Stomatitis is a very common pathology of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity of inflammatory origin.
This is one of those diseases that causes a lot of discomfort to the baby, so I want to know how to quickly cure stomatitis in a child.
The sooner therapy begins, the easier and faster the recovery will come.
What is aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis in children is a chronic inflammatory disease of the oral cavity, in which scarring aphthae form on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, vestibule of the mouth and gums.
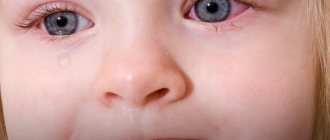
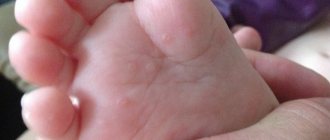
Aphthous formations are covered with a grayish-yellow coating and are located on the inflamed area of the mucous tissue. As a rule, the disease progresses with alternating exacerbations and remissions. Examples of aphthous lesions in the mouth of children can be seen in the photo.
Description of the disease
Aphthous stomatitis is a type of common inflammatory process of the oral mucosa, which is characterized by the formation of aphthous stomatitis. These are small ulcers, white in color and with a red border, formed in the form of an oval or circle. Occur singly or in large numbers.
The main symptoms of the disease include burning and pain, aggravation of which is observed when eating. Healing of neoplasms occurs on the tenth day. There are no traces left.
With aphthous stomatitis in both adults and children, the lips, inner surface of the cheeks, and palate are affected. In isolated cases, rashes are visible on the tongue.
How to identify and treat ulcerative stomatitis
Therapeutic measures to eliminate pathology are selected based on the patient’s age category, his immune system, the type of disease and the reasons that provoked it.
Complete cure occurs only with ordinary aphthous stomatitis. Infection with this disease is possible only when a healthy person uses the same objects that the sick person uses.
Symptoms of aphthous stomatitis in children and causes of the disease
The clinical picture and symptoms of aphthous stomatitis in a child depend on the form of the disease. Almost always, with lesions of the oral mucosa, children complain of:
- excessive fatigue and weakness;
- pain in the mouth when eating and brushing teeth;
- change in taste perception;
- increased salivation;
- loss of appetite.
The temperature with stomatitis is higher than normal, regional lymph nodes are enlarged, foci of infection are covered with bacterial plaque. As the infection develops, erosions with a diameter of 3–5 mm form at the site of the aphthae. In the photo of aphthous stomatitis in children, you can see foci of inflammation and changes in the tissues surrounding them.
The causes of dental disease are not fully understood. The following factors in the development of aphthous stomatitis in childhood are widely discussed by dentists:
- vital activity of coccal bacteria and Escherichia coli in the mouth;
- mechanical or thermal damage to the system;
- gastrointestinal and blood diseases;
- endocrine disorders;
- hypovitaminosis (lack of B vitamins);
- decreased general and local immunity;
- viral infections (ARVI, influenza, herpes virus);
- hereditary predisposition.
Due to the similarities between canker sores and oral herpes, people confuse the two diseases with each other. With the virus, small blisters filled with a grayish liquid appear on the cheeks. After the exudate is removed, ulcers form in place of the blisters, which makes the infection very similar to stomatitis. It is very important to correctly diagnose a dental problem, because the further treatment plan depends on it.
Cheilitis
How does it manifest?
Gray-yellow crusts appear on children's lips, lips crack until they bleed, and jams appear in the corners. What are the reasons? Children have poor control over their sensations and often lick and suck their lips on the street. If you add to this insufficient hygiene and mouth breathing, cheilitis will not take long to occur.
How to treat?
You need to visit not only a pediatric dentist, but also a neurologist, allergist and endocrinologist. Almost everyone licks their lips on the street, but not everyone gets cheilitis. Doctors from different fields, after conducting an examination and collecting the necessary information about the child, will be able to make an accurate diagnosis.
What can parents do?
Some babies' lips are sensitive to ultraviolet light. Therefore, jams, crusts, and cracks on the baby’s lips can appear in warm and sunny weather. For prevention, of course, everyone without exception needs to use special protective creams or hygienic lipsticks before going outside. And if the child has any allergic problems, this skill should be brought to automaticity.
Types of aphthous stomatitis
According to ICD-10, aphthous stomatitis and other infections with the formation of aphthae are coded as “K 12.0”. Each form of the disease has its own clinical picture.
| Form of aphthous stomatitis | Clinical picture |
| Fibrous | It is characterized by impaired blood circulation in the epithelial layer, resulting in the formation of aphthae covered with bacterial plaque. Localization of lesions is the inner side of the lips, the sides of the tongue, the zone of transitional folds. |
| Necrotic | Occurs with slight destruction of epithelial cells. Necrosis of the epithelium leads to the appearance of numerous aphthae and ulcers with necrotic masses. Aphthae are not painful. |
| Glandular | Changes in the ducts of the minor salivary glands are noted, which causes partial or complete disruption of their functions. Aphthae are localized in places where salivary ducts accumulate. |
| Scarring | Grandulons (structural units of the salivary glands) are affected. The lesions are located on all parts of the oral cavity, in particular on the pharynx and soft palate. Aphthae quickly develop into painful ulcers up to 2 cm in diameter. |
| Deforming | It is considered the most severe form of stomatitis in children. There are profound changes in the connective tissue layer. Ulcers can migrate to all parts of the mouth. As wounds heal, scars and welts form. If the lesions are localized in the corner of the mouth, microstomy (narrowing of the oral cavity) may form in the future. |
Recommendations for parents
Before the baby gets to the doctor, ease her condition - let's rinse her mouth more often with decoctions of medicinal herbs. Do not give rough and hot food, or better not force him to eat at all. More warm drinks and rest. You can numb the pain with a weak anesthetic solution.
Always make sure that your child eats well, or better yet, regularly takes a complex of vitamins for children, like Doromarin, which has shown itself to be effective for the prevention and treatment of thrush (in combination with medicinal drugs). The recovery process goes very quickly, the baby becomes more active and copes with many diseases more easily, including stomatitis.
The natural composition of children's vitamin DoroMarine (Far Eastern kelp, also known as angustata, sea cucumber extract and sea calcium plus fruit juice for taste) allows it to be taken by children from 3 months to 16 years. Pleasant to the taste, healthy, it will strengthen the general condition of the child’s body, including a guaranteed effect against stomatitis.
Thanks to the strong immunocorrective ability of the components of Doromarin a, it is effective against most childhood diseases. These vitamins do not cure, they give the body strength to defeat pathogenic cells on its own. Doromarin not only strengthens the immune system, it provides relief from symptoms plus comprehensive recovery from stomatitis.
For stomatitis (treatment or prevention), the following properties of Doromarin vitamins are important:
- reduce the aggressiveness of microflora;
- protect the mucous membrane by covering it with a thin layer of jelly-like substance;
- absorb harmful substances from the oral cavity;
- reduce dysbacteriosis, microflora thrush;
- heal wounds, burns, ulcers, cracks;
- suppress the activity of harmful bacteria, especially Candida;
- slight antimicrobial effect;
- immunostimulating effect;
- effective against gum disease.
Most of the properties of the DoroMarine complex are due to the effectiveness of alginic acid and its derivatives, the content of which in DoroMarine is up to 55% (of the dry residue). This natural therapeutic and prophylactic product for children is ideal for children who are very physically active, whose environment has changed, who have contact with sick children (kindergarten, school, sanatorium), who suffer from allergies, various infections and viruses more often than twice a day. year.
These vitamins are indispensable for immunity for weakened children who eat poorly or have metabolic problems (specific diseases, hormonal, including diabetes, hypothyroidism, etc.). It is definitely recommended for children who constantly watch TV or sit in front of the computer. This will allow them to improve their vision and have a beneficial effect on the condition of the whole body. There are many positive reviews from satisfied parents who recommend taking the vitamin complex for children Doromarin.
Remember, stomatitis is not scary for healthy kids!
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis in children
The dentist will tell you how to treat aphthous stomatitis in a child, based on the clinical picture. In 96% of cases, in the inter-relapse period, sanitation of the oral cavity is carried out, including treatment of carious lesions, removal of pigmented plaque and tartar. Further treatment is prescribed by the doctor and carried out by the patient at home.
Mouth rinses
Antiseptic solutions such as:
- 0.05% chlorhexidine solution;
- miramistin;
- hydrogen peroxide;
- Furacilin.
Antiseptics are active against various types of bacteria and protozoa. In the presence of aphthae, rinsing is carried out to cleanse the wounds of plaque, and in case of ulcers, to prevent secondary infection.
Local treatment is carried out up to 4 times a day after brushing your teeth.
To combat dental disease, “Rotokan” and “Stomatofit” are also used. The preparations contain plant components that have anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and wound-healing functions. Rinsing should be done every 4 hours.
Local treatment of aphthae
After antiseptic treatment, to accelerate epithelization, use:
- citral solutions;
- vitamins: A, E, C and P;
- ointments with Kalanchoe juice and propolis.
Medicinal substances are used in the form of applications for 3–5 minutes 2 times a day. Under the influence of biological substances, local immunity rises and tissue regeneration accelerates.
Drug treatment of aphthous stomatitis in children
Drug treatment of dental disease in children includes:
- To reduce pain, use a suspension of anesthesin in oil or a 2% solution of lidocaine (topically).
- To stop the growth of aphthae, use corticosteroid ointments (“Hydrocortisone”).
- Immunomodulators - drugs that activate the defenses of the immune system (“Cyclosporine”);
- Orally – antihistamines: “Tavegil”, “Suprastin”, “Gistaglobin”.
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics (for extensive lesions): Amoxicillin, Flemoxin Solutab, Amoxiclav suspension.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes as an additional source of nutrients for food.
Aphthous stomatitis in children should be treated with medications under the strict supervision of a physician. Since many medications have side effects, to prevent the consequences, the dentist selects the dose of the substance that will not harm the child’s health and cope with the treatment of the disease.
Folk remedies
At home, infusions of medicinal herbs and freshly squeezed vegetable juices are used to treat aphthous stomatitis. Among the folk remedies that can be used:
- fresh carrot juice;
- white cabbage juice;
- horseradish pulp diluted with boiled water;
- decoction of onion peel;
- Linden blossom;
- chamomile flowers;
- Oak bark.
Each product is infused in a water bath and used when the substance has cooled to room temperature. Vitamins and other biological substances work in the same way as therapeutic drugs. But due to the low concentration of active ingredients, the use of traditional medicine alone will not bring the desired result.
Inhalations and physiotherapy
For a quick recovery, doctors refer children to physiotherapy. Effective treatments for aphthous stomatitis include:
- laser therapy (to accelerate tissue healing);
- irradiation with ultraviolet rays (to destroy infectious agents).
Procedures are carried out once every 1–2 days. The treatment period is 7–10 days.
Homeopathy for aphthous stomatitis
Homeopathic remedies are used only at the initial stage of the disease. Treatment of aphthous stomatitis using this method involves the use of products based on borate and mercury oxide: “Borax”, “Mercurius solubilis”. These drugs fight halitosis, bleeding gums, excessive salivation and swelling of the mucous tissue.
"Arsenicum album" and "Acidum uldum" are prescribed for multiple ulcerative lesions of the oral mucosa, accompanied by severe pain in the mouth.
Maintaining hygiene rules
In the treatment and prevention of dental diseases, the correct technique for cleaning the oral cavity plays a special role. Hygienic rules include:
- Brushing your teeth with a toothbrush and toothpaste should be done 2 times a day: in the morning and after dinner before bed.
- When brushing your teeth, the brush is placed at an angle of 45 degrees to the surface of the enamel.
- The correct movements of the brush are from the gum to the cutting edge.
- Every evening it is recommended to use dental floss or irrigator to clean the interdental spaces.
- The final stage of the hygiene procedure is cleaning the tongue using the back of a toothbrush or a special oval scraper.
- After each meal, you should rinse your mouth with clean water or special rinses.
If you have orthodontic structures, crowns and orthopedic bridges, it is recommended to consult with your dentist about oral care products and items. Based on the condition of the child's mouth, the doctor selects individual items for cleaning teeth and gums.
Diet for stomatitis
The nutritional habits of a child with aphthous stomatitis will vary depending on the severity of the infection.
During the acute period, it is better to give food in semi-liquid form (fruit and vegetable purees, cereals). The diet should be rich in vitamins, minerals and amino acids. Lean meat soups are served at room temperature.
To normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, you need to give your child a decoction of chamomile, lactic acid products and freshly squeezed juices from vegetables and fruits.
Nutrition during rehabilitation should be varied. The diet includes: boiled fish and meat, fresh vegetables and fruits, decoctions of anti-inflammatory herbs.
Prohibited consumption: carbonated drinks, flour products, fried and spicy foods.
Prevention
- Be careful when feeding your baby with a spoon or bottle;
- remove all small objects and objects with sharp edges (plastic, metal toys) higher up;
- give the child non-traumatic toys (soft, rubber);
- establish the correct diet for the child: exclude hot, very cold, pickled and foods containing acetic acid;
- exclude seeds, ensure that bones are removed from the fish;
- Do not self-medicate with medications without consulting a doctor.