A newborn baby, and especially a premature one, is very dependent on the ambient temperature, which is associated with the still emerging thermoregulation system. In premature babies, this dependence is also due to other physiological characteristics: a thin layer of subcutaneous fat, a slower metabolism. In this regard, in the first months after birth, under uncomfortable environmental conditions or improper wrapping (excessive or insufficient), the child may be subjected to both overheating and hypothermia.
A temperature of 36 in a baby, especially with low birth weight, is normal.
Causes of low temperature
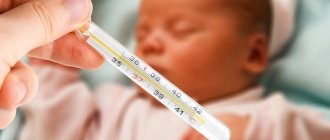
A complex temperature indicator is one of the important indicators of the condition of the whole organism. This biomarker makes it possible to timely identify the development of dangerous diseases and determine all current processes in the body. The norm for the human body is a thermometer reading of 36.6°C. If the indicator falls below this mark, this indicates little heat production or increased heat transfer from the body.
Risk factors and symptoms of low temperature in a child:
- Chronic pathologies. Cold extremities may indicate problems with the respiratory system, dysfunction of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands. With excessive sweating, there is a risk of developing anemia.
- Hypothermia. May occur after a long walk in the fresh air or swimming. A temperature of 35°C in a newborn baby in the morning is not a sign of pathology. This is due to the unformed system of natural thermoregulation; over time it normalizes.
- Psychological trauma, severe stress. Low body temperature in a child may be accompanied by weakness and dizziness.
- Congenital hypothermia. The condition does not require treatment if the child feels and develops normally.
- Consequence of vaccination. If a child has a temperature of 35.5°C after an illness or vaccination, the condition will normalize within a few days.
- Viral diseases. Risk factors to pay attention to: lethargy, drowsiness, headache. If a child has a low temperature for 3-5 days, parents should consult a doctor.
- Disturbances in the injury of internal organs. Temperatures up to 35°C are a symptom of diseases such as diabetes, pneumonia, anemia, and malignant tumors. Often accompanied by poor health and pain.
The reasons for a decrease in body temperature in schoolchildren may be:
- overwork;
- physical and mental stress;
- lack of fresh air;
- insomnia;
- stressful situations.
If the cause is not identified and eliminated in a timely manner, this can lead to the development of neuroses, gastritis, myopia and scoliosis.
Change in temperature in a baby:
- A temperature of 35.5°C in an infant born prematurely is normal. This condition indicates low mobility and less development, so it goes away as you grow older.
- Viral disease. Sometimes there are no characteristic signs. The condition is accompanied by rapid fatigue and increased drowsiness.
- Reaction to the DPT vaccine. More often, the body's immune response is characterized by an increase in temperature, so many parents give their children antipyretic drugs immediately after vaccination. Experts recommend stopping taking medications and measuring your temperature every 2-3 hours to avoid life-threatening complications.
What body temperature is considered low?
Temperature is a special physical indicator, the value of which fully reflects the general condition of the body and indicates various biochemical processes occurring in it.
Although in different parts of the body the temperature level may differ by several degrees, due to the thermoregulatory system its complex distribution occurs.
Contrary to popular belief that the normal temperature for a child is 36.6°C, in practice this value is wider - on average from 36°C to 37°C. During falling asleep, a decrease occurs more often, and the peak value is detected in the late afternoon. At the same time, daily changes can vary dramatically, even in the same patient.
Any deviation from the norm can lead to a febrile state or hypothermia - a phenomenon characterized by low temperature.
Also in medical practice, there is a definition of a lower indicator - 34°C or less. In this case, the most dangerous complications arise not only for the muscular-tissue system, but also irreversible consequences for the mental development of the child.
Types of Hypothermia
The indicator of normal body temperature is not absolute and largely depends on several factors.
These include:
- age;
- Times of Day;
- individual characteristics.
In children, normal temperature can fluctuate between +36.5…+37.2°C. Hypothermia is a sign that the balance between heat production and heat loss is imbalanced. There are two main types of condition:
- +35…36.5°С.
- Up to 34.9°C. Divided into 3 degrees of severity: mild - +32.2...+35°C, moderate - +27...+32.1°C and severe - up to +26.9°C. The limit of 32°C is recognized as critical and requires auxiliary methods of warming the body.
Physiological changes in the body with stages of hypothermia
All types have characteristic symptoms, by which one can clearly determine the line between safe and severe for health:
- Mild hypothermia manifests itself in the form of trembling, mild convulsions, increased metabolism and vasoconstriction. This reaction of the body allows you to combat large heat loss, so the most effective ways to restore the level of heat are warming measures.
- Moderate hypothermia is characterized by low mobility, increased drowsiness, and heart rhythm disturbances. In this condition, the patient's blood glucose levels increase. The pathological condition is relieved by local methods: warm drinks, dry clothes. A mandatory examination for moderate hypothermia is an ECG.
- Severe degree refers to danger to the life and health of the patient. If a child has a temperature of 34°C or lower, there may be a disruption in the functioning of the main body systems. First of all, mental activity slows down and metabolic processes are suspended, the functioning of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems is disrupted. The critical level is 27°C. At this temperature, without emergency assistance and active warming of the body, a coma or death of the child may occur.
What else could be causing the low temperature?
There are several risk factors that can cause an imbalance of heat exchange in the body. If a child’s temperature of 35°C lasts longer than 3 days or there is a sharp decrease, immediate contact with a specialist is required to determine the underlying cause of the condition.
Risk factors and prerequisites:
- Physical. Excessive heat loss is caused by a functional failure in the process of thermoregulation. Most often occurs as a result of dilation of blood vessels due to low blood pressure. This category includes endocrine diseases that cause increased sweating. Hyperhidrosis is the cause of natural thermoregulation.
- Chemical. This category includes: weak immunity, intoxication and low hemoglobin levels. Risk factors also include excessive physical and emotional stress.
- Behavioral. The group includes all conditions that are characterized by a negative reaction of the body to the environment. Often the reasons may be the body's response to a vaccine or long-term use of medications.
Causes of low temperature in children under 1 year of age:
- Cold air. A weak immune system reacts to fluctuations in the environment, which may result in mild hypothermia.
- Infections. Pathogenic bacteria can often cause dysfunction in the pulmonary and genitourinary systems. They contribute to the development of infections in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid. At risk are newborn babies with a weak immune system, premature babies, and those born to mothers who have not undergone prenatal examination.
- Vitamin deficiency and mineral deficiency. Symptoms are more severe in infants. Mild signs of hypothermia appear in children in the first months of life due to hunger and thirst. Malnutrition leads to a slowdown in metabolic processes. If timely feeding does not relieve symptoms, the condition may indicate a lack of iodine, iron and other minerals necessary for the body. Characteristic signs appear with heart defects, disturbances in the development of the maxillofacial apparatus, or problems with the gastrointestinal tract and digestive system.
- Neuralgia. Thermoregulation disorders occur as a result of improper functioning of receptors in nerve fibers, skin or hypothalamus. Injuries and tumors in the brain can lead to a pathological condition, so prolonged mild to moderate hypothermia requires specialist examination.
- Metabolic diseases. Disturbances in the functioning of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands and pituitary gland negatively affect the child’s health. Lack of timely treatment slows down metabolism and slows growth.
A temperature of 35.5°C in a child under 1 year of age is considered normal. In children older than 12 months, additional research is required to establish the causes. Depending on the results of the examination, a course of treatment may be prescribed in an outpatient or clinical setting.
The reasons why a child over 5-7 years of age may also experience a sharp decrease in body temperature depend on a number of social reasons. Being in preschool institutions and studying at school often causes stress in a child’s body. The main reason for this is a change in the usual lifestyle and overwork.
Hypothermia in children 7-17 years old occurs due to:
- heavy workload (lessons, extra classes, clubs);
- active physical activity;
- mental overstrain;
- lack of necessary time for rest;
- oxygen deficiency and limited time for walking in the fresh air;
- lack of sleep;
- nervous and emotional stress, experiences.
Causes
There are a number of typical causes of the problem. Here are the three main ones:
- The children's thermoregulation system is imperfect and at first may malfunction in both directions. In infants, especially premature babies, under the age of 1 or 2 months (however, this can happen not only in a month-old baby, but also at 3 and 4 months), a short-term decrease in temperature for no apparent reason or other symptoms is not such a rare phenomenon and completely normal. Such hypothermia lasts no more than a couple of hours and disappears without a trace.
- The second common reason for the characteristic drop in body temperature below normal in children of different ages is hypothermia. It can be caused by cold indoors, inappropriate clothing while walking, exposure to rain in cool weather, or swimming in a pond for too long. Even slight hypothermia is not dangerous for a child, but it increases the risk of a cold.
- The temperature can drop to about 36⁰ and even lower due to excessive fatigue - both with mental overstrain and in case of physical fatigue. Another similar reason is malnutrition, either one-time or long-term in the form of diets with too few calories and nutrients necessary for the child’s body.
However, everything is not limited to these three reasons.
As for diseases, the condition when the temperature has dropped is accompanied by poisoning and other intestinal disorders, viral and bacterial diseases. Moreover, we can talk about both the beginning of the disease and, conversely, the period of recovery.
A figure of 36⁰ and below 36 degrees on a thermometer can also indicate more serious health problems - congenital pathologies, diseases of the upper respiratory tract, adrenal glands, thyroid gland and other components of the body’s hormonal system.
The sensitive child's body often reacts with an excessive drop in temperature when taking antipyretics. This happens especially often if the fever is difficult to control at first, and therefore the baby is given two different medications or two servings of one in a short period of time.
And finally, we must not forget about such a banal reason as a malfunction of the thermometer. This is especially common in safe, but not as accurate as mercury-based, electronic devices. In such a case, it is worth having both of these options at home. The temperature should be measured at least half an hour to an hour after the child wakes up, when he has moved at least a little and is in a calm emotional state. Data obtained immediately after sleep, eating, or heavy crying will be the least reliable.
What to do when your child has a low temperature
At the first signs of hypothermia, the child's condition should be determined. In case of a mild degree, it is necessary to immediately perform several mandatory measures:
- undress the child, remove his wet clothes;
- take a warm bath, prepare warm, dry pajamas;
- the room should be above +25°C, so turn on heating devices if necessary;
- Children over 6 months must be given warm tea and wrapped in a blanket;
- Infants should be kept in a neutral thermal environment to reduce metabolic rate - use a warm envelope, heating pads, blanket, etc.
In case of moderate or severe hypothermia, immediate contact with an ambulance or the pediatrician on duty is required. First of all, it is necessary to measure the pulse and monitor the respiratory system. Sometimes the patient may require resuscitation, so it is important to immediately report the child's condition to a healthcare professional.
If a child has a temperature of 35.5°C, what to do and in what ways heat exchange can be restored should only be determined by the attending physician. Depending on the underlying cause, a physiotherapeutic course of recovery or complex treatment of pathological conditions may be prescribed.
Depending on the reasons that caused the decrease in thermoregulation of the body, the actions of parents should be as follows:
- If the reaction was caused by long-term use of medications during the treatment of colds, ARVI and other infectious diseases, it is necessary to introduce fruits and vegetables rich in vitamins into the child’s diet. An additional course of vitamin therapy may be prescribed.
- Viral diseases require immediate treatment. The attending physician should be informed of all symptoms that accompany the condition.
- If you suspect a pathology of internal organs, you should immediately consult a doctor. In this situation, self-medication is contraindicated.
- If the cause of hypothermia is fatigue, it is necessary to reduce the load. The child should choose the right diet, which must contain vitamins B, E, iron, iodine and other organic substances.
- In case of hypothermia, it is necessary to ensure that the feet are warmed. For infants up to one year old, you can prepare a warm bath. If the cause is a stressful situation or emotional tension, you should change your daily routine and reduce your load.
In cases where the condition lasts more than 5 days, it is necessary to contact a medical institution for a full examination. The main tests are: blood test, electrocardiogram, ultrasound of internal organs. When making an accurate diagnosis, treatment is required in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations.
Prevention of low body temperature in children
The main cause of mild to moderate hypothermia is a weakened immune system. To reduce the risk of developing a pathological condition, it is necessary to strengthen the body’s resistance to negative environmental factors from the first day of a child’s life.
The natural ability to resist viruses and other pathogenic organisms can be ensured by a complex of preventive and therapeutic measures, including:
- Hardening. The procedures should be carried out from the first months of life. It is necessary to harden a child under 5 years of age at least once a week, schoolchildren - every 2-3 days.
- Physical education and sports. Classes should be gentle, but regular. Excessive physical activity should be avoided. A special exercise therapy course is recommended for preschoolers.
- Proper nutrition. The optimal feeding schedule for children is at least 5 times a day. It is advisable to organize meals in such a way that children receive nutrients along with food. In the winter season, the amount of vitamins needs to be increased.
- Daily regime. Maintaining a daily routine is important for the health of infants and preschool children. Planning of all activities must correspond to the age schedule and condition of the child.
Parents should be aware that hypothermia can be an individual feature of the child’s body. In some cases, 1-3° below the generally accepted standard does not cause physical or psychological problems for the child. If the child is in good health and there are no hidden or obvious signs of severe pathologies, it is possible that this condition is normal for him.
However, it should be borne in mind that the main cause of low body temperature can only be determined after a comprehensive examination. At the first symptoms of the phenomenon, you should report them to your doctor. Only a medical professional can determine an accurate diagnosis. This will help avoid the development of serious and life-threatening diseases.
What do we have to do?
Now let's figure out what to do. As always, the main indicator for parents should remain the condition of the child. If he is active, not capricious, eats approximately the same amounts as usual, and generally does not display any atypical behavioral traits, then there is no reason to worry. Temperature fluctuations are normal even for an adult, and even more so for a child with his sensitive body and imperfect thermoregulation system.
Infant hypothermia requires only close monitoring from parents. If it lasts for a few hours or less and is not accompanied by other obvious painful symptoms, then no further measures need to be taken.
If the child is hypothermic, it is necessary to quickly warm him up - put him in a warm shower, give him hot tea, dry him, and dress him warmly. And, of course, monitor his condition for several days after this, so that in case of a cold he can quickly take action.
A similar reaction - providing the child with warmth - is also necessary in the event of an excessive drop in temperature while taking antipyretics. As a rule, no additional measures are required.
The pathological cause of low body temperature will be indicated by lethargy, apathy and drowsiness of the child. It is also possible, on the contrary, the appearance of increased irritability and bad mood. In addition, there is often a severe deterioration or complete disappearance of appetite and headaches.
In all these cases, consultation with a doctor is necessary. Before his arrival, children should be provided with peace, plenty of fluids and a comfortable temperature in the room. In case of chills, it is advisable to wrap the child additionally warmly; you can put a heating pad on him or lie down next to him to warm him with your own warmth.
If a lower temperature is observed during recovery, this means that the child should not be overtired either. But it is necessary to restore the body weakened after illness. This means that regular feeding of not too heavy food and, of course, plenty of fluids will be required.