Causes of pathology
There are many factors for the development of fistula. Education itself is not an independent disease. The fistulous tract is more of a symptom of other dental pathologies.
In the photo, periodontitis at the apex of the root of the chewing tooth in the form of darkening
The main reasons for the formation of a fistula are:
- ratified milk teeth;
- chronic periodontitis;
- sinusitis;
- complications of treatment of pulpitis and periodontitis;
- damage to bone tissue;
- infection of the problem area as a result of mechanical trauma;
- severe form of periodontitis;
- weakening of the immunological status during a change in occlusion;
- excessive consumption of sweets;
- poor quality oral care;
- general hypothermia of the body;
- infectious diseases;
- poor quality root canal filling.
The video in this article explains in more detail why fistulous tracts occur in the periodontium in children.
Symptoms
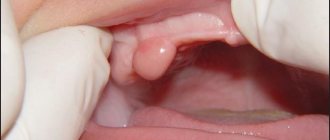
The main symptom of the disease is the appearance of a fistulous tract, which visually looks like a tubercle or a small abscess. It can be located on the outer or inner side of the gum. Through it, the purulent contents come out.
Other signs:
- general weakness;
- poor appetite or lack thereof;
- increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels;
- pathological mobility of the affected tooth;
- discomfort while eating and when performing daily hygiene procedures;
- swelling and redness of the gums;
- bad breath;
- disappearance of pain after the pus comes out.
Symptoms of a child's fistula on the gum
The appearance of a neoplasm largely depends on the diseases that caused it. But when the infectious focus lasts for a long time and reaches a large size, general symptoms of the pathology appear.
The typical clinical picture is:
- Painful sensations . They observe not only when touching the fistulous tract, but also when touching the tooth, if it was the cause of the pathology.
- Discharge of purulent exudate . The surrounding gums during this period are already quite hyperemic and swollen. There may be loose teeth and bad breath. This picture most often appears during the formation of chronic granulating periodontitis in the primary dentition.
- Difficulty breathing . It is observed during a long course of the disease. Purulent exudate accumulates, the inflammatory process intensifies, which leads to blockage of the nasal passage. The child complains that it is difficult for him to breathe, both at rest and during physical activity.
- Spread of inflammation . As the disease progresses, swelling is observed in the mucous membrane of the cheek, then it moves to the orbit and eyelids. Typically, the inflammatory process spreads with a significant decrease in immunity. This can lead to osteomyelitis of the jaw. As the pathological focus progresses, the child’s body temperature begins to rise and the lymph nodes enlarge. The swelling spreads to the lips, neck, and facial asymmetry appears.
In older age, the inflammatory process spreads not only to the maxillary part of the nasopharynx, but also affects other air sinuses.
A 6-year-old child has a fistula in the gum of the upper jaw in the area of the chewing teeth.
The general picture of the disease is increasing, there is a sharp swelling of the soft tissues of the face, pain along the innervation of the trigeminal nerve. Palpation in the area of the canine fossa causes pain.
Attention!!! An incorrectly erupted tooth can cause a fistula tract. In this case, there is a risk of wound infection and the formation of a cystic formation. Therefore, it is worth clearly monitoring how teeth appear and at the slightest suspicion, be sure to contact the clinic so that the doctor can rule out this complication.
A fistula on the gum is very easy to detect with the naked eye. It looks like a tubercle that rises above the level of normal gums and differs in color and structure.
Its localization is mainly in the area of the root tips, or just below their projection. In rare cases, a fistulous tract is observed under the tongue; this manifestation can occur when the chewing teeth in the lower jaw are affected.
Often there are no symptoms of the disease. But under certain conditions, severe pain occurs both independently and while chewing food.
Symptoms and possible complications
A fistula characterized by bloody, purulent discharge is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pain if the fistula on the child’s gum is touched by food or the touch of a hand;
- looseness of the tooth near which the tubercle is located;
- bad breath;
- Sometimes it is possible to increase body temperature;
- feeling of gum swelling.
Failure to treat the symptoms of the pathology can provoke the development of the following complications:
- chronic inflammatory process of the tonsils when purulent masses come into contact with them;
- inflammatory process of the gastrointestinal tract;
- destruction of soft tissues, development of sinusitis;
- flux formation.
If pathology occurs, the baby should be immediately shown to a doctor. The specialist will determine the severity of the inflammatory process, refute or confirm the presence of a cyst or wen, and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Professional treatment of fistula
A doctor can explain how to treat a child’s fistula on the gum only after a thorough examination. Therapeutic measures can be conservative and surgical. But the therapeutic effect is primarily aimed at preserving the problematic tooth.
Conservative treatment of the fistula tract will consist of the following:
- removal of the old filling;
- root canal filling;
- treatment of teeth with medications;
- root canal expansion;
- opening the apical opening of the roots;
- placement of medications in the root canal;
- placing a temporary filling.
In a normal course, medications should stop the inflammatory process. The temporary filling is replaced with permanent material after several sessions. Usually it takes about 3 visits to the doctor.
During this period, additional treatment of the tooth is carried out, physiotherapy and rinsing with antiseptics are used. If a purulent process forms on a baby tooth, then it must be removed. This procedure is necessary to prevent damage to the permanent tooth germ in the future.
In some cases, when the inflammatory process has spread greatly and is manifested by severe general symptoms, a course of antibacterial therapy is necessary. Before using them, be sure to study the instructions and exclude contraindications.
For this purpose, drugs are used in the form of tablets or solutions for intramuscular administration. Antibiotics can stop the inflammatory process and rid the body of pathogenic bacterial microflora in a short time.
All medications should be prescribed only by a doctor. Their choice will depend largely on the causes of the fistula. Usually, preference is given to Gentomycin or Lincomycin for a course of up to 10 days. Administration of drugs is sufficient once a day.
In addition to these drugs, the following can also be used:
- Amoxiclav;
- Trichopolum;
- Doxycycline;
- Amoxicillin;
- Flemoxin.
In treatment with antibiotics and antimicrobial agents, an important point is compliance with the course of treatment and the absence of contraindications.
Laser exposure is a modern and effective method of treating fistula
If a fistula occurs on the gum of a child, treatment can be carried out using a laser.
This procedure has a number of advantages compared to other methods of exposure, namely:
- high accuracy of treatment;
- low morbidity;
- painlessness;
- maintaining absolute sterility;
- short rehabilitation period and rapid tissue regeneration process;
- stimulation of metabolic processes and improvement of local blood circulation.
To influence the fistula tract, doctors often prescribe antiseptic rinses. Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Betadine are excellent for this. Various ointments and gels with anti-inflammatory and regenerating effects are also recommended.
These products include Asepta, Metrogyl Denta and Solcoseryl. The price of drugs does not depend on their effect. Before use, you should familiarize yourself with the composition of the medicines.
Possible reasons
A fistula on the gum near a tooth looks like an inflamed canal of soft tissue of the oral mucosa, breaking out from a purulent inflammatory sac.
Excessively accumulated purulent masses come out through it, mixing with saliva, and can be swallowed by the baby, which provokes intestinal inflammation. The causes of pathology are:
- Periodontitis. Pathology develops due to the lack or untimely treatment of caries. Periodontitis is characterized by a change in the color of soft tissue to bright red. The inflammatory process affects healthy cells, gradually growing in size. External factors, such as hypothermia, infectious diseases, nervous system disorders, lead to the formation of a fistula;
- Osteomyelitis. When bone tissue is affected by infection, a tumor appears on the oral mucosa and rapidly grows upward. This process contributes to the formation of a fistula;
- Cyst. A fistula on the gums of a 1-year-old child is quite common due to the eruption of baby teeth. The occurrence of a cyst is also possible due to the anatomical structure of the jaw, untimely treatment of the oral cavity, untreated teeth;
- Sinusitis. The development of the disease in the maxillary zone can also be complicated by the formation of a fistula;
- Traumatic lesions. With mechanical impact on the gum tissue (fall, eating hard food, damage from a toy), this pathological process is also possible.
If the baby complains of severe pain, microbial damage to the pulp (pulpitis) can be identified. We wrote about it here:
Pulpitis in a child: photos, common causes, symptoms, complications, treatment
This process is accompanied by suppuration of the root system of the bone tissues of the oral cavity. Pathogenic microflora, formed as a result of damage to the mucous membrane by dangerous bacteria, leads to general intoxication of the body.
The accumulation of pus in the area where the teeth meet the soft tissue spills out, finding a weak spot in the gum. In this case, an abscess first forms, after some time it bursts. To prevent a pimple from rupturing, if it forms, you should consult a doctor.
An infection can be caused by improper treatment in a dental clinic. If the canals of the teeth are not cleaned well enough, after applying filling material to them, bacteria continue to multiply under the bone tissue.
Traditional methods of influencing a child's fistulous tract on the gum
Pathological formation must be treated only in traditional ways. But folk remedies can be used as an auxiliary therapy. They are great for eliminating pain and relieving inflammation.
The following remedies are most effective:
- An infusion of three flowers: chamomile, calendula and sage. This product can be used to rinse every three hours.
- Natural propolis. To use, you need to take a piece of propolis the size of a small pea, chew it on the healthy side of the jaw, 10-15 minutes in the morning and evening, for 5 days.
- Onions and mountain mummy tablets. To prepare, you need to take one large onion, chop it finely and add 10 tbsp. spoons of black mumiyo tablets. All this must be poured with 1 tablespoon of olive oil and mixed thoroughly. The mixture is laid out on gauze and applied to the fistula tract. The exposure is 5 minutes, two to three times a day.
- Aloe leaf, garlic and kalanchoe. All three components should be passed through a meat grinder, mixed vigorously, placed with new items or gauze and applied to the inflamed area for 10 minutes every day.
Possible complications and prevention
Most often, fistulas accompany the chronic form of periodontitis. In the early stages of disease development, it is very difficult to identify pathology. Even during the development of periodontitis, a fistula may not cause much trouble.
If the necessary treatment is not provided, the inflammatory process spreads, further affecting the bone tissue of the alveolar process, causing the formation of periostitis and osteomyelitis. All this is fraught with the death of the permanent tooth germ, as well as the development of septic shock.
To avoid such problems, simple but effective preventive measures should be taken:
- visiting the dentist twice a year;
- performing proper oral hygiene;
- timely treatment of oral diseases;
- maintaining proper nutrition and eating patterns;
- compliance with all dentist recommendations.
When a fistula is diagnosed in a child on the gum, it is worth understanding that full treatment at home is impossible. First of all, this pathology requires professional help.
Delaying contact with the dentist can result in quite serious complications. It is also worth understanding that the fistula itself is only a symptom of some more complex disease, which often requires the slow intervention of a doctor.