Illnesses with fever and abdominal pain
Children often complain of stomach pain, and this can be caused by several reasons. For example, a low-quality product or just a nervous experience
. Sometimes babies can eat a large amount of fruit, which can cause one-time diarrhea. In this case, an increase in temperature and umbilical pain are not typical; most often the feces are normal - the baby’s stomach will hurt and it will go away.
But if a child has a stomach ache and fever, this cannot be attributed to nervous tension and overeating fruit, especially if the child has vomited. Abdominal pain and high temperature indicate an inflammatory process in the body. Which one exactly - the symptoms will tell you.
Main diseases:
- intestinal infections;
- acute appendicitis;
- acute pancreatitis;
- acute cholecystitis;
- acute diverticulitis;
- peritonitis.
Intestinal infections are accompanied by an elevated temperature of 38.5 or 39 degrees, broken stools, nausea, abdominal pain and vomiting. Diarrhea, fever and vomiting are dangerous due to rapid dehydration of the body of a small sick child, especially under one year of age
. It is urgent to bring down the fever and call a doctor.
In case of acute appendicitis in a child, a high temperature is accompanied by severe abdominal pain - the baby does not allow him to touch his tummy. The child has abdominal pain in the navel area without diarrhea, and is characterized by a frequent urge to urinate without defecation. The skin turns pale and you may feel very thirsty.
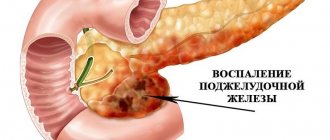
Pancreatitis is not a rare occurrence in childhood. Inflammation of the pancreas is accompanied by a slight increase in heat - temperature 37. Characteristic are girdling pain, spasms, dry mucous membranes, coated tongue
.
The child diarrhea (not always), he feels sick
. The baby refuses to eat due to frequent bouts of vomiting.
Acute cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder. The child's temperature rises to 40 degrees. The stomach does not hurt below - pain is felt in the right upper part of the peritoneum, the stomach is tense
. The baby complains that his right arm and right side also hurt. The child may vomit with an admixture of bile, and stool may be disturbed.
Diverticulitis symptoms resemble acute appendicitis - temperature and pain in the abdomen (characteristic pain in the navel), sometimes the lower abdomen - the pubic part - hurts. The baby is worried and refuses to eat
. This condition requires hospitalization.
Peritonitis most often affects girls 4, 5 years old or older. The child's temperature rises to 40 degrees. Complaints: tummy hurts everywhere
. Sometimes foul-smelling diarrhea may occur. However, at high temperatures the child does not vomit - vomiting is not a symptom of peritonitis.
Causes of pain in a child
Acute abdominal pain:
- inflammatory causes: gastroenteritis;
- appendicitis;
- mesenteric lymphadenitis;
- peritonitis;
- hepatitis;
- pancreatitis;
- intussusception, volvulus;
Chronic abdominal pain:
- colic of three-month-old children;
- gastroesophageal reflux;
- chronic constipation;
- inflammatory bowel diseases;
- chronic infections, such as parasites;
- peptic ulcer;
- tumors in the abdominal cavity;
- psychosomatic pain (functional abdominal pain).
When the cause of pain is acute appendicitis (inflammation of the appendix), the pain is usually localized in the navel area. Sometimes the pain extends to the lower abdomen (the abdomen may be soft to the touch). As a rule, in such cases the child’s temperature rises and vomiting begins. If your child has symptoms of appendicitis, contact your pediatrician immediately. In such a situation, delay can result in serious complications.
Sometimes the cause of abdominal pain can be emotional stress associated with an unfavorable psychological climate at home or at school. For a school-age child, such stress is a common occurrence. The cause of stress can be divorce or other family troubles, problems in relationships with peers, with teachers. Some children experience abdominal pain in the morning, and this is most often associated with nervous tension before the start of the school day. Such pains usually disappear within 24 hours; If necessary, allow the child to stay at home. Try to identify the main cause of emotional stress and solve the problem as soon as possible.
Urgent help
Under what conditions should you immediately call an ambulance? Mothers should know that the baby’s health condition may be critical in the following cases:
- age up to three months;
- the child is vomiting without diarrhea;
- oncological diseases;
- with a temperature of more than 40 degrees;
- the child has a stomach ache and vomits/bloody stools;
- the child has a temperature of 38 and hard abs;
- the baby has trouble breathing;
- The child’s stomach hurts and it’s painful to have bowel movements;
- trauma to the soft tissues of the abdomen.
In this condition, the baby needs help. However, let's look at what not to do
. There are different diseases, and stomach pain can occur in different ways - help should be provided by a doctor.
Prohibitions:
- You cannot give your baby medications other than antipyretics;
- You can’t give an enema or warm your stomach with a heating pad;
- You cannot offer food if the baby is sick;
- You cannot apply compresses - with hot compresses the temperature will only rise.
You need to provide the baby with peace, turn off the bright lights, humidify the air in the room and wait for the doctor.
How to recognize an emergency
When a child has a stomach ache and fever, it is very important to get a diagnosis as soon as possible. Seek medical help immediately if:
the baby is less than three months old, he has diarrhea and vomiting; the child is currently undergoing treatment for cancer; there is vomiting without diarrhea (and it is not possible to empty the intestines); blood in vomit and stool (especially if the blood is very dark or tarry black); intense abdominal pain that occurs suddenly; abdominal muscles are tense; frequent, shallow breathing; recently had an abdominal injury; burning during urination.
Prevention
What to do to prevent stomach diseases? First, feed your baby correctly: exclude fatty and fried foods. Proper drinking regimen plays a big role in your diet—watch this all the time. Do not overfeed the baby: let the baby eat small portions of food, but more often
. Usually the child who does not eat properly gets sick.
Note! A nervous environment in the home and frequent quarrels between parents can cause nervous illnesses. In a scandalous family, the baby gets sick more often than in a friendly one.
It is undesirable to accustom your baby to carbonated drinks - they are extremely harmful to the stomach and the entire digestive tract. Remember that the child should lead an active lifestyle, especially for plump kids
.
Teach to always wash your hands with soap - after coming home, after using the toilet,
etc. d.
Preventive measures
To prevent and reduce the likelihood of symptoms that accompany serious illness, follow these tips:
The baby’s diet should be balanced and healthy with a high content of vitamins, minerals and nutrients; do not forget that the amount of water a child should drink per day is about 1 liter; Feed him less fatty, sweet foods, as well as those that are rich in preservatives, flavors and flavoring additives; spend more time outdoors, playing active games, playing sports; Explain to your child the importance of washing hands before eating and after using the toilet; do not forget about the importance of keeping your apartment clean
Conclusion
Why do babies get stomach upset? This condition is caused by various reasons. If the temperature rises, the baby has diarrhea and complains of nausea - call an ambulance
.
Of course, this condition does not normalize, and only a doctor can find out the reasons. Take care of your children all the time - whether your baby is a month old, 6 years old or 10 years old
. Teach him personal hygiene and cleaning his room.
Take care of strengthening your child’s immune defense, strengthen him and teach him to play sports. Don't scold often, because children react to scandals with stomach pain and even fever
. Your baby should get plenty of rest—make sure you go to bed on time. Lack of sleep, nervous overload and poor quality food are the path to gastrointestinal diseases.
Check your child for helminthiasis - infection with parasites often causes upset of the digestive system and is accompanied by abnormal bowel movements. Helminths can cause appendicitis and other digestive tract ailments. Helminths are especially dangerous during hot periods - their eggs are found in the soil and on animal fur.
. Preventive measures will help get rid of parasite infestation.
If your baby complains that his stomach hurts and his temperature has risen, consult a doctor immediately. Such symptoms may indicate serious disorders in the digestive tract and more.
.
What reasons can cause abdominal pain and fever?
A qualified specialist must understand the etiology of pain in the abdominal area, since mistakes and delays in this matter are unacceptable. Here is just a short list of diseases that can be suspected if a child has a stomach ache and a fever (even low-grade fever - 37-38 degrees):
- Appendicitis
is an inflammation of the appendix of the cecum, requiring urgent diagnosis and surgical intervention.
The clinical picture of the disease largely depends on the age of the child. Thus, pronounced symptoms in the form of acute pain and high fever may be absent in infants
.
In older children, the signs of the disease appear in full force: the temperature rises rapidly, and the tummy hurts so much that the baby does not allow him to touch it
.
Appendicitis may be accompanied by vomiting (usually one-time) and diarrhea
. - Peritonitis
is inflammation of the serous lining of the abdominal cavity.
Girls aged 4-9 years are especially susceptible to this disease
. With peritonitis, the child has a high temperature above 39 degrees and severe abdominal pain in all parts. In this case, there is a white coating on the tongue, pallor of the skin, and foul-smelling yellow-green stools. - Acute diverticulitis
is inflammation of Meckel's diverticulum. The disease is characterized by: constipation, vomiting, fever and pain in the navel area. - Cholecystitis
is inflammation of the gallbladder. The clinical picture of the disease is as follows: the temperature rises to 40 degrees, the child refuses to eat, nausea and vomiting appear, a grayish-white coating is observed on the tongue, the pain is localized in the upper right quadrant, radiating to the lower back and right arm. - Pancreatitis
is an inflammation of the pancreas, in which the child has abdominal pain (in the left hypochondrium) and the temperature fluctuates within 38 degrees, dry mucous membranes, nausea and vomiting are also observed. - Intestinal infections
can cause severe pain, diarrhea, vomiting, confusion and fever This condition appears due to the penetration of harmful microorganisms into the gastrointestinal tract, such as E. coli or dysentery coli, streptococci, staphylococci and others.
Abdominal pain not associated with abdominal diseases
Many children experience painful sensations in the tummy due to viral and bacterial infections. So, for example, the clinical picture of ARVI, acute respiratory infections, sore throat, whooping cough, pneumonia, scarlet fever, pyelonephritis and other diseases is supplemented by abdominal pain
. This is due to the reaction of the pleura to the infectious process, as well as inflammation of the abdominal lymph nodes.
Also, answering the question of why a child has a stomach ache and a high temperature, one cannot exclude the possibility of a psychological origin of the symptoms. Sometimes painful sensations arise due to stressful situations, exorbitant demands, and frequent intra-family conflicts. Most often, such problems appear in emotional and impressionable children.
. The clinical picture is supplemented by general malaise, lethargy, headache, confusion, and hallucinations.
In any case, parents must understand that if a child’s stomach hurts and continues to hurt, then the temperature rises, they must act radically. Any delay in the presence of such symptoms is unacceptable, as it can lead to irreparable consequences.
| Appendicitis, or inflammation of the appendix, can occur at any age. But it is more difficult for a child to understand what is wrong with him and to explain the condition to his parents. Therefore, the latter should familiarize themselves with the signs that will help identify the disease in children. | If your child smells strange of acetone, it is better to go to the pediatrician as soon as possible, because... this may be a symptom of a serious illness requiring urgent therapeutic action . Read more about possible reasons further in the article. |
| Asthma is a fairly common disease among young children and, unfortunately, it is always chronic, since it is most often the result of neglect or improper treatment of diseases of an allergic nature. |
Every child sometimes feels pain in the abdomen, it may not be dangerous, but if a high temperature is added to the abdominal pain, then a serious problem can be assumed. A high temperature is always a symptom of the presence of a viral or bacterial infection in the body.
.
Painful sensations in the abdomen are not necessarily a sign of abdominal pathology; they can signal that the child has some other hidden disease. Therefore, any mother should definitely consult a specialist before taking any measures
. After all, painful sensations in the abdomen against a background of high temperature may require immediate surgical intervention.
Causes of the condition
10% of children periodically experience slight abdominal pain, which goes away on its own without causing any consequences. For example, after eating a large number of unripe apples, when the stool is normal or one-time diarrhea occurs. But pain combined with elevated temperature always indicates some kind of disease - acute or chronic. In this case, children lose their usual activity, refuse to eat, usually develop diarrhea or, conversely, stool retention, nausea, vomiting, and pale skin. With severe pain, the skin may become covered with sweat.
Major diseases
Appendicitis (inflammation of the vermiform appendix of the cecum, or appendix). It occurs in children and adults, but more often in 9-12 years old. In children under 3 years of age, the temperature often rises to 39.5°C, the general condition quickly deteriorates, the child does not allow touching the stomach. A child 3-7 years old has a high temperature (up to 37.5°C, but can be normal) and a stomach ache in the navel area. The pain then spreads to the right side. He takes a characteristic forced position - lying on his right side, with his legs bent, he may vomit once. During the transition to purulent inflammation, the baby experiences severe thirst, the skin and mucous membranes are dry. In combination with viral infections (hepatitis, measles) and intestinal infections, vomiting, diarrhea (diarrhea) and nausea are observed. Peritonitis (streptococcal, pneumococcal). Inflammation of the serous covering of the abdominal cavity most often affects girls 4-9 years old. The disease develops within several hours, the child has a high temperature (up to 40°C) and abdominal pain in all its parts. The skin is pale, there is a white coating on the tongue, the baby is clearly suffering. Diarrhea (intestinal contents are yellow-green in color with a very unpleasant odor) may occur. If these symptoms occur, you should immediately seek medical help. Acute diverticulitis. Inflammation of Meckel's diverticulum (a bulge in the colon wall caused by a birth defect) is accompanied by fever, vomiting, constipation and general restlessness. Soreness is most often observed in the navel or lower abdomen (above the pubis). The symptoms of the disease are very similar to acute appendicitis, but, in any case, hospitalization is required. Acute cholecystitis. Inflammation of the gallbladder in children is accompanied by a sharp rise in temperature (up to 38-40°C), the stomach hurts in the upper right quadrant, when pressed, the child pulls your hand away. The child may note that the pain radiates to the right side of the lower back and right arm. There is anxiety, refusal to eat, nausea, vomiting (an admixture of bile is visible in the vomit), diarrhea or constipation, the tongue is covered with a grayish-white coating, the oral mucosa is dry, the abdomen is slightly swollen and hard to the touch. Acute pancreatitis. Inflammation of the pancreas is a common disease in childhood. It begins acutely - there is a characteristic girdle pain, fever up to 37°C, nausea, diarrhea and frequent vomiting, refusal to eat. Pale skin, dry mucous membranes of the mouth, tongue covered with a white coating. Intestinal infections. Acute inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, in which the child has abnormal bowel movements (severe diarrhea, constipation), nausea, vomiting, high fever and abdominal pain. Confusion and hallucinations may occur due to high fever. This condition causes typhoid fever, acute enterocolitis, dysentery, salmonellosis and other bacterial infections. Due to very loose stools and vomiting, there is a high risk of rapid dehydration, so you should seek medical help as soon as possible. Pain not associated with abdominal pathology. With viral and bacterial infections (sore throat, measles, whooping cough, acute respiratory infections, etc.), inflammation of the lymph nodes, including abdominal ones, often occurs. A characteristic symptom is that the pain intensifies when inhaling, as the descending diaphragm puts pressure on the abdominal lymph nodes. Abdominal pain of psychological origin. In very emotional children, abdominal pain may occur and be accompanied by fever, constipation or diarrhea, migraine-like headaches, lethargy, and pale or red skin. Sometimes confusion, auditory hallucinations, and visual impairment occur. Between such attacks the child feels absolutely normal. This phenomenon can be observed in children growing up in a tense psychological environment, and children for whom parents or teachers make excessive demands.
If abdominal pain in a child lasts more than two hours, is accompanied by elevated body temperature, refusal to eat, apathy, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, you must call an ambulance. If such phenomena are observed in an infant, then help is required immediately, since even two hours of dehydration is extremely dangerous for infants.
Causes
Almost 20% of babies may often complain of pain in the abdomen, and these uncomfortable sensations end on their own without causing any complications. For example, a child ate something unusual (green fruit) and thereby provoked loose stools (several times)
. But if a child’s temperature begins to rise against the background of diarrhea or constipation (any bowel disorder), vomiting, pale skin, then the child can be assumed to have an acute or chronic disease. In this state, the child loses his appetite, he becomes lethargic, inactive, and beads of sweat may appear on the skin (if the pain is very severe).
If an elevated temperature is added to the pain in the abdomen, then the cause may be a malfunction of the stomach or intestines; often diarrhea and vomiting are added to these symptoms.
Abdominal pain along with fever can be a sign of severe pathologies:
- appendicitis;
- Meckel's diverticulum;
- stomach ulcer;
- food poisoning.
The causes of pain can be both diseases of the abdominal cavity and diseases of other organs:
- acute appendicitis , the attack of which may depend on age, the younger the child, the less pronounced the signs of pathology will be, often the disease is diagnosed in children aged 9-12 years, the main signs of appendicitis can be considered: slightly elevated temperature, diarrhea, frequent vomiting, hearth the pain is concentrated in the navel area, the child becomes lethargic and loses appetite;
- streptococcal peritonitis , a very serious disease that affects girls from three to five years of age, this disease can be triggered by infection through the bloodstream or lymphatic tract into the abdominal cavity, accompanied by a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition, the temperature jumps to 40 degrees (not reduced by antipyretic drugs), with In this case, unbearable pain appears in the lower abdomen, stool becomes liquid, with a very unpleasant fetid odor, yellow-green in color, the children become lethargic, the skin color becomes sallow, a white coating appears on the tongue, the skin turns pale;
- problems with the stomach, intestines
, such as gastroenteritis, enteritis, colitis, the causative agent of which can be E. coli, various coccal microorganisms (streptococci and staphylococci), dysentery bacillus, they can be picked up by the fecal-oral route. The temperature rises slightly, discomfort can spread throughout the abdomen, a characteristic symptom of this disease is diarrhea, in which you can notice pieces of undigested food, inclusions of blood, mucus, in this condition, if the baby is not given timely help, then such a disease can lead to fatal outcome; - acute pyelonephritis - pain begins to radiate to the lumbar region, the main symptoms of this pathology are frequent urination, which is accompanied by pain, a feverish state, signs of intoxication of the body, and occasionally diarrhea appears;
- inflammatory process , which develops when the wall of the colon protrudes, is usually accompanied by symptoms of fever, constipation, vomiting, the pain is localized around the navel or in the lower abdomen;
- acute cholecystitis, in which there is a very high temperature (up to 40 degrees), discomfort is concentrated under the right rib, but can also radiate to the right arm and lower back, the child loses appetite, nausea, vomiting appears, with an admixture of bile, bowel dysfunction, grayish -white coating on the tongue, swollen belly;
Abdominal pain can also appear with other pathologies that are not related to the peritoneum:
- infections caused by viruses and bacteria (tonsillitis, measles, whooping cough), which are characterized by the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the lymph nodes (abdominal), the symptoms of which appear when inhaling, when the descending diaphragm presses on the inflamed lymph nodes;
- Abdominal discomfort can also be caused by psychological reasons, while in overly sensitive children the pain may be accompanied by a fever, confusion, and auditory hallucinations.
The main causes of a condition in which a child has a stomach ache and fever. Diagnostic methods
Diseases associated with inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract
Appendicitis
Suppuration of the appendage of the cecum, which is also called the appendix.
Children older than one and a half years are susceptible to appendicitis; it practically does not occur in infants; it most often affects them in primary school and adolescence.
Diagnosis of appendicitis
Children under 3 years of age experience high fever (from 38° to 40°C), fatigue and weakness. The child will not let you touch his stomach.
In children over 3 years old, the temperature may increase slightly (37.5 ° C is the upper limit) and abdominal pain is observed around the navel, vomiting is possible, but not more than once. Then the pain moves to the area of the right ileum and intensifies when changing position or pressing on the abdomen. The child lies on his right side, tucking his legs to his stomach.
Pancreatitis
Inflammatory process in the pancreas. Most often the disease occurs in adolescence.
Diagnosis of pancreatitis
The vast majority of children feel pain in the epigastrium, it radiates to the back and is girdling in nature. At this time, the child feels nauseous and may vomit several times.
Streptococcal and pneumococcal peritonitis
Inflammation of the peritoneum. Girls in kindergarten and primary school age are most often affected.
Diagnosis of peritonitis
The disease develops over a period of several hours. Abdominal pain radiates to the lower region, but usually the entire abdomen hurts.
The child’s skin turns pale and a coating appears on the tongue. The temperature can rise to 39°C, symptoms of fever are pronounced.
A characteristic symptom is frequent yellow-green diarrhea with a pungent odor. The child feels general weakness and malaise.
Important! If symptoms of peritonitis are detected, you should immediately call an ambulance!
Acute intestinal diseases
Damage to the gastrointestinal tract caused by dysentery or E. coli. This group includes salmonellosis, gastroenteritis, colitis, dysentery, and typhoid fever.
Diagnosis of acute intestinal diseases.
The temperature rises to 39° - 40°C, fever is observed, and in rare cases, hallucinations. The pain spreads throughout the abdomen, severe diarrhea and incessant vomiting begin, which quickly lead to dehydration, especially when it comes to small children.
Cholecystitis
Inflammation of the gallbladder. More often girls suffer from this disease.
Diagnosis of cholecystitis
The most characteristic symptom is vomiting bile. The pain radiates to the right side of the lumbar spine. A coating appears on the child’s tongue, the stomach swells and hardens. The temperature is usually up to 39°C.
Diseases not related to the gastrointestinal tract
Diagnosis of infections (acute respiratory infections, sore throat, whooping cough)
With these diseases, the lymph nodes increase in size. Therefore, the general symptoms of infections include abdominal pain, which intensifies with inhalation.
Types of abdominal pain
Unpleasant sensations in the abdomen may vary, depending on the type of disease that caused them:
- periodic pain can appear due to poor nutrition, discomfort occurs in some part of the abdomen and lasts for a long period;
- pain, which is accompanied by diarrhea and high fever, nausea and vomiting, can be the cause of food poisoning;
- pain in the pelvic area signals pathologies of the genitourinary system;
- if the pain is also accompanied by periodic increases in temperature, stool disturbances, vomiting of bile or blood, and blood in the stool, then this may be jaundice.
If a child has a stomach ache, and even with a fever, urgent consultation with a specialist is necessary; self-medication is unacceptable here. Refusal of medical assistance in such a situation can lead to serious consequences.
Complaints of abdominal pain generally predominate in children. Some children point to their stomach even if they have a headache
.
But even the smallest patients can easily be exposed if they are weak, lethargic, pale, occupy a forced position lying on their side, and have their legs drawn up
. Well, if this is accompanied by an increase in body temperature and vomiting, it becomes obvious that the situation becomes threatening.
A child has a stomach ache due to a high temperature: a review of causes and treatment methods
Sometimes parents simply don’t know what’s happening when their child starts to have a stomach ache and a fever. What to do and what are the causes of such symptoms? What is the reason for the sharp increase in temperature to 39˚C? What do we know about the causes of abdominal pain in children? What diseases are accompanied by pain, diarrhea, nausea and high fever? Let's talk about this in more detail.
From time to time, every little one may experience abdominal pain. The most harmless reasons are associated with the wrong food or low-quality products, as well as with the influence of strong emotional and nervous stress.
Parents should be seriously concerned about the health of the baby when pain is combined with high body temperature. She, in turn, says that an inflammatory process is occurring in the body, which the child is trying to cope with.
The most common variant in children is acute intestinal infection
Abdominal pain and fever that occurred approximately on the 1st–3rd, sometimes on the 7th day after lunch in an unfamiliar restaurant or cafe, visiting, consuming dubious (or seemingly not at all dubious!) dairy or fermented milk products, or maybe Perhaps even ordinary ice cream should suggest an infection.
Symptoms as repeated vomiting that brings relief or repeated loose stools usually help make the diagnosis Separately, we can consider rotavirus and enterovirus infections, which may not be associated with food taken, but are caused by the transmission of the virus from one child to another both during play and through shared toys, writing utensils, and dishes.
.
Rotavirus infection will also be characterized by the appearance of a cough, possibly copious nasal discharge, 1–2 days before the onset of abdominal pain and fever. This “preparatory” (prodromal) period can serve as a differential diagnostic feature that distinguishes this type of infection from the “acute abdomen”
. For enterovirus infection, the development of sore throat in the prodromal period of the disease is more typical.
- What not to do . You should not start self-medication: antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, it is also dangerous to give an antipyretic if the temperature does not exceed 38 degrees.
- What to do. Ask the parents of the children with whom you were in the cafe, relatives who met you 1–3 days before the development of the disease, and the kindergarten teacher. It is important to see if similar symptoms were noted in children (and maybe adults) who were near your baby
. If someone is similarly ill, it may turn out that the diagnosis is in your pocket.If there is vomiting or diarrhea, try to provide the child with plenty of fluids, you can give smecta. If the condition worsens within 4–6 hours from the onset of the first symptoms and vomiting does not stop, the child will require hospitalization
. Most modern antiviral drugs for children are relatively safe and can be used at the first symptoms of the disease, even if the diagnosis is not yet entirely clear.
First aid
When a child gets sick, the main thing is not to get confused and remember what can and cannot be done.
And so as not to cause harm:
If you have abdominal pain, never warm your stomach, which is extremely dangerous if the appendix is inflamed, because it may burst; Before the doctor arrives, do not give painkillers and antipyretics (the exception is a temperature exceeding 38.5 degrees), because this may disrupt the overall picture of the disease; do not induce vomiting again if there is no improvement from the first, this causes irritation of the diseased organ and the pain intensifies.
What can and should be done:
call a pediatrician or an ambulance; do not leave the child alone unattended; put you to bed and if you have abdominal pain, put something cold on the area of pain; in case of poisoning, remember what you ate, when and where. If there were other children in your company, then call and ask about their well-being.
A rise in temperature in a child should always alert any parent. She talks about some hidden and not yet identified disease. If abdominal pain appears at the same time, then these are no longer comic symptoms, but an ominous warning of impending danger. And the child’s life may depend on how quickly an ambulance is called.
Note!
The presence of symptoms such as:
Abdominal pain, bad breath, heartburn, diarrhea, constipation, belching, increased gas production (flatulence)
If you have at least 2 of these symptoms, then this indicates a developing
gastritis or ulcer.
These diseases are dangerous due to the development of serious complications (penetration, gastric bleeding, etc.), many of which can lead to
LETHAL
outcome. Treatment needs to start now.
Read the article about how a woman got rid of these symptoms by defeating their main cause using a natural method. Read the material…
Abdominal pain and fever are a dangerous condition in a child. This may be a signal of the development of an acute intestinal infection or other serious illness. If the child has a stomach ache or fever, the mother should immediately notify the pediatrician. Let's consider the symptoms of dangerous diseases of the internal organs that can cause this condition.
The most dangerous option is “acute stomach”
“Acute abdomen” is a somewhat outdated name for diseases in which inflammation of the internal organs located in the abdominal cavity spreads to the peritoneum - the inner lining of the abdominal cavity (this is called peritonitis).
In addition to the severe pain experienced by the patient, a whole cascade of physical and biochemical processes is launched, resulting in a very high probability of shock, sepsis, or even death. Of this group of diseases, the most common in children is appendicitis or other acute surgical pathology of the intestine (intussusception or volvulus, as well as peritonitis due to prolonged constipation; there may also be a violation of the integrity of the intestinal wall by a foreign object when accidentally or intentionally swallowed).
- What not to do. Under no circumstances should you warm the stomach: use heating pads and compresses. These actions in most cases lead to aggravation of symptoms, the development of diffuse peritonitis (when not only the peritoneum enveloping the problem organ is inflamed, but also those parts of it that are located away from the appendix or a loop of intestine).
It is dangerous to give a child antipyretic and painkillers - this is due to the fact that an imaginary short-term improvement in the patient’s condition confuses the diagnostic process. A visiting doctor, examining a patient, may miss important symptoms indicating the development of peritonitis, only because they are masked by an anesthetic. There is no need to try to make your child vomit again, especially if the first time did not make him feel better.. The fact is that vomiting with peritonitis in general and appendicitis in particular is caused not by toxins contained in the stomach and intestines (as happens in the case of infection), but by irritation of the peritoneum, which envelops the abdominal cavity and the organs in it from the inside.
- What to do . If technically possible, perform an ultrasound of the abdominal organs on the child: this can be done not only in paid clinics, but also in municipal medical institutions - clinics, emergency departments of children's hospitals
. This will give a chance to “catch” peritonitis at an early stage and hospitalize the child in time. And, of course, you can call an ambulance at any time.
Appendicitis
Acute appendicitis is a well-known horror story for most mothers, but it often happens that, when faced with this disease face to face, they do not recognize it, and the child is left without medical care for an extra day, or even more. Abdominal pain with appendicitis is one of the most striking, but not the only symptom. Moreover, in the classic case, appendicitis begins not with abdominal pain, but with a single vomiting that does not bring relief.
Body temperature in acute appendicitis may remain normal during the first day after the onset of symptoms, or rise slightly - up to 37-37.5 degrees. As events progress, when appendicitis gradually reaches the purulent stage, significant fever is noted - up to 38.5-39 degrees
.
Usually the intensity of the pain at this point is such that the need to call an ambulance leaves no doubt
. It is better to prefer calling a team to transporting the patient to the hospital independently.
Exclusion diagnoses – pancreatitis, systemic diseases
A diagnosis of exclusion is a situation when a disease is established by screening out versions of the development of more severe, life-threatening pathologies. If the patient does not have an acute surgical condition or an infectious process, a search for other diseases of the internal organs is carried out
.
Of these diseases, the combination of paroxysmal pain in the upper abdomen and elevated body temperature most often occurs with pancreatitis. Children may also be bothered by bloating, diarrhea (and the color of the stool will be unusually light), and less commonly, vomiting
. True, it is somewhat reminiscent of both appendicitis and acute intestinal infection.
Pancreatitis rarely goes away on its own, but symptoms may gradually subside with a fasting diet. As the pain subsides, the temperature also decreases
. Systemic diseases, accompanied by abdominal pain and fever, have a wave-like course: exacerbations alternate with remission (periods of complete well-being); in the early stages, as a rule, they do not require treatment. For the most part, this pathology is found among representatives of small nations of the North Caucasus and Mediterranean regions, but there may be exceptions.
- What not to do . Do not try to cure the child yourself. What at first glance seems similar to pancreatitis or Mediterranean fever may turn out to be the same appendicitis after a few hours.
- What to do . If the child’s condition does not deteriorate significantly from the moment the pain begins, the body temperature at the height of the pain does not exceed 37.5 degrees, the symptoms gradually subside on their own - contact a gastroenterologist
. He will give the child a full examination, including blood tests and ultrasound.
Many children complain of abdominal pain from time to time. They often resolve on their own and are not a cause for concern, even if one-time diarrhea occurs. But if a high temperature appears among the symptoms, this is a clear sign of the disease.
. If a child has a stomach ache and a normal stool temperature of 38, what to do?
Major diseases
Diseases of the abdominal organs
Fever and abdominal pain in a child can occur with various intestinal infections, such as dysentery and salmonellosis, as well as with the onset of inflammatory processes in the abdominal organs, for example in the gall bladder, pancreas, appendix.
Dysentery
It is an infectious intestinal disease in which general intoxication of the body occurs with damage to the large intestine. The culprit of the infection is a bacterium of the genus Shigella, which enters the body through the oral cavity when eating food with dirty hands, when using unwashed or washed vegetables, fruits, and berries with contaminated water, and when dairy products are not properly heat treated.
The disease affects all age groups of the population at any time of the year, but it occurs more often in summer and autumn in children. It can be widespread with a large concentration of children in a limited area, for example in camps, resorts, hiking, etc.
The disease manifests itself in the period from 2-3 to 6-7 days after the microbes enter the body. With severe intoxication, the disease can manifest itself within a few hours.
In this case, the following picture is observed: children begin to feel sick and vomit, the temperature rises, they develop headaches and abdominal pain, dark green diarrhea occurs, often interspersed with mucus, pus, and blood, which can occur up to 20 times a day.
When complicated, the pain may be accompanied by delirium, confusion, chills, and the temperature may rise to 39 degrees. The disease is dangerous due to dehydration of the body, which can be fatal.
That is why sick children must be isolated and transported as quickly as possible to the infectious diseases department of the hospital, where a final diagnosis is made based on external manifestations and laboratory research methods - blood, urine, feces. In case of any doubt, consultation with other specialists (gastroenterologist, proctologist), as well as instrumental diagnostics - sigmoidoscopy, which is used to determine the level of damage to the mucous membrane of the rectum and colon, may be required.
The goal of treatment is to destroy bacteria and neutralize the toxins that they have released. The use of antibacterial agents, saline and colloid solutions, immunomodulators and a special diet, as a rule, gives a positive result.
Salmonellosis
The disease develops as a result of food poisoning, from which neither adults nor children are immune. The causative agents of the disease are microbes that belong to the genus Salmonella.
The source of infection can be rodents, wild and domestic animals, as well as meat and dairy products obtained from infected animals or exposed to contamination as a result of violation of the rules of processing, preparation and storage. In such cases, mass poisoning of people occurs when purchasing and consuming sausages, pates, milk, cheese, eggs and culinary products.
When infected, symptoms of the disease can appear after a minimum of 6 hours, maximum by the end of the second day, and usually include:
a sharp increase in temperature to 38-39 degrees; cramping nature of abdominal pain; the appearance of nausea and vomiting; diarrhea leading to dehydration.
With severe intoxication and/or inadequate treatment, complications such as:
infectious-toxic shock; vascular thrombosis; meningitis; hepatitis; renal failure; joint inflammation; respiratory diseases.
The diagnosis is made based on laboratory tests:
urine and feces; vomit; blood; stomach contents after washing it.
The patient is hospitalized and treatment is carried out aimed at destroying salmonella, detoxifying the body, restoring water-salt balance and intestinal microflora. In addition to medications, a special diet and general strengthening measures are prescribed.
Acute cholecystitis
It is an inflammatory disease of the gallbladder, which can be caused by inflammatory processes occurring in the gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary system, respiratory tract, the activity of helminths, and also become a complication of cholelithiasis, as a result of a violation of the outflow of bile.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of the disease are:
constipation; irregular meals; monotonous food rich in fats; problems with blood vessels; endocrine disorders; pregnancy; heredity.
When an attack occurs, the following are observed:
pain in the right hypochondrium, of a paroxysmal or acute nature, extending under the right shoulder blade and into the shoulder; nausea and vomiting; temperature rise to 38.2-39 degrees.
Most often, pain occurs unexpectedly, usually a few hours after fatty and spicy foods, and is so severe that the child simply cannot find a place for himself. A few days after the attack, the child’s skin and sclera may acquire a yellow tint, and the urine may darken.
When these symptoms appear, the child is hospitalized, and already in the hospital, based on blood, urine, feces, bile tests and the results of instrumental diagnostics (ultrasound, FEGDS, X-ray with contrast), a diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed. It is carried out with choleretic agents, antispasmodics, antibiotics, hepatoprotectors, and vitamins. Equally important in recovery are diet and adherence to a special diet.
Acute pancreatitis
It is an inflammation of the pancreas, in which its swelling is observed; in severe cases, hemorrhage, necrosis, and toxemia can occur. In childhood, this form is not common, but since the causes and symptoms are similar to the manifestation of reactive pancreatitis, which is more often diagnosed in children, people far from medicine do not see much difference between the forms.
So, the causes of acute/reactive pancreatitis can be:
diseases of other gastrointestinal organs; helminths; complication of an infectious disease; taking nonsteroidal or steroidal drugs; abdominal trauma; poor nutrition; heredity.
The disease is characterized by the appearance of severe girdling pain in the abdomen, which is more localized in the upper part, i.e. on the back it is given under the right shoulder blade. In this case, heartburn, belching, nausea, turning into vomiting with mucus and bile, flatulence, and diarrhea are observed.
Severe pain can cause shock, to avoid this you must:
take measures to hospitalize the child; put the child to bed; Place something cold, such as an ice pack, on the area of pain.
Diagnosis includes a visual examination, during which the child is found to have an unusual dryness of the tongue, which is coated with a white or brown coating; upon palpation the patient feels a sharp pain, as well as a number of laboratory tests (general and biochemical blood tests and stool analysis for coprogram and lipid profile) and instrumental (ultrasound, computed tomography, plain radiography) studies.
Treatment is carried out in the hospital with strict bed rest and a special diet; antibacterial, analgesic, antispasmodic agents and special medications are used that suppress the enzymatic activity of the pancreas.
Appendicitis
This disease occurs when the appendix, an extension of the cecum, becomes inflamed. This disease can occur unexpectedly in a child, and the main thing is not to get confused, and you should not think that this disease can only affect adults.
According to statistics, the disease is most often diagnosed in children 8-12 years old. In children under 3 years of age, pain is very pronounced not only on the right side, but also on the entire abdomen, in the umbilical region.
Inflammation can be accelerated by:
worms trapped in the appendage; compression of the lumen of the appendix and its blockage with feces.
Initially, the pain symptoms of this disease are similar to pain in a child, which occurs, for example, during a long run, when suddenly a tingling sensation begins in the right side. As inflammation progresses, abdominal pain will intensify with changes in body position, and pain may occur in the pit of the stomach, in the left side, and in the right.
The child’s condition and behavior will instantly change, and pain will begin to be accompanied by:
temperature rise to 37-38 degrees; nausea; unusual pale face; diarrhea; sweat on the skin; feeling of thirst.
If these symptoms occur, an ambulance is immediately called, and before it arrives, the child must be put to bed and a bag, or preferably a heating pad, with cold water placed on the right abdomen.
The disease is diagnosed:
general inspection; palpation; laboratory methods for blood testing; laparoscopy.
Treatment for appendicitis involves surgery to remove the inflamed organ.
Delay during attacks of appendicitis is dangerous! An inflamed appendix can burst and pus can enter the abdominal cavity, which can lead to serious complications and a risk to the child’s life.
Diseases of other organs
Abdominal pain accompanied by fever can appear in children with diseases of organs not located in the abdominal cavity. Let's look at the most common options:
Diseases of the urinary system
The organs that make up this system include the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. In childhood, diseases of these organs are usually associated with infection, which can penetrate from the outside or from the inside (through the blood, lymph during tonsillitis, caries and other inflammatory processes), resulting in the development of pyelonephritis, cystitis, and urethritis.
Provoking factors are:
frequent colds; hypothermia; lack of hygiene; constipation; injuries; congenital pathologies; presence of a catheter.
Up to 1 year of age, infectious diseases in this area are more common in boys, and after a year - in girls.
In children under 2 years of age, the disease usually manifests itself with an increase in temperature to 37.5-38 degrees, weakness, lethargy, apathy, and weight loss. Older children, against a background of elevated temperature, sweating, and chills, report pain in the lower back and/or abdomen, a burning sensation when urinating, which becomes frequent, and the urine acquires an unpleasant odor and becomes cloudy, and pus may even appear. You may also notice irritation of the external genitalia, which turn red.
If, due to pain in the lower back or lower abdomen, the temperature rises above 38 degrees, vomiting, diarrhea, agitation or lethargy that is not typical for a child appear, then it is necessary to call an ambulance, because these may be signs of acute pyelonephritis.
The presence of infection is diagnosed using a clinical urine test, and specific pathogens are identified using a urine culture test. Identification of pathologies of the urinary system that could cause infection occurs using instrumental methods - ultrasound, x-rays, radioisotope studies.
Treatment is usually carried out at home, with the exception of infants under 2 months, and consists of taking antibiotics, as well as bed rest and a diet that excludes spicy, smoked, fatty foods and includes more “wet” fruits and vegetables - watermelons, cucumbers, zucchini, etc. Hospitalization may be required if there is a sharp deterioration in the condition or ineffectiveness of home treatment.
Respiratory system diseases
This system consists of the nasal cavity, larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs, which participate in gas exchange between the environment and the body. When this process is disrupted by infectious pathogens, various pathologies of the respiratory system arise, which, in percentage terms, occupy a prominent place among other childhood diseases. Among them, the most common are bronchitis, laryngitis, rhinitis, tonsillitis, and pneumonia.
These are dangerous diseases for a fragile child’s body; there is no immunity against them. Influenza viruses, respiratory viruses, staphylococcus, streptococcus, and E. coli bacteria are involved in the occurrence of acute diseases.
In addition to provoking factors, which are overheating before going outside, hypothermia during a walk, the presence of diathesis and other diseases in children that weaken them physically, the unfavorable ecological situation of the area or the difficult psychological atmosphere in the family, diseases of the respiratory system in children are directly related to features of its structure and the process of child breathing.
The specificity is as follows: while the child’s body is developing (usually this process lasts until the age of 14-15), the mucous membrane in many parts of the respiratory system is dry and vulnerable, while almost all of its parts (nasal passages, nasopharyngeal space, pharynx, trachea, bronchi ) are narrow, which causes difficulty in nasal breathing, and also contributes to inflammation at the slightest irritation. In addition, the breathing rhythm in children is unstable, its depth is small, and its frequency is high, which contributes to the frequent “entrance” of cold air, which does not have time to warm up at all. And if a child cries or screams on the street, then the likelihood of him getting sick increases significantly, since the volume of inhaled air increases by 5-6 times.
Table. Frequency of respiratory cycles (inhalation and exhalation) per minute, depending on age:
| in newborns | 45-60 |
| in a one-year-old | 33-36 |
| at 6 years old | 23-26 |
| at 10 | 19-21 |
| At 18 years old | 16-17 |
If you have a respiratory disease, the following symptoms may occur:
pain in the chest or abdomen, as a result of a strained dry cough, which can be paroxysmal, constant and periodic; cough with phlegm; dyspnea; nasal discharge; unnatural breathing (difficulty, rapidity, weak); pain when swallowing; temperature increase.
Cyanosis may also appear, i.e. the skin and mucous membranes acquire a bluish tint, as a result of severely difficult breathing, in which the child almost suffocates, a puffy face and a rapid heartbeat become noticeable. All this can lead to seizures due to the fact that the brain does not receive enough oxygen.
Diagnosis consists of an external examination of the child and listening to his breathing by a pediatrician; if bronchitis or pneumonia is suspected, the following may be prescribed:
fluoroscopy; radiography; bronchography; general and biochemical blood tests;
Treatment is aimed at restoring airway patency and eliminating the inflammatory process in the mucosa. For this, antiviral drugs (Acyclovir, leukocyte Interferon, Immunoglobulin), expectorants (Mukaltin, infusions or decoctions of medicinal herbs: coltsfoot, plantain, oregano), and warm drinks are used. Good results in treatment can be achieved by using cups and mustard plasters, rubbing the chest with alcohol compresses.
When pneumonia is diagnosed, treatment with antibiotics is necessary, preferably in a hospital setting.
Colds
Most often, all of the above respiratory diseases are caused by a cold - acute respiratory disease (acute respiratory disease) or ARVI (acute respiratory viral infection), if it is laboratory proven or empirically assumed that the leading role of viruses in the occurrence of the disease.
Depending on the type of virus - adenovirus, rhinovirus, etc., a specific organ of the respiratory system is affected and diseases occur - rhinitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis, often complicated by sinusitis, otitis, conjunctivitis, etc.
We discussed above the reasons why children catch colds much more often than adults. Here, I would still like to note that the highest percentage of morbidity is observed in children from 1 year to 3 years and from 5 to 7 years. Moreover, the incidence rate can reach 8-11 times a year, and it increases when visiting preschool institutions.
So, all colds are characterized by: an increase in temperature no higher than 38 degrees; weak and short-lived trembling in the body; moderate intoxication of the body;
In this case, the following are usually observed:
a sore throat; cough; runny nose; abdominal pain, especially in young children;
If there is no temperature, although there is severe pain, then this indicates that the body’s protective functions are not working well. This condition is the most dangerous for a child.
Diagnostics carried out by a pediatrician include:
examination of the child’s pharynx, throat, tonsils, nasal passages and whites of the eyes, as well as the skin of the child; checking for noises and wheezing when breathing; measurement of pulse and pressure; palpation of the abdomen; Finding out from the parents the general condition of the child, his appetite, and the presence of temperature.
Based on the data obtained, a diagnosis is made, and in case of doubt, referrals are issued for tests - blood, feces and urine.
If a child has a stomach ache, vomiting, diarrhea and a high temperature, then the issue of his hospitalization is decided.
Treatment, regardless of the general condition of the sick child, includes bed rest, which helps to avoid complications and also does not make the patient a carrier of infection.
The following has a positive effect:
antitussive drugs; antipyretics; inhalations with essential oils; drinking plenty of fluids in combination with infusions and vitamins that strengthen the immune system; Sanorin and Glazolin drops for a runny nose
Paracetamol, Pertusin cough medicine, and Pectusin cough tablets are not harmful for children, even infants. But all medications must be given only with the permission of the attending physician.
Main reasons
Let's look at the main diseases that can lead to abdominal pain and fever with normal bowel movements.
Appendicitis. Most often, this disease occurs between 9 and 12 years of age, although it can appear at other ages.
.
At the same time, general health worsens, the temperature rises, and it hurts to touch the stomach
.
After some time, pain from the navel area moves to the right side
. Nausea and a feeling of extreme thirst may occur. Diarrhea is present only when combined with viral or intestinal infections.
Peritonitis. It is characterized by sudden increases in temperature and pain throughout the abdomen. Sometimes diarrhea occurs
. Girls under 9 years of age are most often at risk, but there may be exceptions.
Abdominal pain caused by inflammation of the abdominal lymph nodes. This condition occurs, for example, with acute respiratory infections and other viral and bacterial infections.
. A characteristic symptom is increased pain during inspiration.
Psychological disorders. This may seem strange to some, however, abdominal pain can occur due to emotional overload
. Abdominal pain is accompanied by headache, pallor or, conversely, redness, hearing and vision impairment. In this case, care must be taken to eliminate the factors causing this condition.
In any case, it is necessary to call an ambulance as soon as possible, especially if the described symptoms appear in an infant.
How to protect your child from health problems?
Abdominal pain can occur in all children.
Most often they appear due to poor quality food eaten for breakfast, lunch or dinner, or due to severe nervous tension. But sometimes discomfort in the abdominal area is accompanied by a strong increase in temperature, which is a consequence of the presence of some pathological processes in the baby’s body.
Abdominal pain and fever are often accompanied by symptoms such as diarrhea and vomiting. The presence of a complex of these symptoms is a reason to consult a doctor.
If your child is in pain and you want to somehow alleviate his condition, then read the following information that will be useful to you.
Under no circumstances should you give your baby any medications until the doctors arrive. The effect of medications can soften the symptoms of the disease and doctors will not be able to determine what exactly is causing the problem that is bothering your child.
In addition, you should not wrap your baby in blankets or apply a heating pad to his body, even when he is freezing.
A local increase in temperature can intensify the course of the pathological process and significantly worsen the child’s condition.
If the baby is crying and fidgeting restlessly, then do not pick him up, but put him in bed and just be there. Stroke his head and talk to him.
If your child is vomiting, then take care of some kind of bowl for vomit; do not force your child to get up and go to the toilet on his own.
This information will help doctors form a more accurate clinical picture.
This article describes several of the most obvious reasons that can trigger severe abdominal pain and increased body temperature (more than 38 degrees) in children.
If you want to protect your child from the occurrence of such diseases or at least minimize the risk of their occurrence, then listen to the following advice:
- feed your child healthy and balanced food, rich in vitamins, minerals and other necessary components;
- Monitor how much your child drinks. The daily water consumption rate for children is one liter;
- limit the amount of sweet, fatty foods and foods rich in flavorings and preservatives;
- play sports with your child, take walks more often and play active games with him;
- Explain to your child why you need to wash your hands before eating and after going to the toilet;
- keep the apartment clean.
Parental mistakes in acute conditions
If the child’s condition can be visually assessed as acute, in no case should you resort to self-medication; to alleviate the condition, you must wait for doctors. In this case, the main mistakes of parents are:
- use of an anesthetic or other drug that alleviates the condition;
- using an enema;
- using a heating pad for the abdomen;
- feeding.
The listed actions can only aggravate the course of the disease and prevent a correct diagnosis.
Prevention
To avoid unpleasant consequences, you should worry about your child’s health in advance. To prevent abdominal organs, you need to follow these tips:
- moderate consumption of fatty and fried foods;
- replenishing water balance during the day;
- It is better to eat food in smaller portions, but more often;
- perform physical exercises daily to maintain body tone;
- compliance with hygiene rules;
- ensuring a normal psychological environment for the child.
These simple rules will help save your baby from suffering, and you from additional troubles and worries.
But if it so happens that a child has a stomach ache and a fever, you should not resort to self-medication, since unqualified intervention can result in serious complications.
How to avoid abdominal diseases
It is impossible to know in advance about the possibility of the disease occurring. However, you should adhere to several rules to avoid illnesses due to your own fault:
- no need to give a lot of fatty and fried foods; - you need to give the child fluid in normal quantities to avoid dehydration; - feed the child often and in small portions; - It is worth limiting your child’s consumption of carbonated drinks; — the child’s diet should be balanced and contain a sufficient amount of fiber; - You need to provide your baby with daily physical exercise; — it is necessary to teach children personal hygiene from childhood; - You need to provide a cozy environment and a calm atmosphere at home.