebenka-vidyi-klinicheskie-proyavleniya-i-osobennosti-lecheniya/