A fairly large percentage of infants suffer from jaundice from the first days of life. This disease manifests itself against the background of increased bilirubin in the blood of the newborn. If it is not treated, then in the future the advanced state of the disease can have a detrimental effect on the baby’s nervous system. Of course, no parents want to stuff their baby with pills. And it's not necessary. After all, jaundice can be cured through phototherapy. A phototherapeutic irradiator for the treatment of neonatal jaundice can do this. How does this device work? How long does a newborn need to lie under it? What is phototherapy method?
UV therapy for jaundice in newborns is not harmful and relieves symptoms well.
Neonatal jaundice
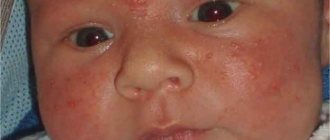
Jaundice in newborns is the body’s reaction to an increased level of bilirubin in the blood. Characterized by yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes of the eyes. It appears on the 3-4th day, in 60-70% of cases it does not require treatment and goes away on its own.
Depending on the clinical manifestations and etiological factors, physiological and pathological are distinguished.
The physiological condition is due to the body's natural reaction to the destruction of hemoglobin F. The fetal type is required during fetal development. After birth it is replaced by hemoglobin A.
Increased breakdown of hemoglobin against the background of infantility of the organs involved in the metabolism of bilirubin leads to its accumulation.
Bilirubin is a yellow pigment; an increase in volume to 70 µmol/l in the baby’s blood turns the skin and mucous membranes yellow.
Possible side effects
Light therapy not only brings benefits, but can lead to unwanted side effects. Usually they do not greatly affect the general condition of the baby, but sometimes they lead to health problems. The most common body reactions are:
- increased frequency of bowel movements;
- increased drowsiness and apathy;
- excessive dryness and flaking of the epidermis;
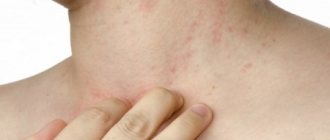
- the appearance of an allergic reaction;
- bronze skin tone;
- headache;
- pain in the eyes and tearing.
The specialist decides how long to lie under the lamp for jaundice in a newborn individually; sometimes continuous stay in the box is indicated. The procedure is stopped if the baby overheats, redness appears on the skin or other symptoms. Side effects are extremely rare and usually do not require additional treatment.
Clinical picture
With pathological neonatal jaundice, clinical manifestations occur one day after birth. In addition to the presence of yellow pigment on the skin, the condition is accompanied by:
- discoloration of stool;
- darkening of urine;
- deterioration of health;
- lethargy;
- poor appetite;
- excessive regurgitation;
- monotonous scream;
- the appearance of pinpoint hemorrhages on the child’s body;
- hepatomegaly and splenomegaly.
Laboratory blood tests reveal accelerated hemolysis of red blood cells and the development of anemia.
Phototherapy at home
Many parents do not want to constantly visit the clinic for a session. They wonder if it is possible to do radiation at home. This is permitted subject to the following rules:
- The whole process requires strict control; the parent is not allowed to leave the room even for 5 minutes.
- The lamp should be installed no closer than half a meter above the child.
- The visual organ and groin area are qualitatively protected from exposure.
- The baby's position changes every 2 hours.
- Temperature measurements must be taken hourly.
- Before starting the course, you must take tests and consult a doctor.
A photolamp for the treatment of jaundice in newborns can be rented, or you can buy a device for personal use. It is impossible to carry out the procedure on your own, without the advice of a specialist, since the cause of yellowing can be serious diseases, which are aggravated by the action of UV rays.
A lamp for the treatment of jaundice in newborns is used in pediatrics for the purpose of relieving jaundice and rehabilitation. It is also used when a child has hematomas or hemorrhages on the body, or if preparation for an upcoming operation is necessary. It is carried out in a hospital or at home, depending on the condition of the baby. The duration of exposure and the duration of the course are determined by the doctor, taking into account all key factors. Therapy will be ineffective if the cause of yellowing of the skin is hidden in impaired liver function.
Causes
Factors for the development of pathological jaundice:
- hereditary pathologies – Gilbert, Crigler-Najjar syndrome;
- hypoxia;
- birth injuries;
- hormonal disorders in the mother;
- incompatibility by blood group and Rh factor;
- congenital structural disorders of hemoglobin;
- enzymopathies;
- hemoblastosis;
- hereditary metabolic pathologies;
- intrauterine infection;
- mechanical damage to the bile ducts, intestinal obstruction;
- toxic effects of drugs.
Diagnostics
The condition is diagnosed using laboratory and instrumental methods:
- blood test - general and biochemical analysis;
- identification of blood group and Rh factor of mother and child;
- Analysis of urine;
- conducting an antiglobulin test;
- test for thyroid hormones;
- conducting tests to detect intrauterine infections;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- abdominal x-ray;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
Premature babies are at risk for developing jaundice.
Hyperbilirubinemia can lead to the development of kernicterus with a toxic effect on brain cells, the appearance of seizures, the development of deafness and developmental delays.
How it works?
Jaundice is, in fact, a difficulty in removing the excess substance bilirubin from the body, which is normally released in all babies, and the immature functioning of the newborn’s liver. It contains yellow pigment - hence jaundice.
Bilirubin is released free and bound. Both together are called common.
Bound, also known as straight, is soluble in water. It is filtered by the kidneys and safely excreted in the urine.
Free, also known as unbound, also known as indirect bilirubin, is insoluble in water and can penetrate cell membranes. Therefore it is toxic. It is absorbed by special liver cells, converted into bound and only then excreted in feces or urine.
Read more about jaundice here:
https://dochki-materi-blog.ru/zheltuha-u-novorozhdjonnyh-budut-li-posledstvija/
Difficulty in excreting bilirubin for a newborn is physiological in 90% of cases. But a strong excess of it is considered a pathology and requires treatment - this occurs in 10% of cases. The biggest danger is damage to brain cells, which can be fatal.
It is important to know. Jaundice is one of the most dangerous types of disease if the pathology is not diagnosed in time, but also one of the most healed unnecessarily.
Read about the signs of jaundice here:
https://dochki-materi-blog.ru/priznaki-zheltuhi-u-novorozhdjonnyh-kak-otlichit-normu-ot-opasnoj-bolezni/
Phototherapy for jaundice is very common.
The purpose of using lamps is to provoke the breakdown of bilirubin. As a result, less toxic substances are formed; 5% lumirubin and 85% water-soluble isomers of indirect bilirubin. These substances are more easily excreted by the body in feces and urine. The rate of formation of new isomers is determined by the spectrum and total dose of radiation. As a result, the amount of bilirubin in the blood serum decreases, and jaundice recedes.
In parallel with phototherapy, medications may also be prescribed. If phototherapy does not cope with the pathology, then an operation to replace the blood of an adult is prescribed. This is a more serious event that requires more careful monitoring of the baby.
The following lamp characteristics are important for phototherapy:
- Spectral limits (and peak wavelength). Bilirubin absorbs visible light with a wavelength of 400-500 nm, which leads to its breakdown. 460 +/- 10 nm is considered the most effective.
- Light (radiation) intensity is the number of photons that one square centimeter of irradiated skin receives. Measured in W/cm2.
- Spectral intensity is the intensity of radiation that is quantified within the effective wavelength. Measured in μW/(cm2* nm) using radiometers.
Phototherapy: principle of action
Neonatal jaundice is treatable. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the root cause of the problem. Phototherapy is used to reduce bilirubin concentrations.
Phototherapy for neonatal jaundice is considered an alternative to medications. The method is based on the healing properties of light. Blue radiation is used to eliminate jaundice. The length of the ultraviolet ray is 450-460 nanometers. Therapy is carried out using lamps.
A lamp for jaundice is a special device with a wavelength of 450-460 nm in the blue spectrum. Acts on the upper layers of the skin, becoming a catalyst for chemical reactions of bilirubin conversion. Bilirubin, under the influence of blue color, turns into lumirubin, becomes non-toxic and water-soluble, and is excreted from the child’s body along with urine.
Indications for treatment
When prescribing light treatment for children, the following signs are taken into account:
- yellow sclera;
- decreased appetite;
- iron deficiency;
- decreased sucking reflex;
- drowsiness;
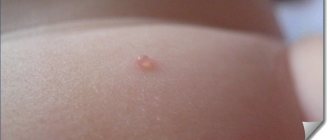
- spontaneous appearance of hematomas on the skin;
- low temperature - less than 35 degrees;
- Apgar score is 4 points;
- the child’s weight does not exceed 2 kg;
- bilirubin concentration – over 240 µmol/l.
During visual inspection, the degree of pigmentation of the body surface is recorded. The Cramer scale is used for assessment:
- 1st degree – the presence of jaundice on the baby’s face and neck;
- 2nd degree - spread of pigment to the upper half of the body to the navel;
- 3rd degree – characterized by staining of the upper thighs;
- 4th degree – the entire surface, except the palms and heels;
- Grade 5 – pigmentation of the entire body, including the heels and palms.
The level of bilirubin is taken into account:
- one day after birth – 119 µmol/l – no pigmentation;
- Day 2 – 153 µmol/l – skin is not colored;
- Day 3 – 187 µmol/l – slight pigmentation;
- 4-5 days – 200 µmol/l – strong staining;
- Day 6-7 – bilirubin levels decrease.
Contraindications
The results of the studies are taken into account in combination with the examination, phototherapy is prescribed in the absence of contraindications:
- Increased sensitivity of the skin. Dryness, peeling, minor damage.
- Disorders of the thyroid gland.
- When prescribing dermatological medications and phototherapy, a malfunction of the digestive organs is possible.
- Hormonal disorders.
- Purulent-septic infection.
- Presence of anemia.
- When diagnosing obstructive jaundice.
- High concentration of conjugated bilirubin.
- Presence of pathology of the organs of vision.
The lamp is contraindicated if there is a risk of negative effects on the nervous system.
Indications for light therapy
There are many cases when the use of this technique during the treatment of jaundice is required:
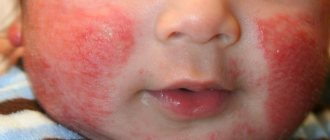
- pronounced yellowness on the skin of a newborn;
- yellowed eyeballs;
- the rich yellow color of the fluids secreted by the baby’s body.
Premature babies with low birth weight who require urgent resuscitation procedures may need a lamp with ultraviolet rays. Newborns with multiple hematomas, hemorrhages, deep anemia, body temperature less than 35 C, and who have a low Apgar score may lie under ultraviolet light.
The predisposition of the fetus to an increase in bilirubin after birth, revealed during pregnancy, and Rh conflict with the mother can become a reason for the development of neonatal jaundice and the use of an ultraviolet lamp.
Carrying out the procedure
To stimulate the removal of bilirubin from the child’s body, it is recommended to put the child to the breast more often. If there is a shortage of milk, it is permissible to give the baby a non-concentrated infusion of rose hips and water. Increased drinking regimen removes a lot of harmful substances, and the presence of vitamin C in rose hips will strengthen the immune system.
In the maternity hospital, the procedure is carried out in a box equipped with an ultraviolet lamp. To do this, the following manipulations are performed:
- The undressed baby is placed in an incubator.
- Lamp goggles are used to protect the eyes.
- The groin area is covered, a diaper is allowed.
An ultraviolet lamp is installed at a distance of 50 cm. An effective method is to combine ultraviolet lamps with daylight devices.
You need to lie down for 2 hours. The break between sessions can be 2-4 hours. If the bilirubin level is elevated, therapy is carried out without interruption. The duration of the course is 96 hours.
To ensure uniform exposure to ultraviolet radiation, it is recommended to change the position of the child’s body. Body temperature is measured every 2 hours to avoid overheating.
The baby needs breastfeeding; mother's milk will speed up the process of removing bilirubin. If it is impossible to breastfeed, you should bottle-feed your baby with expressed milk. Ultraviolet radiation can lead to overheating and dehydration of the child’s body, so you should replenish water loss by frequent breastfeeding.
The presence of a health care professional during phototherapy is mandatory. During the course, it is necessary to draw blood to assess the level of bilirubin concentration and weigh the baby.
Treatment at home
When using the lamp at home, you should carefully read the instructions. It is important to stay close to the child during the procedure and monitor the process.
- Before starting therapy, the lamp must be installed. The distance from the lamp to the child is at least 50 centimeters.
- Be sure to use eye protection and a tight bandage to cover the groin area.
- Periodically change the position of the newborn.
- Measure your temperature every hour.
- Consultation with a doctor and laboratory tests are required.
The duration of the course is determined by a specialist.
Sunbathing can also help jaundice disappear. You should spend more time in the fresh air, avoid the scorching sun - prolonged exposure will cause burns on the baby’s delicate skin.
When sunbathing, it is necessary to ensure that the child does not become hypothermic.
This method is not as fast as using special lamps, but it does not require strict instructions.
Diagnosis of the severity of the pathological process and the prescription of treatment are the prerogative of the doctor.
Reasons for stopping therapy
Treatment time is reduced if the following indicators are present:
- overheating of the child;
- intense redness of the skin;
- decrease in bilirubin in the analysis.
A persistent decrease in total bilirubin in the absence of an increase in free bilirubin is an indication for discontinuation of treatment.
Adverse reactions
A photo lamp for a newborn can provoke the development of negative manifestations:
- dehydration;
- allergic reaction in the form of peeling of the skin;
- apathy, excessive drowsiness;
- with prolonged use, the skin may turn bronze;
- greenish stool;
- temperature increase;
- tearfulness;
- hypothermia;
- bowel dysfunction.
How and for how long should you lie under the lamp?
Phototherapy is carried out in a prepared box equipped with a special photo lamp with blue ultraviolet rays. The newborn is undressed and placed in the incubator. A thick bandage is put on his eyes to protect the retina. The newborn's groin is also covered, since exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the genitals is not desirable. A diaper or any thick diaper folded in several layers is suitable for this task.
The child should lie under the blue lamp for at least 2 hours. If the levels of bilirubin in the blood are too high, then the babies lie under ultraviolet radiation until the bilirubin completely disappears. You can take a short break while feeding your baby.
While the baby lies under the lamp during phototherapy, it must be periodically turned from side to side, from back to tummy and vice versa, so that the ultraviolet radiation evenly reaches all parts of the baby’s body.
A newborn exposed to a blue ultraviolet lamp must be breastfed frequently, as the mother's milk tends to weaken. This will speed up the work of the intestines and increase the frequency of bowel movements, which will quickly remove broken bilirubin from the baby’s body. Even if the baby is sleeping, it is worth waking him up to breastfeed.
When a child lies under ultraviolet radiation, his body intensively loses water, which can lead to overheating and dehydration. Therefore, liquids in the baby’s body should be 20% more than the daily norm. Foremilk, provided frequent breastfeeding, compensates for this loss.
A newborn exposed to ultraviolet light during phototherapy should be closely monitored by a health care professional. If the toddler's condition worsens, blood tests should be performed periodically. This will show how much bilirubin remains in the baby’s body and what is the intensity of its decomposition.
Lamp selection
A wide range of phototherapy devices allows you to be treated at home. There are specialized instruments and devices for independent use. Lamps are classified according to the type of source and the direction of the rays.
They are distinguished by area of influence:
- Designs affecting the entire surface of the human body. For example, cabins where a baby can fit. Installed above the bed. Disadvantage: it is not possible to direct the rays to a specific area of the body.
- Lamps with local exposure option. It can be used against jaundice for infants with visual pathologies and for those who cannot lie under broadband devices.
Types of devices
Devices may vary in type:
- Emitters fixed with tripods are used in medical institutions. Before the procedure, the child is undressed, and exposure to rays stops during the feeding period. The devices are located next to the bed, the light source is fixed above the newborn.
- Portable devices are made like a hammock, the impact is carried out from below. Used in maternity hospitals and at home.
- The type of blanket allows you to feed the baby without stopping the phototherapy process.
Types of lamps
The fluorescent lamp has a massive design and comes in the following types:
- blue;
- cold light;
- red;
- green;
- white.
Blue fluorescent lamp
A lamp with a blue light spectrum is considered the most effective. Its use will help get rid of jaundice.
This type of lamp has distinctive features:
- the range of light waves is 380-450 nm;
- It is recommended to use safety glasses and bandages to cover the groin;
- minimal presence of harmful ultraviolet radiation;
- during therapy, the child should lie at a distance of at least 30 cm;
- treatment under the lamp lasts up to two hours;
- over time, the efficiency of use decreases;
- can be used for 1000-2000 hours.
Light-emitting diodes - the light wavelength reaches 420-500 nm. The most effective are:
- no flicker, continuous exposure;
- low electrical energy consumption;
- can work for 20,000-50,000 hours;
- minimum of adverse reactions;
- high impact rates;
- radiation safety;
- low electrical energy consumption;
- compactness.
Halogen fluorescent lamp
The halogen lamp is considered dangerous and must be used with caution. When operating, it is important to follow the rules.
Close proximity to the skin may cause burns.
- light wave – 380-600 nm;
- the lamp generates a large amount of heat, so it is not recommended to install it near a child;
- difficulties in determining the required dosage;
- It is obligatory for the child to use safety glasses;
- lack of range control;
- the treatment process must be supervised by a medical professional;
- can function for 700 hours.
Fiber Optic Lamp
The fiber optic irradiator is used in special blankets and pillows. A distinctive feature is constant contact with the child, a comfortable design allows you to hold the baby in your arms:
- light wavelength – 400-550 nm;
- uniform effect on the entire surface of the body;
- the possibility of alternately using different types of radiation;
- eliminates the risk of overheating;
- suitable for home use;
- for the procedure, the baby is placed in a blanket or overalls;
- There is no need to use protective glasses and bandages.
Lamp selection
The choice of lamps should be made taking into account important factors:
- the ability to hold the baby in your arms, but such a device has low power;
- a halogen lamp can cause harm, so safety rules should be followed;
- Additional products are required: safety glasses, screens, heated mattresses.
Phototherapy of newborns for jaundice: treatment in hospital and at home
2643
Newborn children often suffer from various pathologies.
Quite often, such disorders are not associated with infection of the body by any harmful environmental agents, but are of natural origin.
The most common disorder of this type is infantile jaundice. Most studies show that this disorder occurs in 20% of completely healthy children.
To avoid the appearance of various negative effects, infantile jaundice must be treated, and the most effective therapeutic method is the use of blue phototherapeutic lamps.
Treatment with drugs in the maternity hospital
The doctor will definitely advise giving the baby additional fluids other than formula or breast milk. This recommendation is also useful not only when bilirubin levels increase, but also when there is a tendency for it to increase.
For the treatment of jaundice, intravenous administration is often used:
- glucose;
- ascorbic acid;
- phenobarbital;
- plasma;
- albumin.
Until recently, it was believed that all of these drugs were capable of converting free bilirubin into a bound form, thus reducing its toxicity.
Recently, more and more pediatricians have tended to believe that these methods are ineffective and potentially dangerous. For example, the production of liver enzymes that is significant for a child after the administration of phenobarbital occurs only after two weeks of life, when the jaundice has already passed.
In addition, phenobarbital produces a side effect, inhibiting the activity of the newborn. In this regard, there are calls to use infusion therapy in exceptional cases whenever possible. The prescription of “hepatoprotectors” such as Essentiale and LIV-52 is also questionable.
Jaundice in children and its causes
Jaundice is a physiological disorder that occurs due to an increase in the concentration of bilirubin. Symptoms include yellow discoloration of the whites of the eyes, drowsiness, a slight increase in temperature, loss of appetite, etc.
Jaundice can occur not only in adults, but also in newborns. In this case, infantile jaundice occurs for completely natural reasons due to the breakdown of old red blood cells that were formed during the intrauterine development of the fetus.
The mechanism for increasing the concentration of bilirubin in the blood is as follows: after the appearance, the body requires additional blood cells, as a result of which the breakdown of prenatal hemoglobin, which includes bilirubin, occurs, which provokes the appearance of jaundice.
At the same time, the body independently utilizes excess bilirubin quite well, and over time the concentration of this substance returns to normal. Medical studies show that infant jaundice usually appears at the age of 3-4 days, and it disappears by itself somewhere around 2-3 weeks of life.
The following factors influence the occurrence of jaundice in children:
- Physiological factors. Due to the developmental characteristics of the child's body, excessive accumulation of bilirubin occurs, which ultimately leads to the appearance of jaundice. At the same time, excess bilirubin is normally associated with special proteins, which gradually break down this compound into components that are safer for the body. However, in the case of an excessive concentration of harmful bilirubin, the proteins do not have time to utilize them, which leads to jaundice. Research shows that this reason is the main one, and about 70% of cases of jaundice in children are associated with physiology.
- Lack of breastfeeding. Mother's breast milk contains special immune cells that can fight excess bilirubin, so jaundice may develop in the absence of breast milk. However, this factor should not be overestimated, since medical studies show that only 10-15% of cases of jaundice can be attributed to lack of breastfeeding.
- Low quality breast milk. In some cases, jaundice occurs due to poor quality milk when it contains some toxic components that stimulate the production of bilirubin. At the same time, studies show that nutrition and lifestyle in this case are of very little importance, and harmful substances are released due to the physiological characteristics of the mother’s body. At the same time, it is very important not to overestimate this factor, since low quality milk causes jaundice in children only in 2-5% of cases.
- Incompatibility of the Rh factor in mother and child. If the blood composition of the mother and the child is very different, then there is a small probability (about 5%) that the mother’s body will begin to synthesize blood antibodies, which will provoke an increase in the concentration of bilirubin in the baby’s body, which will lead to the appearance of jaundice immediately after birth. However, today there are a large number of effective medications that can prevent such a disorder. For this, the mother is given a special injection, which weakens the production of protective antibodies, which leads to a slowdown of negative processes in the body, so the baby does not develop jaundice.
Phototherapy for newborns
One of the most effective and safe treatments is phototherapy. Bilirubin, which causes jaundice, is a pigment that can be found in the form of various isomers, one of which, lumirubin, has a greater ability to dissolve in water and, accordingly, is quickly excreted from the body in the urine.
For the conversion of bilirubin, light with a wavelength of 400-500 nm is optimal (the maximum absorption is at 460 nm) . Visually, the part of the spectrum with the wavelength necessary for treatment is perceived as blue light.
Accordingly, using lamps capable of emitting light in a given wavelength range, you can quickly remove excess bilirubin from the body.
Diagnostics
There are various methods for diagnosing jaundice, both laboratory and instrumental. Usually a general blood test is required to check the level of bilirubin and gland enzymes. If necessary, ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of internal organs, celiacography and other, more complex methods of identifying the disease and its causes are performed.
To diagnose the cause of the disease and choose the right treatment, the doctor must evaluate liver function, and if necessary, perform a biopsy or special radiation. Treatment may involve medication or surgery.
Treatment of newborn jaundice under a lamp
Phototherapy is carried out:
- for the treatment of physiological jaundice;
- after the first exchange blood transfusion (EBT) for 1-2 days and to prevent repeated EBTs;
- for the prevention of hyperbilirubinemia if the newborn’s body weight is less than 1250 g;
- to accelerate the resorption of hematomas and hemorrhages;
- in preparation for surgery or during the rehabilitation period.
The course of treatment is considered complete when the concentration of bilirubin reaches a safe level and there is a steady tendency towards its further decrease.
Indications for phototherapy depending on the child’s body weight at birth
| Body weight at birth, g | Bilirubin level µmol/l |
| less than 1500 | 85-140 |
| 1500-1999 | 140-200 |
| 2000-2500 | 190-240 |
| more than 2500 | 255-295 |
Treatment can be carried out continuously (24 hours) and with breaks of 2 hours. At the same time, treatment lasting less than 12 hours a day is considered ineffective. Typically the course is 72-90 hours.
The treatment procedure is as follows.
- Before phototherapy begins, a special goggle mask (Natus billiband, Philips) is put on the baby’s face to protect the eyes.
- A bandage made of reflective material is applied to the genitals.
- The lamp is placed at least 50 cm from the child’s body and the baby is turned every two hours to avoid overheating and burns.
- The duration and frequency of procedures is prescribed by the doctor. Most often, two-hour radiation sessions alternate with an equal break.
- With severe jaundice, the newborn will lie under the lamp almost constantly, with breaks for feeding, hygiene or other procedures.
- In severe cases, the mother and child will most likely be in the hospital, since if there is a threat of bilirubin encephalopathy, the bilirubin level is measured at intervals of 6 hours.
What side effects may there be?
The therapeutic procedure is safe, but we still must not forget about the risk of side effects. Doctors call negative consequences a decrease in fluid levels in the body, the appearance of white scales on the integument, and a change in skin color.
To prevent dehydration during a course of phototherapy, it is recommended to provide the child with sufficient amounts of fluids; try to maintain breastfeeding as much as possible.
If the baby is not supervised enough:
- there is a risk of burns of varying severity;
- Some patients experience changes in skin color
When a child’s body cannot tolerate light rays, it is possible to develop allergic reactions associated with itching, skin rashes, and redness of the body. If anxiety or changes in skin color occur, phototherapy should be stopped immediately.
Newborn phototherapy at home
If we are talking about ordinary physiological jaundice, you can treat the baby at home. The lamp can be purchased or rented. Your doctor will probably tell you where such a service is available in your city. You can also check with your doctor about the price level and other nuances of renting a lamp.
The most convenient systems for use at home are: BiliBlanket Plus, BiliBed, Wallaby. At the end of the article you can find general information about different lamps, systems, devices for the treatment of jaundice in newborns, their advantages and disadvantages.