Even in the maternity hospital, blood tests are taken from each newborn to make sure that everything is in order with the baby’s health. But after three months, the baby will again face a similar test - it is necessary to go through the same procedure again, albeit in a somewhat simplified version. What is it for? What information does the doctor need? Today I’ll tell you what tests my son and I took in the first year of life. Also, perhaps our readers will find some purely practical information on how to prepare for baby tests useful.
What are preventive vaccinations
Preventive vaccination is a method of developing immunity in a person against certain diseases that are difficult to treat. The vaccine consists of weakened microbes that cause the corresponding disease, against which the body produces antibodies.
Vaccination against hepatitis B.
Hepatitis B is a serious viral disease that is transmitted through blood or saliva and leads to liver damage. If the new mother has a positive hepatitis status, then the child should be vaccinated within the first 12 hours of life.
Contraindications for vaccination are prematurity, when the baby weighs less than 2 kilograms and a low Apgar score. The vaccine is injected intramuscularly into the anterior/lateral surface of the thigh. Revaccination is required at the ages of 1 and 6 months.
Vaccination against tuberculosis
Better known to us as BCG. It is also placed in the maternity hospital from the 3rd to the 7th day of the baby’s life. The danger of tuberculosis is that it is transmitted by airborne droplets without direct contact with a sick person. According to the World Health Organization, about 2 million people die from tuberculosis every year around the world. The infection affects the lungs and bones and leads to disability. An important point is that immunity against tuberculosis is not transmitted from mother to child, so the baby’s body must develop it itself. The injection is given intradermally in the left shoulder. Many mothers are concerned about the wound that forms after the BCG vaccination. But there is no need to panic. The main thing is that when the baby reaches one year, the injection site is completely healed. Babies weighing up to 2 kilograms are also not given this vaccine. Other contraindications are: the presence of people in the family with immunodeficiency, damage to the central nervous system, infectious processes in the body. Immunity from tuberculosis remains in the body of a child of 6-7 years old, therefore, if the Mantoux reaction is negative, revaccination is carried out at 7 and 14 years old.
Taking blood from the umbilical cord from a newborn
The very first blood test in the maternity hospital, when blood is taken from the umbilical cord, is done immediately after the birth of the baby - a test for bilirubin and determination of the baby's blood type and Rh factor .
Determining the Rh factor in an infant is important because if the child inherited it from the father and not from the mother, then he may develop hemolytic disease, a blood conflict.
For example, if the baby has a positive Rh factor and the mother has a negative Rh factor, this means that their blood has slightly different red blood cells. A positive Rh factor is characterized by blood whose erythrocytes contain the D antigen; a negative Rh factor is blood that does not contain the antigen.
Thus a conflict of blood . The mother’s immune system begins to perceive the baby’s blood as a “hostile element”; it “sends” antibodies that penetrate the child’s blood and “kill” its red blood cells (as they consider them hostile because they differ in composition). As a result, the level of hemoglobin in the baby’s blood drops and bilirubin increases.
It is the analysis for bilirubin (if its elevated level is detected) that indicates that the baby has anemia and jaundice (little hemoglobin and a lot of bilirubin).
Possible conditions after vaccination
In addition to the fact that vaccination causes stress for the child, other conditions may also occur:
- the child is capricious, crying;
- the child's temperature rises;
- redness and thickening of the skin at the injection site appears;
- there are allergic reactions, rash;
- the child eats worse and sleeps more restlessly.
All these manifestations are considered a normal reaction of the body. Only if the temperature is very high should the child be given an antipyretic drug. An increase in temperature is a signal that the baby’s immune system has activated and is actively producing antibodies against the virus, and an increased body temperature is an antimicrobial factor, since many microbes are not able to survive at high temperatures.
Is it possible to refuse vaccination of a child?
Of course yes. Responsibility for the health of the child lies entirely on the shoulders of the parents. If you have made an informed decision to refuse, you must write a corresponding statement in two copies. The first copy must be included in the exchange card, the second must be given to the doctors in the postpartum department. It is also necessary to verbally notify the employees of the medical institution about the refusal to vaccinate.
If parents have decided to refuse vaccination, then the expectant mother should mentally prepare for the possibility of psychological pressure and agitation from medical personnel in favor of preventive vaccinations. This pressure is due not so much to good intentions as to the “vaccination plan” in force in all public medical institutions.
Most modern doctors still agree that it is necessary to vaccinate newborns against hepatitis B and tuberculosis. The risks of complications after vaccination are much lower than the possible consequences after infection with these diseases.
If parents are not ardent opponents of vaccinations, but do not want to expose the fragile body of a newborn baby to danger, vaccination can be delayed. In this case, the local pediatrician must draw up an individual vaccination schedule in accordance with the wishes of the parents.
How to take blood from infants
Children's blood is taken from the ring finger. This is done in the morning. In some laboratories, instead of sharp metal “feathers”, special devices are provided specifically for infants, with the help of which blood is drawn without any pain at all. You can search for such a device via the Internet. It is rarely available in pharmacies. This is in case you go to get tested in a city laboratory, and not in a private clinic, where the equipment is usually modern. Surprisingly, when we arrived at the laboratory, not a single one of the babies that their mothers carried out of the blood collection room cried. As they say, what technology has come to! Tests can be taken without pain. Only older toddlers (three or four years old) were shouting in the queue, who already understood that they were not brought here to feed them ice cream. And the assurances that “it doesn’t hurt at all” had no effect on them. In general, donating blood with a baby, as it turned out, is even easier than with an older child. Mothers of babies are more worried than the little patients themselves.
Certificate of preventive vaccinations
A certificate of preventive vaccinations is a document containing information about vaccinations given, indicating the date of vaccination and the patient’s reaction to them. Since the first vaccinations for a newborn are given in the maternity hospital, this document should also be issued there.
But in practice this rule is often not observed. In this case, you should remind the maternity hospital staff of their duties, or wait and ask for a certificate from the local pediatrician at the clinic.
The certificate will be required when a child enrolls in kindergarten, school, and also when traveling abroad.
Scheduled tests for babies at 3 months
At two months, Igor and I, as expected, came to the clinic. While the doctor examined her son and admired how well “we” were eating and growing, the nurse was writing directions for tests. "For what? - I was surprised, “everything is fine with him.” It turns out that this is necessary. 3 months is a critical age. It is during this period that there is a risk of developing anemia. In addition, at this age, the toddler will have to be vaccinated - DTP and against polio. Before doing this, you need to make sure that the child has no pathologies. After all, vaccinations are given only to completely healthy children. You need to find out the level of hemoglobin in the blood, as well as the content of leukocytes, red blood cells and other components. For this, a general blood test is taken.
In addition, it is necessary to submit your urine for analysis. The analysis is also general. It will give information about whether the child’s kidneys and genitourinary system are in order. Any deviations will be noticeable by lowered or lowered readings. The color of the liquid, its transparency, pH level, as well as the amount of protein, sugar, and the content of leukocytes and red blood cells are important.
So, the baby, provided that the tests taken from him in the maternity hospital correspond to the norm, and also if the pediatrician has no “complaints” about his health, takes 2 tests:
- general blood analysis;
- and general urinalysis.
Referrals for these tests are usually issued at the second visit to the pediatrician, when the child is 2 months old. By three months, the test results should already be in your hands, so there is no need to delay going to the laboratory.
conclusions
So what vaccinations are given to newborns in the maternity hospital in 2016-2017? Vaccination against hepatitis B and vaccination against tuberculosis.
Despite the fact that pediatricians and neonatologists encourage parents to vaccinate their children without fail, the decision still remains with mom and dad. When making this most important decision for a child's health, one should take into account not only the pros and cons of preventive vaccinations, but also the fact that the child is a member of society. This means that we are responsible not only for our children, but also for the people around us. Of course, if you live in a cave, in the taiga, in the desert, in the crater of a volcano, on a desert island, then most likely the question of vaccinations is not on your mind. But if your place of residence involves contact with people, then you should still think about vaccination.
Screening. Genetic analysis
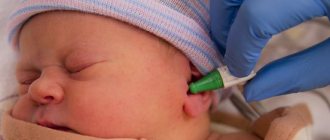
Newborn screening is the process of taking blood from an infant. Blood is taken from the heel, because finding a vein in newborns is difficult, and it is impossible to get the required amount of blood from the toe.
A genetic blood test can reveal whether a child has such congenital dangerous diseases as hypothyroidism and phenylketonuria , as well as almost 50 other rare diseases.
Early diagnosis of the two diseases mentioned above allows treatment to begin sooner, which in turn can play an important role in the child’s future life. Hypothyroidism and phenylketonuria are severe congenital diseases that are caused by metabolic disorders in the baby’s body, which lead to serious consequences - mental and physical retardation, lifelong disability.
A blood test for hypothyroidism in a newborn done in the maternity hospital shows the amount of TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) in the blood.
Hypothyroidism is associated with dysfunction of the thyroid gland. This greatly affects the development of the child’s nervous system and his brain. Hypothyroidism can cause neurological disorders and mental retardation in a child.
A test for phenylketonuria is done to detect phenylalanine; its elevated level in the blood indicates that the baby has phenylketonuria.
Phenylketonuria is a hereditary disease; we wrote about it in detail in our article here. A gene mutation causes a deficiency of a special enzyme in the body, which causes disturbances in amino acid metabolism. Pheninalanine is not converted into tyrosine in the body of a person with phenylketonuria. Because of this, pheninalanine intoxication occurs, the activity of the central nervous system is disrupted, the proper functioning of other organs is disrupted, and the human body is gradually destroyed.
Blood sampling from the heel for genetic analysis is done on the 3rd-5th day of a newborn’s life, if he was born at term and the pregnancy proceeded normally. And on the 14th day, if the baby is premature or there is reason to assume the worst, for example, when mom and dad are carriers of a mutated gene that causes severe hereditary diseases.
Tests of the newborn taken in the maternity hospital are interpreted in special laboratories. If the result is negative, that is, the baby is healthy, then neither the maternity hospital, nor the clinic, nor the parents are notified of anything. If the result is positive, the laboratory calls the clinic to which the baby is assigned after discharge from the maternity hospital so that mother and baby come to the clinic for the test again. Therefore, if you did not receive a call, it means that everything is fine with your child .
You should wait about a month for the results of such tests.
First tests of newborns
Since at the birth of a child, signs of phenylketonuria and hypothyroidism are not always expressed in developed countries, including Russia. In order to detect these diseases early, all newborns without exception undergo a blood test (this test, which is mandatory for everyone, is called screening). Early detected hypothyroidism and phenylketonuria are easier to treat than other congenital diseases.
To identify and prevent hypothyroidism, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is determined in the blood of newborns, the amount of which increases sharply in congenital hypothyroidism, as well as phenylalanine, which is found in large quantities in the blood during phenylketonuria. On the 3-5th day of life in a full-term baby and on the 7-14th day of life in a premature baby, several drops of blood are taken from the heel and applied to a special filter paper - a form, which is subsequently sent to the regional screening laboratory. The child has undergone a screening test, the doctor will definitely note it in the newborn’s exchange card.
If the test results are negative, the information is not communicated either to the clinic or to the parents. If a positive result is detected, it is immediately reported by telephone to the clinic where the child is being observed. In this regard, it is important for parents to correctly and clearly indicate the address where the baby will live in the near future after discharge from the maternity hospital. Parents should know that if the baby was born outside the maternity hospital (in a regular hospital or at home), then a screening test for congenital diseases was not performed on him, so to have it done, they must go to the clinic at their place of residence or to a medical genetic consultation.
What are hypothyroidism and phenylketonuria?
In congenital hypothyroidism, there is insufficient function of the thyroid gland. As you know, thyroid hormones are absolutely necessary for the development of the central nervous system in the prenatal period and in the first years of a baby’s life. With a lack of these hormones, the process of brain maturation is disrupted, which causes mental retardation and the appearance of neurological disorders.
A disease such as phenylketonuria also leads to the development of profound mental retardation. This is a congenital, inherited metabolic disorder. Its cause is a lack of an enzyme (phenylalanine hydroxylase), necessary for the normal metabolism of amino acids that make up the body's proteins. In the absence of this enzyme, the amino acid phenylalanine is not converted into another amino acid, tyrosine. As a result, the concentration of phenylalanine in the blood increases sharply, which has a toxic effect on the central nervous system.
The disease manifests itself in a gradual disruption of the central nervous system, in particular the brain, which leads to mental retardation. Since the screening test falls into the category of indicative tests, having received information about positive results, the pediatrician at the clinic prescribes a more in-depth examination for a child with suspected hypothyroidism, namely: consultation with an endocrinologist, additional testing of all thyroid hormones, ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland , x-ray examination.
Early diagnosis of the disease is very important, since the beginning of treatment (prescription of drugs containing thyroid hormones) before 4-6 weeks of the baby’s life ensures further full physical and mental development in most children. In addition to the timely administration of medications, it is very important that a baby with hypothyroidism is fed breast milk from the first days of life, since it contains the mother’s thyroid hormones in an amount that can provide the child’s minimum daily need for them. If phenylketonuria is suspected, special studies are also carried out for babies after discharge from the hospital, including more accurate methods for determining the amount of phenylalanine (an amino acid that accumulates in large quantities in the child’s body) and its derivatives not only in the blood, but also in the urine.
For a baby with phenylketonuria, it is considered optimal to make an early diagnosis and prescribe a special diet no later than the 21st day of life. Early treatment (namely, a diet low in phenylalanine) can prevent mental retardation. In addition to diet treatment, molecular genetic therapy for such diseases is currently being developed. However, the main treatment that children with phenylketonuria receive today is diet. To feed such children, special milk formulas have been developed in which milk protein is replaced with protein with a low phenylalanine content. If you follow a diet, excess acid does not accumulate in the body, which has a detrimental effect on the developing brain, which means that the baby grows healthy. Thus, phenylketonuria and congenital hypothyroidism can be considered one of the few congenital diseases that humanity can cope with.
For children at risk
If the health condition of the newborn is of concern, the necessary tests will be carried out in the maternity hospital, including a general blood or urine test, a biochemical blood test, determination of antibodies to infections and many others. If a baby was born from a mother with Rh-negative blood, then in the first minutes of life the doctor will definitely determine the child’s blood group and Rh factor, regardless of his state of health. If the baby’s blood is Rh positive (the Rh factor is inherited from the father), then a small amount of blood will be taken from the umbilical cord to confirm in the laboratory that it belongs to it and determine the level of bilirubin, a substance that is released when red blood cells are destroyed in the event of a Rh conflict. This must be done in order not to miss the onset of the development of hemolytic disease of the newborn, which is characterized by increased destruction (hemolysis) of erythrocytes (red blood cells) of the fetus and newborn due to the incompatibility of its blood with the mother’s blood.
During pregnancy, fetal red blood cells, which have the Rh factor antigen on their outer shell (Rh-positive), entering the body of the mother (who does not have this antigen), are capable of causing the formation of antibodies in her - proteins that destroy these unfamiliar antigens. Under certain conditions (maternal illness, bad habits, pathological pregnancy, previous abortions, etc.), antibodies can penetrate the placenta and cause the death of red blood cells in the fetus, subsequently leading to the development of anemia and jaundice (a similar conflict can arise in case of incompatibility maternal and fetal blood based on blood group antigens).
From destroyed red blood cells, bilirubin enters the bloodstream, which is toxic to tissues and, in particular, to the baby’s nervous system. If the liver does not have time to neutralize free (indirect) bilirubin (i.e., bind it to glucuronic acid), it accumulates in the bloodstream and begins to penetrate the tissues, turning the baby’s skin yellow. This is especially dangerous for the baby’s brain cells, since free bilirubin can penetrate nerve cells and cause disruption of their activity and even death, leading to the development of so-called bilirubin encephalopathy (brain damage).
To prevent the development of such complications, the newborn's blood bilirubin level will be determined and its increase will be monitored for several days. However, the appearance of jaundice in a newborn may be due to other reasons: hypoxia (lack of oxygen), birth injuries, viral or bacterial infections. If jaundice appears in a premature baby or in a child born with signs of intrauterine growth retardation (small for its gestational age), then a determination of bilirubin in the blood will be prescribed, even if the skin color is only slightly jaundiced. And all this is because the level of bilirubin in the blood of such newborns can be much higher than the intensity of skin coloring would suggest. Newborns at risk for the development of hemolytic disease in the maternity hospital must also be prescribed a general blood test, since increased breakdown of red blood cells is accompanied by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and the number of red blood cells, and therefore the occurrence of anemia. A general blood test will be prescribed for newborns born prematurely, with signs of intrauterine growth retardation, as well as for children with twins, triplets, i.e. born as a result of multiple pregnancy.
What will a general blood test tell you?
Blood is the most sensitive indicator of all changes occurring in the body. If the baby is unwell, a general blood test will help determine whether there is any inflammatory process in the body. In case of infectious diseases in the blood of a newborn baby, the level of leukocytes sharply increases, immature forms of cells appear in large numbers, and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) also becomes high. Such changes in the blood can appear much earlier than the symptoms of the disease, which is very important in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases in newborns. It should be noted that the blood of a healthy newborn has some characteristics. It has a significantly higher number of red blood cells, white blood cells, and hemoglobin level (180-240 g/l). At birth, the baby has two types of hemoglobin. The first is fetal (80%), which has a greater ability to bind and transfer oxygen to organs and tissues, which is very important during intrauterine development. The second - adult - HbA (20%), necessary to obtain oxygen through the lungs; Almost all the baby’s red blood cells will contain it by the age of 4-5 months.
Why is blood taken from the heel?
Don’t worry about having to take drops of blood from your baby’s heel for analysis. This is just a more convenient way, since a newborn’s fingers are still very small to carry out this procedure.
For sick kids
If the newborn is unwell, in the maternity hospital he may be prescribed a urine test, which will not only help assess the condition and function of the organs of the genitourinary system, but will also allow one to judge the presence of certain disorders of the organs and systems (liver disease, metabolic disorders, etc.). However, this is not a frequent study in the maternity hospital, since collecting urine from a newborn may present some difficulties due to its physiological characteristics (transient oliguria - excretion of a very small amount of urine in the first 3 days of life). Therefore, in seriously ill newborns, urine collection for testing is often performed using a urinary catheter. So, we have seen that there are cases when only early diagnosis of the disease helps to preserve the baby’s health in the future. If tests carried out in the maternity hospital reveal any problems, the newborn will be prescribed additional examination and, possibly, treatment in a specialized hospital.
Urinalysis in newborns
A urine test in newborns is often prescribed simultaneously with a clinical blood test to assess the general condition of the body and the urinary system in particular.
In the first week of life, a newborn's urine is clear, but later it turns yellow. A feature of urine analysis in newborns is the physiological appearance of protein, especially in premature babies.
Often parents of a newborn child do not know how to collect urine for analysis. The easiest way to do this is to buy a special sterile urinal for infants at the pharmacy. There are urinals for boys, girls and universal ones that are suitable for children of both sexes.
If it is not possible to use a special urine bag, a regular plastic bag can help. It is washed with soap and placed under the child. Naturally, some of the urine will get past the bag, so you need to put a diaper under the baby.
Before collecting urine for analysis, it is necessary to wash the newborn’s genitals with clean boiled water (necessarily at room temperature).
Other blood tests taken from children
1. A biochemical analysis of the newborn’s blood is examined to obtain a detailed picture of the condition of the child’s internal organs. It is prescribed for symptoms similar to rickets and frequent abdominal pain. Such an analysis is recommended if liver and digestive diseases are suspected. The analysis is taken from a vein, so for infants up to 3-4 months it is taken from a vein in the head, leg or forearm. It is not possible to find a vein in the baby’s elbow. Biochemical analysis shows detailed parameters of the child’s blood, which are not included in the standard blood test. Such as bilirubin, protein, glucose and others.
2. A blood test for bilirubin in newborns is collected at birth from the baby’s umbilical cord. It is carried out in order to determine whether the baby has jaundice. Its increased content in the body gives a yellow color to the child’s body. The color of urine and feces depends on the content of this substance. At birth, bilirubin levels in the baby's blood are very high. A healthy person cannot have such indicators. However, for infants, 60 micromol/liter is considered normal. After a few days, the amount of bilirubin can reach up to 200 µmol/liter, which also should not be a reason for panic. After some time, the indicators decrease. The child’s body begins to produce enzymes that reduce the amount of bilirubin in the body. To track the dynamics of these changes, blood is taken from the baby within a few minutes after birth.
3. Newborn screening is carried out to identify rare genetic diseases in the early stages. If the disease is detected before symptoms appear, then it will be much easier to alleviate the child’s condition, and in some cases, even completely prevent the development of the disease. Newborn heel samples are collected 1-2 days after birth. The blood sample is dried and sent to the laboratory. This analysis takes a long time to prepare, but it makes it possible to conduct research on 51 dangerous diseases. Due to the fact that a genetic analysis of a newborn is carried out in the maternity hospital, it is possible to take action even before the disease manifests itself in full force. Typically, most children are not at risk for these diseases, but 100 out of 140,000 children are at risk for these diseases. In many countries, such an analysis is a mandatory procedure in the maternity hospital.