The peak of the infectious disease chickenpox, as experience shows, occurs precisely at 3-5 years of age in patients. As with any other pathology, in practice a severe form of chickenpox can occur in children. This aggravated course is due to the fact that the little patient’s immunity is quite reduced and is no longer able to fight the viral process.
What are the causes and symptoms of this viral infection, what complicated types of pathology occur and how to deal with this condition. Knowing the above points will help parents remain calm during illness and act more consciously and rationally.
Symptoms of the disease
The initial symptoms of the incubation period of chickenpox are similar to the flu or a common acute respiratory viral infection. Then characteristic signs appear that are difficult to confuse with another disease.
In order to avoid complications, early and correct diagnosis is important. So, the very first symptoms include:
- headache
- temperature increase
- chills
- sore throat
- muscle aches
- loss of appetite
- general weakness, fatigue, fatigue
- enlarged lymph nodes
The characteristic features are as follows:
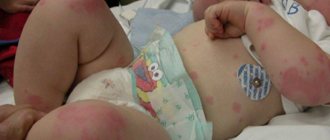
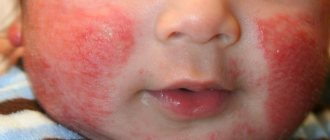
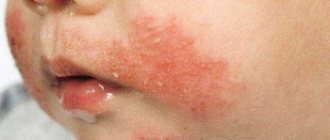
- red rash
- formation of papules (vesicles) at the site of the rash
- itching (the resulting blisters are very itchy)
Severe form of the virus
Severe forms of chickenpox are most difficult to tolerate in young patients. Here, in addition, the psychological component also plays a depressing role. Children are not ready to adequately respond to the manifestations of severe symptoms of the disease. In general, the picture of severe chickenpox looks like this:
Severe forms of chickenpox
- increase in body temperature to 40 degrees;
- numerous rashes on the skin, sometimes forming entire rash-affected areas of small papules;
- rashes can last 7-9 days;
- severe itching haunts the little patient;
- signs of intoxication (weakness, chills, nausea, vomiting, restless sleep) do not leave the patient until the rash stops forming.
Important: severe manifestations of viral infection are rare in children. Most often, the disease in severe form overtakes adult patients and adolescents.
Characteristics of the disease
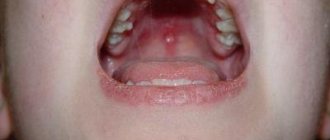
The disease begins with the penetration of the virus into the respiratory tract, causing damage. Quickly spreading throughout the body, penetrating the skin and internal organs, inflammation occurs in the form of a rash. Rashes are present not only on the skin, but also on mucous membranes, for example in the mouth, eyes, under the hair.
The virus multiplies quickly in humid conditions. A complication may also occur in the form of damage to internal organs, for example, nerve cells.
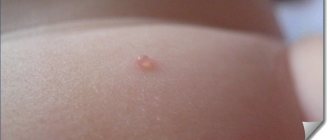
The rash on the body soon turns into blisters filled with clear liquid, approximately 2 mm in size, which is clearly visible in the photo of the incubation period of chickenpox.
Then the papules begin to become cloudy and gradually dry out, turning into crusts.
Final healing occurs after 2-3 weeks, the most important thing is to control the desire to scratch the affected areas. The fact is that if you do not treat with an antiseptic and constantly “comb” the scabs, then scars may remain or infection may occur. It should be remembered that the crusts will fall off on their own, and age spots will also disappear over time.
Complicated forms of chickenpox
- Vestigial form. There is no intoxication. Body temperature is within normal limits. There is a roseola rash on the body.
- Pustular form. The disease lasts quite a long time. Symptoms of intoxication and fever may occur. The liquid in the bubbles becomes cloudy. You can see blood and pus in it. After the blisters dry, blood crusts appear. Scars often remain on the skin.
- Bullous form. The main symptom is the appearance of large blisters on the skin. In addition, there are vesicles and symptoms of intoxication.
- Hemorrhagic form. A particularly complex form of chickenpox. Often occurs with complications. Inside the vesicles is hemorrhagic fluid. Petechiae appear on the skin, and hemorrhages appear on the mucous membranes. The patient may experience nosebleeds and vomit blood.
- Gangrenous form. Manifested by dystrophy and vitamin deficiency. In addition to hemorrhagic blisters, a purulent inflammatory process and necrosis occurs on the skin. Septic complications are also not uncommon.
- Generalized form. Most often, it is infants who encounter this form of chickenpox. May be fatal. The rash occurs on the spleen, lungs, brain, liver, kidneys, pancreas and adrenal glands and leads to necrosis of internal organs.
Where does it come from?
It is possible to find out that a person has contracted chickenpox only 2-3 days after the onset of the disease. The fact is that it does not manifest itself immediately, so it is difficult to diagnose it.
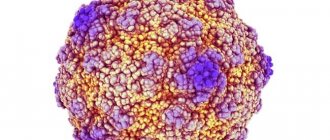
Chickenpox is caused by a virus from the Herpetosviridae family, called Varicella Zoster. A large amount accumulates in characteristic bubbles - vesicles.
The characteristics of the virus are as follows: it is highly volatile (it easily penetrates distances of up to 20 meters, even from floor to floor), and is well preserved at room temperature. Therefore, a short duration of contact with an infected person is sufficient.
The only thing is that the external environment is unsuitable for the virus, as well as very high or low temperatures. There is even such a thing as an epidemic of chickenpox, so you need to understand from whom and how you can get it.
Can this course of the disease cause complications?
With a mild form of chickenpox, the likelihood of complications is less than with moderate and severe ones. This is explained by strong immunity, which prevents the virus from causing significant harm to the body. However, the child’s condition should be carefully monitored, and if any suspicious symptoms appear, immediately report them to the doctor.
Even if there is little rash with chickenpox, it is very itchy and itchy. Therefore, scratching and the development of a secondary bacterial infection cannot be ruled out. To avoid this, you need to cut the patient’s nails short, and treat the rashes with special anti-itching agents and antiseptics.
Regardless of how the baby suffered from chickenpox, he develops stable lifelong immunity to the Varicella-Zoster virus. Recurrent disease is possible only in case of immunodeficiency.
How is it transmitted?
Chickenpox is not transmitted through household means; the route of infection is only airborne, from a sick person to a healthy person. In other words, you can become infected through the air that contains the virus. Infection occurs quickly. Very rarely, the disease occurs when the blisters open through the skin, but this is rather an exception.
For prevention, it is enough to avoid communicating with carriers of the virus. And here it is necessary to understand how long the incubation period of chickenpox lasts in order to protect yourself and your loved ones, especially if there are children in the family.
The infection is predominantly in children; cases of rapid infection in kindergarten or school are not uncommon.
Therapeutic measures for chickenpox without rashes
A mild form of chickenpox has no specific treatment. The child needs constant care and supervision so that he does not scratch the resulting blisters, as a secondary infection may additionally develop.
It is also necessary to follow a certain diet, which excludes the consumption of spicy, salty and smoked foods, as well as sweets and carbonated drinks. If not a single rash appears on the skin, this does not provide an exact guarantee that they did not occur on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. In this case, the baby should eat soft food, preferably in a liquid state. Because formations tend to very quickly degenerate into erosion.
In order not to irritate the skin of a small patient, his sleeping suit should consist of natural materials. Cotton fabrics that have good air permeability and minimally irritate the affected skin are ideal for these purposes.
Those few inflammatory elements that have appeared should be treated as early as possible with a 1% solution of brilliant green, which has an antibacterial effect. It will be possible to take water treatments (bath, bath, shower, sauna) only after the last pimple has disappeared.
Despite the mild course of the disease, the child remains a potential carrier of the disease for healthy people. And therefore, for 10-14 days the baby must be in temporary home quarantine for the safety of other people.
Today, the Varilrix vaccine is an effective prevention of chickenpox.
When and how can you get infected?
Despite the fact that infection depends on the individual characteristics of the organism, there is a certain dangerous period. It lasts about 10-21 days from the moment of infection. During this time, the virus, having entered the mucous membrane through the respiratory tract, begins to accumulate.
In other words, a person is a carrier of the virus as soon as it enters the body. The incubation period of chickenpox in adults and children may differ slightly from each other, for example, in children, especially weakened ones, it is shorter. The average is about 16 days for an adult, 14 for children.
The end of the period occurs on the 5th day after the first bubbles have formed. Then they begin to close educational institutions for quarantine. But there is an opinion that you can infect others until the last scab falls off.
It is divided into 3 stages:
The beginning is when the virus enters the body. During this period, it begins to adapt and reproduce; this process occurs asymptomatically.
Development - the multiplication of an infection leads to a primary focus and entry into the blood, due to which it begins to spread throughout the body.
Completion - characterized by the spread of the virus throughout the body, the manifestation of all the symptoms of the disease. The body begins to produce antibodies that provide protection to the body. Immunity to the disease then occurs after the patient has recovered.
How does the disease progress in a mild form if there are few rashes?
Chickenpox in children begins with the incubation period, when the virus enters the body through airborne droplets. The incubation period can range from 7 to 14 days, where there are no symptoms but the child may be contagious.
With a mild form of the disease (without fever), you need to be prepared for rashes. The first elements of the rash usually appear on the torso (in the navel area). Then they quickly move to the limbs (the exception is the palms and feet), and then to the head.
In the absence of fever, chickenpox can be recognized by the following signs.
- At the onset of the disease, the rash will appear as small red spots
- The rash quickly enlarges, turning into papules and watery blisters.
- Soon the watery rashes burst, dry out, become covered with scabs and begin to heal. This usually takes 7-14 days.
If the baby has not scratched the hated inflammations during this time, then after the scabs fall off, there will be no scars left in their place.
A mild form of the virus involves a mild rash, which usually goes away in “one wave” (i.e., new rashes do not appear in place of the blisters).
The child may complain of signs characteristic of ARVI: drowsiness, weakness, malaise, lack of appetite. Severe itching, which can prevent the child from sleeping or eating normally, so you should consult a doctor about sedatives or baths that relieve the condition.
How to treat
It should be noted that treatment is aimed at relieving the patient's symptoms. The question arises of how to treat chickenpox during the incubation period.
There is no antiviral medicine, so drugs are prescribed that fight the symptoms, not the virus itself. For example, at high temperatures - paracetamol.
Papules should be lubricated with an antiseptic and scratching should be minimized. In this case, medications can help, especially if the child is sick.
It is often difficult to explain to them why they should not scratch. It’s not for nothing that chickenpox is associated with brilliant green. Drinking regime is important, as with any disease. Nutrition should be gentle.
The virus itself is fought by protective antibodies, which provide lifelong immunity to the person who has recovered from the disease. There is an opinion that it is better to suffer from chickenpox in childhood, because in adults it is more difficult and longer.
Treatment methods for chickenpox in children
In the previous chapter, we talked about how long chickenpox lasts and how the disease progresses. Next, we bring to your attention methods of treating chickenpox in children.
The first and most important step in the fight against chickenpox on the part of the parent of a child 4 years old, 6 years old, 7 years old or 12 years old is to call a doctor at home. It is not recommended to visit children's clinics if you suspect chickenpox. After the examination, the doctor will write out recommendations for treatment and care for the child. Their contents are as follows:
Attention. It is not recommended to rely on the following information when treating a child without consulting a specialist.
- Bed rest. Can be prescribed to children for a period of 3-5 days to relieve additional stress on the body;
- Diet food. Sour, spicy, fried foods are excluded. It would be desirable to include fresh fruits and vegetables in the diet;
- Daily change of underwear and bed linen;
- The room where the patient is located should not be stuffy or hot;
- Treatment of rash lesions with antiseptic aqueous solutions. For this, the familiar brilliant green or potassium permanganate is suitable for all of us;
Treatment of the rash must be carried out precisely using a cotton swab. Otherwise, there is a high probability of infection in the sores.
- To relieve itching, you can use various ointments and creams: Fenistil Gel (reviews about it are very positive, it is used to relieve an allergic reaction, has a pronounced antipruritic effect), Acyclovir (an antiviral ointment, used mainly to combat herpetic viruses), Infagel and Viferon ( immunomodulators, reduce itching, relieve swelling, accelerate rash healing);
- It is possible to use new generation antihistamines that reduce allergic reactions and calm the nervous system. At the same time, they have a relatively small list of contraindications. The safest drugs for children include Loratadine and Citirizine (be sure to consult your doctor before use);
- It is possible to replace antihistamines with homeopathic ones. They have no contraindications and their use is possible from a very early age: Valerianahel, Nervohel, Note and many others;
- To combat fever, paracetamol-based antipyretics are used. Aspirin is prohibited for use in case of chickenpox infection. It is worth noting that temperature is a consequence of the body’s reaction to the virus and this is quite normal. It is recommended to lower the temperature above 38 degrees;
- Multivitamins to improve the overall tone of the body, as well as to increase and strengthen the immune system;
How long do children get chickenpox? - not such an important question. The important question is how quickly will your child recover? If all treatment rules are followed, this will happen immediately and easily. So, if your baby gets chickenpox, don't be upset.
Chickenpox photo
Transmission routes
Chickenpox is transmitted by airborne droplets. This can happen while talking, while coughing or sneezing. The disease is very contagious, and susceptibility to chickenpox in those who have not yet had it is almost one hundred percent, although the virus itself is unstable in the external environment and dies within a few minutes. Children in contact with sick people become infected in 90% of cases. Chickenpox vaccination is recommended for children after one year of age. But remember, it is better for a child to get chickenpox as a child than to become infected as an adult, and the vaccine is only valid for a few years. In an adult, the disease is much more severe.
You can become infected and get sick with chickenpox at any age. However, as a rule, by the age of 15, almost everyone gets chickenpox.
Those infected with chickenpox within a day, even before the appearance of pronounced symptoms and rash, are contagious. After contact with someone with chickenpox, it may take 10 to 21 days for symptoms to appear. It turns out that a person is contagious without even knowing that he is sick. And after the last rash goes away, the person is contagious for another five days.
It is possible to get chickenpox, except in very rare cases, only once, since the body develops a strong immunity to the causative agent for the rest of its life.
Antihistamines
With their help you can relieve itching and burning on the body. Basically, a child can be prescribed:
- Suprastin;
- Tavegil;
- Cetrin;
- Pipolfen.
In some cases, complications of chickenpox may occur. The mucous membranes are affected, the temperature does not go down, and chickenpox may even develop.
In this case, a solution with Miramistin, which is diluted in warm water, will be effective. They need to gargle three times a day. You can also use a solution of furatsilin. It copes well with relieving inflammation and will help you recover faster.
Antibiotics can be prescribed, but only under the strict supervision of a doctor. You cannot drink them on your own.
General rules for the treatment of chickenpox:
- Rashes must be treated from the first day after they appear.
- Itching is well relieved with antiallergic drugs.
- You need to bring down a temperature that has risen above 38.1 degrees.
- You need to give your child more vitamins with food.
- You should not walk outside or swim if you have acute chickenpox.
- The child needs to lie down more.
- Scratching wounds is contraindicated.
It is also not recommended to self-medicate, as negative consequences are possible.