05.24.2019 bracatuS (2457 articles)
Clothing for the feet of a newborn requires special attention from parents or those caring for the baby. The temperature of a child's body largely depends on how much and what kind of clothing is on the child's legs. Our body is designed in such a way that we almost always produce heat. While the newborn’s body is still learning to regulate temperature, not only overheating can be dangerous, but also hypothermia - a condition in which the body temperature drops below normal.
Common mistakes when dressing babies' feet
Too many socks
Put on two pairs of socks at the same time - one on top of the other. Often parents, and even more often grandmothers, consider it necessary to insulate their feet as much as possible, practically isolating them from the outside world. For grandmothers, it seems that one pair of socks or booties is not enough, and therefore they wear at least two: the first is thin cotton socks, the second is thick synthetic or woolen. As a result, the socks compress children's feet too much, to the point of impairing blood flow, and, as a result, thermoregulation is disrupted - the feet may become cold even under a thick layer of socks.
Falke
Extra socks
In the summer heat, especially in calm weather, it may be enough to dress the baby in rompers or even leave the legs open. Socks may become unnecessary when the air temperature approaches body temperature.
Wrong socks
Babies grow quickly, and therefore socks bought for birth may turn out to be small by the first month of life. It is important to ensure that the socks are exactly the right size, or a little too big.
Fashionable does not mean comfortable
Some mothers, and even grandmothers, roll up the edge of their socks or fold the top several times too long - they find it beautiful or comfortable. As a result, the elastic band puts more pressure on the ankle than is acceptable. If the socks do not fit properly on the child’s foot, you should choose others that are more suitable in shape.
So how to choose and put on socks for a newborn baby correctly? First, a little theory.
Healthy legs for your baby - Without wasting time.
In children with X-shaped curvature of the legs, when the baby stands or walks, the main load falls on the inner edges of the feet. At the same time, the knees come closer together, and the feet “move apart” to the sides. In the future, if the baby is not helped in time, the structure of the ankle joints is disrupted and toscovalgus occurs, and then deformation of the feet. A valgus deformity develops in the knee joints, in which the inner end of the femur begins to protrude, as if hanging over the lower leg. The degree of curvature in the legs varies, so in advanced cases, the pelvis is distorted and, as a result, poor posture and curvature of the spine occur.
Three features of thermoregulation of the legs in infants
Falke
Children's feet are very sensitive to temperature changes in the environment. The skin on them is the first to react to cold or heat. At the same time, the legs of a newborn are not only an indicator of the process of thermoregulation of the whole organism, but also actively protect it from temperature fluctuations. How does this happen?
- If your baby's feet become cold, this means that the skin has triggered a heat-saving mechanism in the body. There is a narrowing of the skin vessels on the legs, due to the need to maintain an acceptable body temperature in conditions of decreased temperature in the environment.
- If the baby overheats, his feet are the first to react to the increase in ambient temperature - they become hot and then sweat, giving off excess heat along with evaporated moisture.
- The quality of clothing for a newborn’s feet is an external factor that significantly affects the temperature of the baby’s feet.
They note that it is in the early infantile period that it is especially important to properly train the vessels of the legs, teaching them to react to cold and heat. In the future, this will help the child easily tolerate a drop in temperature without colds or runny nose.
What does a newborn look like? 16 facts that will surprise you
A newborn's skin is usually bluish due to lack of oxygen.
A newly born baby's skin is usually bluish in color.
This is due to the lack of oxygen that the child experienced while passing through the birth canal. The bluishness of the newborn's skin will disappear within a few minutes, when the baby begins to breathe independently and his blood is saturated with oxygen. The newborn's skin usually becomes bright red. This is due to the condition of the subcutaneous vessels, which first narrow after childbirth due to a sharp change in temperature, and then reflexively expand. This redness of the skin persists for the first 2–3 days of life. If the baby is premature (born before 37 weeks of pregnancy), the skin may be dark red. This is due to the fact that the subcutaneous vessels in such children are located very close to the surface of the skin due to the fact that the subcutaneous fat layer is very thin. This is why the skin of premature babies easily folds and forms wrinkles.
The baby's palms and feet may remain bluish for some time. This is explained by the imperfection of the circulatory system: parts of the body more distant from the center are less well supplied with blood in the absence of active movements. As soon as the child becomes more active, he moves his arms and legs more, the skin of his palms and feet will turn pink.
Vernix lubrication on the skin of a newborn has a bactericidal effect
Another feature of the skin of a newborn baby is a cheesy lubricant consisting of fallen skin epithelial cells and fats. Before birth, it protected the skin from getting wet, since the baby was in a liquid environment (amniotic fluid). During childbirth, this lubricant helps the baby pass through the mother's birth canal. It also has bactericidal properties, preventing the penetration of infection. More lubrication occurs on the back surface of the body, on the face, ears, and in the folds of the skin (axillary, cervical, groin, etc.). During the first toilet of the newborn, which is carried out by the midwife already in the delivery room, the vernix lubrication is removed because it becomes useless.
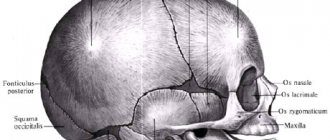
The head of a newborn usually has an elongated shape
A newborn baby's head looks large compared to its body. The head circumference of a newborn is on average 33–35 cm, while the chest circumference is on average 30–33 cm. This is normal. These two values level out only by 3 months of the baby’s life, and then the chest circumference gradually becomes larger than the head circumference.
The slightly elongated shape of a newborn's head can frighten the mother. The fact is that the bones of the skull of a child in the womb are very mobile, this is due to the fact that the sutures connecting them are soft. Therefore, during the birth process, they shift relative to each other, adapting to the shape of the birth canal, and this makes it easier for the baby’s head to pass through. When squeezed, the head takes on an ovoid shape, which is what the mother sees immediately after the birth of the baby. This takes place already in the first days of a child’s life: the moving bones of the skull take their usual position, and the head acquires a rounded shape.
In addition, on the head of a newborn there is sometimes a small swelling filled with blood - a cephalohematoma (bleeding between the periosteum and the skull bone). More often it forms on the crown or back of the head. Cephalohematoma occurs due to compression of the baby's head during passage through the birth canal. This can be facilitated by the use of obstetric forceps during childbirth (a medical instrument placed on the fetal head to remove it according to strict indications).
Typically, small cephalohematomas disappear within 6–8 weeks and do not require treatment; large ones can resolve within a few months. In rare severe cases, complications may occur, such as hematoma suppuration, requiring medical intervention.
Often there are so-called birth tumors - swelling localized on that part of the fetal head that first passed through the birth canal. The birth tumor is most often located in the occipital region or parietal part of the head. The slower the child walked through the birth canal, the more pronounced the birth tumor was. It usually resolves on its own within 3–4 days.
Increased muscle tone in a newborn is normal
A child is born with clenched fists, bent arms and legs tightly pressed to the body. This was his position in the womb, and this will remain so for some time after birth. This is a physiological increased muscle tone of the newborn. Gradually, the palms will open, the arms and legs will become more mobile. Hypertonicity of the arms normally goes away in the fourth month of the baby’s life, and hypertonicity of the legs – in the fifth.
Newborns may be born with hair
At birth, a newborn's hair may be long, but it may not be there at all. Hair color may vary. Most often, during the first year of life, the first hairs fall out, and new ones begin to grow in their place. Their color may also change over time.
Eye color in newborns often changes during the first six months of life.
New parents are often concerned about what color eyes their child will have: like mom, dad, or maybe grandma? Unfortunately, it is difficult to determine this before six months. Most babies are born with blue eyes. By about 1 month, eye color begins to gradually change. And only by 6 months is a permanent eye color established. In a newborn, the iris (color) of the eye contains little pigment, which causes the blue color. And as the child grows, the amount of pigment may increase (then the eyes darken) or not increase, and then the eyes remain light. It depends on heredity.
The whites of the baby’s eyes may be red immediately after birth due to hemorrhage from blood vessels in his eyes that burst during childbirth. This goes away on its own in the first days of a newborn’s life.
Is the baby not born yet? Use the service to find out what color his eyes will be
A newborn has fontanelles on his head
While stroking the baby's head, the mother can feel two soft indentations. These are the large and small fontanels of a newborn. Fontanas form at the junction of the bones of the skull. The large fontanelle of a newborn has a diamond shape, is located on the top of the head at the junction of the frontal bone with the two parietal bones and comes in different sizes (usually about 2x2 cm). By placing your hand on it, you can feel its pulsation. The large fontanel closes by 12 months. The small fontanel of a newborn has a triangular shape, is located in the occipital region and is formed at the junction of the parietal bones with the occipital bone. Its larger size is about 0.5 cm. But most often, by the time of birth, the small fontanelle is already closed. If it does exist, then after 2-3 months it will completely close.
The face of a newborn may be swollen in the first hours of life.
And sometimes, due to swelling, the baby cannot even open his eyes. This occurs due to a disruption in the outflow of venous blood from the face due to compression during passage through the birth canal. There is no need to worry about this. Such swelling quickly disappears in the first days of life.
Some babies may also have red streaks or irregularly shaped spots on their faces - newborn vascular spots. These are nothing more than bundles of blood vessels visible through thin skin. Most often they are located in the upper eyelids, between the eyebrows, on the back of the neck and in the ear area. Some babies are born with these spots, and in some they appear on the 2nd or 3rd day of life. They usually disappear by the age of three without outside intervention.
There may be vellus hair on the body
In many newborns, the original down – lanugo – can be seen on the skin of the body. This fluff covered the entire body of the fetus from about the 7th month of pregnancy. Most of the original down falls off before birth, but some of it can be seen after childbirth, most often under the shoulder blades and on the shoulders. And in premature babies, the cheeks may also be covered with fluff. As a rule, vellus hair disappears by the age of two weeks.
A newborn's genitals appear very large
The appearance of the newborn’s genitals can also raise many questions among mothers. At birth, both boys and girls' genitals are most often swollen and appear very large. This is due to the presence of placental estrogens in the blood. This is a temporary phenomenon. The swelling usually subsides within one to two weeks of the baby's life.
A newborn's skin may have a yellowish tint
This is physiological jaundice of newborns. It occurs in many babies; their skin and mucous membranes become yellowish. Jaundice most often appears on the 3rd–4th day after birth. It is associated with the breakdown of red blood cells (erythrocytes) containing fetal hemoglobin (a protein found in red blood cells that carries oxygen to the body's cells) specific to the fetus. One of the breakdown products of red blood cells is bilirubin. The enzyme systems of the liver are still imperfect and do not have time to quickly remove bilirubin, as a result of which it accumulates in the blood, causing a yellow coloration of the mucous membranes and skin of the newborn.
Jaundice disappears within one to two weeks as the bilirubin excretion systems mature and due to the completion of the breakdown of red blood cells containing fetal hemoglobin.
With severe jaundice, the baby may be prescribed intravenous infusions of glucose, UV irradiation, and choleretic drugs that help remove excess bilirubin from the body. Thus, doctors help the child’s body cope with this condition. Ignoring severe jaundice can cause irreparable harm to the child’s body due to the pronounced toxic effect of increased bilirubin levels on the baby’s body. General intoxication of the body occurs, the nervous system is especially affected, in particular the brain, as well as the liver and spleen of the newborn.
You can often see “pimples” (milia) on a newborn.
On the 2nd–3rd day of life, the child may develop a small rash in the form of yellowish blisters filled with clear liquid. These are the so-called milia, or “millet spots”. Their appearance is associated with blockage of the sebaceous glands of the skin. Usually milia go away in the first months of life and do not require special treatment.
Newborn skin becomes very flaky
On the 3rd–5th day, peeling of the skin may begin, which is more common in post-term babies (born after 42 weeks of pregnancy). In this way, the skin adapts to new environmental conditions. Since this condition is not a pathology and does not require any medical intervention, you should not lubricate the newborn’s skin with moisturizer: this will only interfere with the natural process. Peeling goes away on its own within 5–7 days.
The newborn's mammary glands swell
It happens that on the 3rd–4th day, both boys and girls experience swelling of the mammary glands. They may increase in volume over the course of a week. Moreover, they swell symmetrically, there is no redness around, but a white liquid similar to milk may begin to discharge from the nipples. The composition of this liquid is similar to the mother's colostrum. Such changes occur due to the circulation in the blood of the newborn of the mother's sex hormones - estrogens (they are transmitted to the child through the placenta). Soon these hormones will be eliminated from the body, and within a month the mammary glands will return to normal.
After birth, the baby will have an umbilical cord
The navel of a newborn does not immediately take on its familiar appearance. After the umbilical cord is tied during childbirth and then cut off, an umbilical cord remains, which doctors remove in the maternity hospital on the 2-3rd day. In its place an umbilical wound remains, which heals by about the 20th day of the baby’s life. Until that time, it requires careful care and respect. In the maternity hospital, the children's nurse will show you how to properly treat the umbilical wound. For this, hydrogen peroxide and an antiseptic solution (potassium permanganate, brilliant green, chlorophyllipt solution) are used. During processing, you need to carefully remove dried crusts. You need to treat the wound twice a day in the morning and after bathing the baby until it is completely healed. Until the umbilical wound heals, it is recommended to bathe the child in a baby bath, adding a solution of potassium permanganate to the water until it turns slightly pink.
You need to constantly monitor the condition of the wound. If you notice redness of its edges, an unpleasant odor, or various discharges (usually white or yellow), you should immediately consult a doctor, as all of these may be signs of infection.
Strabismus of a newborn is a normal variant
Another feature of some babies is squint. The eyes may periodically move apart in different directions or, conversely, move towards the bridge of the nose. This is a completely normal phenomenon due to weakness of the eye muscles. The child cannot fix his gaze on an object for a long time; the eye muscles get tired and stop working normally. For most children, this goes away by 3 months, but for some it lasts up to six months - this is the norm.
How to properly put on socks for a baby?
Falke
For a long time, our grandmothers wrapped their children as warmly as possible, putting several pairs of socks on their feet (especially before going for a walk). But is this right? Based on the fact that the feet must be trained to get used to external temperature changes, we can come to the conclusion that the constant warmth of the feet is a negative factor in this process. Excessive thermal insulation limits the body’s natural thermoregulation capabilities, locking it in “greenhouse” conditions from the very beginning.
Of course, we are not talking about the fact that a newborn should be cold! We are talking about elementary hardening, and the development of a certain resistance to lowering ambient temperatures.
Useful facts
The temperature of the baby's legs is always lower than the temperature of the body. Therefore, if a baby has cold feet, then, provided the ambient temperature is normal (at least 22 degrees), there is no need to worry and put on a hundred pairs of socks.
Clothes for legs must meet the basic requirements:
- It is worth wearing socks according to the temperature conditions in which the child is. For example, for a winter walk in a stroller, you can wear warm cotton terry booties under your overalls.
- The quality of the materials from which clothing for little feet is made undoubtedly has an impact on whether the baby gets cold or sweats. Synthetic fibers attract cold when the weather is cold and do not allow air to pass through in warm weather. Thus, it is better for newborn babies to choose products made from natural hygroscopic materials, which themselves have a conditioning effect. These are natural cotton and silk, as well as wool. But due to the relative allergenicity of wool, it is better to prefer the first two.
- We must not forget that warm socks for baby’s feet should be of high quality and also comfortable. Not all socks can be worn on bare feet. Options with elastic bands can pinch the baby's skin, and wool socks can tingle. Socks are often worn over tights or rompers. If the latter have a transverse heel seam, then the sock can press it into the baby’s skin, which is undesirable, as is excessive compression in general.
Take care of the warmth and health of your child by dressing his feet correctly!
Falke
Hung crosswise at the foot of the bed with pins stuck in them, the stockings warded off nightmares and evil spirits.
Healthy legs for a baby - Patience and work will grind everything down.
Success is achieved by those mothers who make the most of the entire arsenal of treatment means and work patiently and persistently.
Once, a mother and grandmother came to an appointment with a 3.5-year-old baby. They complained of an X-shaped curvature of the baby's legs. The grandmother asked to pay attention to her daughter’s perfectly slender legs. Having enjoyed the effect produced, the woman said that at about the same age she had the same legs and that, leaving all other matters, she cured her baby in 4 months. And then for some time she consolidated the brilliant results of treatment with massage courses.
To get rid of X-shaped curvature of the legs, in addition to courses of electrical stimulation of the internal group of muscles of the legs, as well as professional massage for 15-20 sessions at least 4 times a year, a set of measures is required that requires a lot of time, effort and patience of the mother.
30% of toddlers have one leg shorter than the other by about 0.3-0.5 cm, and 4-7% have one leg shorter than the other by more than 1 cm. This is a lot for such a small child. Because of this, the shape of both legs may also be disrupted.