Causes of wet cough in children
Phlegm is mucus that is produced by the glands of the trachea and bronchi. Sputum is pathological in nature, that is, it appears with the development of any disease. Although normally mucus is also produced, but in an amount that does not cause a cough reflex.
The sputum is often mixed with sinus secretions. This occurs in children suffering from a runny nose, in which mucus from the nose flows down the back of the throat into the trachea, where it mixes with sputum and is coughed up.
- Non-infectious (overproduction of mucus, allergies, bronchial asthma).
- Viral infections (ARVI, viral rhinitis).
- Bacterial infections (sinusitis, tracheitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, whooping cough).
Based on the color of the coughed up sputum, you can suspect the cause of a wet cough:
- Transparent, liquid, mucous membrane appears due to allergies or viral infections.
- Transparent, thick, glassy cough in bronchial asthma.
- With impurities of pus, yellowish or green sputum due to a bacterial infection.
A wet cough can be cured only based on the cause of its occurrence. Since standard treatment is often prescribed, cough in children develops into a protracted cough, when it becomes unclear whether there is any disease or whether it is simply overproduction of mucus.
Important! Children under 2 years of age are strictly prohibited from giving mucolytics - drugs that thin out sputum. It is also not always advisable to prescribe these drugs to older children, since compliance with simple hygiene rules successfully replaces the use of mucolytics.
How and with what to treat a wet (wet) cough in a child?
Treatment of wet cough in children should include the following principles:
- An allergic cough goes away when the child’s contact with the allergen is limited. Until this point, taking antihistamines only relieves symptoms. Therefore, in order to get rid of a prolonged allergic cough, you should devote all your efforts to searching for the allergen, cleaning and purifying the air in your living space.
- The viral infection goes away on its own in 5-7 days if hygiene is observed. Most antivirals have no effect on the duration of a cold. But it should be remembered that in case of a viral infection there is no point or indication to take antibiotics.
With or without fever
An increase in body temperature is caused by specific compounds - pyrogens. They can be infectious or non-infectious. Infectious include fragments of the shell of bacteria, viruses, and protozoa. This explains the increase in body temperature at the onset of infection. Further, immune mechanisms are added to the mechanism of development of fever; they also ensure a rise in temperature during exacerbation of allergies.
A wet cough in a child without fever may be a consequence of uncomplicated rhinitis, a sluggish allergic process, or hyperproduction of mucus while taking expectorants.
Important! If the child is lethargic, feels unwell, behaves inappropriately, is choking, does not want to drink at a temperature below 38 °C, then an antipyretic drug should be given immediately.
For colds, acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections
With a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract, expectoration of sputum is a consequence of rhinitis. That is, first the development of inflammation of the sinus mucosa occurs. Mucus drains down the back of the throat, spreading infection and irritating cough receptors.
This cough should be treated as follows:
- Rinsing the nose with saline solutions. You need to buy a 0.9% sodium chloride solution, which is sold in every pharmacy. The solution is poured into a washed nebulizer from under the vasoconstrictor drops and applied up to 5-6 times a day. You can pour the solution into the nose directly from a syringe without a needle and let the child blow his nose or use a blow dryer. Pharmacy salt drops – Aquamaris, Salin.
For obstructive bronchitis you should:
- Observe all of the above.
- Antispasmodics, such as No-shpa to relieve bronchospasm and eliminate bronchial obstruction.
- In some cases, Eufillin is prescribed to expand the lumen of the bronchi.
Bacterial bronchitis with coughing up purulent sputum and high fever can only be treated with antibiotics. If all the symptoms are accompanied by shortness of breath, then we are talking about pneumonia - pneumonia.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of an X-ray examination of the lungs. The disease is treated only under the guidance of specialists and often in a hospital setting.
Medications
Treatment of wet cough in a child in cases of severe bronchitis and pneumonia includes the use of drugs:
- Expectorants are represented by herbal preparations - Alteyka, Mucoltin, Gerbion. Synthetic medications with a mucolytic effect - Ambroxol (Lazolvan), Bromhexine. Medicines are sold in the form of syrups, tinctures, tablets and injections. (Useful article - selecting expectorant syrup for a child with a cough)
List of the most effective oils:
- Eucalyptus.
- Tea tree.
- Coniferous.
- Cypress.
- Mint.
If you have a device - a nebulizer, then with its help you can recover from a wet cough much faster. In severe cases of obstructive bronchitis and frequent attacks of suffocation, drugs that dilate the bronchi are used - Berodual, Budesonite (Pulmicort). Medicines are prescribed only by a doctor. It is strictly forbidden to take them on your own.
How to treat a wet cough in a child. How to treat a prolonged wet cough in a child
The disease is capricious and insidious. She knows how to cleverly disguise herself and not give herself away for many years. But, even with timely treatment, the stubborn disease reminds itself for a long time with painful symptoms. We're talking about a cough. A prolonged wet cough in children is a headache for mothers.
What is this – the beginning of the development of a new disease or a long period of recovery? Is a wet cough that does not go away for a long time dangerous? What to do and how to help the baby?
This insidious cough
Nature has endowed humans with a powerful set of defense mechanisms. One of the guardians of health is cough. Cough is the body’s innate reflex ability to clear the airways of unnecessary fluid and contaminants (bacteria, toxins, dust, foreign substances, smoke).
The mucous membrane of the human lungs and bronchi regularly produces specific mucus. Mucous secretions are produced by glandular cells that line the lung tissue. Immune bodies contained in mucus combine harmful substances and help remove them. Doctors call this cough productive (wet).
A healthy baby coughs up to 10 times a day (usually in the morning), freeing the respiratory system from harmful microparticles.
In infants, the natural cough reflex is often caused by milk, mucus from the nose or tears entering the respiratory tract. A healthy cough occurs in babies when teething (the cause is excessive salivation). “Dental” cough lasts throughout the entire period of teething.
When inflammatory processes begin in the body, the number of expectorations increases by 2-5 times. In this case, mucus acts as an irritant, provoking a defensive response from the body - coughing. The following situations in children become alarming signals:
- There is a loss of appetite.
- When coughing, chest pain begins.
- Cough with sputum is accompanied by shortness of breath.
- The high temperature rises to +38-39⁰ C.
- A wet cough does not go away for a long time (from 2 weeks).
- The color of the mucus discharge becomes green and brown.
- The cough is accompanied by wheezing and heavy breathing.
- The cough reflex interferes with a good night's rest.
- The baby becomes lethargic, sleepy and irritable.
- The child coughs continuously, unable to stop.
Patient care and suitable microclimate
If a child has a wet cough without a high temperature or with an increase in temperature, there is no need to limit the baby’s life activities. The child should move actively to avoid sputum stagnation, walk outside and breathe fresh, cool air. The apartment must be wet cleaned at least twice a day and dust must be removed well. It is important to roll up carpets and replace down pillows and duvets with synthetic ones.
The thermometer in the room should be below 20 °C. The air should not be overdried by heaters. You can place a bowl of boiling water next to the bed so that the water vapor humidifies the air. It is better to use special humidifiers. If the baby has allergies or bronchial asthma, then air purifiers have a therapeutic effect.
source
Can a child cough due to snot?
One of the common causes of cough is a large amount of mucous secretions in the nasopharynx. Coughing from snot can occur at any time, but children cough more often at night. In a horizontal position, the mucous secretion does not come out through the nasal passages, but flows inward, irritating the respiratory tract.
When a pediatrician performs auscultation, wheezing and extraneous noises are not detected, the doctor can confirm that breathing is clear and even. In this case, the cause of the development of the cough reflex is the mucous secretions produced in the nasal cavity.
The nature of cough with rhinitis depends on the volume of discharge that flows down the back wall of the nasopharynx. A dry cough with snot occurs if mucus constantly gets into the larynx and trachea. This is how the child’s body gets rid of foreign bodies in the respiratory tract.
Thanks to the cough reflex, the possibility of mucus entering the bronchial tree is prevented. If they drain into the lower respiratory tract, breathing will become difficult.
A wet cough from snot occurs in situations where mucous secretions from the nasopharynx flow into the trachea. With bronchospasm, the child begins to cough it up, and the sputum comes out through the mouth. This development of events is possible when the baby’s snot has a consistency similar to water and flows uncontrollably. Due to mucus entry, the functioning of the respiratory system may be impaired. In children, such a wet cough, which appears due to snot, often provokes the development of secondary inflammation in the bronchi and trachea.
Parents should be alerted to a wet, strong cough in children who develop thick snot in their nose. They cannot drain into the larynx, so it is necessary to show the baby to the pediatrician. There is a high probability that the inflammatory process affected not only the nose, but also the lower respiratory tract.
Causes of coughing from snot
Under the influence of various irritants, the nasal mucosa secretes mucus to mechanically remove the irritating agent. Since the nasal cavity has two communications, secreted mucus can be expelled or flow down the walls of the respiratory system, causing a cough reflex. It is difficult to explain to young children that when snot accumulates in the nasal cavity, they need to blow their nose out. The result is snot getting into the child's throat and other respiratory tracts.
There are several reasons why mucus is released in the nasal cavity:
Cough due to an allergic reaction
- allergic reaction;
- physiological runny nose;
- inflammation of infectious etiology;
- foreign body in the nasal cavity;
- sudden changes in ambient temperature;
- hypothermia of the child's body;
- injury;
- runny nose from teething.
Main reasons
Parents of children under 3 years of age are more likely to experience a reflex cough that appears against the background of rhinitis. The likelihood of developing such a problem in a 1-year-old child is higher than in a schoolchild. This is due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the respiratory tract in children. In addition, at this age, children cannot blow out mucus that has accumulated in the nose.
Most often, the reflex cough reflex appears at night and after sleep. In this case, the child will complain not only about snot and cough. Discomfort is caused by a sore throat, rising temperature, swollen nasal mucosa, causing nasal congestion.
Among the main causes of rhinitis, which leads to cough, are:
- damage to the respiratory tract by viruses and bacteria;
- allergic reactions;
- improper indoor microclimate (drying of mucous membranes due to excessively dry air);
- entry of a foreign body into the nasal cavity;
- enlarged adenoids;
- anatomical features of osteochondral tissue, changes in structure as a result of injuries;
- dysregulation of the tone of blood vessels passing through the nasal cavity.
Sometimes a child coughs and suffers from increased production of mucous secretions due to malfunctions of the digestive organs. If you have problems with the stomach, pancreas, or gall bladder, the upper parts of the gastrointestinal tract—the pharynx and nasopharynx—are affected. Their irritation leads to the development of chronic inflammation and causes increased production of mucous secretion.
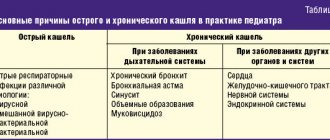
How to distinguish coronavirus from colds, flu and ARVI: distinctive signs!
There are several long-known types of colds in medicine - acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, influenza. Due to the emergence of a new virus, it is important for every person to know how to distinguish coronavirus from a cold. Experts are conducting serious research to explain how COVID-19 differs from other viral infections.
Coronavirus traits
The new virus has added “diversity” to a number of acute inflammatory diseases. The difficulty for scientists is that the symptoms of all infections of this kind are similar, differing only in the severity of the disease.
Research results make it possible to understand how to distinguish coronavirus from a cold. Coronavirus infection differs in symptoms and effects on the human body. Yes, such diseases have quite a lot of similarities, but there are some that clearly indicate the penetration of the SARS-CoV-2 virus into the body.
Main signs of COVID-19 disease:
- Heat.
- Dry cough.
- Feeling of lack of air, shortness of breath.
- A sharp deterioration in health, general weakness, thirst, lack of appetite.
When studying a new virus, scientists first take into account the clinical picture of the disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. WHO and experts from the Center for Disease Research have systematized the signs of coronavirus disease, colds, and flu. The differences between them are presented in the table below.
The table is compiled on the basis of comparative diagnostics carried out by specialists from WHO, CDC, American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, Business Insider. The presented data will make it possible to determine with a high degree of probability which disease is beginning in a person, how to distinguish coronavirus from a cold, coronavirus from the flu.
The difference between COVID-19 and colds
Some symptoms of influenza and coronavirus infection are common, but a runny nose when infected with SARS-CoV-2 practically does not occur. Flatulence, sneezing, and intestinal upset do not occur with COVID-19.
A common cold is characterized by a runny nose, sneezing, sore throat, and joint pain. They are usually not accompanied by fever or cough. These symptoms distinguish coronavirus from ARVI.
With influenza caused by any strain, there is always a high fever, dry cough, pain in the joints, head, and severe weakness. Sometimes severe flu is accompanied by a runny nose, which is not typical for COVID-19.
- Have you been checked for the presence of coronavirus? The symptoms of all colds, including coronavirus, are especially similar in the first stages of the disease, in its latent course, in a mild form. The further course of the coronavirus infection is accompanied by an increase in temperature to critical values, and a sharp dry cough is added.
Severe forms of COVID-19 lead to the infection penetrating the lower respiratory tract, and the disease becomes similar to atypical pneumonia.
Symptoms added:
- temperature rise to 39 °C;
- dry hacking cough;
- shortness of breath, lack of air;
- tightness, pain in the chest.
When a person who thinks he has a cold develops such symptoms, he should immediately call a doctor at home. It is not a fact that coronavirus will be diagnosed. Maybe it will be a protracted form of ARVI, with a bacterial complication.
Therefore, it is important not to miss the moment when a cold becomes severe and to urgently begin targeted treatment. Qualified advice on treatment can only be given by a local therapist who has known the person for a long time and will take into account the somatic pathologies he or she has when choosing prescriptions.
The doctor will confidently, based on visible symptoms, clarify the type of cold and explain to the patient how coronavirus differs from influenza. A medical consultation will allow the patient to reassure that he has a cold and not the SARS-CoV-2 virus, and to feel confident in taking the prescribed treatment.
Coronavirus is different from flu:
- manifestation of fever, chills;
- the appearance of an annoying dry cough with shortness of breath;
- general deterioration in health to extreme fatigue.
The incubation period of coronavirus infection is from 2 days to 2 weeks. At this time, a person does not feel the symptoms of a cold and becomes an active carrier of infection.
The flu literally “knocks down” the sick person from 1-2 days from the moment of infection. Symptoms similar to COVID-19 - high fever, cough, exhaustion, headache - should not alarm a person; it is more important to undergo an examination as soon as possible and begin symptomatic treatment.
It is important to know the difference between coronavirus and ARVI in order not to miss the onset of the disease. These pathologies are transmitted through contact and respiratory routes.
The key point of pathogens is that coronavirus disease is provoked by the penetration of a mutated RNA-containing virus into the body. ARVI is caused by more than 3 hundred types of infection - the most common are rhinovirus, adenovirus, and reovirus.
The source of infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus is almost always an infected person. Viruses spread through breathing, especially actively - from sneezing, coughing, and talking at close range. Once on the mucous membranes and in the respiratory tract of a healthy person, viruses quickly penetrate into their lower sections and actively multiply.
Another method of transmission is contact. When sneezing or coughing, a sick person covers his face with his palms. It is important to already have a supply of disposable paper napkins and change them every time.
Interesting! How to make hand sanitizer
To prevent the virus from settling on the skin, you must frequently wash your hands with soap and disinfectants. Otherwise, the tenacious coronavirus passes to a healthy person during a handshake or when using common household items.
At the end of the incubation period, the symptoms of all colds begin to increase at different rates. With ARVI - gradually, with influenza and COVID-19 - at a rapid pace.
The duration of the incubation period is different for each person who is a carrier of the virus. It depends on the strength of the immune system and the presence of vaccinations.
During the incubation period, the virus lurks in the body, then, against the background of stress, hypothermia, and other factors, it begins to rapidly perform its destructive function. During its latent course, the presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus can be determined using special diagnostic equipment.
Summing up
- The presence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the body can be determined during the incubation period if the clinic has special equipment, a laboratory, and a sufficient number of tests.
- The difference between the course of a cold, flu and coronavirus infection can be determined by the expressed symptoms. At the initial stage of the disease, the virus manifests itself weakly, but when it “takes root” in the body and finds vulnerable spots, its symptoms appear sharply.
- It is important to know the differences between colds and acute respiratory viral infections so as not to panic and treat an incipient disease calmly and confidently.
You may be interested in other news:
A lonely old man was starving for several days in home quarantine!
She could have stopped the coronavirus epidemic, but she was silenced!
Russian mission to assist Italy is a cover for intelligence gathering, says British expert!
How soon will the coronavirus end in Russia? Forecasts and news!
Doctors warn of a new wave of coronavirus!
Chinese doctor disappeared after complaining about concealment of facts about coronavirus!
The Americans attacked the French! How will France respond to this?
The date for peak mortality in the United States from coronavirus has been determined!
The coronavirus pandemic will change the world order forever!
A new deadly virus from China has begun to kill!
Will Putin remain in power after the coronavirus epidemic?
Please leave your comments! Thanks for liking and subscribing to my channel! You will find even more interesting news on my website!
Source: https://zen.yandex.ru/media/id/5e6f33d33e1cee725cf96a15/kak-otlichit-koronavirus-ot-prostudy-grippa-i-orvi-otlichitelnye-priznaki—5e8ccfe347d6d36af987eb6f
How and how to treat a child’s cough from snot
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to determine the reason for the cough and rhinitis. It is important to stop the source of infection and normalize nasal breathing. A cough that appears from a runny nose cannot be ignored; it can provoke the development of pneumonia.
In infants, excess mucus in the nasopharynx, which flows down the back wall, can cause worse weight gain. Due to difficulties with nasal breathing, children of the first year of life have difficulty sucking milk.
If during rhinitis you can see mucus flowing down the back wall, then a combination therapy regimen is prescribed. Necessary:
- change the microclimate in the room;
- regularly rinse the nasal passages;
- use vasoconstrictor drops.
Depending on the causes of a runny nose, antiviral, antibacterial and antihistamine medications are prescribed.
Inhalation with active substances can alleviate the condition. In case of pronounced edema, it is recommended to carry them out with children's Naphthyzin mixed with saline. If nasal breathing is slightly impaired, then you can breathe using a nebulizer with mineral waters (Essentuki, Borjomi) or saline solution.
If a cough with rhinitis appears due to the anatomical features of the structure of the nasal septum (or its curvature, fracture as a result of injury), then nasal breathing can be alleviated and the condition can be normalized through surgery.
It is recommended to humidify the air as much as possible in the rooms where the baby is, and use essential oils, which, when inhaled, activate the body’s defenses. The most commonly used esters are tea tree, eucalyptus, fir, pine, and thuja.
Sinus rinsing
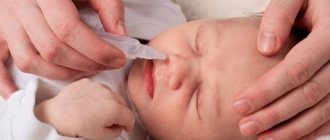
The technology for rinsing the nose depends on the age of the child. Infants who cough due to rhinitis can be instilled with 1-2 drops of saline solution or saline solution prepared at home. You can make it from 9 g of salt diluted in a liter of water.
After instillation, the contents of the nose liquefy and can be drawn out using an aspirator. The crusts are removed with ordinary cotton swabs.
Children who know how to blow their nose can rinse it with a five-cc syringe. Saline solution is drawn into it and injected under pressure into one and the other nostril alternately. These washes remove bacteria and viruses.
Also, to clean the nasal cavity, pharmaceutical medications made from sea water with the addition of trace elements (calcium, zinc, magnesium) are used. For nasal discharge, AquaMaris, Humer, Quicks, Salin are indicated. Aqualor norm in the form of a spray is prescribed to children from 6 months.
Vasoconstrictor drops
If it is necessary to normalize nasal breathing, relieve swelling and reduce the amount of mucus produced, then use nasal agents designed to constrict blood vessels. These are symptomatic medications that do not eliminate the cause of the disease, but alleviate the symptoms.
The effect occurs within 10 minutes after instillation. It lasts for several hours.
Uncontrolled use of vasoconstrictors is unacceptable, because they are addictive. You can put drops into the nose of a child who coughs in his sleep for no more than 5–7 days in a row.
They can appoint:
- Nazivin;
- Sanorin for children;
- Nazol Baby;
- Vibrocil;
- Otrivin;
- Tizin-xylo.
When choosing, they are guided by the age of the child, his condition, and the density of the secreted secretion.
Antiallergic drugs
A prolonged runny nose with clear or white snot, in which discharge flows into the pharynx or trachea, can be allergic. With this type of rhinitis, the child may cough at night. The condition can be alleviated by using appropriate medications that block H1 histamine receptors. Zyrtec, Cetrin, Fenistil, Alerzin are often recommended.
In case of confirmed allergic rhinitis, medications that constrict blood vessels can be used simultaneously with taking antihistamines. Vibrocil is a remedy that has a local antiallergic effect. Nasal spray Cromohexal, Histimed, Tizin Alergy can also be prescribed.
The duration of treatment is determined individually for each patient. Systemic medications are prescribed for 5–10 days, and nasal antiallergic sprays can be used for a long time even after snot, if it is impossible to eliminate the action of the pathogens (for example, if you are allergic to poplar fluff or pollen).
Antiviral drugs
If the cause of rhinitis and cough reflex is a viral infection, then Interferon, Grippferon, Nazoferon are more often used.
These drugs have anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and immunomodulatory effects. They also help the body fight germs. In children with a cough without snot and fever, these medications can be used to stimulate the body's defenses. But they must be used at the very beginning of the disease; treatment lasting more than 5 days is not advisable.
Antibacterial drugs
When rhinitis is complicated by a bacterial infection, it is necessary to choose the right treatment. A night cough, in which the baby has yellow-green snot, should alert you. It is necessary to prescribe competent treatment.
Local antibacterial agents popular among adults (Bioparox, Polydex with phenylephrine) are not allowed for use by children. Pediatricians prescribe Isofra for ages over 1 year. This drug also has an anti-edematous effect.
If inflammation begins in the paranasal sinuses and a wet cough appears, then it is necessary to use systemic antibiotics. Doctors usually prescribe broad-spectrum antibacterial agents that can help the body cope with upper and lower respiratory tract infections.
How to treat a cough from snot in a child
How to treat a cough from snot in a child? This is the question parents ask when their baby has no fever or feels unwell, but has a cough. As a rule, children begin to cough after a runny nose develops, especially if the mucus produced is liquid. What is the reason for this, is it necessary to treat the disease with cough medicine?
Where does the problem come from?
Coughing is a reflex reaction of the body to irritants that enter the respiratory tract. The anatomical shape of the nasopharynx has such a structure that sometimes when you have a runny nose, mucus flows down its wall, gets on the ligaments, irritates them, resulting in a cough from snot. Even if a child blows his nose, sputum still gets into the respiratory tract. It is the mucus from a runny nose that irritates the throat.
Therefore, you need to fight not with the consequence, but with its cause - a runny nose. It is known that the body protects itself by coughing, so if the nose treatment is correctly prescribed, the problem will be eliminated as such. If you do not pay attention to such a “trifle,” a runny nose can develop into quite serious complications: the appearance of sinusitis, rhinitis, cysts. Likewise, improper treatment of cough can turn into chronic forms. It is necessary to show the child to the pediatrician and ENT specialist. The pediatrician will listen to the lungs for wheezing, and the ENT specialist will examine the condition of the nose.
When it turns out that a cough from snot appears due to damage to the upper respiratory tract, this may indicate developing laryngitis or tracheitis.
Symptoms of laryngitis: dry mouth, burning throat, periodic bouts of dry cough, swelling, sore throat. Laryngitis is treated with inhalations.
Tracheitis is characterized by inflammation of the larynx. Symptoms: a strong cough without clearing the throat in a child appears in the morning. So, it is absolutely impossible to suppress the disease with cough medicine, because the deterioration of the condition is not caused by the virus, but by the appearance of a runny nose.
What should I do?
Discharge from the nose appears as a result of changes in the functioning of its internal membranes. The reasons can be very diverse: allergies, foreign objects, acute respiratory viral infections, other diseases, and so on. The nature of snot is divided into two types: thick and liquid. Most often, a cough occurs with liquid secretions, which more easily fall on the back wall of the nasopharynx.
To treat this problem in children, it is better to primarily use drops.
They are gentler than sprays. Only a doctor can prescribe an effective drug against the common cold. There are many remedies of varying degrees of action for the appropriate age. It is not worth buying drops or prescribing the dosage yourself because parents do not know what caused the runny nose. Plus, the treatment must be comprehensive, since there is a runny nose and cough. First you need to eliminate the snot, and then soothe your irritated throat.
However, despite this, parents can take a number of measures that will ease the course of the disease in the baby. Treating with home remedies should also be done with caution. First of all, you need to promptly remove mucus from the nose, as well as the mucus that the child coughs up, and make sure that it is not swallowed.
This should be done with a soft napkin or handkerchief so as not to create irritation around the nose. In addition, it is necessary to teach children to blow their nose, since snot interferes with full breathing. Avoid overheating or hypothermia of the baby. Feet should always be kept warm.
The children's room must be kept clean, and the room temperature should not exceed 20 degrees. Airing before bed is useful. Air humidification with special devices is allowed.
Walking in the fresh air is not prohibited if the baby does not have a fever and the weather outside is warm enough.
Aromatherapy will help relieve a runny nose. Just add a couple of drops of eucalyptus or mint oil to your bath. Healing steams can actively fight germs in the nose.
It is allowed to rinse the nose with sterile sea water, especially with very heavy mucus secretions.
Drinking plenty of fluid also has a positive effect. Linden tea and drinking warm milk with honey at night will help eliminate colds and runny nose. It is worth remembering that honey cannot be dissolved in hot liquid, as it loses its healing properties.
During a cold, a child should consume sufficient amounts of vitamins. This will strengthen the body's natural defenses.
Massaging the wings of the nose helps remove snot. In addition, you can massage the bridge of your nose from top to bottom. Do it at least three times a day.
Conclusion on the topic
Cough and snot are interconnected. When a child feels fine, but suffers from a cough and runny nose, then the reason lies in the mucus that has entered the respiratory tract.
Parents should never try to treat symptoms on their own, thinking that the problem will go away on its own. If medical assistance was prescribed on time, it will relieve the baby from painful discomfort, so do not neglect a visit to a specialist.
lor03.ru>
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion
Many parents are interested in knowing how Komarovsky proposes to treat the cough reflex that appears due to excess mucus in the nasopharynx. In his opinion, self-medication has no place when coughing attacks occur at night. A sick child must be shown to a doctor. Therapy is selected individually depending on the established diagnosis.
According to Dr. Komarovsky, before visiting a doctor, you can alleviate the condition if you ventilate the room where the baby sleeps before going to bed and do a wet cleaning in it. It is advisable to place a pillow under your head so that the mucus can drain out. It should not accumulate in the nasopharynx or sinuses. Drinking plenty of fluids will be helpful. Children over 3 years old can be given a glass of warm milk at night, in which ¼ teaspoon of butter is dissolved. Thanks to this method, it is possible to avoid drying out of the larynx and oral cavity at night.
source
Cough from snot in a child: how to treat it? Child coughs in his sleep
A sharp exhalation through the mouth, or cough, is a vital reflex: its task is to free the respiratory tract from foreign substances, including a runny nose.
If a child’s cough from snot recurs regularly, be sure to contact a pediatrician or otolaryngologist.
Especially in infants, rhinitis can lead to unpleasant consequences, like otitis media, or cause more serious harm to health. Treatment depends on the nature of the attacks and accompanying symptoms.
How and how to treat a cough from snot in a child?
Every parent wonders why coughing from snot occurs in a child, how to treat coughing from snot? Before drawing up a medication treatment regimen, the doctor must find out about the source of irritation through a visual examination of the patient and instrumental examination methods. Curing the pathology is aimed at eliminating sources of infection and establishing the baby’s natural breathing. If coughing occurs after snot, treatment should be started as soon as possible. With this pathology, the risk of pneumonia progression greatly increases. Therapeutic and preventive measures are aimed at changing environmental conditions in the room where the child is located. The microclimate in the room should be at 50-60%. It is recommended to hang wet towels and sheets on radiators. Due to the child's snot, mucus flows into the middle ear, so the baby should sleep on a bed with a high headboard.
Sinus rinsing
If a child coughs from snot at night, then it is advisable to start rinsing the nasal hollows. Cleansing can be done at home. This procedure can be done for children of any age category. If the baby is less than 1 year old, then carry out the actions while lying on the bed with a pillow under the head. To ensure that all actions are carried out correctly, you must follow the instructions:
- First, instill 1-2 drops of saline into one nostril, then into the other. You can prepare it yourself. To do this, stir 1 small spoon of salt in 1 liter of water.
- Wait a couple of minutes until the crusts soften. After this, they can be removed very easily using cotton swabs.
If the child is older than 1 year, then the procedure should be performed in a standing position. The head should be in a horizontal position. Hold it over the sink. Instill the medicine using a syringe without a needle or a specialized device in one pass. If all steps are performed correctly, the liquid will easily come out through the second passage. Inject the medicine alternately into both passages. Cleansing the sinuses with a saline solution improves the absorption of medication components. Completely safe preparations for rinsing the nose include:
- Aquamaris;
- Humer;
- OtrivinBaby.
This product contains all the necessary microelements.
Vasoconstrictor drops
The relationship between cough and snot is known. The therapeutic goal is to normalize the child’s natural breathing through the nose. It is important to reduce the amount of mucus discharge and eliminate swelling of the mucous membrane. The disease can be cured through complex therapy with medications from various pharmaceutical groups. Emergency medicines for cough include sympathomimetics. They significantly reduce blood capillaries, eliminate swelling, help restore drainage function and fight snot. These products contain special moisturizing components that relieve excessive dryness. The effect can be observed within 10 minutes after the start of use. This effect can last up to 8 hours. For children who develop snot or cough, pediatricians prescribe:
- Nazivin;
- Brizolin;
- Otrivin.
The duration of therapy is quite short, only 5 days. In case of unsystematic use of drugs in children, the risk of addiction to the drug increases significantly. Frequency of use, daily dosage - all this is prescribed only by the attending physician after an individual examination of each small patient. It all depends on the child’s well-being, his age, medical history and the severity of the disease.
Antibacterial drugs
Snot and cough cause a lot of discomfort to the baby. Antibacterial medications are prescribed to patients with a bacterial runny nose or chronic rhinitis. Local antibiotics include:
- Bioparox;
- Polydex;
- Isofr.
If a child coughs, then the following is prescribed for instillation into the nose:
- Novoimanin;
- Neomycin;
- Framycetin.
The frequency of use and daily dosage can only be prescribed by the attending physician. Quite often you can encounter attacks of coughing from snot in a child, how to treat such a pathology? It is recommended to combat pathological disorders with the help of herbal remedies. The appearance of muconasal secretions can be eliminated using products based on eucalyptus and sea buckthorn drying oils. It is recommended to drip them into the passages or lubricate them using cotton swabs treated with drying oil. With their help, it is possible to carry out therapeutic inhalations in combination with healing mineral waters or saline. Before inhalation, you should consult your doctor, as allergic reactions occur very often. Dry cough due to a runny nose with anatomical changes in the integrity of bone tissue, adenoiditis, and deviated nasal septum can only be resolved through surgical intervention.
Antiviral drugs
Restoring the upper respiratory tract during viral diseases requires the use of antibacterial medications. The following drugs are prescribed for treatment and prevention:
- Interferon;
- Nazoferon;
- Grippferon.
Nasal medications easily cope with the integrity of pathogenic bacteria. Antibacterial sprays are very effective in the initial stages of the disease. Their action is limited to the intercellular level, for this reason the duration of cure is only 3-4 days.
Causes of night cough in a child
It is important for parents to remember that coughing attacks are not an independent disease, but a symptom. It appears both during the day and at night.
But more often it occurs only during sleep. This is explained by the horizontal position of the body.
In this case, sputum, accumulating in the bronchi, dilutes and makes it difficult to breathe freely.
To the frequent question whether a child can cough due to snot, pediatricians also give a positive answer. This is one of the reasons for such attacks.
Provoking factors also include:
Also, snot flows into the throat and provokes a cough due to bacterial pathogens that cause inflammation of the sinus mucosa; it develops against the background of sinusitis. This mucus takes on a greenish tint and becomes thick.
This often affects infants and children under one year of age, especially when there is no pillow provided and sleep takes place on a flat, smooth surface.
If it is excessively dry or wet, or contains aerosol particles, a night cough sometimes develops.
Parents can independently observe the background against which it occurs: does a heavy dinner, a runny nose or fever, or a feather pillow have anything to do with it?
Does the cough reflex develop only in the children's room or in other rooms? Does mom use aggressive detergents to wash bed linen? Answers to these questions will help your doctor make an accurate diagnosis. Source: nasmorkam.net to contents?
How to determine that a cough is from snot?
Correct treatment is possible with an accurate diagnosis. But a pediatrician can recognize the cause - after listening in the chest area, and an otolaryngologist - after examining the throat, nose and ear canals.
Before determining that the cough has developed specifically against the background of snot, parents can conduct independent observation.
Features of such attacks:
- In infants, nasal secretions provoke a wet cough more often than in children 3.5 - 4 years old.
- Increased body temperature, lethargy, weakness, intestinal upset, lack of appetite indicate that a cold or viral infection is developing.
In this case, treatment requires an integrated approach, which only a doctor can provide: how to understand that there is no disease, and the cause of the pathology is in the nasal mucus? Contact a specialist.
The suspicion that a child is coughing due to snot can be confirmed or dispelled by adult observation.
When coughing from a runny nose, there is no wheezing or other noise in the breathing, which is determined by listening to the area of the bronchi and lungs. Mucus caused by rhinitis can be seen when it is coughed up. This secret is almost impossible to blow your nose away.
Sometimes another type of respiratory spasm develops: a dry cough from snot in a child; it is associated with irritation of the larynx, through which nasal secretions can flow.
Such attacks are not productive, and it is not necessary to treat them, but to eliminate the root cause - rhinitis, or to fight the causative agent of the disease.
Dry mouth, dry throat and itchy nose are signs of the initial stage of the disease. If nothing bothers you other than a runny nose, and it lasts more than 7 days or chronic attacks, a physiological cough due to a runny nose can be relieved using home methods.
Diseases that cause coughing from snot
Excessive mucus production in the nasal cavity is caused by several diseases. Among which are the following:
ARVI causes cough from snot
- sinusitis (sinusitis, sinusitis, etc.);
- ARVI (acute respiratory viral infections);
- rhinitis (inflammation of the nasal mucosa of various etiologies).
Of course, these diseases require an individual approach to treatment. It is important to differentiate and understand how these diseases differ. Sinusitis of any etiology, in addition to a severe runny nose, will be accompanied by pain on the face in the projection of the location of the bone cavities in which the pathological process develops. Such projections are located in the forehead, cheeks or nose.
The development of an acute respiratory viral infection will be accompanied by an increase in the child’s body temperature, weakness, lethargy and the release of clear snot.
If these symptoms (pain in the projection of bone cavities, fever) are not observed in the child, the cause is inflammation of the mucous membrane. It is necessary to determine what origin of rhinitis caused the excessive discharge of snot. Rhinitis of any etiology (allergic, hypertrophic, catarrhal) should have individual therapy.
The appearance of dry and wet cough
Dry cough due to snot
When snot is caused by an infection, there is a risk of germs spreading down the respiratory tract. Mucus contains a large number of substances that have an antibacterial effect, and normally they neutralize the infectious agent. But a small percentage of living pathogenic organisms remains in the mucus, which can flow down the nasopharynx, larynx, etc. A dry cough occurs when there is not a lot of snot and the cough receptors react well, the child will cough up the mucus and spit it out. In this case, you need to teach your baby to blow his snot correctly. Medications can be used to remove mucus. Moisturizing the mucous membrane of the nasal passages using various saline solutions will be very effective for dry cough.
A wet cough occurs when mucus constantly drains from the nasopharynx into the trachea and is expelled when coughing.
The development of a wet cough occurs when mucus constantly drains from the nasopharynx into the trachea and is expelled when coughing. This happens if the snot has a very liquid consistency, reminiscent of water. This is a dangerous condition, because the respiratory system can suffer from an excess of foreign biological fluid. There is a possibility of developing a secondary inflammatory process in the bronchial tree.
If a child develops a wet cough against the background of snot, which has a thick consistency, then there is a high probability that the baby has a cold and the disease develops in the lower parts of the respiratory system. In this case, parents need to pay special attention to the treatment of pulmonary disease in the child in order to prevent the development of severe pulmonary complications.
How to help a child urgently?
Before giving a child a medication or folk remedy, parents must be aware of the responsibility of these measures. Lack of treatment, especially in newborns,
But even in older children, nasal mucus may drain into the bronchi and develop bronchitis, into the ear canals - and otitis media is possible.
When treating infants from the first months of life to 2 years, it is necessary first of all to change the environmental conditions in which they spend the night. Before going to bed, thoroughly ventilate the room and use a humidifier. If it is not there, hanging wet laundry in the room is acceptable.
Clearing your nasal passages before bed is also helpful. It is enough to clean them of crusts after bathing. If they formed at night and caused a cough reflex, they are removed by instilling 1 - 2 drops of mother's milk into the nasal passage.
During a runny nose, it is advisable for infants to place a low pillow under their head, which will protect the baby’s ears from mucus getting into them.
Children over 2 years of age are allowed to wash with saline solution. Prepare it yourself - take from ¼ to 1 whole teaspoon of salt per 200 ml of warm boiled water.
They wash and irrigate the nose. For younger patients, sprays or drops are used; the latter are more convenient because they do not throw the contents into the Eustachian tubes.
Doctors warn parents against using interferon or antiviral drugs on their own, especially in the case of infants. Improper medication use reduces immune function and leads to complications.
Drug treatment
If you have already gotten rid of your child’s runny nose, but the cough still does not go away, you need to pay attention to the environment in which the child is. Dry air does not help cure a cough caused by a runny nose, so it needs to be humidified.
Doctors also recommend the following to treat cough from snot:
- carry out inhalation procedures. Warm steam will help soften the mucus and make it easier for your child to cough up. If you use natural essential oils or other special-purpose medications for the inhalation procedure, you will be able to get rid of the cough much faster. At the same time, the risk of developing inflammatory processes in a child will decrease several times;
- take mucolytic drugs. A dry cough can be very debilitating for a child and does not bring relief, so doctors recommend using medications to soften the cough and remove mucus. Suitable preparations for these purposes include syrup based on plant components “Gerbion” and syrup “Bromhexine”, which is approved for use even by infants;
- gargle. If the child is of a sufficiently conscious age to carry out the rinsing procedure, he needs to be provided with this opportunity. You can gargle with solutions based on salt, chlorhexidine or chlorophyllipt;
- take antihistamines. They will help reduce swelling caused by infection or inflammation, as well as reduce the urge to cough;
- take antibiotics. If inflammatory processes occur in the bronchi, the doctor may also prescribe antibiotics, but if you notice the symptoms of this type of cough in time, then antibiotic treatment is not necessary.
How to treat?
Pediatricians warn: treatment of cough begins with finding out its root cause. If the provoking factor is nasal secretion, you should not take medications.
This applies to both cough and cough medications. In this case, they are ineffective and sometimes cause harm.
If a cough develops due to snot on the back wall, it is impossible to fully inhale and exhale through the nose, you have to breathe through your mouth, and there are no signs of a general illness, parents resort to the following methods:
For children under 1 year of age, nasal mucus is removed using a rubber bulb. Rinse with saline or saline solution.
It is recommended to bury the nose with children's drops Otrivin, which contains xylometazoline, or Aquamaris. This product is based on sea water from the Adriatic Sea and resembles saline solution. For patients under 2 years of age, it is better to use drops.
The substance xylometazoline is included in the list of vital drugs, but has contraindications, so the instructions for Otrivin must be studied before use. Indicated for sinusitis, rhinitis, acute respiratory infections.
Folk remedies are also allowed. These include mixtures of aloe juice and honey, beet or onion juice. But sometimes they cause dryness, burning, and an allergic reaction.
Important! When asked by parents whether it is necessary to treat an independent runny nose, pediatricians answer that no. It is better to create conditions for its termination.
If a child coughs in his sleep: Dr. Komarovsky
If your child has a severe cough from snot and not for another reason, the pediatrician recommends taking the following measures.
Initially, install a humidifier in the room or carry out wet cleaning before going to bed. A low pillow is placed under the patient's head so that mucus does not accumulate in the sinuses and does not enter the ear canals.
The doctor considers an excellent remedy to drink plenty of warm drinks during the day and a glass of warm milk before bed; you can add a quarter teaspoon of butter to it.
This applies to patients over 3 years of age, when the body can already cope with the digestion of milk protein on its own.
This remedy has an enveloping property, prevents drying of the mucous membrane of the mouth and larynx, fights cough attacks and warms.
The next morning, Dr. Komarovsky advises showing the patient to a pediatrician who will make a diagnosis. The further treatment regimen or elimination of the cause of night attacks will depend on it. [ads-pc-1][ads-mob-1] The doctor advises you to refrain from self-administration of antibiotics, antiviral and cough suppressants. He believes that coughing during sleep due to nasal mucus does not need to be treated. It is better to focus your energy on strengthening the immune system: a physiological runny nose goes away on its own within 7 to 10 days.
Cough from snot in a baby: what to do?
Infancy is a difficult period for diagnosing sinusitis and cough syndrome. Parents are especially careful about medications can
If the body temperature is normal, there is no redness of the throat or weakness, the baby is active, and the mucous discharge is clear in color and liquid in consistency, there is often no cause for concern. The body goes through one of the stages of adaptation to environmental conditions.
You can also help by eliminating sources of possible allergies, such as pets, dust in the room, dry air.
Residual cough attacks are also not treated when children have had an acute respiratory infection or a cold. If there is discharge and crusts in the nose, this may indicate that the baby is not properly attached to the breast or is overeating: milk from the stomach, when regurgitated, enters the nasal passage.
If a baby coughs due to snot for more than a week, which is accompanied by dryness and fever, immediately contact a pediatric consultation. A possible cause is sometimes the onset of a viral disease.
It is also necessary to cure a runny nose if the discharge has a yellow or greenish tint and is streaked with blood. Lack of therapy at this stage sometimes leads to sinusitis and chronic sinusitis.
Eliminating mucus with a rubber bulb, using saline solution, ventilating the children's room and humidifying the air are the best methods for preventing runny nose and cough syndrome due to snot.
But if this phenomenon is accompanied by symptoms of a general disease, make an appointment with a pediatrician or otolaryngologist, only he knows how to help children find health.
Cough from snot
The mucous membrane of the nasal cavity produces snot, which appears as a result of an allergic reaction or against the background of an infectious disease.
Mucus can be thin or thick. It’s easy to deal with liquid snot; just arm yourself with a handkerchief and blow your nose if necessary. If the snot is thick, you need to make it liquid. In this case, saline solutions help well.
How to treat cough from snot?
Doctors right and left prescribe expensive medications that do not always help. Cough medications have many side effects. Overdose is considered especially dangerous. Before giving your child medicine, you need to think about the advisability of its use.
A cough is a reaction of the respiratory tract to chemical, mechanical or bacterial irritation. The body needs a cough to protect itself and clear the airways. That is why suppressing a cough is not recommended, because in this case, the situation can only become more complicated.
In order to get rid of a cough, it is not at all necessary to take medications, it is enough to ensure plenty of fluids and humidification of the air.
If a person coughs, sneezes, his voice drops and snot flows, it means that the process of inflammation has begun. Viruses and bacteria entering the body cause inflammation. A runny nose and cough are often treated with antibiotics, but in most cases you can do without them.
How to treat cough from snot? It is necessary to provide the patient with plenty of fluids, install a humidifier and rinse the nose with sea water or saline.
Viruses are transmitted by airborne droplets, in order not to get sick, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system, eat right, spend a lot of time in the fresh air and during epidemics do not visit public places unless absolutely necessary.
This is interesting!
Children suffer from acute respiratory infections more often than adults because they have weak immunity, which is not able to adequately fight off infections.
American scientists conducted a study and came to the conclusion that if a child gets sick once a month, this is normal. There is no need to drug your child at the first sneeze; many medications are much more harmful to the body than snot and cough.
True, infections often lead to complications, for example, a runny nose can develop into purulent otitis media or pneumonia. If your child is sick, it is better to go to the pediatrician and begin treatment after his visit.
Cough from snot
Mucous secretions appear as a result of the functioning of the nasal membranes. The causes of this phenomenon can be various diseases, irritations, allergic reactions and other factors. Nasal discharge can be of two types: thin and thick. The nasal cavity is open on both sides, so if the discharge is liquid, it flows either out or in. When the snot is thick, it remains in the nose.
What measures should be taken
Liquid discharge from the nasal cavity must be promptly wiped off with a handkerchief or a special rag, otherwise an irritated surface around the nose may form. Any snot that gets inside can come out when you cough, and you should also wipe it off. It is advisable to teach your child to blow out the snot that is in the nose and interferes with breathing.
If the nasal discharge has a thick consistency and makes breathing very difficult, then it is necessary to soften it first. This can be done using saline solution. After softening, the snot will most likely flow out on its own. It is better not to put anything into the nasal passages: neither pears, nor pipettes, nor sticks, nor suction, nor other means.
Sucking snot from the nose of a child or adult using a vacuum cleaner or your mouth should also not be used.
Very often, when a child gets sick, parents complain of a cough from snot. At the same time, they often begin to give their baby various cough medications. However, many of these drugs have a large number of side effects, as well as possible consequences in case of overdose. Therefore, you should not start taking such drugs without a good reason.
Where does the cough come from?
Cough is a reflex reaction of the body that occurs in response to irritation of the respiratory tract of a mechanical, infectious or chemical nature. With the help of coughing, the organs of the respiratory system are cleared of foreign objects that have entered there.
In some conditions, such as cystic fibrosis, asthma and others, large amounts of mucus are produced in the respiratory system. In such cases, coughing is used by the body to remove it and clear the airways. If you start taking cough suppressants, the child’s well-being may worsen.
The structure of the nasopharynx is such that quite a lot of nasal discharge during a runny nose ends up on the vocal cords. In this case, they become irritated and, as a consequence, a cough occurs.
If your infectious runny nose is mild, you should not immediately take medications to relieve the cough. In such situations, the patient should be provided with plenty of warm fluids, sufficiently humidified air and rest.
kashelb.com>