Any sore throat is a sudden, acute infectious process in which the lymph in the tissues of the pharynx is the first to react. Almost every child sooner or later suffered this unpleasant disease.
Herpes sore throat in children is always an acute, spontaneous inflammatory process provoked by viruses.
This pathology occurs mainly among children from the younger age category to adolescence.
Once the virus enters the body, the disease does not appear immediately. The incubation period lasts up to 14 days, but is often 3-4 days. During the incubation period, the child is already a carrier of the infection.
Further, within 7 days after the onset of characteristic symptoms, it is still a source of infection for others, and then, while continuing to be ill, it is considered non-contagious.
Causes of the disease
This problem is caused by infectious agents - Coxsackie enteroviruses or ECHO viruses, which enter the body through airborne droplets. Infection occurs by contact or fecal-oral (nutritional) route much less frequently. The source of viruses is humans, sometimes animals (for example, birds, pigs, dogs) can be an intermediate link.
Entering the body through the mucous membrane of the nose or mouth, viruses spread through the blood and accumulate in the lymph nodes (mainly cervical), where they actively multiply. The blood carries pathogens throughout the body, but in some places they are localized in large quantities, causing severe inflammation there, including a necrotic process. Enteroviruses especially like to accumulate in the cells of the mucous membranes, then spread to the nerve tissues and muscles if there is no treatment.
Herpetic sore throat very often occurs together with other viral infections. At the same time, the patient may suffer from influenza and adenoviral diseases. Despite the fact that after recovery the child develops immunity, if another strain of the virus enters, the infection can arise with renewed vigor.
Symptoms
Briefly, herpetic sore throat manifests itself in a child’s body as follows:
- fever,
- weakness,
- increased irritability,
- a sore throat,
- loss of appetite,
- formation of ulcers and blisters in the throat,
- severe runny nose,
- enlarged lymph nodes,
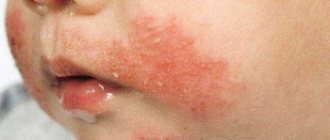
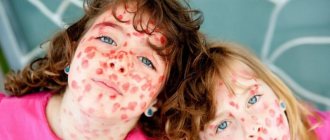
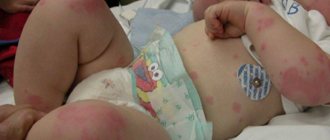
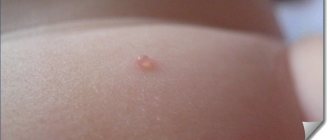
- sometimes - a rash on the body.
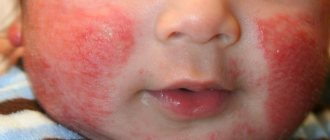
At the same time, there are no rashes on the face, bleeding of the mucous membranes, inflammation of the gums and increased salivation. These symptoms are signs of other diseases.
During the first 7-14 days, specific manifestations of the disease are not observed. There may be general symptoms, even vomiting, diarrhea, and other severe symptoms. The picture of the disease is somewhat reminiscent of the flu and a cold, but after a while it becomes more complicated. Patients complain of a sore throat, enlarged lymph nodes and other characteristic signs of pathology.
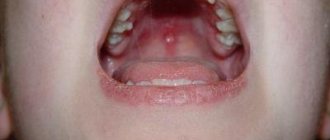
A cascade of local symptoms appears quite quickly. Papules form on the mucous membrane of the tonsils, uvula, palate and other organs of the oral cavity, which are soon filled with serous contents. After a while they burst and ulcerate. If left untreated for a long time, ulcers can unite into entire pathogenic areas of erosion; they are quite painful. Patients are forced to refuse food and water, which causes them general weakness and lethargy. The cervical and submandibular lymph nodes increase significantly in size.
As a rule, the fever lasts 3-5 days, and the rash on the throat heals after a week. If proper treatment is not provided, the disease can develop to the point of complications in the form of damage to other organs. The virus quickly spreads throughout the organs and enters the nervous tissue, causing severe damage to the brain and other central nervous system organs.
Diagnosis of herpangina
Herpes sore throat can be diagnosed by its characteristic rashes on the palate, tonsils and back wall of the pharynx.
A final diagnosis can be made after the isolation of pathogens in the contents of the follicle or antibodies to the Coxsackie virus detected during analysis. Accurate diagnosis of herpangina is made on the basis of virological and serological (elimination reaction) studies. The source of the first is pharyngeal swabs. For the second type, serum is used. The most effective laboratory method is the immunofluorescence method.
Distinctive diagnosis is based on the age characteristics of children and depends on the season and the distribution of vesicles in the mouth. Herpangina is not characterized by a rash on the face, hemophilia of the mucous membranes, there is no increased salivation and inflammation of the gums. Often these signs are accompanied by other symptoms of herpes sore throat: pain in the abdominal area, which is a consequence of muscle pain.
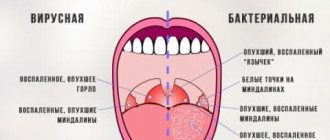
Experienced specialists can identify herpangina during examination of the throat by specific rashes. Laboratory tests are carried out to substantiate it. However, they can show pathology during the course of the disease, for example, if a bacterial infection has occurred, which will require clarification of the diagnosis and new prescriptions.
The disease can occur either alone or in combination with other enteroviral pathologies - meningitis, encephalitis, myalgia, which are also caused by this type of virus. This is why herpes sore throat in children is considered very dangerous, and the appearance of such signs signals that it is time to go to the doctor.
Photo
With the herpetic form, there are characteristic rashes in the throat, but the disease must be differentiated from many other forms of throat damage.
Content may be difficult to view
Diagnostics
If tonsillitis has a typical picture, a pediatric ENT specialist can diagnose it without problems. You don't even need to order additional tests for this. The presence of papules, vesicles and ulcers on the back of the throat, palate, and tonsils speaks for itself.
Additional studies are ordered to identify the causative agent. To do this, swabs are taken from the nasopharynx, which are sent for serological analysis methods - ELISA and PCR.
Other organs and systems are also examined to exclude complications. The child should be examined by a neurologist, cardiologist and nephrologist. It is possible to prescribe instrumental tests.
In general, in order to establish herpetic sore throat and distinguish it from other forms, the following studies are carried out:
- blood analysis;
- collection of swabs from the nasopharynx and analysis for viruses;
- examination of throat swabs;
- taking serology tests to determine the presence of antibodies to viruses in the body;
- PCR to determine the type of pathogenic viruses.
If there is damage to the central nervous system, a spinal puncture may be prescribed for subsequent analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid. If myocarditis is suspected, an ECG and echocardiography are performed.
Treatment
Diseases caused by viral agents are combated in a comprehensive manner. Sick children are isolated from society and given general and local therapy. It includes not only taking medications, but also a rest regimen, frequent drinking, and a diet that does not irritate the mucous membranes of the mouth and pharynx.
Drug therapy is aimed at relieving the main symptoms (fever, sore throat), fighting inflammation, and increasing local and general immunity. They are also treated with antiseptics to prevent the occurrence of bacterial pathologies.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Among the physiotherapeutic procedures for herpetic sore throat, ultraviolet irradiation is most often prescribed. Areas of the nasopharyngeal mucosa are irradiated with light. Thanks to the influence of ultraviolet radiation, an immunostimulating, desensitizing, restorative and anti-inflammatory effect is observed.
It must be remembered that physiotherapy is an auxiliary method that is practiced only during the recovery period, when the main symptoms of the disease have gone away. In addition, any physiotherapeutic effects based on warming the body, in particular compresses, are excluded. Due to the surge of heat, the blood supply increases, which leads to an even greater spread of viruses throughout the body. And this is a direct path to complications and increased infection.
Rinsing and irrigation
Rinsing is prescribed to prevent the development of a secondary infection. For this, solutions such as Miramistin, Biocide, Furacilin, etc. are used. The procedures are done every hour. You should not eat or drink for half an hour after the procedure so that the active substances remain on the surface of the throat. If the child is too small and cannot gargle, then draw the solution into a syringe, remove the needle, then irrigate the mucous membrane with the liquid.
You can also gargle using anti-inflammatory decoctions of various herbs. Thanks to this procedure, the swelling of the tonsils is reduced and pathogens are washed away.
As for irrigation with aerosols, they are also practiced. Sprays have an antiseptic effect, relieve pain, and coat the throat. Givalex, Ingalipt, Anginal, Hexoral and other drugs are used.
Inhalations
Compresses, inhalations and other procedures associated with the effect of heat on the body are contraindicated in the treatment of the herpetic form. Until the virus is defeated, increased blood circulation only leads to its further spread throughout the body. Therefore, in the presence of viral forms of sore throat, this method of treatment is not practiced.
Treatment with tablet forms
More often, such a sore throat is treated on an outpatient basis. The doctor selects several medications for the child that have a complex effect.
The following groups of funds are used:
- antiallergic drugs (Loratadine, Cetrin, Tavegil);
- anti-inflammatory and antipyretic (Paracetamol, Ibuprofen);
- vitamin therapy.
It should be remembered that for a viral infection, antibiotic treatment is not practiced - it has no effect.
Tonsil removal
Usually, with herpetic sore throat, the tonsils are not removed. Such a radical method in children is resorted to only during frequent outbreaks of the disease. By removing the main site of infection, the virus stops attacking the body, which eliminates possible serious complications. But not all doctors see surgical intervention as rational.
Diet
Diet recommendations are quite simple. The diet is designed so that food does not irritate the affected pharyngeal mucosa. It should be mild, unsalted, liquid or semi-liquid, light. It is also recommended to drink a lot - plenty of fluid will help you quickly overcome intoxication in the body and recover.
Folk remedies
The most popular recipes are:
- Make a decoction of string flowers, violets and calendula (1:1:2). For this, 2 tbsp. l. The resulting mixture is kept in 250 ml of boiling water for half an hour, filtered, cooled, and then used to gargle every 2 hours.
- Mix equal amounts of pine buds, elecampane root, calendula, St. John's wort, licorice root, mint, and thyme. Take Art. spoon of the mixture and leave overnight in a glass of boiling water. The recipe is enough for 2 doses.
- Prepare cold compresses with essential oils on the forehead to reduce body temperature. For this they use lavender, bergamot, lemon. The procedure is done no more than 5 times a day.
General recommendations
So, this type of sore throat in children is treated using integrated approaches. They include not only medications, but also proper patient care.
By following the tips below, you can significantly speed up your recovery and minimize the likelihood of complications:
- Maintain bed rest.
- Isolate the patient from others, since herpangina is contagious and can be transmitted to other children.
- Provide the patient with plenty of fluids. In this case, the temperature of the drink should be optimal.
- Do not warm your throat with any means to prevent the spread of infection.
- Ventilate the room 2 times a day, but do not cool it too much, so that the child feels comfortable staying there.
- Do not practice traditional medicine without prior approval from your doctor.
Sources and routes of infection
The main causes of herpes sore throat in children are periodic activation of enterovirus, especially Coxsackie. The infection can appear in the weakened body of a child with ARVI. The following factors provoke the disease:
- seasonal weather;
- decreased immunity;
- influenza or herpes viruses;
- allergy;
- intestinal disorders;
- colds, wet feet, excessive consumption of ice cream;
- drinking too cold water;
- repeated stressful situations.
There is a version that people continue to be sources of infection for quite a long time after recovery.
The herpangina virus is transmitted in the following ways:
- airborne when a sick person sneezes and coughs;
- in everyday life when using shared objects;
- contact – when communicating with a sick person, the risk of saliva and secretions from the nose and throat increases.
Once in the body, the enterovirus reproduces in the intestinal lymph nodes and then spreads throughout the bloodstream. The duration of the latent stage is 2-14 days. The strong defense developed will not work if the cause of the disease is another virus.
Prevention
The most effective method of prevention against herpetic sore throat is specific vaccination against the causative agents of this disease. Those who have recently been in contact with the patient can be given a specific gamma globulin vaccine in a specific dosage.
It is necessary to understand that herpetic sore throat is a viral infectious disease, the carrier of which can quickly spread it among peers. This means that during an outbreak of the disease in schools and kindergartens, preventive measures are immediately taken that will reduce the risk of mass incidence of herpetic tonsillitis.
Prevention consists of following the same principles as for other viral diseases.
Pediatricians recommend following the following recommendations:
- if an epidemic of herpetic sore throat has begun, isolate your children from communication with already infected peers;
- improve the immunity of the whole family;
- get rid of any infectious diseases in a timely manner;
- do not allow hypothermia and long stays outside in cold weather;
- feet should always be kept warm and dry;
- you should limit the amount of ice cream you eat so that your throat does not get too cold;
- exclude soft drinks;
- try to exclude the child from contact with substances to which he is allergic;
- Avoid stressful conditions in children - they can contribute to a decline in immunity;
- organize a course of complex vitamin therapy every six months;
- carry out hardening;
- Make sure your child has normal, sound sleep;
- walk outside more often.
Herpetic sore throat itself is of little danger to children, but its possible consequences are severe, so they must be prevented. It is better and more profitable to follow preventive advice than to later try to overcome an existing disease.
If the child is already sick, you should not self-medicate at home. Be sure to contact the appropriate pediatric specialists so that they can diagnose and prescribe treatment, which must be strictly followed. Only in this case can you defeat the disease as soon as possible and return the baby to the previous state.
Herpes sore throat in children: prevention measures
Doctors do not offer any special measures to completely eliminate the possibility of infection with the Coxsackie virus.
To prevent your baby from getting sick, follow the key rules of hygiene:
- try to reduce contact with sick people to zero;
- avoid visiting crowded places during times of exacerbation of viral infections (especially in autumn and spring);
- If your child is infected with the virus, create quarantine conditions for him.
To prevent this disease from affecting your child, give him multivitamin complexes that will strengthen the immune system.
Provide your baby with good rest and sound sleep, a balanced diet, and try to take him for walks in the fresh air more.
Treatment of herpes sore throat means combating the unpleasant symptoms of the disease and eliminating the likelihood of complications.
In general, the disease does not pose a particular danger if therapy is started in a timely manner.
A baby who has had it once becomes immune to it for the rest of his life.
Complications and consequences
If herpetic childhood tonsillitis is not treated or therapy is abandoned when the disease has not yet been completely defeated, serious complications may occur. These pathologies significantly affect the child’s health. The Coxsackie virus, which most often causes the formation of herpetic sore throat, can infect not only the cells of the throat mucosa, but also the nerve fibers.
If treatment is not started in time, this can lead to many serious consequences, namely:
- nephritis,
- encephalitis,
- meningitis,
- rheumatism,
- liver damage,
- myocarditis,
- heart defects,
- conjunctivitis,
- sepsis, etc.
All these diseases are quite serious. They undermine the child’s health irreversibly for the rest of his life. Some of them complicate not only physical, but also mental development. This means that the disease must be dealt with in the early stages and the prescribed treatment must be carried out fully. In addition, preventive measures should not be ignored if your child is healthy.
Pediatrician advice
- In case of herpes sore throat, it is very important to provide constant support to the baby’s immune system. You can do this with fortified drinks, such as freshly squeezed juices or fruit drinks. At the same time, it is allowed to use vitamin complexes purchased at the pharmacy.
- All food that the baby eats must be freshly prepared and of liquid consistency. In addition, you should exclude irritating foods from your diet, for example, very cold or hot, salty and, especially, spicy.
- Under no circumstances should you open the blisters that form on the mucous surface of the throat. The puncture can lead to very serious complications, and the illness will drag on for several weeks.
- When caring for a child, you should not wrap the throat to warm it up. Otherwise, microbes will multiply much faster, and as a result, the healing process may be significantly delayed.
- The same applies to warm compresses.
- Make sure the room is regularly ventilated. If herpes sore throat catches your baby in the winter, then you shouldn’t cancel the ventilation, you just need to cover the baby with a warm blanket and you can safely open the window wider.
- If you have been treated for several days and all symptoms have already passed, you should not stop treatment. Since the absence of symptoms may indicate that the disease has entered a latent form, you may soon experience a relapse. It is necessary to stop treatment only after the doctor’s permission, otherwise not only the recurrence of the disease, but also the development of complications is possible.
Contagiousness of herpetic sore throat
The disease is predominantly caused by Coxsackie viruses, which belong to the enterovirus family. This is one of the most common groups of pathogens that are found everywhere. This means that you can catch the infection in different ways.
Herpangina is considered a contagious disease and can easily be transmitted from one child to another. There are different routes of infection - airborne, fecal-oral, contact. Viruses can enter a child’s body through dirty water, unwashed food, through dirty hands, or through contact with household items on which sputum with the virus is left.
Most often, the virus spreads through the air from a sick child to a healthy child. Less often - by contact. Although the pathogen is transmitted from person to person, occasionally animals can also be its sources.
Children under three years of age are especially at risk of contracting herpes sore throat during an epidemic. But the disease does not spare schoolchildren, teenagers, as well as adults who have already had a sore throat.
Who is at risk?
The disease rarely develops in newborns and children in the first year of life, provided that the child is breastfed .
Breast milk contains immune cells that protect the baby. Children aged 3-10 years are most susceptible to infection.
This is due to the fact that the child actively explores the world around him, tastes all sorts of objects that may be infected with the virus, and actively comes into contact with animals, children in kindergarten or school.
In addition, young children have not yet developed certain hygiene habits (for example, washing their hands before eating, after using the toilet or going outside).
Children from disadvantaged families living in unsatisfactory sanitary conditions are also at risk.