| Although molluscum contagiosum is a common type of skin rash in children, many parents have never heard of it. The most important thing to know is that for most children the rash is not serious and will go away over time, but this does not mean it can be ignored. |
Fast passage:
- Causes of molluscum contagiosum in children
- Symptoms of molluscum contagiosum
- Diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum in children
- Treatment of the disease in children
- Complications of molluscum contagiosum
- Prevention of disease in children
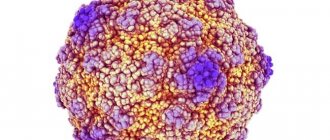
Molluscum contagiosum is a contagious skin infection caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV), which results in small, raised, pearl-like nodules or growths called molluscum or condylomas on the skin. The virus belongs to the family of viruses called Poxviridae and is known as Molluscum Poxviridae.
Molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) does not affect animals, only humans. The disease is most often observed in children under the age of 15 years, about 80% of reported cases are children aged 1 to 4 years, who are most susceptible to this disease.
The infection is most common among children aged 1 to 12 years, but also occurs in:
- Teenagers and adults.
- Some athletes, particularly those involved in wrestling, swimming or gymnastics.
- Among people with weakened immune systems due to HIV, cancer treatment, or long-term steroid use.
This skin disease is contagious and can be transmitted from one person to another. It is not known how long the rash and the virus itself can be contagious.
What is it and what does it look like
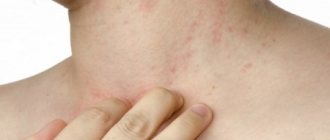
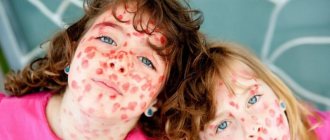
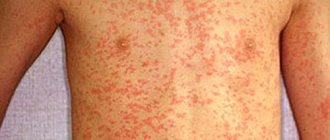
Molluscum on a child’s face manifests itself in the form of a rash that looks like nodules that rise above the general level of the skin and have an oval shape. They either match the color of the skin or have a more pink tint.
Molluscum on a child’s face looks like purulent pimples.
At the beginning, the size of each formation is small - only 12 mm, but then the disease progresses, and papules can grow up to 7-10 mm, and with weakened immunity and lack of treatment, large nodules absorb neighboring ones, resulting in the formation of especially large formations.
There is also a reticular form of the disease, in which the nodules are connected to the skin through a thin stalk.
Once it appears, the rash quickly spreads. Some nodules (about 10-15 percent of the total) have indentations in the center. If you press on it, a white mass comes out. When examining the contents under a microscope, the mollusks themselves will be visible. Nodules develop in the absence of an inflammatory process.
The disease does not lead to any complications associated with internal organs, but does not look aesthetically pleasing. If you do not undergo special treatment, it will go away on its own within up to 4 years.
How does infection occur?
The disease spreads through contact and household contact, when the contents of the nodules, due to friction on clothing or scratching, fall on household items.
If we talk about children, we should especially be wary of infection:
- children who do not yet go to school;
- for allergy sufferers;
- those who are forced to take hormonal medications;
- non-compliance with hygiene rules;
- living in unhealthy environmental conditions;
- exposed to stress and overwork.
Infection with molluscs can occur through common household items, such as bedding, hygiene items, toys, and through touching surfaces in a kindergarten, on the playground, or in the pool. The virus is present in both the air and street dust. A child can become infected not only from children, but also from adults, since in them molluscum contagiosum also appears on the face and body.
Primary signs in the form of a rash appear no less than 2 weeks later. after contact with a virus carrier. In some cases, the hidden period can last up to six months. Since the contents of the papules are infectious, the virus quickly spreads to new areas. The carrier of the disease is only humans; symptoms of the disease are not registered in animals and they are not its carriers.
Not everyone who comes into contact with a sick person becomes infected, since the virus dies when the body’s protective functions are developed.
Consequences of the disease
Molluscs in a child are not dangerous to health and life, but the external manifestations of the disease look unaesthetic, so it is better to remove them. The disease may have the following consequences:
- general decrease in immunity;
- the appearance of an inferiority complex in a child due to a rash on the face;
- difficulties in communication;
- infection of other children and adults.
If a child has been diagnosed with molluscum contagiosum, attending kindergarten and school is not prohibited. However, other children should understand that any close contact with a sick person will lead to infection. Avoiding contact is easier than removing the rash later.
Symptoms
Initially, single nodules appear on the body, then new ones appear nearby - the faster, the weaker the child’s immunity. How quickly the nodules grow in size also depends on the body's resistance.
Apart from the fact that the disease manifests itself as a rash, no other symptoms are observed, including hyperthermia, weakness, or loss of appetite. Sometimes patients note slight itching in the area of the rash. If the formation is damaged, for example by scratching, a secondary bacterial infection is likely to spread.
Diagnostics
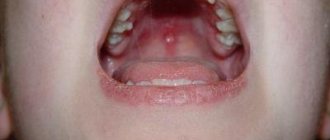
Molluscum on the face of a child manifests itself as a rash, like most childhood diseases, for example, chickenpox, measles, rubella, it is often confused with them, but it is the release of a pasty mass from the papule that is a distinctive feature. The face is often affected; nodules appear extremely rarely on the palms and soles.
To exclude diagnostic errors, you need to consult a dermatologist. An experienced doctor is able to determine the disease by appearance without additional tests . The correct diagnosis is confirmed by analyzing the contents of papules or scraping the epithelium.
Causes
A child has a rash on his hands - what is it, the causes of the rash
Molluscs can appear on a child’s skin for various reasons. The most common of them:
- poor nutrition and vitamin deficiency;
- increased susceptibility to viruses;
- exchanging clothes and toys with infected children;
- warm and humid climate in the southern regions.
This disease can be easily contracted while vacationing in the south. The incubation period of the disease ranges from two to eight weeks, depending on the characteristics of the individual’s body. In children with weak immunity, the disease manifests itself earlier, and in children with strong immunity, later.
Molluscum often affects the skin of children with weakened immune systems
Attention! One of the most common causes of the disease is visiting a swimming pool or a polluted natural body of water. Therefore, after any swimming (in a pool or river (pond, sea)), the child must take a shower.
Stages of development of molluscum contagiosum
The development of the disease occurs in stages.
There are three stages in total:
- At the first stage, papules are scattered, isolated, and do not cause discomfort.
- At the second stage, the volume of the rash increases, the rash covers more and more new areas of the skin, and the density of the nodules increases.
- In the third article, the formations grow several times, cause not only psychological, but also physical discomfort, itching and inflammation appear. When tactilely applied, mollusks are released from the papules.
Treatment
Doctors do not recommend removing papules for children; they advise waiting until the signs of the disease disappear on their own. However, self-healing from molluscum contagiosum can take a long time, so in some cases they resort to traditional, medicinal or surgical methods of treatment.
Ointments and solutions
After diagnosing the disease, the doctor may prescribe medications based on the child’s age.
| Preparations with the active ingredient Tretinoid (Tretinoid, Retin-A, Vesanoid, Lokacid) | Spot application on papules | 1-2 rubles/day | The area is washed with water 6 hours after application. |
| Containing Canteridine (homeopathic preparations) | 1-2 rubles/day | No need to rinse | |
| 3% trichloroacetic acid solution | 1 rub./day | Wash off after 30-40 minutes | |
| Salicylic acid (3%) | 2 rubles/day | Do not wash off | |
| Medicines containing interferon (for example, Acyclovir) | 2 rubles/day | Leave until completely absorbed | |
| Aldara cream | 3 rubles/day | No need to rinse | |
| Fluorouracil ointment | 2-3 rubles/day | Do not wash off | |
| Based on eucalyptus extract (Chronotan, Chlorophyllipt) | 2 r/day | ||
| Oxolinic ointment | Spotwise layer 3 mm | 2-3 rubles/day | Do not wash off |
| Preparations based on benzoyl peroxide (Ekloran, Effezel, Baziron AC, etc.) | 2 rubles/day | Do not wash off |
The drugs most recommended by doctors from the above are: oxolinic and fluorouracil ointment, Baziron AC, Ecloran, as they do not have a significant systemic effect. It is necessary to smear the nodules until the rash is completely eliminated. According to practical observations, this takes from 3 weeks to 3 months. But in any case, follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Antiviral agents are widely used, for example Viferon cream or Infagel. Apply to formations 4-5 times a day for a weekly course. Viferon can be prescribed in the form of suppositories. Antibiotics are rarely prescribed, only in case of a bacterial infection.
Antiviral tablets Isoprinosine are also prescribed. They stop the virus from multiplying, which makes the rash disappear.
Removal
Options:
- Mechanical removal. It is performed by a doctor using tweezers or a Volkmann spoon. Sterility must be maintained during the procedure. The papule is removed, its contents are scraped out, and then the wound is cauterized with an iodine solution. Since this method is painful, anesthesia with any superficial painkiller, for example, Emla, is recommended. It is not recommended to use this method to remove papules on the face, since tissue scarring is possible after removal. Doctors also do not advise removing formations on your own, as there is a high risk of significant damage to the skin and the formation of scars afterwards.
- Cryo-freezing. Papules are treated with liquid nitrogen using hardware or manually, after which swelling and a bubble appears around the lesion. Healing formations may itch, but this should not be done. To speed up healing, antiviral ointments are prescribed. This is the removal option recommended by Dr. Komarovsky. Its advantage is that it is painless, but after removal, scars form, so it is not suitable for the face. In addition, children may have an allergic reaction to cold.
- Cauterization with laser . Compared to the above methods, it is most effective, since the virus is killed by the laser, healthy tissue is not affected, the affected cells are destroyed, and the method does not cause such severe pain as mechanical removal. However, when treating a large area of skin, anesthesia is recommended. Damaged cells are heated to 180 degrees and evaporated, after which no blood flows. Several sessions are necessary, however, after the first procedure, 90% of papules are completely burned out. Subsequent care consists of treatment with iodine or a solution of potassium permanganate and a ban on swimming for at least 3 days. This method is most suitable for removing papules on the face and around the eyes.
- Electrocoagulation . The formations are exposed to electric current. Rarely there is discomfort from the current discharge, but there is no serious pain. However, when removing papules in children, it is recommended to use painkillers.
It is important to know that with any removal option, new foci of the disease may appear, therefore, even after careful removal of all formations, it is necessary to periodically conduct a preventive examination.
Traditional medicine recipes
Molluscum on a child’s face can be successfully treated with folk remedies:
- The juice released from the broken green branch of celandine is lubricated with new growths 2-3 times a day. According to reviews, the nodules disappear after 7-10 days.
- Garlic juice also helps quickly. You can wipe the papules with a cut slice or grate the garlic on a fine grater, put it in gauze and blot the nodules 3-4 times a day. They also apply a paste of grated garlic and butter, mixed in a 1:1 ratio, to the nodules, sealing them on top with a band-aid. Under the influence of juice, the formations will darken and fall off.
- Juice squeezed from crushed bird cherry leaves also destroys the manifestations of the virus. Within a few days a significant improvement is noticeable. The product can be stored in the refrigerator.
- You can buy an alcohol tincture of calendula or eucalyptus at the pharmacy and wipe the nodules with it 3 times a day. It is important that the contents of the papules are not squeezed out, otherwise the infection will spread further.
- It is recommended to wipe the nodules with a decoction of the string. Proportions: 1.5 tbsp. dry ingredient per 1 tbsp. water. The herb must be boiled and left for 45-60 minutes. Rub the cooled infusion over the formations 3 times a day.
- An infusion prepared from pine needles, birch buds, eucalyptus, yarrow inflorescences, and juniper berries is used internally and externally. You will need 2 tbsp. each ingredient. Brew 1 tbsp daily for 10 days. mixture 1 tbsp. boiling water Let it sit for an hour, filter, give it to the child to drink and smear the education with the same infusion.
- When choosing any remedy, it is recommended to consult a doctor, especially if the child is very small - 1-2 years.
Mode
During the treatment of the disease, it is necessary to observe a strict hygiene regime:
- Every day it is necessary to change the child’s underwear and clothes to clean ones;
- bed linen and hygiene items, such as towels, are also changed frequently;
- things are washed at a temperature of 90-95 degrees;
- after washing, the laundry is ironed on both sides;
- disinfect toys and surfaces in the house;
- when the child comes into contact with other children, cover the papules with an adhesive plaster so that others do not become infected;
- wash your hands often with soap;
- The formations are wiped with antiseptic solutions several times a day.
The disease called molluscum contagiosum is harmless from the point of view of its effect on the body, since only cosmetic defects appear in children. But papules can take a long time to go away on their own, so cosmetic and folk methods are used to remove rashes. Laser removal is most suitable for the face.
Removing shellfish from children
Dermatologists do not recommend removing molluscum contagiosum nodules in children on their own to avoid complications on the skin in the future. Only an experienced doctor can prescribe a treatment method. When a disease occurs, the child cannot attend school, kindergarten, or swimming pool. An infected baby should undergo a full course of therapy from a dermatologist. As a rule, removal of molluscum in children is rarely resorted to, because The rash may disappear from the skin on its own over time. Although in rare cases, mechanical removal of papules is simply necessary. Removal is indicated in the following situations:
- if there is a high risk of spreading the infection;
- in the presence of concomitant skin diseases (atopic dermatitis);
- if the rash is localized on the neck or face.
Mechanical removal
The doctor can remove the papules using tweezers and an alcohol solution of iodine. During this procedure, young children are often anesthetized with Emla cream or another surface anesthetic. To remove the nodules, the doctor squeezes the jaws of the tweezers and squeezes out the contents of the papules, after which he carefully removes the curdled mass and cauterizes the wound with iodine or hydrogen peroxide.
To remove molluscs from the skin, a specialist may use curettage or husking. This method involves mechanically scraping out the papules with a sharp Volkmann spoon. The procedure is unpleasant, and removal is often accompanied by bleeding, so the specialist uses local anesthesia with lidocaine. After removing all nodules, the wounds should be treated with a 5% iodine solution. This method of removal may leave scars on the body.
Surgical removal
As the infection progresses, the specialist may prescribe one of the following surgical treatment methods:
- Diathermocoagulation. You can remove a child's rash by cauterizing the papules with an electric current. This procedure is practically painless, but can sometimes be accompanied by burning, discomfort, and tingling.
- Laser therapy. Modern medical equipment makes it possible to quickly remove the mollusk with a laser using local anesthesia. This removal helps to achieve the destruction of 90% of papules after the first session. In this case, each nodule is irradiated with a laser during the procedure, after which the skin is treated with iodine (5% solution). If after a week the papules have not crusted over, then another irradiation session is performed.
- Cryodestruction (cryotherapy). Removing nodules with liquid nitrogen. Cells with the virus are frozen and killed during the procedure. When cryotherapy is carried out correctly, there are no scars on the skin.