Lymph nodes are a natural barrier to infection entering the body. However, they cannot always protect against various diseases. If you notice inflammation of the lymph nodes in a child’s neck, this may be the first sign of the presence of certain diseases. However, do not panic, because nothing fatal happened. The doctor will tell you what to do in this case, and you should make an appointment with him as soon as an inflamed lymph node in the neck is discovered.
The reasons for this phenomenon can vary greatly; only by identifying them can we begin treatment. The symptoms may be identical, so the task of establishing the correct diagnosis is quite difficult.
What are lymph nodes?
Lymph nodes are elements of the lymphatic system that transport lymph, which is involved in metabolism and serves as a protective filter for cells and tissues from various infections. The fact is that in healthy lymph nodes protective cells are formed - lymphocytes, which protect the body from the invasion of pathogenic microorganisms and foreign substances. Inflamed lymph nodes are no longer able to fully perform their functions and the body becomes open to viruses and bacteria.
Lymph nodes in the neck
There are several groups of lymph nodes in the neck: posterior cervical, retropharyngeal, mental, parotid, occipital, anterior cervical, etc. Their main functions include:
- Protection of the head and organs located on the neck from tumors.
- Fight against foreign cells and substances.
- Protection against infectious diseases.
- Elimination of pathogenic bacteria that have entered the body in one way or another.
In a healthy state, the lymph nodes are not visible.
Why does the child have enlarged lymph nodes in the neck?
Lymph nodes are strongly connected to the immune system, so if they are even slightly enlarged, this indicates that not everything is in order with the body. So, common causes of enlarged lymph nodes in a child include:
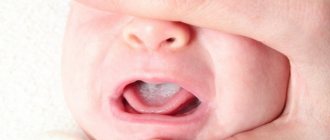
- Teething in infants. The fact is that the lymph nodes begin to work harder during this period and therefore increase in size. But don’t worry or panic; over time, they will shrink on their own and return to their usual size.
- Presence of boils or abscesses on the neck. According to doctors, inflammatory processes on the skin contribute to the enlargement of lymph nodes.
- Pathogenic bacteria in the oral cavity (including in dental diseases). In this case, the retropharyngeal lymph nodes become inflamed.
- Colds (flu, acute respiratory infections, ARVI). There is an enlargement of the lymph nodes in the occipital part. Signs of lymphadenitis usually go away on their own within a few weeks.
- Inflammation of the throat and respiratory organs. In this case, the increase occurs in the back of the neck or on the side.
- Infectious diseases of the facial skin. In this case, the nodes under the jaw most often become inflamed.
- Felinosis. This pathology is often found in owners of furry pets - dogs and cats. The causative agent of the disease is the bacterium Bartonella, which penetrates into the bloodstream through existing scratches on the skin. In this case, the wound does not heal for a long time, simultaneously causing enlargement of the lymph nodes. Most often, the pathology resolves itself.
- Mononucleosis and other viral infections. In this case, the supraclavicular lymph nodes become inflamed. The pathology requires urgent medical attention.
If the child’s lymph nodes are enlarged from the moment of birth and do not cause pain, there is no need to worry. This symptom goes away on its own within 2 years.
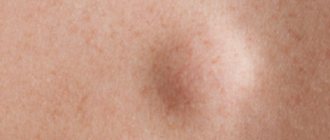
Symptoms of enlarged lymph nodes
Enlarged lymph nodes, even if painless, are easy to detect at a glance - they will become even more obvious during a tactile examination. The size of the growth up to 15 mm, if the tubercle was found by chance, during palpation and was not accompanied by complaints and anxiety of the child, is not considered a reason to consult a doctor.
The situation can be controlled at home, without taking any therapeutic measures.
If the onset of visible symptoms is associated with discomfort or pain - the child has difficulty turning or bending his head, there is an increase in temperature, or the area of the bulge is filled with redness, calling emergency services is the only reasonable measure and should not be delayed.
If the manifestations are extremely painful, independent palpation cannot be performed. If this is possible, then the first thing you need to pay attention to is the structure of the inflammation.
A pliable, soft formation is characteristic of a normal inflammatory process not associated with the growth of a malignant tumor or tuberculosis. The harder the designated lump, the more alarming the sign is considered.
Drug treatment
For inflammation of the lymph nodes, it is recommended to take the following medications for 2 weeks:
- Antibiotics (Ceftriaxone, Ampicillin, Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin, etc.). They are used only if there is some kind of infection in the body.
- Means for strengthening the immune system (Arbidol, Interferon, Immunal, ginseng tincture, etc.). They enhance the therapeutic effect of the main drug used for treatment, and also speed up the healing process.
- Antihistamines (Cetrin, Diazolin, Suprastin, etc.). They are used to reduce the risk of allergies.
- Antifungal agents (Clotrimazole, Ketoconazole, etc.). They are recommended in the rarest cases, when the cause of the inflammatory process is a fungal disease.
- Vitamin complexes. Necessary for maintaining the body and strengthening the immune system.
It is not recommended to use medications without a doctor’s permission, as the child may have side effects or worsen the disease.
Types of lymphadenitis
It can become inflamed:
- one lymph node ( local lymphadenitis
); - group of lymph nodes ( regional lymphadenitis
); - all lymph nodes at the same time.
Also distinguished:
nonspecific and specific lymphadenitis.
Nonspecific lymphadenitis
develops when exposed to pathogens that are dangerous only under certain conditions:
- streptococci;
- coli;
- staphylococci;
- protea;
- Klebsiels.
With the inflammatory process involving more dangerous microorganisms or viruses (tuberculosis, HIV, syphilis), specific lymphadenitis develops.
Under certain conditions, lymphadenitis can also be a primary disease, when the penetration of infection and the development of inflammation occurs directly in the lymph nodes, bypassing the internal organs and blood vessels.
It happens:
- in case of wounds, scratches;
- in severe cases of diaper or allergic dermatitis;
- with eczematous skin lesions with the addition of purulent complications;
- with other types of violation of the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes.
In childhood, lymph nodes often become inflamed due to cat scratches or boils.
Also in childhood, there are cases when the cause of enlargement and inflammation of the lymph nodes is malignant formations.
At the same time, the lymph nodes have the function of a “biological filter” and do not allow cancer cells to actively spread throughout the body.
Traditional methods of treatment
Treatment with folk remedies is effective with minor inflammation of the lymph nodes and the absence of complications. So, the following recipes are most effective:
- Oats with milk - a handful of oat grains are poured with a liter of milk and boiled over low heat for 40 minutes. The product should be drunk in small portions (50-100 ml) 3 times a day before meals. Course of treatment: 7 days.
- Rosehip decoction - 2 tbsp. l. Rose hips are poured with a glass of boiling water, cooled and given to children half a glass 2 times a day. The product is indicated to strengthen the immune system. Course of therapy: until complete recovery.
- Peppermint decoction - 1 tbsp. l. dried mint is poured into a glass of boiling water, cooled, then filtered and given to the baby to drink 2 times a day (50 ml each). The product helps well with inflammation. Course of treatment: 2 weeks.
If a child has an allergic reaction to one or another drug, it is necessary to temporarily stop therapy and consult a doctor.
Determining the cause
You should immediately visit a doctor if your neck is swollen; there are many reasons that provoke the formation of tumors of different nature. Only a qualified specialist can identify the provocateur of the disease. In certain cases, a preliminary diagnosis is confirmed only by the results of clinical studies.
Swelling is formed under the influence of the following factors:
- Inflammation of the ENT organs. Diseases of the ear, nose and throat provoke enlarged lymph nodes. Swelling causes laryngitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, otitis, diseases of the teeth and oral cavity. Metabolic products, penetrating the cervical nodes, lead to swelling of the lymphoid tissue.
Thyroid diseases
Swelling in the front of the neck is a symptom of damage to the endocrine organs. This swelling is formed in several pathologies. Goiter occurs against the background of iodine deficiency. The disease mainly affects women over 50 years of age. In addition to swelling of the thyroid gland, accompanying symptoms are noted:
- profuse sweating;
- increased irritation;
- fatigue, weariness;
- anxiety;
- weight loss
There are 3 types of goiter: nodular, diffuse and mixed. With diffuse goiter, swelling in the affected area is distributed evenly. If the thyroid gland is enlarged to a greater extent on the right or left, a nodular form of goiter occurs.
Acute inflammation of the glandular tissues is a typical process that explains why the neck under the chin swells. The disease occurs rarely, but is always severe. Symptoms appear suddenly.
Patients suffer from several problems at once:
- heat;
- sore throat;
- development of edema (the neck can become very swollen);
- increased fatigue, weakness.
Swelling on the gland leads to enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes.
Diseases of the lymphatic system
A bulge in the neck is formed if the local lymph nodes are swollen. Swelling of the lymphatic tissue is caused by infections. Doctors often determine the disease by the place where the neck is swollen; enlarged lymph nodes under the chin indicate stomatitis, acute respiratory infections, diphtheria, and rubella.
Bumps on the back of the head, coupled with high fever and sore throat are symptoms and signs of the development of sore throat, pharyngitis, and acute respiratory infections. With frequent colds, inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes occurs.
Tumors that form under the influence of uncontrollably multiplying cancer cells are lymphoid in nature. Multiple lumps on both sides of the neck indicate cancer.
Tissue inflammation
Swelling of the soft tissues of the neck appears with the development of inflammatory processes. Due to dysfunction of the sebaceous glands, boils or carbuncles form on the epithelium. Ulcers form on the scalp, usually on the back of the head.
Patients complain that the neck:
- swollen;
- swollen;
- hurts;
- blushed;
- A purulent blister has formed on the surface of the skin.
Flux causes swelling of the neck. If the tissue is swollen due to a diseased tooth, treatment is carried out by a dentist. Such inflammations can rarely be suppressed by conservative methods. Usually the doctor resorts to surgical intervention (opening the abscess, removing a tooth).
Tumors
Malignant or benign neoplasms form on the cervical tissues. Cancerous tumors occur less frequently. Benign growths include:
- Lipomas are non-painful soft or hard wen. Swelling of this type occurs in the area of the back of the head and trapezius muscle.
- Papillomas are single or clustered formations from flesh-colored to dark brown. Similar swellings form on the neck on the right or left.
- Fibroids are the growth of connective structures that appear on the sides and in the lower part of the organ.
- Lymphangioma is a neoplasm formed by lymphatic vessels.
- Neurogenic outgrowths arise in the carotid triangle.
Disease prevention
To avoid lymphadenitis, it is recommended to follow a number of the following preventive rules:
- Treat damaged areas of the skin (scratches, abrasions, etc.) as soon as possible so that the infection does not have time to penetrate the skin.
- Strengthen the immune system (hardening, taking vitamins, etc.).
- Undergo regular preventive examinations.
- Resolve dental problems in a timely manner.
- If enlarged lymph nodes are detected, immediately show the child to a specialist.
In most cases, inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck in children is a symptom of some disease. Therefore, first of all, you need to find out the cause of this phenomenon and only then begin treatment. When the underlying cause is eliminated, lymphadenitis most often goes away on its own. Antibiotics, drugs to strengthen the immune system, vitamins and folk remedies can be used as therapy.
Symptoms
With inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes, the symptoms in most cases are visible to the naked eye. First of all, this concerns increasing sizes. Depending on the specific case, the lymph node can become the size of a chicken egg. At the same time, it may hurt and become hard. If you notice such symptoms, you should immediately seek help from a doctor. Otherwise, the disease may progress to the chronic stage, which will bring trouble throughout life.
An inflamed lymph node can cause a deterioration in the child’s well-being. In this case, the temperature can often rise to 37-37.5 degrees Celsius. And this is far from uncommon. Other symptoms include sore throat, cough, runny nose. The child may also feel pain and aches in the bones. The motor functions of the neck also deteriorate, and the patient will also feel pain.
If a child has pain in the lymph node in the neck, do not delay treatment; you should immediately consult a doctor. Only an experienced specialist can tell you how and how to treat these manifestations in each specific case.
Even if only one of the above symptoms occurs, it is better to seek help from a specialist. Lack of appetite and general lethargy may also indicate disturbances in the functioning of the body.