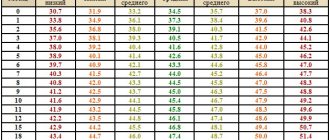
Plagiocephaly in children is a common pathology characterized by flattening of the head on one side. In most cases, there is a functional form of the pathology, which is well corrected by osteopathic treatment. Surgery is rarely required.
Osteopathic treatment is an effective treatment for functional plagiocephaly. Make an appointment with me for osteopathy in St. Petersburg by phone. or write to the chat (bottom right corner) if you have any questions
Promotion. Treatment of plagiocephaly in children in St. Petersburg with a 10% discount
All Instagram (direct) subscribers or when registering via chat on the website receive a 10% discount on the treatment of plagiocephaly in children.
With plagiocephaly, there is a change in the configuration of the skull, the relationship of the bones, stress on the sutures of the skull occurs, and the size of the openings at the base of the skull may change. These changes may result in:
- difficulty sucking
- difficulty swallowing
- disturbance of nervous tone
- colic, belching, regurgitation
- otitis
- sleep disturbance
- risk of developing scoliosis
- and etc.
Plagiocephaly requires timely diagnosis and correction by an osteopath, since changing the configuration of the skull is possible only during the active growth of the child’s skull.
What should parents do?
The work of an osteopath is necessary, but 80% of the success of treatment will depend on the parents. If the skull is severely deformed, the doctor cannot fix anything alone. A thirty-minute session once a week will not correct the situation if, in 7 or 15 days following the session, the baby lies in his favorite position and no one controls his position.
The success of the treatment will depend on three people. From the mother or nanny, the osteopath and the baby himself. Mothers need to use a special device that allows the child to maintain exactly the position recommended by the osteopath. It is useful for up to 5 months. To begin with, they put it on during daytime sleep and make sure that the child does not throw it off until he gets used to it. From birth to one month, the child allows this to be done and maintains the position in which he is placed. From one to two months it is already more difficult. After three months this will become impossible, as the child will become very mobile.
The support device must fit snugly to support the head in the desired position. The child should not be able to move his head freely. Required for security reasons. For the baby to sleep on his back. But a lateral position is also possible if, as a precaution, the child is under constant supervision to avoid the slightest risk. In this way, it is possible to give a gentle position to the deformed side of the skull, thereby ensuring its correction.
When the baby lies on his back, the mother stimulates, as often as possible, rotation of the head in the direction opposite to the baby’s favorite. This can be done with the help of toys or by turning the baby 90 degrees from the stimulus toy.
If mom follows all my instructions correctly, then progress becomes obvious from session to session, even with pronounced asymmetries. The more diligent the mother is, the sooner the success of the treatment is visible, the fewer sessions are required for correction. In general, asymmetries can be corrected.
Causes of pathology
Flattening of the skull in children is in most cases provoked by prolonged pressure on the head from one side or another. A child may already be born with plagiocephaly; in this case, the following are considered predisposing factors for the development of anomalies in the fetus:
- Lack of space for the baby in the uterus, which often happens with multiple pregnancies;
- Low water;
- Breech presentation of the fetus;
- Early prolapse of the head, as a result of which the unstretched muscles of the abdominal press and uterus put strong pressure on the head.
Functional plagiocephaly after birth can be caused by:
- Weakness of the neck muscles;
- Frequent use of devices for carrying infants, in which the head is on a hard surface;
- Premature fusion of fontanelles.
Very often, a child’s skull on one side becomes flat if, during sleep, the child’s head is almost always in the same position.
Plagiocephaly is often a consequence of torticollis, cervical and upper thoracic restrictions, and pathologies in the development of the muscles of the anterior surface of the chest. The likelihood of plagiocephaly in children is increased if labor took a long time or if obstetric pins were used. More often, pathology is detected in premature babies.
What is the connection between asymmetry and receptors?
Eyes
They are located inside two bony orbits, left and right. To ensure normal vision, at least a minimum of symmetry of one eye relative to the other is necessary.
Normal vision is impossible if there is a violation of the symmetry of the facial part of the skull. If correction is not made, the child may develop functional strabismus, hypermetropia, astigmatism or early myopia.
Ears
The ears are located on the temporal bones and should normally be symmetrical.
Dr. V. Fraiman writes that the axes of the temporal bones normally intersect at the level of the body of the sphenoid (the main bone of the skull) bone in the area of the sella turcica. When one ear is asymmetrical in relation to the other, this axis loses its central position.
The osteopathic concept says that imbalance creates the conditions for hearing impairment at a certain stage of life. I believe that such a damaging factor is the “cause of causes” for the occurrence of the so-called “primary lesion”, which can give rise to purulent otitis media, chronic otitis media, a violation of spatial orientation, in which the child becomes awkward and has poor control of his body. Other pathologies at the level of the ear, nose and throat may also appear.
Nose
Located along the central axis of the face. In fact, it consists of two parts, left and right, separated from each other by a partition. If the skull is symmetrical, the nose will be located strictly in the center, and its parts will function harmoniously. The harmony of function will be disrupted if the nose is displaced, i.e. the symmetry of the face will be disrupted. The central bone of the nose and its lateral partitions, being asymmetrical, will make it difficult for air to pass through the nose. The moisture content of the nasal mucosa will decrease. The bactericidal property of the mucous membrane will be less effective, which will lead to permanent sinusitis, rhinitis, nasopharyngitis, tonsillitis, otitis, etc.
Mouth
The oral cavity has a hard palate, divided into four parts. The oral cavity will also be affected by the asymmetry of the skull. If the left side of the palate is asymmetrical in relation to the right, then the symmetry between the jaws is disturbed and teeth bite problems arise. The swallowing process may be impaired. In 90% of cases, a child will be doomed to wear a special orthodontic apparatus or braces. Jaw deformation may occur and the jaw may shift to one side or the other. Over time, this can create problems at the temporomandibular joint level with difficulty opening and closing the mouth, clicking sounds when chewing, and yawning.
Spinal column
He also needs symmetry. The head rests on the first cervical vertebra. It is not for nothing that he bears the name Atlanta. On it lies the lower bone of the skull, the occipital bone. It is the occipital bone that suffers greatly during childbirth. It is she who is subjected to the strongest compressions, loads, and displacements. If the occipital bone is flattened, displaced anteriorly, posteriorly, to the right or left, or deviated from its central axis, that is, the balance is disturbed, all this will be reflected in the articular surfaces of the condyles with which the first cervical vertebra or atlas articulates. Atlas will try to compensate for the imbalance. It will adapt to imbalance. He is obliged to do this so that the person’s gaze remains horizontal and his head is placed straight. This is necessary for the semicircular canals of the inner ear, which provide balance to a person in motion.
All other vertebrae, both cervical, thoracic and lumbar, will adjust to compensate for the imbalance. False congenital torticollis and scoliosis will appear. For example, idiopathic scoliosis, i.e., scoliosis that does not have an obvious cause, may still have one: it can be provoked by “cranial scoliosis,” i.e., an imbalance at the level of the skull during childbirth.
That is why you should not ignore cranial asymmetry, mistakenly believing that this problem is associated only with aesthetics, and it will resolve itself - by itself or it will be covered by hair.
The skull and face are formed by the connection of many sutures and bones, which, articulating with each other, form an intelligent and coherent structure, homogeneous and functional.
It is quite obvious that the structure of the skull, due to its structure and shape, ensures the protection and functioning of everything that depends on it: organs, nerves, blood and lymphatic vessels. This is very important, since the senses and all sensitive receptors connect the newborn’s body with the environment. Vision, smell, hearing, taste and touch are senses that are directly or indirectly related to the totality of structures and functions of the head.
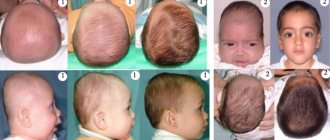
Signs of plagiocephaly
Parents can pay attention to the formation of a flat area on the back of the head, on the sides of the head, and much less often on the forehead. More often than not, the hairs in these places quickly come out.
Plagiocephaly in children
In more advanced cases, other symptoms are added to these signs, these are:
- Ear asymmetry - one of the ears moves forward or upward;
- Uneven formation of jaws;
- Oblique position of the eyes.
Osteopathy for plagiocephaly at this stage allows you to cope with the problem in several sessions.
In severe cases, flattening negatively affects the mobility of the occipital bone, the shape of the jugular and occipital foramina through which the nerves pass. As a result, compression of certain pairs of nerves can lead to impaired sucking and swallowing in the baby, increased nervous tone, belching and colic, and convulsions. Recurrent otitis media is also considered an indirect sign of pathology in young children.
Lack of timely treatment for plagiocephaly can cause impaired speech and hearing function, a tendency to fatigue, and malocclusion.
What should you think about the shape of the skull?
Here are three examples taken from practitioners.
Example 1
Some children have an asymmetrical skull without any noticeable abnormalities. They feel well, eat with appetite, and sleep normally. They behave calmly and develop correctly. Osteopathic tests are almost normal at every level. Despite the asymmetrical shape of the head, a relative balance is possible between structure and function. The baby is not in danger of any health problems in the near future. But what happens next? As a teenager or adult? Over time, it is possible that some ailments may appear, the roots of which go back to asymmetry that no one has eliminated. If you eliminate cranial asymmetry, you can avoid big troubles in the future.
Example 2
Other babies have a relatively symmetrical skull shape. But osteopathic tests indicate dysfunction on many levels. This means that compensation and adaptation could not take place. This condition, whether large or small, disrupts the performance of certain functions. The baby may suffer from various minor health problems or ailments that cannot be classified as illness. In this case, with timely osteopathic treatment, it is easy to remove excess tissue tension and alleviate some symptoms and ailments.
Example 3
And finally, newborns often have obvious asymmetry of the skull and its facial part. Osteopathic tests confirm the presence of osteopathic lesions. These babies have less mobility of some spinal joints at different levels, including the sacroiliac. There is compression of the cranial sutures and overlapping of the skull bones. The bones of the skull experience various types of deformation: flattening, curvature, asymmetry. The equilibrium of the mutual tension membranes is disturbed. Their deformations are visible at the level of the skull and especially in the facial part. The process of compensation and adaptation is absent or ineffective. There is over-excitability and irritation, or, conversely, a decrease or complete absence of some functions in terms of their output, efficiency and competence. Every minute these disturbances interfere with the calm flow of life of the baby and his parents. Such children constantly suffer. You should not hesitate to treat them. We need to start by “correcting the shape” of the head, the asymmetry of which is the root of all evil.
Classification of plagiocephaly
If signs of head flattening are detected in young children, parents should contact a qualified osteopath. This is a doctor with a medical education who is able to identify and correct the slightest violations. Based on the examination, the doctor will suggest a course of treatment for the disorder and/or give additional recommendations for your child.
Pathological (early) fusion of the skull bones in an infant is rare and leads to two forms of plagiocephaly, these are:
- Synostotic frontal anomaly. It occurs due to premature ossification of part of the coronal suture of the skull. Externally it manifests itself as flattening of one half of the forehead with simultaneous protrusion of bones in the frontoparietal region on the other side;
- Compensatory frontal form. The main reason is early ossification of the lamboid suture. The skull moves anteriorly and inferiorly or posteriorly from the ear.
Early ossification of the skull bones is termed craniosynostosis. With this pathology, children should be treated by a neurosurgeon.
However, in most cases, children are diagnosed with functional plagiocephaly, which in turn is divided into two types:
- Deformation. The pathology is detected immediately after the birth of the child;
- Positional. After birth, no abnormalities in the shape of the newborn’s head are detected. Flattening appears in the baby closer to 4-5 months.
It is important for parents to know the signs of the functional form of the pathology and the principles of osteopathic treatment of plagiocephaly in children.