Staphylococcal infection and carriage
The human body is inhabited by more than 500 species of microscopic inhabitants. Normally, friendly relations are maintained between them and the human body, benefiting both parties.
The nasal cavity is no exception: it is characterized by a relatively constant colonization of certain types of peaceful microorganisms and a negligible number of their hostile relatives. In extreme conditions, the latter can cause serious illness.
To this day, the mechanisms of staphylococcus uprising remain unknown. Apparently the reason lies in the weakening of protective reactions in the body of a child and an adult, as well as in the habitat itself. Staphylococcus aureus multiplies and lives in the cells of the mucous membrane of the anterior sections of the nose, without making itself felt by any symptoms.
This condition is called carriage, and the microbe can be transmitted to other organisms. Carriers of staphylococcus can be people with frequent exacerbations of chronic infections of the ENT organs, as well as employees of food industry enterprises, the service sector, employees of preschool educational institutions and schools, doctors - healthy people who come into contact with a wide range of the population, including children.
Factors contributing to infection
Staphylococcus aureus in the nose is an opportunistic bacterium that, under certain circumstances, can cause infectious, sometimes extremely serious, diseases.
Such circumstances include:
- massive infection, in which many staphylococcal microbes enter the body or they act for a long time;
- mutations and increased virulence of staphylococcus - the emergence of resistance to treatment and an increase in the ability of the bacterium to infect the body;
- disruption of the functioning of all parts of the child’s immune system and the reasons leading to this (unfavorable environment, poor nutrition, stressful situations, concomitant diseases, medication, and others);
- intranasal problems that cause disruption of the outflow of mucus and the movement of air flows (swelling of the mucous membrane - that is, inflammatory and allergic diseases, deviated nasal septum, polyps, enlarged adenoids, foreign objects).
Treatment at home
To treat Staphylococcus aureus in the nose in adults, several groups of drugs are used:
Antibiotics; immunostimulants; antihistamines (if necessary).
Antibiotics are traditional medicines in the fight against bacterial infection. They use, first of all, synthetic penicillin with clavulanate (Amoxiclav, Panclave, Flemoclav, etc.). Staphylococci can demonstrate resistance to certain types of antibiotics. If improvement does not occur within 2 days, you need to replace the product with a more effective one. These may be antibiotics from the group of cephalosporins or macrolides.
Medicines that stimulate the immune system for streptococcal infections in the nose:
Streptococcal bacteriophage - the drug is instilled into the nose, destroys bacteria; IRS-19 - inhaled into each nasal passage several times a day; complex vitamins are an indispensable element of immunostimulating therapy.
If the immune system is significantly suppressed, complex immunostimulation regimens may be prescribed, including, but not limited to:
Immunoregulatory peptides (eg, Taktivin); synthetic immunomodulators (eg, Polyoxidonium); antistaphylococcal immunoglobulin.
Antihistamines (Diazolin, Tavegil, etc.) are traditionally taken to relieve severe swelling of the mucous membrane and other irritation reactions.
Local procedures performed in the following sequence play a significant role in the treatment of staphylococcus in the nose:
vasoconstrictor drops; rinsing the nose with salt water; rinsing the nose with Chlorhexidine; instillation of Chlorophyllipt solution.
Chlorhexidine is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial antiseptic.
Chlorophyllipt is a product based on eucalyptus leaf extract, active against streptococci. An oil solution of chlorophyllipt is instilled 3-5 drops three times a day for a week.
It is advisable to use antibacterial ointment for staphylococcus in the nose if areas of purulent inflammation are observed in the nasal passages. Use 2% Fusiderm ointment. The cream is applied to the affected areas of the nose visible to the eye three times a day for a week. Only directly on the affected areas: ulcers, ulcers.
Risks in children
I have been detecting and treating parasites for many years. I can say with confidence that almost everyone is infected with parasites. It's just that most of them are extremely difficult to detect. They can be anywhere - in the blood, intestines, lungs, heart, brain. Parasites literally devour you from the inside, at the same time poisoning your body. As a result, numerous health problems appear, shortening life by 15-25 years.
The main mistake is delaying! The sooner you start removing parasites, the better. If we talk about medications, then everything is problematic. Today there is only one truly effective anti-parasitic complex, this is Toximin. It destroys and sweeps out all known parasites from the body - from the brain and heart to the liver and intestines. None of the drugs existing today is capable of this.
Within the framework of the Federal program, when submitting an application before October 12. (inclusive) every resident of the Russian Federation and the CIS can receive one package of Toximin for FREE!
According to Dr. Komarovsky, a child is not a smaller copy of an adult. A small person has its own structural characteristics and physiological processes in the body.
Anatomically and physiologically, a child’s body is very different from an adult’s. And this nuance must be taken into account when health issues similar to adults arise. Regarding the carriage of staphylococcus in the nose, children may experience serious problems, and an adult may not even notice any changes.
In a child, unlike an adult, the nasal passages are much narrower. At the slightest inflammation, nasal breathing is immediately disrupted. The child breathes with his mouth slightly open, which, in turn, can lead to inflammation of the pharynx.
The auditory tubes (canals connecting the nasopharynx and middle ear) in a child, on the contrary, are wider than in adults. They are always slightly open and located horizontally (in adults their direction is almost vertical). When you blow your nose incorrectly, mucus infected with staphylococcus enters the middle ear and causes a life-threatening disease for the child - otitis media.
The child's throat is rich in lymphoid tissue (tonsils, including adenoids), which performs a protective function (these are organs of the immune system). It immediately reacts to foreign elements entering inside, including staphylococci.
This reaction can occur in the form of acute (adenoiditis, tonsillitis) or chronic inflammation (enlarged adenoids). This also leads to congestion in the nose. The species ratio of microorganisms on the mucous membrane, including staphylococcus, is disrupted. As a result, opportunistic flora, in particular Staphylococcus aureus, begins to predominate.
The younger the child, the faster and more complex all pathological processes occur. It’s easy to miss the beginning and quite difficult (even in a hospital and intensive care unit) to maintain the baby’s health. The physiological immaturity of the child’s immunity only aggravates the condition of staphylococcal infection.
Quite serious factors causing staphylococcus infection are conditions that the child himself (and subsequently the adult) cannot influence. These are intrauterine development, childbirth and feeding.
Following the birth canal, the newborn becomes infected with the mother's microflora. The child moves from a sterile environment into an environment inhabited by various microorganisms.
From this moment the formation of its own microflora begins. Over the next few hours, non-pathogenic microorganisms, including staphylococcus, colonize the skin and mucous membranes. The child's normal microflora becomes stable. By about the fourth month of life, it is similar to the microbiota of adults.
The type of child's nutrition (breastfeeding or artificial feeding) greatly influences the normal development of microflora.
These are very important moments that influence the entire future life of the child. The health of the mother, the sanitary condition of the environment in which the birth took place, and proper nutrition determine the healthy functioning of the baby’s mucous membranes (including the nasopharynx) and determine the normal formation of the immune system, including its ability to resist bacteria.
Don't forget about standard hygiene rules. Routine principles will help maintain the child’s health at the proper level, protecting him from staphylococcus infection. You just need to wash your hands before eating and after walking, ventilate the room where the child is and often be in the fresh air, eat only freshly prepared food rich in vitamins, protein and fiber.
Methods for recognizing staphylococcal infection
The classification of Staphylococcus aureus into the group of opportunistic microbes indicates the possibility of its ambiguous behavior. In one person it will live quietly in the nose, without disturbing the owner. For others, staphylococcus will create a lot of trouble. Knowing the main targets of the bacteria, you can try to overcome the consequences associated with them.
Lesions caused by Staphylococcus aureus:
- ENT infections;
- bronchitis, pneumonia;
- eye infections;
- staphylococcal infections of the urinary system;
- skin pustular infections;
- food poisoning;
- wound staphylococcal infections;
- endocarditis of staphylococcal nature;
- toxic shock syndrome, sepsis.
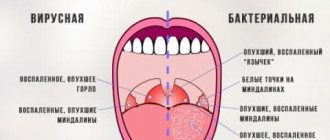
Symptoms of the pathogenic action of staphylococcus can be very diverse and depend on the location of the lesion. If we are talking about the nasopharynx, the child will be bothered by:
- nasal discharge;
- impaired nasal breathing (due to swelling of the mucous membrane or inflamed enlarged adenoids);
- headache;
- weakness, rapid fatigue;
- increase in body temperature.
If you do not pay attention to the initial manifestations, staphylococcal inflammation can spread to the middle ear (and lead to otitis media, then meningitis), pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, which ultimately leads to pneumonia.
The presence of staphylococcus in the human microflora is a normal variant, therefore microbiological detection of the pathogen alone is not enough. Quantitative analysis is necessary - it is important to determine how many units of staphylococcus bacteria are in the material being examined.
Due to the total resistance of staphylococcus to antimicrobial drugs, it is immediately necessary to determine which antibiotics the microbe is sensitive to. The only drawback of this method is the length of time it takes – the result is usually ready on the seventh day.
Today there are many rapid tests for drug resistance of staphylococcus, among them the Pathogenic System Double. The principle of their action is at the intersection of microbiology and biochemistry, which allows you to determine the result the very next day. This is a significant help, which allows the doctor to begin precise treatment of staphylococcal infections, practically without wasting precious time.
Staphylococcus aureus: what is it and why is it dangerous?
Staphylococcus aureus is a dangerous bacterium
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most dangerous bacteria, which can cause various serious diseases. This type of staphylococcus has several strains that differ from each other in the set of toxins they produce.
Under a microscope, the bacterium appears as round, yellow clumps. Staphylococcus is characterized by high viability and can survive for about 6 months in a dried state. Bacteria do not die when exposed to direct sunlight or freezing.
If the infection is not destroyed, it will actively multiply and affect other organs.
Untimely treatment of staphylococcal infection can cause serious complications:
If a large number of strains of pathogenic bacteria are detected, treatment should be started in a timely manner to prevent the development of serious diseases.
Nasal culture is an effective diagnosis of staphylococcal infection
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most dangerous bacteria, as it contributes to the development of serious diseases. It got its name from its color. Most often it is localized in the nasal cavity, and then penetrates the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body.
Infection can occur through airborne droplets, household contact and oral routes. The infection can reach a child through kissing, sneezing, breastfeeding, through the birth canal, or with food. In medical institutions, if sterility is violated during procedures, there is also a high probability of Staphylococcus aureus getting inside.
Staphylococci are opportunistic microorganisms and are present on mucous membranes. With accompanying factors, their number exceeds the norm, which leads to the inflammatory process.
The main factors contributing to the penetration of staphylococcal infection into the body:
- Weakening of the immune system.
- Poor nutrition.
- Caries.
- Long-term use of vasoconstrictors.
When diagnosing Staphylococcus aureus in children, other family members must be examined. And all members must undergo treatment, as there will be a risk of re-infection.
More information about Staphylococcus aureus can be found in the video:
Staphylococcus aureus is a very insidious infection and is very easy to confuse with a cold or respiratory diseases. Symptoms depend on the number of reproductions of pathogenic bacteria. The main signs of Staphylococcus aureus in the nose include:
- Mucous discharge from the nose.
- Itching and redness of the mucous membrane.
- Temperature increase.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Feeling of nasal congestion.
- Enlarged tonsils and adenoids.
- Formation of crusts in the nasal passages.
- Intoxication.
- Prolonged runny nose.
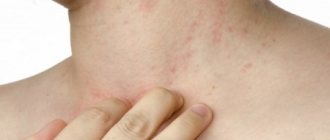
Symptoms differ between adults and children. A characteristic sign of a staph infection will be a skin rash. Staphylococcus aureus can be detected only through laboratory tests - culture of mucus from the nasal cavity.
Necessary measures in case of infection
If a child develops threatening symptoms of a staphylococcal infection, it is necessary to immediately contact competent specialists (pediatrician, ENT, pulmonologist).
The doctor will quickly assess the child’s condition, take into account complaints and find out whether there were contacts with carriers, but he will decide on the tactics for treating the infection only on the basis of the necessary examinations.
For this reason, you should not self-medicate staphylococcal diseases, since irrational use of antibiotics or improper use of them can lead to the fact that humanity will sooner or later be left face to face with dangerous infections.
The doctor must insist on a second consultation if the child’s condition worsens while taking an antibiotic or the symptoms last longer than five days.
Staphylococcus in the nose is not always a reason to panic, see Dr. Komarovsky’s video about this:
Home remedies for raging staphylococcus are:
- Acetaminophen (Paracetamol) or Ibuprofen; Do not use acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin) in children and adolescents due to the risk of developing Reye's syndrome;
- rinsing the nose with saline solutions and/or gargling with warm salt water (1/4 teaspoon of salt per glass (230 ml) of water);
- gentle dairy-vegetable diet;
- drinking large quantities of warm drinks;
- complex herbal preparations (Table 1);
Table 1. Herbal medicines for treating a child from staphylococcal respiratory diseases
| Therapeutic effects | Medicinal plants |
| Antimicrobial (phytoncidal) | Fruits of anise, fennel; herbs of wild rosemary, oregano, St. John's wort, juniper, thyme, sage; buds, eucalyptus leaves |
| Enveloping (mucolytic) | Marshmallow root, plantain leaf and seeds, Icelandic moss, clover flowers, wheatgrass root, cordifolia inflorescences |
| Expectorant | Herbs of primrose, tricolor violet, speedwell; ivy leaf; angelica root |
| Anti-inflammatory | Licorice root, wheatgrass, angelica; linden inflorescences; calendula flowers; sage herb; plantain leaf |
| Bronchodilator | Fruits of anise, fennel; thyme herb |
| Diaphoretic | Linden inflorescences; lingonberries, cranberries, viburnum, berries and raspberry leaf |
| Sedative (antitussive) | Valerian root; chamomile flowers |
Preventive recommendations
It is important to teach your child the basic principles of personal hygiene - do not put your fingers in your mouth, wash your hands before eating. The child must have personal dishes and individual towels. It is necessary to change underwear often, follow a bathing regime, and do not kiss the baby on the face.
The child should receive a complete diet, enriched with natural products of plant, animal and microbial origin, which contain lacto and bifidobacteria, fiber, vitamins, antioxidants, amino acids, and polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Infection with staphylococcus can be prevented by some herbal preparations, which today are considered the safest immunomodulators.
These include herbal medicines containing extracts of medicinal plants: chamomile flowers, horsetail herb, yarrow herb, oak bark, dandelion herb, walnut leaf and marshmallow root. In addition to immunomodulatory, they have antiviral, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects.
Useful information about staph infections in the video:
It is necessary, if possible, to limit contact with carriers of staphylococcus, at least in the closest environment. If one of the family members is infected, he must be sanitized.
Staphylococcus aureus is an opportunistic microorganism. Active growth provokes weakening of the immune system. If the normal levels in the nose are exceeded, external and systemic medications are prescribed.
Prevention of infection
No preventive measures can give a complete guarantee that staphylococcus will not penetrate the child’s body. This microorganism is very cunning and tenacious. However, simple preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of infection:
- teach your child to wash his hands after going outside and going to the toilet;
- Thoroughly wash all the vegetables and fruits you feed your baby with running water; in the hot season, pour boiling water over them;
- a child attending kindergarten must have his own bed, towel, and preferably his own dishes;
- during procedures and other medical manipulations, the mother must ensure that health workers comply with sterility conditions;
- If one of the adults in the family is infected with staphylococcus, it is advisable to protect him as much as possible from communication with the child.
And most importantly, remember that staphylococcus is not so scary for a baby with a strong immune system. The maximum that it can cause is a mild cold-like condition, a slight runny nose and irritation around the nose. Such symptoms usually go away on their own in just 3-4 days.
Therefore, the best thing that can be done is to strengthen the child’s immunity. This requires regular physical activity, good nutrition, hardening procedures, and the correct daily routine.
Staphylococci belong to the opportunistic microflora. They are constantly present on the mucous membranes and skin. When the body's protective functions decrease, they acquire a pathogenic form and cause the development of many diseases. Of all types of staphylococci, Staphylococcus aureus is considered the most dangerous, especially for children.
Normal Staphylococcus aureus in the nose
Staphylococcus aureus lives everywhere; you can become infected by inhaling dust, through close contact, during oral sex, or by eating food without heat treatment. But with normal immunity, bacteria do not multiply in the body, and there are no signs of disease. Viral infections - influenza, ARVI, HIV - provoke active growth of bacteria in the nose. Often the infection develops due to long-term use of vasoconstrictor nasal drops.
Staphylococcus aureus is present in the nose constantly or occasionally in 80% of adults.
The norm for Staphylococcus aureus in a smear from the nasal mucosa is 10*2-10*3 degrees CFU/ml. But the presence of bacteria on the mucous membrane does not mean anything. Treatment is prescribed if there are symptoms of a bacterial infection, if the number of microbes is more than 106 units.
Signs of active growth of Staphylococcus aureus:
- temperature rise to 39 degrees or more;
- runny nose, nasal congestion;
- discharge of mucus and pus from the nose;
- change in voice timbre - hoarseness, nasality;
- pain in the frontal and maxillary sinuses;
- symptoms of general intoxication.
Without proper and timely treatment, the infection spreads further. Purulent processes are localized on the mucous membrane of the pharynx, in the middle ear cavity, and meningitis and sepsis often develop. Staphylococcus aureus causes exacerbation of chronic sinusitis.
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus in the nose
Drug therapy is prescribed only if high levels of bacteria are accompanied by purulent discharge and high fever. Treatment is carried out with antibiotics, immunostimulants, antihistamines, local means for rinsing and instilling the nose. In the absence of characteristic symptoms of infection, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system to prevent the active reproduction of Staphylococcus aureus. Folk remedies help effectively in such cases. Physiotherapy procedures are used as additional methods - phototherapy, laser therapy, electrophoresis, UHF.
The average duration of treatment for Staphylococcus aureus is 4 weeks.
During treatment for Staphylococcus aureus, it is necessary to adhere to a diet so as not to overload the body. Allowed foods are lean meat and fish, fermented milk products, slow carbohydrates, fruits and vegetables. Plenty of warm drinks are recommended - fruit drinks, compotes, table mineral water.
To speed up the healing process, you should stop drinking salt, coffee, and strong tea. Do not eat legumes, cabbage, or rye bread. These foods are difficult to digest and the body spends too much energy. Prohibited foods are junk food, hot spices, alcoholic beverages, fatty meats and fish.
For Staphylococcus aureus, antiseptics are prescribed for rinsing the nose. The drugs destroy bacteria, prevent their active growth, and moisturize the mucous membrane. Additionally, you need to use vasoconstrictor drops to eliminate rhinitis, swelling, and ointments with an antimicrobial effect.
List of external agents:
- Chlorhexidine. Antimicrobial antiseptic with a wide spectrum of action, cleanses and disinfects mucous membranes, removes mucus. To rinse the nose, use a 0.05% solution. Carry out procedures 2-3 times a day for a week.
Nasal drops - Isofra, Protargol, Polydexa. They have antibacterial and vasoconstrictor effects. Place 2 drops in each nostril 2-3 times a day. The duration of treatment is no more than 10 days.
Antibiotics are the drugs of choice for treating bacterial infections. But they are prescribed for oral administration in extreme, especially severe cases. If the norm of Staphylococcus aureus in the nose in adults is exceeded, signs of an infectious process are observed, and an analysis is prescribed to determine the sensitivity of pathogens to antibacterial agents. This helps to choose an effective medicine, since staphylococci are resistant to many antimicrobial drugs.
| Name | a brief description of | Admission rules |
| Amoxiclav | Semi-synthetic penicillin. The active ingredients are amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. | Dosage: 250 mg three times a day for 5-14 days. |
| Ofloxacin | Broad-spectrum fluoroquinolone. | Daily dosage: 200-800 mg, divided into 2 doses. Duration of treatment is 7-10 days. |
| Ceftriaxone | III generation cephalosporin. | The drug is administered intramuscularly at a dose of 1-2 g once a day for 7-10 days. |
| Sumamed | Antibiotic from the macrolide-azalide group. The active substance is azithromycin. | Dosage: 500 mg once a day. The duration of the course is 3 days. |
People with immunodeficiency conditions are prescribed strong antibiotics - Vancomycin, Teicoplanin. These drugs are effective against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. But they have many contraindications and often cause negative reactions.
It is imperative to complete antibiotic therapy to the end, even if the symptoms of the disease have disappeared.
After completing antibacterial therapy, it is necessary to take a course of probiotics and prebiotics to restore the balance of the intestinal microflora. Effective drugs - Linex, Acipol, Maxilak. Additionally, you need to consume more natural fermented milk products.
Since the number of Staphylococcus aureus increases against the background of suppressed immunity, drugs must be included in therapy to activate the body’s protective functions. They are effective, but they must be taken strictly according to the instructions if there are serious indications. Otherwise, you can completely disrupt the functioning of the immune system.
Preparations to stimulate the immune system:
- Streptococcal bacteriophage - used for the treatment and prevention of streptococcal infections. The medicine destroys bacteria; it must be dropped into the nose, or moistened in a turunda solution, and left in the nasal passages for an hour.
For staphylococcus in the nose, medications must be prescribed to prevent the infection from spreading to the larynx - Lizobakt, Miramistin, Furacilin. Antiallergic drugs are prescribed to eliminate swelling of the nasal mucosa. It is better to take the latest generation antihistamines - Levocetrizine, Fexofenadine. These medications do not have a sedative effect, act quickly, and the therapeutic effect lasts 12-24 hours.
Treatment of staphylococcal infection in the throat of a child
During the examination of the child, the specialist will prescribe a bacterial culture of the smear; if the baby has a problem, he will also check the mother’s milk for pathogenic microflora. Therapy for Staphylococcus aureus in the throat in children involves the use of comprehensive health measures. Treatment is aimed at blocking the infectious agent, strengthening the body's defense mechanisms, and sanitizing the throat.
Antibacterial agents will help destroy harmful microorganisms in a child’s throat. The least toxic substances are used to treat children. Etiotropic treatment is carried out for about a week. The selection of medications in this group is carried out after an antibiogram.
The drug is presented in the form of powder and suspension. The substance is prescribed to children from the age of two months.
The effect of the antibacterial drug depends on the dosage. In small quantities, it has a detrimental effect on the growth of staphylococcal microorganisms. If the dose is large, it completely destroys bacteria. Oral administration is allowed for patients over 6 years of age. The daily dose is set by the pediatrician depending on the child’s body weight and is 45 mg/kg body weight. The minimum course of treatment is 5 days. In severe cases, therapy is extended to 10 days.
Amoxicillin is the main component of Flemoklav. It belongs to the penicillin group. An additional ingredient is clavulanic acid. The substance has an extensive bactericidal effect against staphylococci, enterococci, streptococci and other pathogenic microorganisms. The tablets are approved for use from three months of age. For children under 12 years of age weighing up to 40 kg, the dosage is 30 mg/kg per day. Price from 260 rub.
An antibiotic of the aminoglycoside class, it has broad bactericidal properties. The drug is active against many gram-positive pathogenic microorganisms. Children are given it intramuscularly. The daily dose is 15 mg/kg, up to 3 times a day. The treatment regimen may vary depending on the severity of the disease and the effect of drug therapy. Price from 540 rub.
An antibiotic with a broad spectrum of action, belonging to the group of ansamycins. Prescribed from the age of two. For children under 12 years of age, the dosage is from 0.4 to 0.8 g per day in the form of a suspension. The daily volume of the substance is distributed into several doses. For the younger children's group (2–6 years), it is recommended to take 0.2–0.6 g of the drug in 2–3 procedures. The duration of the course is a week.
This drug is sold as a solution for intramuscular administration. It is recommended in complex treatment with simultaneous administration of an antibiotic. The product is effective in severe forms of staphylococcus infection and its manifestations. The medication strengthens immunity to the harmful effects of staphylococcal strains. The treatment regimen is selected by the doctor, it depends on the diagnosis and the age of the child. For generalized staphylococcal lesions, a single dose per 1 kg of body weight in children under 5 years of age is 100 IU. The course will require 3-5 injections every other day or daily. Price for 10 ampoules - 9600 rubles.
A powerful immunostimulating substance that can specifically act on staphylococcal bacteria. The product is used for oral administration, irrigation and administration into the cavity of ENT organs. Recommended dosages for children:
| Age | Single dose (ml) |
| up to 6 months | 5 |
| from six months to a year | 10 |
| 1–3 years | 15 |
| 3–8 years | 15-20 |
| after 8 years | 20-30 |
For purulent-inflammatory pathologies of the throat, the drug is administered in a dose of 2–10 ml up to 3 times a day. Bacteriophage is also used for rinsing and washing. Price - from 550 rub.
The drug is available in liquid form and is a vaccine. The substance consists of staphylococcal toxoid, sorbent and other additives. When administered, it promotes the formation of specific antibodies to the exotoxin of the pathogenic microorganism. The course of immunization for infections in children over one year old consists of two injections of the drug, performed every other month.
Rinsing is recommended for children along with antibiotics. These procedures relieve pain, destroy infection, and restore strength.
The product provides antiseptic and antimicrobial effects. The solution contains chlorophylls, minerals, essential oils, phytoncides, and other compounds that destroy pathogenic microorganisms. The extract is effective against staphylococci, since it affects strains that do not die even after an attack by antibiotics. Treating the throat reduces pain, eliminates redness, reduces cough and other symptoms.
For children, Chlorophyllipt is prescribed in a diluted form for farengitis. To prepare, 10 ml of the product must be dissolved in a glass of slightly warm water. Gargle at least three times a day. Price - 300 rub.
To rinse, 20 ml of solution must be held in the mouth for 45 seconds. Perform the procedure half an hour before meals three times a day. The duration of therapy is 10 days. Treatment with Chlorhexidine is effective, economical and safe. For children under three years of age, the product is allowed only in the form of a spray or gauze swabs moistened with an antiseptic. Price - 12 rubles.
The medicine is often included in the treatment of chronic tonsillitis and tonsillitis along with antibiotics. The solution removes pathogenic bacteria and purulent fluid from the mucous membranes, and blocks the progression of inflammation. The drug is used for local action, so it is recommended for infants.
To rinse, you need a solution prepared from a tablet, which needs to be filled with 100 ml of warm boiled water. Before use, be sure to strain the liquid so as not to injure the mucous membrane with undissolved crystals. The throat should be gargled with a warm mixture at intervals of 2 hours, only after eating.
Parents need to supervise the procedure; when the child cannot complete it, they need to tilt him face down over the sink and irrigate the throat with a syringe or syringe without a needle.
The drug is made on a natural basis, which allows it to be used for the treatment of throat pathologies in pediatrics. Before each procedure, it is necessary to prepare a fresh composition. The dosage for children is 0.5–1 tsp. per cup of warm water, adjusted for age. For children over 12 years of age with good drug tolerance, the amount of the substance can be increased to 2–3 tsp. for the same volume of water.
You cannot use a very hot solution for the procedure, so as not to burn the mucous membrane. Before using the medicine, be sure to shake the bottle, and after preparing the composition for rinsing, it must be filtered. The cost of the drug may vary depending on the volume and ranges from 20–100 rubles.
The presence of a significant amount of staphylococcus is evidence of a significant deterioration of immunity. To help the body, special drugs are prescribed - immunomodulators. They contain deactivated fragments of some bacteria. You can find out how to gargle when you cough here.
When all kinds of bacterial antigens enter the body, the human immune system produces interferon and sets up processes that can improve, if necessary, the immune response.
Such tablets must be dissolved; they are prescribed after the child reaches the age of three. For infants, the pediatrician selects a different drug suitable for a specific age.
Due to the presence of bacteria, which often provoke damage to the mucous membrane of the oropharynx, the medicine provides an immunostimulating effect. As it dissolves, the number of cells of the immune system grows precisely in the area of the pharyngeal mucosa.
After resorption, you should not consume anything from liquids or food for an hour. For children from 3 to 14 years old, the daily dose is prescribed in the amount of 6 tablets, taken every 1–2 hours. For prevention after 14 years of age, it is recommended to dissolve the tablets in a three-week course - one tablet every 2 hours. Such courses are recommended for frequent chronic ailments four times a year, which helps prevent exacerbation of pathologies. You can find out about methods for treating purulent sore throat at home by following the link.
This nasal spray is recommended for the treatment or prevention of infectious pathologies. The preparation contains many lysates of pathogenic bacteria, including fragments of Staphylococcus aureus. The product is allowed to be used in the treatment of a child after reaching the age of three months. Spray price - 465 rubles.
The complex of health-improving measures also includes recipes for alternative medicine. These treatment agents are used in the form of decoctions or teas intended for rinsing and oral administration.
In the treatment of staphylococcus, herbal collection will help alleviate the condition. For the recipe you will need birch buds, wild rosemary, string, yarrow, thyme, taken 1 tbsp. l. Pour 0.5 liters of boiling water over the mixture and let stand for 2 hours. It is recommended to use the resulting volume 3 times a day. You can find out what to spray in the throat when you have a cold in this article.
Propolis effectively fights various types of pathogenic microorganisms. It is used in the form of an alcohol tincture or a water extract. When used on a child, preference is given to a water base.
The product is taken 1/2 tsp. up to 3 times a day. The drug can be used from four months of age. The propolis decoction should be given to drink gradually, in drops, diluting the medicine in 1 tsp. milk and water. The dosage regimen starts with 1 drop, then add a drop every day and bring the total number to 10 per dose. The course of treatment is about 10 days, then you need to start reducing it drop by drop daily. The entire course will take about 3 weeks.
The most commonly used recipe is a decoction of the product. To obtain it, take a couple of tablespoons of ground or crushed propolis in any way. The substance is dissolved in a glass of chilled boiled water, after which the liquid is placed in a water bath. The solution is brought almost to a boil, then, with a low flame, the product is slowly stirred for another quarter of an hour. Afterwards, all that remains is to strain it and cool it to room temperature.
To prepare a water tincture, you will have to spend much more time. First, take 2 g of the material, grind it thoroughly and pour a glass of boiling water into the powder. The liquid is infused inside the thermos for about a day. After this, the tincture must be strained and placed in the refrigerator for a couple of hours.
Gargle with the resulting solution 5 times a day. Children need 120 ml of this infusion per day. Immediately before the procedure, it must be heated to a temperature of 37° C. You can find out how to treat tonsillitis in a child here.
Gargling with these substances helps block the proliferation of staphylococcus. This promotes the rapid process of epithelization of affected cells. For treatment by irrigating the throat, you will need a glass of warm boiled water, 0.5 tsp. salt and 2-3 drops of iodine. Use the product up to 3 times a day during an exacerbation. After the procedure, you should not feed the baby immediately. Salt and iodine therapy can be prescribed from the age of seven.
Before using the products, you must make sure that the baby does not have an allergic reaction to them or hypersensitivity to the components of the solution. If you experience a feeling of dryness or any other unpleasant signs in your throat, it is better to use another product that does not contain iodine for gargling. It is also recommended to use chamomile decoction and special absorbable tablets for children.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods of treating Staphylococcus aureus in the nose in adults are used to strengthen the body's protective functions and cleanse the body of toxins. In therapy, decoctions, infusions and tinctures are used. But without taking antibiotics, folk remedies are ineffective.
Plants with immunostimulating effects:
- Echinacea inflorescences;
- rosehip berries and flowers;
- St. John's wort;
- hawthorn.
Herbs can be used one at a time, or preparations can be made from equal amounts of several ingredients. Brew 1 tbsp. l. raw materials 200 ml of boiling water, leave in a closed container for half an hour. Drink 100 ml of infusion twice a day.
In case of frequent exacerbation of staphylococcal infection, mix chopped parsley and celery roots in equal parts. Grind the mixture in a blender, squeeze out the juice. Drink 5 ml before each meal.
If you have Staphylococcus aureus, you should not warm up the area of the nose, forehead and cheeks; visiting saunas and hot baths is contraindicated.
Thermal procedures contribute to the spread of infection throughout the body. What is dangerous is the development of severe consequences and complications. Hypothermia of the head and entire body should also be avoided so as not to further weaken the immune system.
It is imperative to take vitamin complexes with a high content of ascorbic acid and retinol. Honey, apricots, blackcurrants, onions, garlic, and ginger will help strengthen your immune system. These products should be included in the diet during treatment and during epidemics of colds.
From medicinal herbs you can prepare effective solutions for rinsing the nose, clearing mucus, and eliminating swelling. They act no worse than pharmaceutical products and have fewer contraindications and side effects. Medicinal infusions and decoctions are easy to prepare, and the cost of raw materials is affordable.
- Pour 1 tbsp. l. dry chamomile inflorescences 250 ml of boiling water, simmer in a water bath for a quarter of an hour. Cool in a sealed container to a comfortable temperature, strain. Rinse your nose 3-5 times a day, be sure to before using any local medications.
You can instill fresh aloe juice into your nose - it is a strong natural antibiotic. Mix juice with honey in equal proportions. Place 2-3 drops in each nostril twice a day. Duration of treatment is 1-2 weeks.
Homemade drops can be prepared from burdock or comfrey root. Pour 200 ml of water 2 tbsp. l. raw materials, heat in a water bath for 20 minutes. Cool, strain. Place 5 drops in each nostril three times a day.
Traditional medicine
Staphylococcus aureus can also be eliminated using traditional methods of treatment. Of course, preference should first of all be given to traditional methods, but there are a number of cases when it is not possible to seek qualified help, then home recipes will come to the rescue.
A decoction is prepared from dried chamomile flowers, left for half an hour, and then dropped into the nose. Chamomile is a well-known anti-inflammatory and antiseptic agent, so its use is completely justified.
Dried sage herb is prepared in the same way as chamomile, but the decoction is used to gargle if there are pustules.
Burdock root is crushed and mixed with a small amount of boiled water. The resulting juice and water are placed in the nose, 5 drops every 3 hours.
To gargle, use an alcohol tincture of propolis diluted in boiled water. It allows you to remove the pustular rash and make it easier to swallow with a sore throat.
Compresses are used to eliminate staphylococcus. To do this, you usually use a cotton swab dipped in water diluted with apple cider vinegar. Similar lotions are applied to each nostril for half an hour. According to people who tested the product, the effect will be noticeable after just three uses.
A plant such as aloe has proven itself very well; the juice from this plant not only improves immunity, but also removes staphylococcal infections. You need to instill juice from fresh leaves of the plant 3 times a day. It is important to note that this gives results very quickly, since aloe provokes a sneezing attack in the child. Green clots that interfere with the child’s breathing come out very quickly.
You should not get carried away with traditional medicine, and if it does not give results, then it is better to stop using ancient treatment recipes. Sometimes they can only worsen the child’s well-being and provoke a number of complications, which will be more difficult to deal with than treating the infection itself.
The best effect is achieved when traditional medicine is combined with folk medicine. In such a case, synthetic drugs are used as the main treatment, and as a supplement, restoratives on a natural basis, as traditional medicine advises.
What do you need to remember?
Staphylococcus aureus lives in the nose of 8 out of 10 absolutely healthy people. Symptoms of the infectious process appear only when the body's defenses are weakened. The immune system cannot contain the growth of bacteria, their number is rapidly increasing.
The main method of preventing staphylococcal infection is to constantly strengthen the immune system. A healthy and active lifestyle, proper nutrition, timely treatment of respiratory diseases, herpes. It is necessary to observe the rules of personal hygiene, take vitamins, antiviral drugs during the cold season.
Share with your friends
Do something useful, it won't take much time
A prolonged runny nose and sore throat are often caused by staphylococcal flora. The most dangerous forms of diseases are usually provoked by Staphylococcus aureus. This article will tell parents about the characteristics of such infectious diseases in children.
Prevention
Preventive measures against Staphylococcus aureus are aimed at preventing infection from entering the body.
Basic recommendations on how to avoid contracting a staphylococcal infection:
Ventilate the room frequently and do wet cleaning. Always wash your hands before eating. Children's toys and dishes should be kept clean. Strengthen the immune system. Avoid hypothermia. Take immunostimulating drugs during viral infections. Products that are not exposed to heat must be handled in soapy water. This will significantly reduce the risk of staphylococcus entering the body through food.
An important method of prevention is strengthening the immune system. Children should be taught a healthy lifestyle from a young age. It is necessary to do exercises every day, eat right, take walks, and observe the rules of personal hygiene.
It is useful to do hardening, wet rubdowns and swim in a pond in the summer.
It is necessary to follow the above recommendations and then you can prevent the development of many diseases, including the entry into the body of pathogenic bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus.
Symptoms
Staphylococcus aureus is a very pathogenic microorganism. Once in a child's body, they can cause multiple lesions. The severity of adverse symptoms may vary and depend on many factors. Staphylococcal infection in newborns and infants is quite severe.
One of the favorite localizations for Staphylococcus aureus is the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract. In this case, infection occurs through airborne droplets.
You can become infected from any sick person or carrier of infection who has microorganisms in the nasal cavity and oropharynx. Even a simple conversation with him can lead to infection. Staphylococcus aureus has a whole arsenal of various toxic substances that lead to severe inflammation. A pronounced inflammatory process leads to the appearance of unfavorable symptoms in the sick child. These symptoms appear taking into account the predominant localization of the inflammatory process.
The severe course of the disease is usually accompanied by severe intoxication syndrome. It is manifested by an increase in body temperature. In severe cases of the disease, it rises to 38-39 degrees. A sick child sleeps poorly and often wakes up at night. Children's appetite decreases. They become more moody and lethargic.
Causes and symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus in the throat in children
Staphylococci enter the human body through contact and household contact. Other factors can also cause a child to become infected:
- lack or poor hand and oral hygiene;
- eating dirty, stale foods.
The pathogenic bacteria in the throat is not activated if the baby has a strong immune system, but if the defense is weakened, it spreads quickly. The defense mechanism can be weakened by:
- avitaminosis;
- previous acute respiratory viral infections;
- long-term therapy with antibiotics, immunosuppressants;
- recurrent herpes sore throat;
- physical inactivity;
- poor nutrition;
- nervous disorders.
The presence of staphylococcus in the throat leads to laryngitis or tonsillitis. Often, a sore throat occurs in a more acute form, which is accompanied by symptoms such as swelling, increased body temperature, and pain when swallowing. Associated manifestations of staphylococcal lesions are:
- enlargement and redness of the tonsils;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- the presence of a pale yellow coating in the throat;
- lacrimation;
- chills;
- joint pain or muscle aches.
In the nose
Staphylococci living in the nasal passages cause many adverse symptoms. A characteristic symptom of staphylococcal rhinitis is the appearance of a runny nose. Nasal discharge has a yellow or green light. They are usually thick and difficult to separate. In some cases, the runny nose becomes prolonged. Staphylococcal nasopharyngitis is an infectious pathology in which the mucous membranes in the nasopharynx become inflamed. This clinical variant of infection can occur in children at any age.
The incidence increases during the cold season. Mass outbreaks of the disease occur mainly in crowded groups. Children attending preschool educational institutions have a higher risk of infection.
The development of staphylococcal rhinitis is caused by the influence of some provoking causes:
- Weakening of local immunity. Quite often occurs after severe hypothermia.
- Nose injuries. Wounds to the mucous membrane make it easier for any infection to penetrate. Surgeries on the nasopharynx to remove adenoids or polyps also contribute to the active proliferation of microbes.
- Abuse of drops to treat a runny nose. Excessively long-term use of these drugs contributes to the development of atrophic changes in the mucous membranes of the nasal passages. This leads to the fact that pathogenic Staphylococcus aureus easily enters the nasal cavity.
In the throat
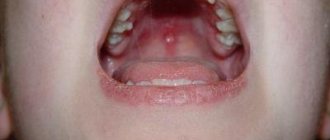
By airborne droplets, Staphylococcus aureus easily penetrates the oropharynx and pharynx. This contributes to the development of a strong inflammatory process in the upper respiratory tract. A fairly common manifestation of staphylococcal infection is bacterial pharyngitis. This pathology is manifested by the appearance of purulent plaque that covers the outside of the tonsils. The palatine arches with staphylococcal pharyngitis enlarge and hang strongly over the entrance to the pharynx.
The neck of a sick baby becomes bright red. The tongue is covered with a gray or yellowish coating. During illness, the child develops severe soreness in the throat and decreases appetite. Breastfeeding babies may refuse breastfeeding or have difficulty latching on to the breast.
Acute staphylococcal tonsillitis is accompanied by the development of many adverse symptoms. In this condition, the pharynx becomes bright red, and in some cases even acquires a flaming color.
The palatine tonsils increase in size and become loose. On the outside, they are covered with a purulent coating, which in some cases can harden and form dense crusts. When you try to remove plaque yourself using a teaspoon or spatula, bleeding occurs. Staphylococcal tonsillitis usually has a fairly severe course. In weakened babies and children with chronic diseases of internal organs, acute tonsillitis can lead to the development of multiple complications and adverse long-term consequences.
A fairly common manifestation is the development of bronchopneumonia.
It occurs in more than 10% of cases of acute staphylococcal tonsillitis.
Diagnostics
When the first unfavorable symptoms appear in the nose or throat, you should definitely show the baby to the attending doctor. A pediatrician or pediatric otolaryngologist will be able to examine a sick child. After a clinical examination, the doctor makes a preliminary diagnosis. To identify the causative agents of infection, additional laboratory tests are required. A general blood test is performed for all children who have signs of bacterial diseases. Staphylococcal pathologies of the upper respiratory tract are accompanied by the appearance of leukocytosis - an increase in the number of leukocytes.
A strong inflammatory process causes an acceleration of ESR. Changes in the leukocyte formula also occur. A blood test allows you to detect any abnormalities at the earliest stages. Infectious agents can also be detected in pathological secretions. Staphylococcal nasopharyngitis or tonsillitis can be determined by conducting a bacteriological examination.
Biological material for such examinations is discharge from the nasal cavity or mucus from the back wall of the throat. Research is carried out in a special laboratory. The effectiveness and specificity of these tests are quite high. A marker test to identify dangerous microbes is a smear. After applying the biological material to a glass slide, it is placed in a thermostat.
The result of the bacteriological examination is usually ready within a week. To conduct the study, in some cases, sputum is taken, which the baby coughs up during the acute period of the disease. To determine the complications of staphylococcal acute tonsillitis, an additional instrumental study is performed - chest X-ray. This method allows you to detect pneumonia at the earliest stages of the disease.
Complications
The prolonged course of staphylococcal rhinitis often leads to the development of inflammation in the paranasal sinuses. This disease develops especially often when treatment is not prescribed in a timely manner. Staphylococcus aureus, entering the sinuses, contributes to the development of severe inflammation in them. Ultimately, this leads to the development of acute bacterial sinusitis or sinusitis. These pathologies are accompanied by the development of a severe debilitating runny nose. Nasal discharge in this condition is quite thick, yellow or brown in color.
A child suffering from sinusitis feels constant congestion. Nasal breathing is severely impaired. The child has an intensified headache, which is bursting and constant. Staphylococcal pneumonia is also a fairly common complication that occurs as a result of the unfavorable course of acute tonsillitis, which turns into bacterial bronchitis. This pathology is accompanied by a pronounced intoxication syndrome. Young children may develop symptoms of respiratory distress. Treatment of staphylococcal pneumonia is carried out only in a hospital setting.
Treatment
Treatment of staphylococcal infections includes the administration of a whole range of different medications. The main goal is to eliminate bacterial foci and normalize the beneficial microflora living in the upper respiratory tract. For this, various antibiotics are prescribed. Reviews from parents of children who took these drugs indicate that these drugs have a pronounced positive effect. The disadvantages of using antibiotics are the development of side effects, which in some cases can be very unpleasant.
Staphylococcus aureus is especially sensitive to antibacterial drugs of the penicillin and cephalosporin series. The dosage, frequency and duration of use are determined individually, taking into account the age and weight of the baby, as well as the severity of the infectious pathology in a particular child. The duration of the treatment regimen may vary. On average, therapy for staphylococcal nasopharyngitis is 5-10 days. Acute tonsillitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus can be treated in 1.5-2 weeks. In some cases, an alternative treatment method is used using specific bacteriophages. These drugs have a narrowly targeted effect and cause the death of pathogenic microbes.
Treatment with bacteriophages has fewer side effects than with antibiotics. This therapy is quite successfully used to treat staphylococcal infections in the youngest patients. Various solutions of sea salt are used to improve nasal breathing. They are used to irrigate the nasal passages. These products help rinse babies' noses and help soften secretions that are too dense. These solutions can be used 3-4 times a day.
In some cases, vasoconstrictor nasal drops are used, which are prescribed by a doctor according to indications, taking into account the age of the baby.
Many beekeeping products also have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. Regular propolis is suitable for rinsing the throat. Such rinses should be carried out 2-3 times a day for 10-14 days. This treatment can be used only for children who do not have allergic reactions to bee products. Regular honey is also suitable for rinsing the throat. If the temperature rises above 38 degrees, antipyretics should be used.
Medicines based on paracetamol or ibuprofen are quite successfully prescribed for children. These medications are taken in age-specific dosages.
Doctors do not recommend taking acetylsalicylic acid to children during the acute period of an infectious disease, as this can lead to the development of dangerous side effects of this drug. During the height of the illness, the baby should stay at home. If a child’s disease occurs with severe fever, then the baby must be kept in bed. Such a forced and simple measure will help to significantly reduce the risk of developing dangerous complications of an infectious disease. During massive outbreaks of staphylococcal infections, quarantine is introduced in educational institutions. All children who have been in contact with sick children are given preventive treatment.
To restore the strength lost during the illness, the baby is prescribed restorative therapy. For this purpose, multivitamin preparations are prescribed. The vitamins and microelements they contain help restore immunity and improve the child’s well-being. They should be used for at least 30 days. Children with severe immune disorders are prescribed immunomodulatory therapy.
Is the detected staphylococcus in the nose dangerous? Watch the following video:
Drug treatment and antibiotics
Only a doctor can prescribe correct and effective treatment!
If Staphylococcus aureus is detected as a result of culture of a nasal swab, the sensitivity of the microorganism to antibiotics is assessed. This is an important step when prescribing antibacterial therapy, since various pathogens are resistant to certain drugs.
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus in the nose is aimed at eliminating the cause of its appearance and signs of the inflammatory process. For each child, treatment is prescribed individually. Drug treatment is usually carried out at home, but more severe cases will require hospitalization.
Treatment of staphylococcal infection in the nose should be carried out comprehensively in compliance with all doctor’s recommendations.
Treating staphylococcal infection with linden decoction
Non-traditional methods of treating Staphylococcus aureus in children should be approached with caution and should not be chosen as the main treatment. Traditional methods are an auxiliary means of drug therapy.
Popular folk remedies for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus:
- A decoction of echinacea and burdock root. Chop the plants and pour 2 tablespoons of the raw material into 800 ml of hot water. Next, boil for 20 minutes and cool. Take orally 3 times a day.
- Garlic compress. Chop the garlic cloves, add warm boiled water and leave for 1.5-2 hours. Next, moisten a cotton cloth and apply it to the inflamed areas of the nose. Repeat the procedure every day for about 2 weeks.
- Linden blossom decoction. Pour 2 tablespoons of raw materials into a thermos and pour a glass of boiling water. After 3 hours, strain and use to rinse the nasal cavity.
- Rinse with eucalyptus essential oil. Take 5 g of salt and 2 drops of oil and dissolve in 1/4 liter of boiled water. It is necessary to rinse immediately after preparing the solution.
- Propolis. Dissolve 20 g of propolis in 1/2 glass of water and place in a water bath for 2 hours. Give the child 1 tablespoon before meals.
It is strictly forbidden to place warming compresses on the bridge of the nose or forehead area. During the entire treatment you should drink more fluid. To strengthen the immune system and it is useful to give the child linden and raspberry tea, a decoction of rose hips, chamomile, and currant leaves.