The feces of a child and an adult have significant differences. This is due to the fact that in children the body is just forming and therefore its intestines function somewhat differently. In addition, the child’s nutrition plays an important role. Baby feces can have a variety of characteristics in color, smell, and consistency.
The fact that there is mucus in small quantities, according to pediatricians, is the norm and the child’s parents should not worry about this. If a lot of mucus appears in the baby’s stool, this may indicate various diseases of the digestive system, and in this case, parents need to consult a doctor in order to avoid possible complications in the child’s health.
First aid
In case of stool upset, the child must be given emergency first aid.
Babies who are not fed their mother's breast milk should not be given food. Products should be replaced with plenty of fluids: during this period it is necessary to take a sufficient amount of rehydration solutions, pure mineral water, herbal decoctions, infusions to avoid dehydration of the body. Frequent bowel movements often provoke itching and burning of the anus. Therefore, after each trip to the toilet, the baby needs to carefully clean the anus with wet wipes or wash it with baby soap, and apply a protective cream to the area. Ventilation and disinfection of the room are necessary throughout the entire therapeutic course.
Causes
Despite the fact that doctors distinguish infectious and non-infectious causes of increased body temperature, doctors are generally inclined to believe that even with supposedly non-infectious sources of the problem there are no signs of infection, but the body tries to remove pathogenic cells with the help of loose stools. Therefore, it is still generally accepted that loose stools, like high fever, are a consequence of an infectious disease. Accordingly, you need to look for the source of infection.
Most often the main reasons are:
- intestinal infection;
- virus infection;
- eating foods that have gone bad;
- chickenpox, measles.
Loose and frequent stools are possible during teething, sore throat, allergies, and acetone syndrome. As a rule, diarrhea can be both the root cause and the body’s reaction to an increase in body temperature.
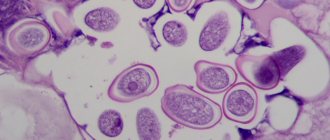
What is mucus in stool
The glands of the adult intestine produce small amounts of a mucous substance to protect the intestinal wall and facilitate the passage of stool. Stool with mucus in a breastfed baby is caused by the immaturity of the enzymatic system and poor functioning of the intestines. If your newborn baby is calm and gaining weight, there is no reason to panic.
At the physiological level, mucus is a clot consisting of products of the secretory work of epithelial tissue cells. The viscous substance performs a protective function due to the content of antiseptics and immunoglobulins. In other words, the appearance of epithelial clots in large numbers indicates that the body is trying to protect itself from some irritating factors.
Causes
Most often, diarrhea with blood is caused by internal diseases. Less commonly, malnutrition and external factors. As soon as parents notice bloody streaks and mucus in loose stools, they need to think about what could have caused such a nuisance.
Nutrition
- Food poisoning.
- The child has eaten too much vegetables or fruits that have a laxative effect.
- Poor quality products.
Diseases
- Keep in mind that diarrhea with mucus in a child under one year old is normal, since the formation of his gastrointestinal tract is not yet complete.
- Pathogenic microorganisms in the intestines.
- Infectious diseases: salmonellosis, gastroenteritis, dysentery, rotavirus infection, colitis.
- Inflammation of the mucous membranes in the intestines, esophagus or stomach.
- Internal hemorrhoids.
- Allergic reaction.
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Ulcer.
- Enzyme or lactose deficiency.
- Cancer diseases.
- Crohn's disease.
- Teething.
- Helminths.
External factors
- Stressful situations.
- Getting into the stomach of small parts that injure the mucous membrane.
- Taking medications.
- Failed operation.
All these factors must be taken into account if a child has diarrhea with blood and mucus. They will help make an accurate diagnosis, on which treatment will depend. Before visiting a doctor, parents can conduct a preliminary examination themselves and draw a conclusion about what is happening to their baby.
Mucus in a child’s stool – what could cause it?
Every mother is concerned about the contents of her baby's potty. And this is quite understandable - the child himself cannot yet tell his parents about what is bothering him, and it is by stool that one can judge the state of the baby’s digestive system, on the quality of which his health depends.
And such a phenomenon as mucus in a child’s stool can cause concern on the part of parents who begin to assume that their child is seriously ill. At the same time, doctors say that the presence of mucus in the stool does not always indicate possible pathologies.
What is mucus for?
Mucus is a jelly-like transparent mass that envelops the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract to protect it from the harmful effects of alkalis, acids and injury from food particles. Therefore, those parents who are interested in the question of what mucus in stool means should understand that this is how the protective function of the intestines is manifested.
Fact! If the digestive system is working normally, the discharge is mixed with the feces and is not visible in the stool.
Almost every child, at least occasionally, may experience mucus in the stool. At the same time, if the baby feels well, and the appearance of discharge is not accompanied by signs of any diseases, this is considered normal. Lack of secretion can threaten the baby with constipation and other problems with stool.
However, in pathological conditions a lot of mucus appears in the stool, it can be seen in the stool or detected during laboratory testing. Let's consider in what cases stool with mucus gives parents cause for concern.
The main causes of mucus
Experts say that the main and most common causes of mucus in stool are as follows:
- Intestinal dysbiosis, which is characterized by the appearance of undigested food particles and sputum in the stool; children experience bloating and colic. In more serious cases, pathogenic bacteria grow in the intestines and microflora beneficial to the body die, and the child develops copious mucous stools, often liquid, sometimes even streaked with blood. Infectious intestinal diseases and long-term use of antibiotics can lead to this condition. With dysbacteriosis, children experience a significant decrease in the body’s protective properties, they are more often susceptible to colds, their appetite is impaired, and such children begin to lag behind their peers in development.
- You can talk about the presence of a parasitic infection if mucus appears in your child’s stool, sometimes with admixtures of blood, while the baby has a decreased appetite, a stomach ache, sleep may be disturbed, tearfulness, irritability appear, the child shows anxiety, he or she experiences allergic manifestations in in the form of various rashes and itching. In this case, the cause of mucous discharge is pinworms, roundworms, amoebas, tapeworms and other parasites, the presence of which can be confirmed by laboratory tests. Moreover, parasites do not always appear due to non-compliance with hygiene rules. Sometimes this may be due to eating meat or fish products that have not undergone proper heat treatment, or going to the pool.
- Intestinal infectious diseases cause an inflammatory process, resulting in mucus, pieces of undigested food, and maybe even pus and bloody spots in the child’s stool. Moreover, leukocytes and mucus in this case are closely interconnected - the more leukocytes, the more intense the yellow color the discharge will be. The cause of bacterial intestinal infections is a banal neglect of hygiene rules, when dirty vegetables and fruits end up in a child’s food, or when hands remain dirty. Leukocytes in the stool of infants and older children can be detected due to the viral nature of the infectious disease. Viral enteritis, salmonellosis, dysentery are characterized by increased body temperature, nausea and vomiting, frequent bowel movements up to 20 times a day, mucus and foam appear in the stool, feces acquire an unpleasant odor and a greenish color. In this case, you urgently need to see a doctor.
- Feces with mucus in a child may also indicate poisoning or toxic infection, which can occur due to eating low-quality food. In this case, the baby may begin to vomit, cold sweat may appear, blood may be present in the stool, the condition may worsen very rapidly, so you must immediately consult a doctor.
- Mucus in your child's stool may appear as a result of pathology in the development of the digestive system: volvulus, diverticulosis, or intussusception. These diseases are possible due to the structure and functioning of the child’s intestines. For example, with intussusception, when one part of the intestine invades another, which leads to its obstruction. The baby begins to feel severe pain in the abdomen when he eats, vomiting appears like a fountain, there is mucus in the stool, and the stool with mucus gradually turns into solid lumps of bloody discharge. This is a very dangerous condition for the child’s health, which threatens the development of sepsis, severe dehydration and death from painful shock; the child needs urgent help from a surgeon.
Breastfed baby
If a child is only breastfed, then most often clear mucus in his feces is a completely natural process and occurs for the following reasons:
- A baby’s intestines may react to their mother’s nutrition if she has eaten fatty, salty, sweet foods, or some fresh fruit has appeared in her diet;
- feces with mucus in a baby may indicate the development of an allergic disease;
- Such discharge may indicate lactase deficiency, in which the baby’s body does not have enough enzymes to ferment breast milk. In this case, using lactase preparations or eating baby food that does not contain lactose, if the baby is already receiving complementary foods, can help;
- the appearance of secretion can be triggered by celiac disease - a chronic disease of the small intestine associated with congenital (occurring in utero) protein (gluten) intolerance.
- The reason why a baby may have poop with mucus is the introduction of complementary foods, or the mother’s failure to follow the doctor’s recommendations for feeding the baby. For example, drinking insufficient amounts of fluid, long periods of time between meals, sudden introduction of new complementary foods, or consuming them in large quantities. In this case, it is necessary to adjust the diet.
Children under one year of age
One of the reasons for the appearance of secretion in feces at this age may be a common runny nose. The child cannot blow his nose on his own, so he swallows most of the sputum. As a result, the discharge passes through the baby’s entire digestive system and is excreted along with feces in the form of mucus.
The appearance of discharge in the stool is also possible during teething. In this case, there may also be a change in the consistency of the stool, and the baby may become capricious and restless. However, if this phenomenon is accompanied by high temperature, the appearance of blood in the discharge, or a change in its color, then it is necessary to see a doctor to clarify the diagnosis.
List of signs and symptoms that are alarming and require immediate medical attention
- Bloody diarrhea.
- The child refuses food and drinks.
- Constant diarrhea.
- Frequent vomiting.
- Signs of dehydration (dry mouth, fatigue, dizziness, infrequent urination - less than every six hours, bloody stools, temperature of 38˚Ϲ or higher).
- Abdominal pain that occurs frequently or is very severe.
- Behavioral changes, including loss of consciousness or decreased sensation.
Whenever you are concerned and feel the need to see a doctor or go to emergency care, it is your choice as a parent. Trust your instincts, they will tell you what to do. You can never be too careless.
If your baby is really sick, take extra care of him so that the child feels that everything is fine. For babies, when they have vomiting or diarrhea, it is a scary moment because children do not know what is happening to them.
When should you call a doctor?
Be sure to contact your pediatrician if your child has the following symptoms in addition to light-colored stool:
- Severe bloating.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Fever.
- Stomach ache.
- Yellow coloration of sclera and skin.
- Dark colored urine.
- Poor appetite and weight loss.
- Weakness, capricious behavior, sleep disturbance.
- Intense thirst.
A happy, cheerful, and most importantly healthy child is the key to parental peace of mind, so the occurrence of suspicious symptoms is always alarming and serves as a reason for a visit to the pediatrician. The appearance of clear mucus in a child’s stool, regardless of age and accompanied by additional symptoms, is no exception, because the well-coordinated functioning of the digestive organs is a guarantee of well-being and good health.
Diagnostics
One of the informative diagnostic methods for identifying the cause of intestinal disorders in children is coprogram. This analysis helps to establish the presence of dysfunctional disorders of the enzymatic system, analyze the quality of the pancreas, detect areas in which the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is impaired, and indicate the severity of the pathology.
The doctor also prescribes a stool test to identify dysbacteriosis. It is effective in determining the type of microbes that provoked digestive disorders. This helps to choose the right and effective treatment method. As a result of this analysis, it is possible to detect damage to the body by parasites such as staphylococcus, enterococcus, Klebsiella and Proteus.
The doctor necessarily prescribes a study, during which the sufficiency or deficiency of lactobacilli colonies in the intestines is determined. It takes a very long time to wait for results, up to a week and a half.
First aid for a child with loose stools
Loose stools in a one-year-old child should be treated immediately. When you have a bowel movement more than 4–6 times, fluid and nutrients leave the body, and there is a risk of dehydration. Therefore, first aid is to support the intestines and reduce dangerous consequences. You can give a special drug, Regidron, containing vitamins and mineral compounds. It restores the balance of microelements, electrolytes, improves condition and well-being.
Various age-appropriate drinks should be offered throughout the day:
- compote of sour berries or dried fruits;
- ;
- weak tea with sugar;
- raisin decoction.
Until the cause of diarrhea is determined, the baby should be switched to a light diet, eliminating milk, sweets, and fatty foods. If the baby is one month old, loose stools can be treated through the mother’s diet: it is necessary to analyze the foods that could provoke the disorder. To avoid dehydration, the baby is placed on the breast every hour or 1 teaspoon of boiled water is poured into the mouth.
Causes of diarrhea without fever in a child
The main factors that provoke stool disorder include:
- Eating disorder. Almost all parents, one way or another, deviate from healthy eating recommendations. The child’s body cannot digest a large amount of “wrong” food (a lot of salty, fried, etc.), as a result, intestinal function increases, and a condition such as diarrhea in a child occurs, which occurs without an increase in temperature.
- Infectious diseases. Viruses and harmful microorganisms often attack the baby’s body, and in this case, diarrhea in a child can last more than 3 days and rarely goes away without fever. The culprits of this condition are dysentery, salmonellosis, enterovirus, influenza, rubella, and intestinal infection.
- Intestinal dysbiosis. If the balance of beneficial and opportunistic flora in the intestines changes, dysbiosis develops - a condition whose symptoms are diarrhea, constipation, weight loss, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and allergies in children.
- Enzyme deficiency. Due to the functional immaturity of the child’s enzymatic system, the body does not always cope with digestion. As a result, diarrhea develops with the presence of particles of undigested food in the stool. Such problems are more common before one year of age, that is, among infants, due to lactase deficiency - the body’s inability to fully absorb lactose. In this case, diarrhea in a child 6 months and older will occur without fever in the form of foamy, copious stools immediately after finishing feeding.
- Diseases of non-infectious etiology. Diarrhea in this case often occurs in the summer as a result of the child overheating in the sun or heat stroke. In addition, stressful situations, allergies, and surgical pathologies in the abdominal cavity can become non-infectious factors.
- Reaction to medications. Each child tolerates medications individually. There are cases when children react to a medicine prescribed by a doctor with digestive disorders - diarrhea and vomiting, skin rashes without fever, which is a side effect of taking a specific medicine, for example, a child who is 4 months old. Most often, such an inadequate reaction of the body is caused by antibiotics.
- Food allergies. A hypersensitivity reaction to foods can also cause abdominal discomfort, itchy skin, diarrhea and vomiting. The temperature in this case may or may not be elevated.
Mucus in a child's stool - Possible diseases, treatment methods
Almost all mothers know that at an early age a child should pay attention to the quantity and quality of bowel movements.
Thus, you can somehow assess the baby’s health status, whether everything is fine with his digestion. Very often, the reason for parents' concern is mucus in the child's stool. The presence of mucus in the body plays an important role. With its help, food and feces are pushed through the intestines. If there is not enough mucus, the baby suffers from constipation or painful bowel movements. Also there should not be too much of it.
If you find an excessive amount of mucous impurities in the stool of children, you should consult a doctor. Perhaps the baby has an intestinal problem or a metabolic disorder.
Mucus in stool is considered to be whitish or yellowish jelly-like particles. When the intestinal glands work more intensely, excess mucus appears, which ends up in the stool.
Why is this happening?
Due to the influence of various negative factors on the baby’s body.
Non-dangerous causes of mucus in stool
- In children under 1 year. With a cold expressed by a runny nose, a one-year-old baby swallows the substance that appears, since he is not able to empty the sinuses himself. As a result, the stool contains excess mucus.
- In children under three months of age, mucus in the baby's stool is natural.
While the baby’s body is not accustomed to its existence, there is a period of adaptation; due to the lack of necessary enzymes, the digestive system is unstable. If the baby is cheerful, active, eats and sleeps well, but there is an admixture of a transparent or yellowish mass, there is no reason for concern. - After three months, children's diet changes and feeding begins. Loss of appetite, diarrhea and feces with mucus indicate that the baby’s stomach does not yet accept this product. This phenomenon goes away over time and does not require treatment.
- In the postoperative period, if a large part of the small intestine has been removed.
In childhood, for this reason, mucous diarrhea is observed for a fairly long period. - After taking colic medicine or herbal teas.
Causes of mucus that cause concern
1. Lactose deficiency (in infants under 1 year). Symptoms: the baby is not gaining weight, pieces of food, mucus in the stool, unnatural smell and color of stool. It is necessary to change the child's diet.
2. Inflammatory processes of the intestines (mucosal colitis). Symptoms: flatulence, appetite disorder, vomiting, nausea, stomach ache, stool disturbance. Feces mixed with blood and mucus, ribbon-shaped.
3. Infections in the intestines (rotavirus). Symptoms: weak loose stools, severe fever, weakness, vomiting, nausea, rumbling stomach. The stool contains light and watery mucus.
4. Presence of helminths . Symptoms: disturbance of the child’s appetite and sleep, tearfulness, decreased activity, abdominal pain, infrequent stool with mucus, blood, and sometimes with parasites.
5. Allergies . Symptoms: the appearance of a rash on the skin, peeling, inflammation of the digestive system, which is why there is mucus in the child’s stool.
6. Pathology of structure and functioning, intestinal obstruction . Symptoms: frequent vomiting, increased abdominal pain. Scanty stool, large amounts of mucus mixed with blood.
7. Toxic or food poisoning . Symptoms: excessive vomiting, abdominal pain, cold sweating, pallor, sometimes loss of consciousness, increased bowel movements, stools with excessive mucus mixed with blood, sometimes green feces.
8. Diverticulitis . Symptoms: bloating, flatulence, diarrhea, lower left abdominal pain.
If mucus is found in the stool of a 2-year-old child, signs such as flatulence, constipation or diarrhea are observed, and the stool contains pieces of undigested food, then this is probably one of the most common types of disease - dysbiosis.
This disease often affects children between one and three years of age. This may result in weight loss, slow growth, inactivity and poor appetite.
A pediatrician will be able to establish an accurate diagnosis only after appropriate tests, for example, a stool test - coprogram.
The easiest thing, of course, is to determine the causes of mucous stool in older children, what hurts them and where, they can tell themselves.
Parents should be more attentive to the condition of their child; failure to consult a doctor in a timely manner can lead to irreparable consequences.
What to do if mucous is found in a child’s stool?
If you notice frequent bowel movements, stool with white jelly-like particles, and the child’s condition is not stable, you should consult a doctor. In case of fever, vomiting, abdominal pain, or the presence of blood in the child’s stool in addition to mucus, you should immediately seek medical help.
This may be an infectious disease or a disease that requires urgent surgical intervention.
If you are feeling normal, but with an admixture of mucus, you need to monitor the quality of food:
- Do not give your child too spicy, salty or smoked foods.
- Not very healthy food for a child is food from eateries, various types of snacks, crackers, chips.
- At least for a while, you should give up chocolate, cocoa, carbonated and coffee drinks.
- It is necessary to drink large amounts of fluid.
To prevent intestinal diseases, it is useful to use drugs that improve intestinal function, carry out anthelmintic procedures in a timely manner, and it is also important to strengthen your child’s immune system.
Parents, creating the necessary conditions for the development and growth of the child with all responsibility, love and care, protect him from many health-related troubles.
Loading…
Source: https://GemoParazit.ru/raznoe/sliz-v-kale-u-grudnichka
First aid
While waiting for the doctor, parents can independently relieve the baby’s condition and prevent dehydration
It is important to know in what situation and how you can help your child:
with frequent, continuous loose stools and vomiting, you need to call an ambulance; before the ambulance arrives, you should give the child a solution of “Regidron”, “Gastrolit” or ordinary mineral water; Smecta, an antidiarrheal drug with absorbent properties, often gives a good effect; you need to drink carefully, offering 1 teaspoon of liquid every 5-10 minutes - otherwise the baby will vomit everything; if the child is so ill that he cannot drink from a spoon, you should use a syringe without a needle or a dispenser included with baby syrups; at temperatures above 38 °C it is important to give an antipyretic (ibuprofen or paracetamol); suppositories for diarrhea are ineffective, they will cause even more discomfort, and analgin is allowed from 12 years of age; Thoroughly washing the baby after each bowel movement will prevent skin irritation; if food poisoning is suspected, the child should be given Polysorb, Enterosgel or analogue absorbents; when the baby’s condition is serious, you should collect the baby’s things before the ambulance arrives - this will save time if hospitalization is required.
READ IN DETAIL: how to give Polysorb to children?
Diarrhea in acute intestinal infections
Diarrhea is the most common manifestation of acute intestinal infections such as dysentery and salmonellosis. The causative agents of dysentery are Shigella. Human infection occurs by consuming food contaminated with bacteria, contaminated water, or through the hands. Shigella secretes various pathogenicity factors (toxins). Abnormal bowel movements are a consequence of exposure to an exotoxin in the intestines. The disease occurs in an acute form. The large intestine is most often affected. The main symptoms are:
- heat;
- diarrhea;
- stomach ache;
- urge to go to the toilet.
In acute dysentery, stool can be up to 20-30 times a day. Mucus, blood and pus are found in the stool. This disease is dangerous due to possible complications (rectal prolapse, dehydration, bleeding, dysbacteriosis). Salmonellosis has similar symptoms. This disease develops when eating insufficiently thermally processed meat, eggs, dairy products, and salads.
Often the disease occurs within the walls of a medical institution. In this case, a nosocomial infection occurs. Salmonellosis is characterized by the following symptoms: headache, myalgia, high fever, nausea, vomiting, pain in the upper abdomen, diarrhea, bloating, rumbling. Diarrhea does not occur immediately. At first the stool is formed, but soon it quickly becomes watery. Feces have a fetid odor and a greenish color (stool like swamp mud).
Why does a lot of mucus appear in baby's stool?
Dysbiosis in infants can cause an increase in the amount of mucus in the stool.
The volume of mucus in a baby's stool may increase for various reasons:
- dysbacteriosis
- acute intestinal infections
- intussusception
- nutritional errors
- lactase deficiency
- allergies
- taking certain medications
Dysbacteriosis. At the stage of microflora formation, the child is most susceptible to various diseases. At this time, dysbiosis may develop - one of the main intestinal problems in infants. It occurs when opportunistic and pathogenic microorganisms begin to prevail over beneficial ones and cause disturbances in the child’s stool. Mild forms of the disease are characterized by the appearance of more mucus in the stool, flatulence and constipation.
Read: Symptoms of colon and rectal cancer: know so you don’t miss it!
More severe forms are characterized by diarrhea, mucous and blood inclusions in the stool. If the mucus in the baby's stool is red, this indicates an ulcer in the mucous membrane of the digestive tract. Acute intestinal infections. Often, an increase in mucus in a baby’s stool indicates the development of an infectious disease. The list of these diseases is quite wide:
- dysentery
- salmonellosis
- stomach flu
- toxic infections
- other diseases
These pathologies differ in that they can cause inflammation of the intestinal mucosa, as a result of which the amount of mucus in the stool increases. In order to distinguish an infectious disease from dysbacteriosis, it is necessary to undergo special tests.
Intestinal invaginitis. This disease is considered one of the most dangerous. If you suspect it, you must immediately call an ambulance. As a result of intestinal invaginitis, partial intestinal obstruction occurs. The disease has symptoms such as severe pain and uncontrollable vomiting. At the same time, the child’s feces become more liquid, have mucous and bloody inclusions, and after a day they completely lose their normal appearance and are a kind of mixture of lumps of mucus with streaks of blood.
Errors in nutrition. An incorrect diet is one of the possible reasons for changes in a baby’s stool. Insufficient fluid intake, irrational introduction of complementary foods and very long breaks between meals are the reasons why the volume of mucus in the stool may increase. In addition to an increase in the amount of mucus, the characteristics of the baby's stool also change.
Lactase deficiency. Some children have a congenital deficiency of a special enzyme necessary for the digestion of milk - lactase. As a result of its deficiency, fermentation processes begin in the intestines, the child suffers from pain, flatulence, diarrhea, and inclusions of lumps of milk and mucus appear in his stool.
Allergies. If a baby suffers from allergies, then the first manifestations of such a deviation are various skin lesions. If an allergic reaction affects the functioning of the intestinal mucosa, then the amount of mucus in the child’s stool increases.
Medications. Sometimes, an increase in the amount of mucus in a baby's stool does not mean that the child is sick. This phenomenon can be triggered by taking certain medications.
If the amount of mucus in the child’s stool increases, and there are other signs of the development of any pathologies, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Causes of diarrhea in children
The list of possible reasons is long. Diarrhea is caused by viruses or bacterial infection.
This condition can appear as a result of the life of a parasite, taking antibiotics, or improper nutrition of the child.
- viral infection. Rotavirus, norovirus, adenovirus and astrovirus cause diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. The child may have a fever of up to 38 degrees, chills;
- bacterial infection.
Bacterial food poisoning can cause diarrhea. Common bacteria that cause food poisoning are staphylococcus, salmonella, shigella, E. coli and campylobacter. If your baby has a bacterial infection, he or she will have severe diarrhea. Less common are abdominal cramps, bloody stools in the child, and fever. There may not be any vomiting. When your baby has symptoms of a bacterial infection, make an appointment with the doctor. He will conduct an examination and may recommend testing feces for flora; - ear infections. Sometimes an ear infection (viral or bacterial) can cause a bout of diarrhea, especially in children under 2 years of age. The baby may have recently caught a cold and is now too capricious. He will pull his ears or complain of ear pain. It may also have other symptoms: nausea, vomiting and poor appetite;
- parasites. Parasitic infections can also cause diarrhea. For example, giardiasis is caused by a microscopic parasite that lives in the intestines. If a child has this infection, he will often experience loose stools, bloating, gas, nausea and painful cramps. These types of infections spread easily among children, and treatment includes special therapy, so the baby must be shown to a doctor;
- diarrhea from antibiotics.
If your baby has diarrhea during or after a course of antibiotics, this is because the medicine kills good bacteria in the intestines along with infectious ones. Talk to your doctor about alternatives and means to restore gut flora, but do not stop giving your child any prescribed medications without consulting a specialist; - drinking large amounts of juices. Drinking large amounts of juice (especially fruit juice containing sorbitol and high levels of fructose) or large amounts of sweetened drinks can upset your baby's tummy and cause soft stools. Reducing the amount of juice should resolve the problem in a week or more. Pediatricians recommend giving your baby no more than one small glass (about 150 - 200 ml) of juice per day;
- food allergy.
When a child has a food allergy, it means that their body's immune system is reacting in this way to normal, harmless food proteins. A mild or more severe reaction occurs either immediately or after a couple of hours. Cow's milk is the most common food allergen. Other foods that cause allergies are peanuts, eggs, soy, tree nuts, wheat, shellfish and fish. Symptoms of food allergies include diarrhea, bloating, abdominal pain, and bloody stools. In severe cases, the allergy causes vomiting, hives, rash, swelling and difficulty breathing. If you think your child has a food allergy, talk to your pediatrician; - food intolerance.
Unlike food allergies, intolerances (sometimes called food sensitivities) are abnormal reactions that are not related to the immune system. One example is lactose intolerance. If your baby is lactose intolerant, it means that their body does not have enough lactase, the enzyme that digests lactose. Lactose is the sugar in cow's milk and milk products. When undigested lactose lingers in the intestines, it causes diarrhea, abdominal cramps, bloating and gas. Additionally, if your baby has a severe case of diarrhea, he or she may temporarily have trouble producing lactase, resulting in symptoms of lactose intolerance for a week or two; - poisoning.
Toddlers are adventurous and always want to try something new. This often leads them to try non-edible substances such as chemicals, plants or drugs. If your child swallows such an item, diarrhea and vomiting may occur. You need to urgently take your baby to the hospital or call an emergency room. Other symptoms of poisoning: breathing problems, loss of consciousness, painful spasms and lethargy; - functional diarrhea. When your baby poops several times a day and the stool is loose, foul-smelling, and contains undigested food or mucus, it may have a condition called functional diarrhea. There is no specific reason other than the possible introduction of new foods or another change in diet.
When to worry
Young mothers are wondering whether it is possible for a baby to replace the formula or continue breastfeeding in full the next time the color of the stool changes.
When white mucus appears in the baby’s stool, you need to sound the alarm, because such symptoms are considered a sign of pathology (atony, polyp, tumor). It is necessary to urgently call an ambulance when the baby becomes worse, he is restless, anxious, frequent regurgitation occurs, the consistency and color of the stool has changed.
In the menu of a nursing mother, new dishes should not be introduced in the first year. Fermented milk drinks should be included in the diet of new products if a dysbacteriosis diagnosis has been made.
Dangerous colors of stool:
- Pink. Indicates bleeding.
- Black or veined. Characterizes gastric bleeding.
- Transparent. Infections, inflammation, colds, hepatitis.
- White slime. It is possible to detect parasites or rotavirus infection.
- Cloudy green substance. Characterizes a bacterial infection.
The condition of the baby should be monitored by a doctor if the temperature has risen, blood is found in the stool, frequent urination or bowel movements, weight loss is observed, and the stool is liquid and changeable color. If there are impurities, such as mucus, biomaterials are donated. Symptoms of disease or bleeding of the upper stomach are characterized by black stool. It can only change when taking medications (iron-containing, activated carbon).
We recommend reading: Why does a baby spit up after breastfeeding?
Features of accompanying symptoms
As a rule, loose stools in children have a number of specific symptoms, which it is recommended to tell your doctor about:
- color of the biomaterial. Diarrhea with admixtures of scarlet blood informs about the development of enterocolitis and dysentery disorders. The burgundy color appears against the background of ulcerative formations, which is rare for a baby;
- production of a significant amount of mucus. This factor indicates the presence of rotavirus infection. The presence of a green tint in the flakes indicates the likely enlargement of salmonella structures and colic infections in the young body;
- significant temperature. Heat and mucus during bowel movements are the first signs of intestinal infections. This type of disorder is characterized by vomiting, severe nausea, and lethargy. At the time of defecation, an unpleasant smell of excrement is felt, the child complains of colic in the abdominal cavity. Sometimes a sharp headache is possible;
- redness of the anus + unpleasant itching are characteristic of hemorrhoids. Pathology requires prompt medical care. Correct treatment is prescribed by a qualified proctologist;
- viral etiology. Symptoms are cough, nasal congestion, sore throat. A respiratory infection is characterized by enlarged cervical and submandibular lymph nodes.
Red streaks in excrement sometimes occur as a result of eating tomatoes or beets. Under such circumstances, mother should not worry. Carefully examine the remains of undigested food so as not to confuse them with blood impurities. After the child's next meal, the structure of the feces will acquire a normal color.
When to rush to the doctor?
Often, parents find white mucus in the children's potty, which differs sharply in color from the rest of the feces. As a rule, this is a sign of intolerance to cow's milk or the presence of parasites in the body. The most dangerous is mucus with blood in a child’s stool, because it can be caused by hemorrhoids, ulcerative colitis, various intestinal infections and even intestinal tumors. The presence of a large amount of mucous impurities in feces can indicate not only a dangerous infection in the body or severe allergies, but also many serious gastrointestinal diseases.
Therefore, if you observe a similar picture for more than two days, and even more so if the baby has a fever, vomiting or nausea, you should hurry up and visit your pediatrician to determine the reasons for such changes. As a rule, pediatricians write out a referral for stool, urine and blood tests, and then, based on the data obtained, prescribe antibacterial and antimicrobial drugs to the patient, as well as antibiotics and absorbents. If indicated, doctors also prescribe anthelmintic drugs. In addition, it is recommended to adhere to a strict diet.
Dangerous symptoms
There is a group of symptoms that cannot be ignored. A person always needs competent medical care. Treatment is usually prescribed after the necessary diagnostic procedures have been carried out.
You should immediately call a doctor at home or go to a clinic if the following symptoms are present:
- significant increase in body temperature;
- severe pain and spasms in the intestinal area;
- nausea and vomiting;
- defecation within 10 times of liquid stool;
- headache;
- bloating;
- green color of stool and foul odor.
If you have several of the above symptoms, it is important not to ignore the condition, but to begin examining the body
Medications
A visit to a specialist is advisable in any case to quickly eliminate the causes of diarrhea and prevent dehydration.
The doctor may prescribe solutions containing glucose and salts; one of these products is “Regidron”.
This remedy will help restore fluid balance in the body, which is an extremely important aspect for diarrhea. The drug is provided in the form of a powder in small sachets; one portion of Regidron should be diluted in 1 liter of water and given to the child after each bowel movement.
The cost of "Regidron" averages 20 - 25 rubles per sachet.
Therapy can be supplemented with various sorbents, among which the drug “Smecta” can be distinguished.
This remedy effectively eliminates problems in the child’s gastrointestinal tract. The drug has an adsorbent effect, so it can eliminate the cause of diarrhea. “Smecta” quickly removes toxins, this drug has no contraindications, it can be used even by newborn babies. The product is available in powder form, which, according to the instructions, is diluted with water.
The average cost of 10 sachets of the drug is 170 - 200 rubles.
Prebiotics, such as Linex, are mandatory medications for the treatment of diarrhea.
The powder contains biologically active substances that help normalize microflora.
The drug is used with caution in case of individual intolerance to any component; the use of the powder is contraindicated for those children who are hypersensitive to dairy products. To improve the functioning of the digestive system, a specialist may prescribe a remedy such as “Creon 10000“
To improve the functioning of the digestive system, a specialist may prescribe a remedy such as Creon 10000.
The drug consists of elements that are determined by analogues of natural enzymes. It actively affects the digestive system and is widely used as an aid in the treatment of diarrhea. This product is available in capsules and is used as prescribed by a specialist. Contraindications include acute and chronic pancreatitis. An analogue of the drug is Mezim.
The average price of this product is 300 - 320 rubles.
Features of diarrhea with mucus
Diarrhea (diarrhea) is a pathological condition characterized by frequent and loose stools. Not everyone knows what normal stool should be like. With normal functioning of the stomach and intestines, the stool should be formed, soft in consistency, with a specific but not fetid odor, light brown or dark brown in color, without blood and a large amount of mucus.
The normal frequency of bowel movements is from 3 times a day to 3 times a week. On average, a person has bowel movements 1-2 times a day. With diarrhea (diarrhea), the stool becomes liquid or pasty. In some diseases, bowel movements occur several dozen times a day. This can lead to significant fluid loss and dehydration.
Mucus in the stool is the result of irritation of the intestinal mucosa. The cause may be mechanical stress, various chemicals, bacteria and their toxins (enterotoxin). At the same time, mucus production increases sharply. It can be seen in feces with the naked eye. This condition develops in adults and children.
Depending on the etiological factor, the following forms of diarrhea are distinguished:
- infectious;
- nutritional;
- dyspeptic (enzymatic);
- toxic;
- medicinal;
- psychogenic.
Infectious diarrhea is the most acute. It is the main symptom of acute intestinal infections. The dyspeptic type is characteristic of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Diarrhea can bother such patients for years, occurring periodically and leading to gradual depletion of the body.
Normal level of mucus in infant stool
Mucus in a baby's stool is normal.
The lining of the gastrointestinal tract is made up of a variety of cell types that perform different functions. Mucosal cells produce mucus, a substance that protects the walls of the intestines and stomach from influences of various natures.
Due to the fact that the infant's gastrointestinal tract is not yet adapted to fully digest food, it produces a significantly larger amount of mucus than the intestines of children over one year of age. A year is the approximate age of the child by which his intestines get used to extrauterine existence and mucus production returns to normal.
The first stool that a baby passes after birth is called meconium. It is a thick, sterile substance of black color and viscous consistency. After a few days, the newborn's stool becomes mushy, golden in color, and has a sour odor. The amount of mucous inclusions in a baby's stool is moderate and constant.
If a baby's stool turns greenish and contains more mucus than usual, then this is not a cause for concern. It is important to monitor how the child behaves. If he is calm and has a good appetite, then there is no reason to worry. An increase in the amount of mucus in the stool is also considered normal if this occurs over a short period of time.
From the moment of birth until about three months, the baby's intestines are gradually populated by microorganisms. By the end of this period, and sometimes a little earlier, the child acquires the natural microflora of his intestines. During this period, mucus is also present in the baby's stool, and its amount varies depending on the state of the digestive system.
Read: Methods for diagnosing and treating intestinal disorders
The intestinal microflora consists of both beneficial bacteria and opportunistic ones. The former are involved in the digestion process, the production of vitamins and amino acids, and the formation of the immune system. The latter occupy a neutral position and normally do neither harm nor benefit if the balance between beneficial and opportunistic intestinal microflora is in balance. When this balance is disturbed, digestive problems and sometimes intestinal infections occur.
Sometimes it happens that the process of formation of intestinal microflora in a child is somewhat delayed. This usually happens to children who are bottle-fed. The body of children who are breastfed copes much faster with the formation of microflora. The type of feeding also affects the presence of mucus in the baby’s stool: with artificial feeding there is slightly less mucus than with breastfeeding.
If complementary foods are introduced in a timely manner - before the age of six months, the baby's stool changes in color and consistency, and the amount of mucus in it increases. If the child develops normally and feels well, then this large amount of mucus is not something dangerous.
As the baby's body grows, its intestines get used to digesting food and other conditions of extrauterine existence, which causes an increase in the amount of mucus in its stool.
Diet for diarrhea
Instead of feeding your child three large meals a day, divide the food into six to eight small meals throughout the day.
What can a child with diarrhea eat?
The following products should be included in the diet:
- bananas;
- White rice;
- toast;
- baked fish, chicken, beef or turkey;
- pasta;
- corn flakes and oats;
- vegetables such as carrots, mushrooms, asparagus, peeled zucchini, beets, green beans and zucchini;
- baked potato;
- boiled eggs;
- pancakes and waffles made from white refined flour.
Let your child eat dairy products, such as yogurt and cheese. However, from time to time they can make diarrhea worse. If this happens, do not give these foods for several days.
Foods to Avoid
Just knowing what to feed your child when he has diarrhea is not enough. You should also be aware of the foods you need to avoid.
Certain foods increase diarrhea symptoms and should be avoided:
- fried and fatty foods;
- processed meat products such as sausages and sausages;
- donuts;
- cakes;
- Apple juice;
- carbonated drinks with caffeine;
- vegetables and fruits that lead to flatulence and gas (broccoli, peppers, peas, beans, prunes, corn and green leafy vegetables);
- concentrated fruit juices.
If you see blood, mucus in your baby's stool, shiny, greasy stool, or very unpleasant odors, this indicates a serious problem such as cystic fibrosis or the presence of helminths. In general, when you notice that your baby's bowel movements are abnormal for several days, consult your doctor.
Ambulance at home
The most dangerous consequence of diarrhea is the loss of fluid and electrolytes, which can lead to heart failure. The younger the child, the faster dehydration develops. Therefore, children need to be given water at any intensity of diarrhea.
The best option is ready-made solutions:
- Hydrolyte;
- Oksolan;
- Regidron.
It is advisable to always have these products in your first aid kit. Homemade version: dissolve 1 tsp in 0.5 liters of water. salt, 2 tbsp. l. sugar, ½ tsp. baking soda, pre-slaked with boiling water.
Tea with 1 tsp is beneficial. sugar and dried fruit compote. Decoctions of raisins, carrots, and rice are used.
The child is fed fractionally. 50–100 ml for children under 2 years of age, 100–200 ml for adults after each bowel movement or vomiting. In case of intense diarrhea, drink 1–2 tsp. every 5–10 minutes.
Temperature does not pose a danger to the child; on the contrary, it reduces the effect of germs and toxins. It is knocked down only when the readings are above 38.1 °C and the child’s condition worsens due to fever.
It is permissible to give medications without a doctor:
- antipyretic suppositories: Efferalgan, Panadol, Tsefekon D (convenient for vomiting);
- Panadol or Ibuprofen in syrup form;
- sorbents: Smectu, Polyphepan.
Causes of pathology
If a child has loose stools with mucus, then the causes of the disease should be immediately dealt with. The main factors influencing the nature of bowel movements include:
- dysbacteriosis;
- disruption of the natural intestinal microflora;
- overeating, fasting;
- incorrect introduction of complementary foods;
- non-compliance with the correct diet of a mother whose baby eats breast milk;
- intolerance to certain categories of food products, components of artificial mixtures;
- intestinal, viral infection;
- the presence of worms;
- colds;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- eruption of baby teeth;
- stressful situation.
The appearance of diarrhea with mucus in a small child is normal. The child’s body has not yet formed; the organs of the digestive system are not able to quickly and efficiently digest and assimilate incoming solid foods. Stomach dysfunction manifests itself in the form of loose stools without fever. This unpleasant symptom goes away after a maximum of 12 hours without the use of medications.
If a child has frequent, profuse diarrhea with mucus, the causes of the pathology are most often the consumption of low-quality products, failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, as well as the entry of pathogenic bacteria into the child’s body - E. coli, salmonella. Diarrhea can be caused by dysbiosis, which is characterized by the destruction of the gastrointestinal microflora due to the use of antibiotics as the main method of treating various diseases.
In a one-year-old child or infant who is breastfed, diarrhea with mucus in the stool is observed when the mother consumes prohibited foods: too fatty, spicy, fried foods, processed foods, fast food, as well as alcoholic beverages. Wrong choice of formula and early introduction of complementary foods are the causes of loose stools.
Mucous diarrhea in children can be caused by chronic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, previous colds, which contributed to a decrease in immunity. The occurrence of diarrhea with blood indicates the formation of hemorrhoids, cracks in the rectum, pathogenic viral infections, as well as the possible presence of cancerous tumors of a benign or malignant nature. External factors that can trigger diarrhea are stressful situations, changes in habitual lifestyle, and climatic conditions.
Causes of stool with mucus
Separation of mucus from a child’s bottom often occurs for natural reasons. It was mentioned above about taking pharmacological drugs to combat colic. Mucus in the feces also appears when using products with digestive enzymes, as well as antibiotics in syrups and tablets, enterosorbents (Smecta, Enterosgel, Polysorb).
This is also observed in the following situations:
- eruption of baby or permanent teeth, causing loss of appetite and poor digestion of food. In babies, teething is often accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication: high fever, pain, swelling of the gums. In such cases, mucus is explained by a temporary deterioration in general health;
- feeding errors. The mucus content in feces almost always increases with the introduction of new, unusual complementary foods - vegetable, fruit or meat puree. Its appearance is also explained by the high fat content of breast milk.
All these causes are reversible and disappear after the provoking factor is eliminated. But in any case, parents should show the child to the pediatrician. After all, the hidden course of diseases leads to the gradual development of complications.
In newborns
A newborn baby almost always poops clear mucus. Its mass fraction in feces can reach 10%, and as the baby grows older, it gradually decreases. But there is a possibility that the newborn suffers from lactase deficiency. This is the name of a pathological deficiency in the child’s body of an enzyme that breaks down milk sugar. Somewhat less frequently, children are diagnosed with celiac disease, a genetically determined disease associated with a deficiency of enzymes that metabolize the gluten peptide.
From year
The main cause of mucus in the stool of a one-year-old child is dysbacteriosis. The predominance of populations of Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella, Clostridia, Enterobacteria, Proteus over Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli is developing. In turn, dysbiosis can be caused by bacterial or viral intestinal infections. In a one-year-old child, abundant mucus in the stool is often provoked by exacerbations of any chronic pathologies, allergies.
Problem for older children
If a child farts with the release of thick mucus, and the stool contains an abnormal amount of it, then it is necessary to rule out food poisoning. Similar defecation disorders also accompany the course of numerous diseases:
- ARVI and influenza;
- candidiasis;
- parasitic infections;
- autoimmune intestinal inflammation;
- spastic colitis;
- irritable bowel syndrome;
- pancreatitis;
- intestinal diverticulosis;
- proctitis, proctosigmoiditis.
The appearance of stool with mucus and an unpleasant odor in a child may also mean the development of an inflammatory process of bacterial or viral etiology in the gastrointestinal tract. Salmonellosis and brucellosis are especially dangerous.