What is considered diarrhea?
Diarrhea in children is called repeated (more than 5 times a day) loose stools. In infants, diarrhea is the constant “leaking” of the anus, accompanied by frequent bowel movements.
In older children, diarrhea may be accompanied by anal incontinence , which puts them in an awkward position in front of others if the disease is taken by surprise.
Parents should be able to distinguish loose stools from diarrhea . Loose stools, or indigestion, occur up to three times a day after overeating, drinking heavily, or eating food that activates intestinal motility.
With diarrhea, the child experiences a frequently recurring urge to defecate, which intensifies after eating or drinking.
Video “Doctor Komarovsky about intestinal infections”
In the video you will learn the opinion and recommendations of Dr. Komarovsky regarding intestinal infections in children.
Do you have any questions? Specialists and readers of the KROHABABY website will help you ask a question
Was this article helpful?
Thank you for your opinion!
The article was useful. Please share the information with your friends.
Yes (100.00%)
No
X
Please write what is wrong and leave recommendations on the article
Cancel reply
Rate the benefit of the article: Rate the author ( 3 votes, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Discuss the article:
Causes
The causes are conventionally divided into two groups - external (environmental influences) and internal (disturbance in the functioning of body systems).
External reasons include:
- food poisoning from low-quality products;
- eating raw fruits and vegetables that excessively increase intestinal motility;
- drug therapy (after taking antibiotics);
- stress;
- systematic overeating.
Internal causes are infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
They can be bacterial (dysentery, typhoid fever, salmonellosis, etc.), viral (rotovirus) or fungal in origin.
- inflammation of the intestinal mucosa (enterocolitis, appendicitis, etc.);
- allergic reactions to external irritants;
- gastrointestinal diseases (ulcers, colitis, internal hemorrhoids, etc.);
- dysbacteriosis, that is, a violation of the natural microflora, making normal digestion of food impossible;
- oncological diseases;
- parasite infection;
- renal failure.
In infants, diarrhea can be caused by the following factors:
- lactose intolerance (milk sugar in breast milk), that is, a lack of lactase (enzyme) in the body;
- teething;
- violation of the diet by a nursing mother;
- unsuitable milk formula for artificial feeding.
Children under one year old, especially in the first month of life, are characterized by frequent bowel movements (up to 10 times a day). Feces during this period of life have a liquid or mushy consistency.
Therefore, it is important for infants to monitor general changes in well-being , as well as the appearance and smell of stool.
Diarrhea and temperature 38 in a child. How to help and what to do
To help your baby you need:
- Call a doctor or ambulance;
- Do not give antibiotics, you can give Smecta, activated carbon.
- To prevent the infection from spreading to other people, isolate the patient until an accurate diagnosis is made.
- Carefully examine the child to see if he has any accompanying signs.
- Do not lower your temperature until the doctor or ambulance arrives.
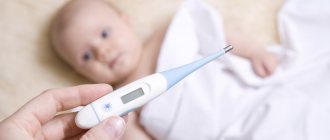
- But if the child has a temperature of 38 °C, 39 °C, then in this case an antipyretic should be given.
- If the baby is one year old, then candles should be used to reduce the temperature. If the child is over two years old - syrup.
To avoid dehydration and improve the child’s condition, you can make the following solutions:
Add a teaspoon of salt, one tablespoon of sugar and half a teaspoon of soda to one liter of boiled water.
To one liter of boiled water, add one teaspoon of salt, eight teaspoons of sugar and fresh orange or lemon juice.
Prepare one of the solutions. Give it to your child in small portions every five minutes .
Diagnostic methods
To clarify or confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a laboratory test:
- Stool analysis for dysbacteriosis;
- Stool analysis to detect parasites;
- kilogram;
- General blood analysis;
- Blood chemistry. It detects dysfunction of the liver or pancreas;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Allows you to detect the inflammatory process of the gallbladder, liver, pancreas.
Based on the test results, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
Causes of intestinal infection in children
The causative agents of intestinal infections are bacteria (Salmonella, Campylobacter), viruses (Rotovirus, Adenovirus) and protozoan fungi (Giardia, Coccidia). Infection occurs through food, dirty hands and dishes, toys. Pets can also be carriers .
Intestinal infection can occur in mild, moderate and severe forms. It depends on the child's immunity.
Treatment with drugs
- To eliminate fever and diarrhea in a child, the following medications must be given: activated carbon, Smecta, Polyphepan, Enterosgel.
- Paracetamol-based medications are given to reduce high fever.
- To avoid dehydration, you need to drink a lot of liquid: mineral water, compote, tea, Regidron.
- In case of food poisoning, it is necessary to rinse the stomach.
- If a child has bloody diarrhea, antibiotics are prescribed.
- To restore the intestinal microflora, bifidobacteria or lactobacilli are taken.
During treatment you must adhere to the following diet:
- If the baby is not yet twelve months old, then you do not need to stop breastfeeding.
- If your child is fed formula, then switch to soy-based formula during the recovery period.
- If your child is over a year old and eats adult food, then during this period you should eat cereals, vegetables, fruits, fish, chicken, and yoghurts.
- Products must be steamed or boiled.
- Salty, fried and sweet foods should not be consumed;
- Before eating, it is better to wipe cooked food so that there are no lumps.
Kinds
According to the nature of its course, diarrhea can be acute (lasts no more than three weeks) and chronic, which exhausts the child for a long time.
According to the mechanism of formation, diarrhea is usually divided into four types:
- Exudative, which is characterized by the formation of purulent exudate in the intestinal cavity as a result of infectious diseases. In this case, feces are colored green and may contain impurities of pus and mucus. The smell of feces is putrid.
- Secretory , affecting only the small intestine as a result of its colonization by foreign microorganisms. This condition can be caused by dysbiosis or thrush. In this case, the stool is watery, copious, and may contain undigested pieces of food.
- Osmolar , associated with gastrointestinal diseases or a lack of digestive enzymes in the body. In this case, the intestines become unable to absorb water passing through it due to damage to the mucous membrane. This type is accompanied by severe abdominal pain. There may be traces of blood in the stool.
- Neurogenic , due to the specifics of the baby’s nervous system, which, when irritated, increases intestinal motility. Sometimes hyperkinetic diarrhea is identified as a separate type, which develops with excessive intestinal activity with a uniform diet poor in nutrients (starvation diarrhea).
How to stop vomiting in a child? Find out about this from our article.
Clinical picture
With normal loose stools, the baby's stool does not change color or smell . Only the consistency of the discharge changes. Diarrhea, which is a symptom of serious disorders, can be:
- White , associated with the presence of the hepatitis virus in the child’s body. But don't be scared right away. This color of stool during diarrhea occurs in infants, associated with the transition to artificial formula, as well as with enzyme deficiency in older children.
- Water - indicates the presence of infection in the body. This clinical picture is typical for rotavirus, but tonsillitis and sinusitis can also be accompanied by watery stools.
- With blood - appears with lesions of the intestinal mucosa, internal hemorrhoids. Dark blood color is a very serious symptom (oncology or duodenal ulcer). Scarlet is most likely associated with bleeding hemorrhoids or disruption of the rectal mucosa due to infections (in this case, mucus is also present in the stool).
- Green is a sign of the presence of a bacterial infection in the child’s body.
- Black is a normal occurrence in the first five days of a baby's life, when meconium formed in utero is passed. In older children, this may be due to the use of activated carbon, preparations with bismuth, and also be a symptom of bleeding in the upper intestine, when the blood “brews” as it moves towards the outlet.
- With foam - this type of diarrhea in infants may be associated with a deficiency of the lactase enzyme, an allergy to gluten (celiac disease) or dysbacteriosis. In older children, this is one of the symptoms of the presence of a viral or fungal infection in the body.
What do fever and vomiting mean?
Infantile diarrhea rarely develops without accompanying symptoms.
with fever due to acute intestinal infections and poisoning. In this case, the thermometer rises above 38 degrees.
The temperature during diarrhea associated with teething rarely rises to this figure and does not last long - one or two evenings.
Without fever, the disease develops with a lack of digestive enzymes, gastrointestinal pathology, dysbacteriosis, and stress.
In this case, it is important to study the nature of the feces.
Changes in color, rotten smell, and traces of blood are serious symptoms that require you to consult a doctor.
with vomiting indicates severe intoxication of the body coming from the stomach. If the condition is also accompanied by a high temperature, then this can be either one of the symptoms of an acute attack of appendicitis, or an intestinal infection or poisoning.
Without fever, vomiting and diarrhea can occur with indigestion, damage to the pancreas, or kidney failure.
Diarrhea without vomiting can accompany inflammation of the intestinal mucosa (enterocolitis), a change in diet (complementary feeding, travel), and dysbacteriosis.
Persistent loose stools without vomiting and fever occur when infected with parasites (helminths and fungi).
Symptoms
High fever and diarrhea in children require observation; it is necessary to examine not only the baby, but also his feces.
This will make it possible to determine the approximate cause of the appearance and establish a diagnosis before the doctor arrives. The symptoms are:
- Bloody feces. This condition is called invasive diarrhea. Children have severe poisoning of the body, fever appears, and symptoms indicate infection of the intestines.
- Feces with mucus. When mucus appears, the cause may be microbes and other parasitic organisms in the intestines, for example, salmonella, lamblia, and other viruses.
- Diarrhea and vomiting. The appearance of symptoms with a high temperature, with additional release of the aroma of acetone from the oral cavity, may indicate an acetonemic crisis. If the skin is pale and the extremities are cold, the baby may have food poisoning.
- Diarrhea, fever and pain. Such symptoms indicate the consumption of the wrong foods, so you will need to analyze the food that the baby ate.
- Swelling of the gums. In children under 3 years of age, with diarrhea and increased temperature, it is necessary to examine the mouth; the cause may be the appearance of teeth. In this case, the gums will be swollen and red.
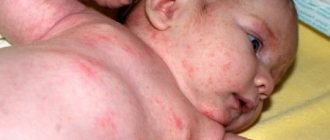
- Rash. If rashes appear on the body and mucous membranes, then this is a sign of rubella or measles. Such symptoms also occur with allergies to medications, especially those containing a lot of iron.
- Cold symptoms. In case of redness of the throat, high temperature, cough, diarrhea signals the presence of colds.
Regardless of the causes and additional symptoms, diarrhea and fever should be treated with doctor's help. Self-medication is not allowed, but before an ambulance visit, you can alleviate the condition of children a little.
Treatment
What should parents do? When treating, you should remember that diarrhea is only a symptom of a disease that only a doctor can accurately diagnose. But parents must be able to alleviate the baby’s condition in order to avoid dehydration, demineralization and a decline in immunity as a result.
Children of any age are advised to be hungry (especially on the first day), drink plenty of fluids, and dehydration solutions (Regidron, Citroglucosolan, saline solution, etc.).
Medicines
How to treat the baby? The following groups of drugs are used to treat diarrhea:
- Enterosorbents - Smecta, Enterosgel. These medications can be given to children from birth. They not only bind toxins, removing them from the intestines, but also heal the mucous membrane.
- Antimicrobial . For newborns in the first month of life, only a doctor can prescribe such medications. From one month to two years, Enterofuril can be used in the form of a suspension to treat bacterial intestinal infections. Older children are allowed to take capsules of this medicine.
- Antiviral based on interferon. Prescribed orally from the first days of life for viral intestinal and stomach infections. For example, Derinat in the form of drops.
For this purpose, phthalazole is prescribed only from the age of six, furazolidone - from the age of five.
- Probiotics - restore intestinal microflora, treat dysbiosis. For this purpose, children are prescribed Hilak Forte, Normobact, Lactobacterin. The products can be used from birth, according to the instructions.
- Enzymes . Infants with lactose intolerance are prescribed the enzyme lactase, and older children are prescribed Creon, which restores not only the normal functioning of the intestines, but also the pancreas.
- Zinc and calcium supplements are necessary to prevent demineralization. Children need 10-20 mg of zinc per day, depending on age, and the doctor prescribes calcium carbonate in an individual dosage.
For neurogenic diarrhea, a drug that reduces intestinal motility is prescribed - Loperamide. It can only be used from the age of six.
Until this age, nervous diarrhea can be combated with the help of folk remedies.
Folk remedies
How else can you stop diarrhea in a child? The best folk remedy for diarrhea in children is a water infusion of oak bark. The raw materials are bought at the pharmacy and prepared according to the instructions on the box.
For diarrhea in breastfed infants, it is recommended that the nursing mother drink the infusion first . If there is no effect, then you can give it to your baby to drink, diluting it with water in a ratio of 1:3:
- up to three months - 2 ml five times a day for three days;
- up to one year - 5 ml five to six times a day for 3-5 days.
After a year, you can offer a diluted infusion of 15-20 ml three times a day. This safe antimicrobial agent can be combined with any drug treatment.
Enterosorbents can be replaced by a decoction of oatmeal (20 g per 150 ml of water). A decoction of white rice or blueberry jelly made from potato starch and sugar will slow down peristalsis.
Compote made from dry pears (not fresh!) has a very beneficial effect on the irritated intestinal mucosa. It soothes the mucous membranes and relieves spasms.
Do not use herbal medicine without a doctor's prescription. This can lead to unwanted complications (low blood pressure, bleeding, allergies).
Diet
For diarrhea, a gentle diet is recommended :
- the first day is hungry;
- second day - pureed cereal soups;
- third - pureed soups, crackers made from ordinary bread (not rich!), slimy porridge with water;
Starting from the fourth day, in the absence of contraindications, you can offer your baby steamed cutlets, low-fat broth, mashed potatoes without oil, baked apples.
Dairy products, fresh vegetables and fruits, sweets, confectionery, fast food and canned food
are undesirable
Recommendations
Not everyone knows what to do if fever and diarrhea do not go away. Useful recommendations will help you replenish your stock of necessary knowledge:
- If you suspect an intestinal infection, be sure to call a doctor at home. Sometimes treatment in a hospital is required; simple cases can be overcome at home. Strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations, do not exceed the dosage of medications.
- Be sure to follow a gentle diet and give your baby plenty of fluids.
- Maintain bed rest. Lack of physical activity speeds up the baby’s recovery.
Prohibited actions:
- You cannot feed your child spicy, salty, sweet foods, or store-bought dairy products.
- Before the doctor arrives, do not give any medications, especially antibiotics. Aggressive drugs can lead to complications.
- Do not delay going to the doctor, especially if there is no improvement within 2-3 days. Normally, the child feels better every hour and his appetite appears.
Komarovsky's opinion
Pediatrician Komarovsky believes that it is better to prevent diarrhea in a child by observing hygiene rules and subjecting foods to heat treatment.
For diarrhea, in his opinion, there are two main remedies - hunger and drinking plenty of small portions at a temperature of 36-37 degrees, which ensures instant absorption.
Among the drugs, Evgeniy Olegovich recommends Smecta , which, thanks to its unique crystalline structure, is instantly integrated into the intestinal mucosa, completely restoring it.
After providing first aid, the pediatrician strongly recommends that you consult a specialist to make a correct diagnosis.
First aid
When a child has diarrhea and fever, a number of actions must be taken to help the baby and prevent dehydration.
Procedure:
- Call the doctor.
- Do not give your child antibiotics unless prescribed by a doctor.
- Isolate the baby until the cause is determined. A necessary measure to prevent the spread of infection if it is the cause of symptoms.
- Examine the baby’s skin and mucous membranes to determine accompanying signs.
- Do not lower the temperature below 38° until the doctor arrives.
- It is allowed to use enterosorbents: Smecta, activated carbon.
- Give the baby warm boiled water until the doctor arrives. This helps reduce dehydration and alleviate the child’s general condition.
Prevention
In order for diarrhea to stop being a frequent guest in your home, you need to :
- teach your child to wash their hands before eating and going to the toilet;
- follow the rules of food preparation and storage;
- eliminate allergens from the diet;
- take tests every six months for timely diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal diseases.
Diarrhea in a child is a protective reaction of the body to intoxication or a signal of problems with the gastrointestinal tract . Therefore, after parents provide first aid, consultation with a professional is required.
About diarrhea during teething in a child in this video: