10/23/2020 Alena Masheva Health
Rotavirus occurs quite often in infants, and almost every child suffers from this disease. The disease manifests itself in the form of vomiting and diarrhea. Often combined with signs of a cold.
In infants, this disease can quickly cause dehydration, so babies need careful monitoring. In this case, the body loses much more fluid than it receives. This can cause serious health problems.
Rotavirus infection spreads quite quickly, being excreted in the feces of a sick child. Outbreaks often occur in winter. The virus is highly contagious and enters the mouth with dirty hands. If you do not thoroughly disinfect all surfaces, it can live on them for several days.
Causes of rotavirus infection in infants
Rotavirus infection in medicine is a viral infectious disease of the gastrointestinal tract.
The causative agents of the disease are rotaviruses. When these pathogens enter the human body, they infect the digestive system, leading to the development of an acute inflammatory process. Newborns rarely suffer from this disease, since thanks to their mother's milk they receive reliable immunity. There are several ways of contracting rotavirus infection:
- nutritional - in this way, infants are infected when feeding them using complementary foods, sometimes consisting of poorly washed vegetables and fruits, as well as low-quality or insufficiently thermally processed meat and dairy products;
- airborne - through direct contact with a sick member in the family (talking, sneezing, coughing);
- contact-household - when simultaneously using toys of an infected child, personal hygiene products or household items in a nursery;
- when drinking contaminated water.
Rotavirus in an infant (1 month old or more - it doesn’t matter) develops when the virus enters the body. The pathogen can be detected in stool during culture. Often, infection occurs directly from the mother, since the baby is in close contact with her.
In infants, rotavirus infection cannot be destroyed directly in the stomach or intestines. It easily overcomes low temperatures and does not lose its properties. Therefore, viruses can persist for a long time and do not lose their harmful properties. In this case, upon penetration into the body, they begin to actively act and multiply.
The source of infection is a person who is a carrier of rotavirus infection, or a patient with an acute form of gastroenteritis. Infection often occurs in the following ways:
- consumption of contaminated water;
- infected products;
- dirty hands, household items, toys;
- through mother's milk.
The virus, having penetrated the digestive organs, affects the small intestine. From the moment the pathogen enters the body until the first signs of illness appear, 1-5 days may pass. The length of the incubation period depends on the level of human immunity and the number of viruses.
general information
Rotaviruses are a large group of RNA viruses, many of which cause dangerous pathologies in humans and domestic animals. Their shape resembles a wheel, which is why they got their name: rota - “wheel” from Latin.
Viruses of this group are transmitted through the fecal-oral route or, in simple terms, through dirty hands and objects. Rotaviruses are extremely contagious - 100 particles are enough to transmit infection.
Rotavirus infections are a global problem. Every year, about 25 million people become infected with them, of which 600-900 thousand die. Most of the victims occur in developing countries. The disease is seasonal; outbreaks usually occur during the cold season.
Characteristics of infection in infants
Harmful bacteria enter the baby's body from hospital workers or the mother. The disease most often occurs as an outbreak. The infection penetrates the digestive system and serves as an impetus for inflammation of the mucous membrane. Against the background of this situation, the risk of exacerbation of pathologies of the upper respiratory tract increases.
Against the background of these symptoms, the child develops almost complete dehydration. If the situation is not corrected in time, the baby begins to actively lose weight.
It is important for a nursing mother to prevent dehydration. She must closely monitor his condition. For example, the baby may begin to cry without tears or often stick out its dry tongue. Parents who are dehydrated may not notice sweating. Urination occurs extremely rarely.
If treatment was not started on time, then the baby actively develops intoxication of the body. It is accompanied by a sharp increase in body temperature, chills and even convulsions. Breastfeeding becomes difficult during this period as the baby refuses to eat.
How to recognize the disease?
In infants, the disease is more serious than in adults. Therefore, treatment should begin when the first signs of rotavirus infection are noticed.
Symptoms of the disease depend on the general health of the child and his age:
- If a rotavirus infection in a baby is mild, then the symptoms will be as follows: fatigue and a temperature of about 37 degrees. Vomiting and diarrhea are then possible. After 5 days the disease goes away, so treatment is symptomatic;
- Moderate severity of the infectious process is characterized by fever up to 38 degrees, repeated vomiting and loose stools up to 15 times a day. As a rule, recovery occurs within a week;
- The severe form of the disease begins acutely, with the peak development of infection occurring on days 3-4. Due to profuse diarrhea and vomiting, dehydration occurs. The baby is tormented by thirst, dry mucous membranes and skin. In addition to the lack of fluid, general intoxication of the body develops. The baby is shivering, has a fever and convulsions, and refuses to feed. If the treatment is effective, recovery occurs within 10 days.
In children aged 1–3 years, rotavirus infection occurs in moderate and severe form. The older the child, the easier he tolerates the disease.
Symptoms such as diarrhea and fever can be confused with other infectious diseases - salmonellosis, dysentery.
But stool is typical for rotavirus infection: it contains no admixtures of blood and mucus, contains a large amount of liquid, and the color and consistency of the stool resembles gray-yellow clay.
Rotavirus infection can be accompanied by the parallel development of pathogenic microbes, then mucus and blood can be found in feces.
There are several signs that indicate that dehydration is becoming critical, and treatment is not helping.
The baby has no tears when crying, the tongue and lips are very dry, there is no sweating, and there has been no urination for more than 3 hours.
In this case, immediate hospitalization is necessary; serious complications cannot be ruled out.
Basic rules for diagnostics
The main preventive measure is hygiene. It is necessary to wash your hands with soap, ventilate the room, carry out wet cleaning, and thoroughly wash fresh fruits and vegetables. A patient with rotavirus must be isolated in a separate room from other family members (the patient must be provided with separate dishes, towels, pillows).
A two-time vaccination with the Belgian drug Rotarix is possible, which is given to children over 1.5 months. This vaccination is not included in the list of mandatory vaccinations, but it is the only one that will help protect your baby from rotavirus.
The very first symptom of rotavirus in an infant is vomiting, after which diarrhea usually begins and the temperature rises. The stool is very liquid without any blood, and quite a lot of it is released. The most severe period of diarrhea lasts 4-8 days, but its residual manifestations can persist even after improvement in health, up to several weeks.
Rotavirus diarrhea, especially when combined with vomiting, can quickly cause dehydration. Therefore, it is very important to feed your baby breast milk as often as possible and be sure to give him water. Among the main signs of rotavirus in infants, the following symptoms should be highlighted:
- dry tongue and lips;
- lethargy, drowsiness;
- sunken eyes;
- deepened fontanelle;
- rapid breathing and heart rate;
- decrease in the amount of urine.
If such symptoms appear, you should immediately call a doctor at home. This can be very dangerous, as it provokes the development of dangerous complications.
Symptoms of rotavirus in infants largely depend on the severity of the disease. In mild cases, the child experiences severe weakness and loss of appetite. Then the temperature rises to 37-37.5 degrees and lasts for 1-2 days. After a few hours, vomiting appears, and this does not depend on whether the stomach is empty or full.
The average form of the disease is characterized by an increase in temperature to 37.5-38 degrees. Vomiting precedes the appearance of loose stools and can be repeated many times within two days. Painful cramps appear in the abdomen, often in the navel area. There may also be watery stools up to 7-15 times a day. Moreover, diarrhea can last 1-3 days, subject to proper treatment. When the child begins to recover, vomiting initially goes away, and then the temperature returns to normal.
Symptoms of rotavirus in infants, which occur in a severe form, are characterized by the fact that the disease has an acute onset. The peak severity of the condition occurs on days 3-4. As a result of severe and prolonged vomiting and diarrhea, dehydration occurs. The level of acidity in the stomach increases. The baby is constantly tormented by thirst, and dry mucous membranes and skin appear.
Laboratory tests of stool, blood and urine are used to detect infection. But basically, treatment begins as soon as symptoms of the disease appear. Tests are required to accurately diagnose, confirm or refute the presence of a bacterial infection. As a result, it will be possible to avoid complications.
There is also a special rapid test for rotavirus that can be done at home. It includes a substance that reacts to the virus. The test is similar to a pregnancy test.
Prevention of rotavirus in infants is important. Often, adults are carriers of the infection, which is completely asymptomatic. To eliminate the possibility of a child becoming infected with rotavirus infection, you need to carefully observe personal hygiene, wash your hands with soap, carry out daily wet cleaning and ventilate the room.
If the child is bottle-fed, then before each feeding you need to thoroughly boil the bottle and pacifier. If one of the family members shows signs of illness, then it is necessary to urgently isolate the baby so that he does not come into contact with a person who has an infectious disease.
After recovery, the risk of re-infection is unlikely, since the child has already developed immunity to this disease. However, if this happens, the disease will be milder and will not cause any complications.
It is worth remembering that when the first symptoms of rotavirus appear in an infant, you should immediately contact a doctor who will be able to provide timely qualified assistance and prescribe the required treatment. This will help avoid complications of the disease and prevent the infection from becoming severe.
To make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a study of stool, urine and blood. The baby must be treated immediately. Tests must be taken in order to confirm or refute the presence of secondary infections or bacterial infections.
Against this background, serious complications of the baby’s general condition may develop in the future. Pharmacies sell an express test that allows you to make a diagnosis at home with a high degree of accuracy. The kit includes a special substance that reacts to the presence of rotavirus infection. The principle of its operation is similar to a pregnancy test.
Only a doctor can choose the right course of treatment
According to the clinical picture, the course of rotavirus infection can be mild, moderate and severe. Most often, the first 2 forms occur in newborns and infants. Information about the manifestations of the disease is presented in the table.
| Form of the disease | Symptoms | Duration of the course with timely adoption of treatment measures, days |
| Lightweight |
| 2-3 |
| Average |
| |
| Heavy | This form is characterized by an acute onset in the form of frequent bouts of vomiting. The frequency of bowel movements reaches 15 times a day. Dehydration of the body leads to dry skin and mucous membranes. | 10 |
Often the disease is accompanied by a runny nose, enlarged lymph nodes in the neck and sunken fontanel. In addition, the child's tummy may hurt and growl - this can be understood by the legs writhing and prolonged crying.
Prevention measures
Prevention of rotavirus intestinal infection in children consists of careful hand hygiene after using the toilet, treating the toilet with antibacterial agents, and maintaining cleanliness in the room.
Treatment of toys with alcohol solutions, regular wet cleaning and ventilation of living quarters and kindergarten groups are recommended. These measures will prevent re-infection and the spread of the infectious process.
Is quarantine necessary?
Isolation of the child is required in the manifest form of the infectious process in order to prevent an outbreak of the epidemic in healthy children and adults. Considering the high contagiousness of the disease, it is important to notify the kindergarten, camp, and school groups about the child’s condition.
Vaccination
The rotavirus vaccine is not included in the preventive vaccination schedule, but it significantly alleviates the course of the disease in children and reduces the risk of immediate and long-term consequences.
Doctors advise vaccination at six months , when maternal immunity weakens and the first complementary feeding begins. Revaccination is carried out after six months. Popular vaccines are Rotarix (UK), Rotatek (Netherlands).
Komarovsky's recommendations
The famous children's doctor Komarovsky recommends protecting your child from rotavirus by vaccination. He believes that in 80% of cases the vaccine helps prevent the development of the disease and always protects against severe rotavirus.
Features of treatment at home
As Komarovsky says, the symptoms and treatment of rotavirus in infants may vary somewhat, but there is a certain algorithm of action that is common to all cases. In case of diarrhea, you need to leave the diaper with the baby's feces. This way the doctor will be able to make a diagnosis faster, and the likelihood of an error will be reduced.
For rotavirus in an infant, Komarovsky does not recommend taking homeopathic medicines. They do not produce the required result, and as a result, the therapy process can only be delayed. Also, you should not give your baby antiviral drugs. Komarovsky recommends treating rotavirus in infants with plenty of fluids.
Therapy is aimed at reducing body intoxication and restoring fluid balance. Parents must provide the baby with all the required minerals. At home, only mild forms of the disease can be treated.
The first step is to eliminate dehydration. For this purpose, the doctor mainly prescribes the drug “Regidron” to the baby. You can also use products such as “Hydrovit” and “Humana”. The powder dissolves in water and is given to the child in small portions. You can give your baby clean water if he refuses to take medicinal solutions.
To eliminate the symptoms of rotavirus in infants, treatment is also carried out using sorbents that help remove the virus. Among them, “Karbolen” and “Smecta” are very popular. They can only be used for a limited time. Otherwise, there may be constipation.
A bacterial infection can be associated with a rotavirus infection. The drug “Enterofuril” is used as a prophylaxis. Antibiotics should not be used for treatment, as they only weaken the body’s protective functions. They are prescribed only in case of emergency, after an examination.
To restore the intestinal microflora, Linex or Hilak are prescribed. It is necessary to bring down the temperature only if it rises above 38 degrees. Antipyretic rectal suppositories are best suited for this. The drug "Cefexon" is well suited, since it can be used from the age of 1 month.
It is recommended to breastfeed your baby as often as possible, since mother's milk perfectly replenishes the loss of moisture in the body. However, if the child is severely weakened, the doctor recommends interrupting breastfeeding for the duration of treatment and giving lactose-free formulas.
It is important to properly care for your baby’s buttocks, as loose stools can cause irritation. Every time you change a diaper, you need to wash your baby with warm water and care for his delicate skin using baby protective products.
Treatment is aimed at reducing body intoxication and restoring fluid balance. Parents must also provide the baby with all the necessary minerals. Only mild forms of the disease can be treated at home. The first step is to eliminate dehydration. To do this, you should give the baby special medications.
Before using them, you should consult your doctor. The medications will help normalize stools within two weeks of continuous use. It is advisable to use drugs for internal administration only if the baby is in serious condition. In this case, you will also need to go to the hospital.
Sorbents will help remove the virus and toxins from the body. Among them, Smecta and Karbolen are very popular. They can only be used for a limited time. Otherwise, constipation may occur. To eliminate dysbiosis, probiotics are taken at the doctor's discretion.
A bacterial infection can also be associated with rotavirus. Enterofuril is used as its prevention. Antibiotics should not be used for treatment, since they can only weaken the body's basic protective functions. They are prescribed only in cases of extreme necessity based on test results.
The child should not be given medications that are aimed at eliminating diarrhea. With their help, only the urge is reduced, but the virus remains inside the body and is not removed outside. In this case, you can only achieve worsening of the disease.
First aid
In general, says Komarovsky, the algorithm for reasonable parental actions in case of childhood diarrhea should always look like this:
- Drink plenty of warm drinks. Frequent and fractional. Plain water and saline solution. If a child pees every 3 hours, it means he is consuming enough fluid to prevent dehydration. If you can’t get someone to drink even with a disposable syringe without a needle, call an ambulance.
- Place the small child on his side so that in the event of an attack of vomiting he does not choke on the vomit.
- Antipyretics - only if the temperature is above 38.5.
- Monitor the child's condition and prevent dehydration. At the first symptoms of dehydration, call an ambulance.
- Don't feed. If he really asks, give liquid porridge or puree in small quantities.
Before the doctor arrives, leave a diaper with stool or keep a sample of the contents of the potty to show the doctor. This way, the doctor will be able to diagnose the disease faster, and the likelihood of an error will be reduced (rotavirus, for example, is very similar to cholera in its initial stages).
Another mistake that can cost parents dearly is the unauthorized prescription of antidiarrheal drugs (for example, Enterofuril). With rotavirus, viral particles (more precisely, their microparticles) are released in the stool. Therefore, stopping diarrhea means prolonging the disease, leaving viral particles in the small intestine, where they will continue to destroy beneficial cells for some time. There is no need to fight diarrhea; it is a defense mechanism of the body.
Another misconception is the effectiveness of antiviral drugs for intestinal infections. A doctor called to your home will most likely prescribe something antiviral, because, according to Komarovsky, no doctor wants to have long conversations about the benefits of drinking plenty of fluids and thereby take responsibility for the situation.
It is worth abandoning homeopathic remedies (“Anaferon”, “Ocillococinum”). The situation with their effectiveness and proven action is even worse, and the purchase of such drugs, according to Evgeniy Komarovsky, will only become an extra burden on the family budget.
Symptoms and treatment are inextricably linked. Therefore, the more accurately you describe the child’s condition to the doctor, the more correct the therapy will be. We will tell you in this article what to do if you suspect rotavirus in your baby.
The digestive system of a person, and especially a child, is one of the most sensitive. Every day, the gastrointestinal tract has to process large volumes of food and liquid. Sometimes the quality of consumed products leaves much to be desired - they are contaminated with viruses, contain heavy metals and microorganisms, and are toxic.
Rotavirus infection is easily transmitted. This is due to the fact that transmission of infection has a nutritional mechanism. Viruses that manage to enter the environment settle in the most unpredictable places (mobile phones, door handles, clothes, shoes, toys). For the infection to begin to spread, it is enough for 1-2 replicas of the virus to enter the oral cavity.
Can you get infected?
Most often, the infection occurs in children under one year of age. Infection of newborns and older children occurs from a carrier, for example, from a mother or brother (sister). If parents were in contact with a person suffering from an intestinal infection, then they could become carriers of the virus, and, having infected the child, they themselves could not get sick.
Virus shedding usually lasts up to 8 days. But sometimes it can take up to 3 weeks. Viruses can be excreted in feces and during asymptomatic disease. Rotavirus is not excreted through the respiratory tract.
There are also cases of asymptomatic disease in children who are breast-fed or mixed-fed, whose mothers (in their milk) have antibodies to the pathogen. In children who have recovered from the disease, antibodies are then detected in the blood.
First signs
The disease manifests itself when the virus invades enterocytes. When a certain concentration of rotavirus in the body is reached, cells begin to die and the infection affects the intestinal environment.
Some viruses are eliminated by the body, but the predominant component continues to poison the body and multiply.
Once in the digestive system, the virus causes damage to the epithelium of the small intestinal mucosa. Desquamation of infected cells leads to their replacement. This leads to functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and intestinal hypermotility with the development of diarrhea is observed.
From the moment an infant is infected with rotavirus until symptoms appear, it can take from 15 hours to five days. The disease begins acutely and progresses rapidly. Therefore, it is important to notice them in time and promptly help the child by prescribing a competent course of treatment.
Rotavirus is much more severe in infants than in older people. The manifestation of symptoms depends on the severity of the disease. Let's look at three typical forms.
Light form
In this situation, the baby's appetite noticeably decreases, the child looks lethargic, cries and is capricious. In most cases, the temperature level rises, but does not exceed 37.5 degrees.
After a few hours, the baby may begin to vomit, regardless of whether he has eaten. In addition, a mild form of infection is characterized by stool disorders and diarrhea.
Medium form
In this case, the temperature rises. The baby regurgitates milk or baby purees, and the frequency of loose stools reaches 7 times per day. With proper treatment, signs of diarrhea should disappear after 2-3 days.
Severe form
It has an acute onset. The child immediately begins to vomit, which is systematic, and diarrhea occurs up to 15 times a day. This condition can be called critical; it threatens life, as it directly leads to dehydration of the body.
Due to a lack of fluid in the body, the child experiences dryness of the epidermal layers of the skin and mucous membranes. If treatment is started on time, the duration of the disease will be no more than 10 days.
Moderate and severe forms of rotavirus infections occur more often in newborns and infants. In some cases, the disease is confused with dysentery and salmonellosis.
Therefore, it is important to correctly differentiate the diagnosis from acute intestinal infections, in the clinical picture of which the gastroenteritis syndrome is decisive (for example, gastroenteritis itself, cholera, foodborne toxic infections).
This disease can also develop gradually. At the very beginning, the baby’s appetite decreases, lethargy and drowsiness appear.
- Parents cannot always immediately pay attention to these primary signs and often perceive them as the child’s whims, which occur due to changes in mood.
- At first, the temperature may rise to 37.1-37.2 degrees, but not everyone takes this as a pathology, since for many children this temperature is normal.
- Often, with the development of rotavirus in infants, the following may occur:
- runny nose appears,
- enlarged lymph nodes in the neck,
- sink a fontanel.
When the stomach growls, the child may cry - this indicates that he is in pain and uncomfortable. Abdominal pain is weak and constant, rarely cramping.
To accurately determine the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct blood, urine and stool tests in a special laboratory. Pharmacies also sell special rapid tests that help determine rotavirus at home.
So, you should immediately consult a doctor if your child:
- is capricious and cries constantly. Draws in the legs - this indicates pain in the abdomen;
- looks lethargic, refuses to take the breast (a bottle with formula), or eat usual or favorite foods;
- complains of nausea or vomits more than twice in an hour;
- diarrhea;
- has a body temperature of 37.2.
If at least two or three signs are present, it is important to suspect the presence of an infection in time and begin to fight the virus in order to prevent it from multiplying in the body.
How to treat
Treatment of rotavirus must be comprehensive. Loss of water and salts in the stool can lead to mild dehydration. You can determine that dehydration in an infant has reached a critical point by the following signs:
- dry tongue
- constant crying for no reason,
- no urination for more than 3 hours,
- no sweat is produced
- convulsions begin, the child loses consciousness.
Replenishing fluid balance. Since the most dangerous thing with this infection is dehydration, the main and primary task will be to replenish the balance of fluid lost in the first days of the disease.
To replenish moisture, experts recommend giving your baby oral rehydration solutions:
- Regidron,
- Hydrovit,
- Humana.
To prepare the solution, you need to dissolve one sachet in 1 liter of boiled water. It is necessary to give it to the child throughout the day. He should drink about 500 ml per day.
It is also important to give your baby clean water and breastfeed him. Mother's milk is half water, so it will well replenish lost fluid in the body. Treatment with rehydration drugs is the only method recognized by the World Health Organization (hereinafter referred to as WHO).
We normalize the balance of intestinal microflora. With rotavirus infections, intestinal disorders occur, in which the microflora is washed out, and an imbalance of beneficial bacteria in this environment occurs. To correct the balance of intestinal microflora, doctors prescribe medications that contain the necessary lactobacilli and probiotics.
Adjusting the temperature. The temperature should be reduced only when it reaches 38 degrees and above. In such situations, antipyretic suppositories help well:
- "Nurofen". Used from 3 months;
- "Cefekon". Possible from birth.
The child must be undressed and the diaper removed. It is recommended to wipe with warm water, then cover the baby with a diaper. You should not wrap your child up, as this may increase the temperature. It is forbidden to rub down with vodka or vinegar, as this can cause intoxication of the body.
How to treat at home
Therapeutic diet
It is important not only to know how to treat rotavirus in an infant, but also what he can eat. Inflammation caused by rotavirus infection is characterized by the fact that it almost completely stops the production of enzymes required for the normal breakdown and absorption of consumed food. In children under one year of age who are breastfed or bottle-fed, the amount of lactase decreases and a general enzyme deficiency develops.
It takes quite a lot of time for the villi on the mucous membrane and their production of the required enzymes to fully recover. In order not to provoke indigestion and not cause disturbances in the functioning of the child’s intestines, it is important to follow a gentle diet throughout the entire period of treatment.
During the active stage of the disease, children under one year of age are not fed (if there is no appetite). It is enough just to feed them with saline solutions during the day. The next day, when the baby feels a little better and has an appetite, the process of restoring villi and lactase production will just begin in his body.
At the beginning of the second week, you can try replacing one lactose-free feeding with breast milk or your usual formula. In this case, it is very important to carefully monitor the reaction of the infant’s intestines.
If the child has already started receiving complementary foods, then part of the lactose-free food can be replaced with dairy-free rice porridge and mashed potatoes. Gradually, pureed meat and dairy products are added to the baby’s diet. The very last thing to introduce is fruit puree.
Infants should remain breastfed. An older child who feeds on his own continues to take his usual food, but its volume must be reduced by 2-3 times. Also, milk, animal fats, sour, spicy, pickled and salty foods are completely excluded from the diet.
Preventive actions
The only effective way to protect a baby from such a disease is vaccination. The vaccine contains a weakened virus. It is administered orally to each infant.
Vaccination is carried out 32 weeks after birth. This drug is absolutely safe and does not cause any side effects in the baby.
An important means of prevention is mandatory personal hygiene. Any person who comes into contact with the baby is obliged to maintain personal hygiene. Before touching the child's body, you need to wash your hands well, always with soap. All of the child’s belongings and utensils must be kept perfectly clean.
If the baby is bottle-fed, you need to thoroughly boil the nipples and bottles before feeding.
If an adult becomes ill with an intestinal infection, everything possible must be done to prevent the child from coming into contact with this person.
When the disease has been defeated, the newborn no longer experiences complications. Partial immunity is formed in his body, protecting the body from secondary infection. But if it occurs, the course of the disease will not be severe.
Development mechanism
In the first days after infection with rotavirus infection, the child does not feel any signs of illness. The appearance of the first symptoms of the disease indicates that the stage of the incubation period is completed, and the intestinal microflora contains an excessive amount of pathogenic microorganisms. The table below shows the mechanism of development of rotavirus infection.
| Disease stage | Clinical characteristics |
| Incubation | This is a latent period in the development of the disease, when the infection virions are already inside the child, but do not yet provoke an acute immune response. The duration of the incubation stage depends on the strain of the virus, the number of virions that have penetrated the gastrointestinal tract, as well as the individual characteristics of the organism. At the same time, it does not exceed 5 days. |
| Acute | Immediately after completion of the incubation stage, the child develops acute symptoms, accompanied by disruption of intestinal function. This period lasts from 3 to 7 days, and in severe cases of the disease it can last more than 1 week. |
| recovery | The recovery stage begins as soon as acute symptoms cease. The period of restoration of intestinal function lasts from 4 to 6 days. |
The development of rotavirus infection is characterized by the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the intestinal walls, as well as the development of acute inflammation of its mucous membrane. The body's immune reaction leads to temporary disruption of the functions of the digestive system. After developing immunity, the symptoms of the disease gradually disappear.
The very first signs
According to statistics, this infectious disease most often affects children aged 6 months to two years. It is believed that up to six months the baby still has immunity to this infection, but later it gradually weakens.
The first signs of the disease do not develop immediately. A viral infection has a certain incubation period. During this time, rotaviruses accumulate in the infected body and “get ready” to exert their effect. The incubation period for this infection usually lasts from several hours to a couple of days. After its completion, the infant begins to experience unfavorable symptoms.
One of the characteristic symptoms of infection is fever. It usually builds up quite quickly. By the end of the first day from the onset of the disease, its numbers can reach 38-38.5 degrees Celsius.
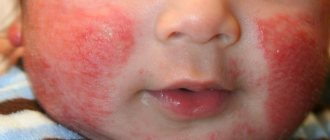
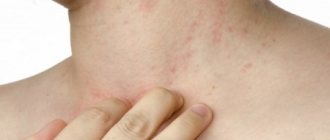
Given this febrile condition, the baby feels very bad. The child becomes lethargic and inactive. The baby's appetite decreases significantly. Vomiting may occur due to high fever. A febrility may also be accompanied by fever. A child's skin may change color - first bright red, and then pale.
In some cases, it can be quite difficult to reduce a baby’s high body temperature. Taking antipyretics does not lead to a quick positive effect. The body temperature of a sick baby returns to normal only 4-5 days after the onset of the disease.
The second no less characteristic symptom of rotavirus infection is stool upset. It is no coincidence that this disease is also popularly called intestinal flu. Diarrhea is a classic symptom for this infection. The baby's stool becomes watery and repeated.
Diarrhea is often accompanied by abdominal pain. A newborn baby cannot yet tell his parents about this in words. To express his own discomfort, he uses another “communication system” - crying. The behavior of a sick child immediately changes.
Experiencing abdominal pain, the baby cries loudly and angrily. Attempts to pick up the baby and calm him down often do not lead to a positive result. Attempts to touch the tummy can lead to increased pain, which is manifested by increased crying.
Possible complications
With timely seeking medical help and adequate care for a sick child, the prognosis for a speedy recovery is positive. The only exceptions are clinical cases when a child is diagnosed with a severe form of the disease.
In this case, the following complications may occur:
- intestinal dysbiosis;
Rotavirus infection in a child causes dysbiosis. Its symptoms are treated with live intestinal bacteria called probiotics. - intoxication of the body;
- decreased immunity;
- chronic diarrhea;
- gastritis;
- gastroduodenitis.
The presence of the above complications is temporary. In most cases, the child’s condition stabilizes within 1-2 months. after complete recovery. The occurrence of gastritis and gastroduodenitis requires compliance with dietary standards.
Rotavirus in infants can be accompanied by a bacterial infection caused by Proteus, Staphylococcus, Klebsiella, and Escherichia coli. Then the child's stool becomes very liquid and foamy, gray in color with a foul odor. The stool often contains blood and mucus. The baby's health deteriorates sharply. In this case, treatment in a hospital is required.
What Komarovsky says
The pediatrician claims that the main causative agent of the infection is failure to comply with basic rules of general hygiene . Therefore it is imperative:
- store food correctly,
- wash your and your child’s hands before eating, after walking,
- Do not allow insects to appear in the house.
To prevent the child from being hospitalized, the main task of the parents is to give the baby water to avoid dehydration. It is only for this reason that the child is admitted to the hospital so that the situation does not worsen without timely medical assistance.
The doctor recommends feeding the baby with pharmaceutical saline solutions . But you can prepare them yourself: mix three teaspoons of sugar (without top) and half a teaspoon of salt with a liter of boiled water. Fluid consumption should correspond to the norm of 100 ml per kilogram of the child’s weight.
If the baby refuses the solution, then give him plain water or dried fruit compote. If there is a categorical refusal, the doctor advises giving the child any liquid.
Rotavirus can cause a rather dangerous disease. Infants are very sensitive to infection by these microbes. This article will tell you what symptoms this disease has and what is the treatment for rotavirus infection in infants.
Laboratory research
To diagnose rotavirus infection, the child must be examined by an infectious diseases specialist or pediatrician. Then you will need to submit stool for laboratory testing.
Isolation of viral microorganisms is carried out using the following diagnostic methods:
- PCR;
- electron microscopy.
At home, you can use a rapid test, which is sold at the pharmacy. The object of study is also the feces of a sick child.
Vaccination against rotavirus
The only effective prevention of rotavirus is vaccination. There are now 2 vaccines that have passed all the required clinical trials. They contain a weakened virus and have almost no side effects.
The vaccine is taken orally. The vaccine is given to children between 6 and 32 weeks of age.
According to reviews, rotavirus in infants is a very complex and dangerous disease, which is mainly treated in a hospital setting, since various types of complications can arise if therapy is carried out incorrectly. All medications and courses of treatment should be prescribed only by a doctor, since the health and life of the baby largely depends on this.
Achieving normal body temperature
For treatment to give a positive result, it is necessary to normalize body temperature. But this should be done only if it exceeds 38 degrees.
For this purpose, special antipyretic suppositories are used, inserted rectally. From birth, the child is treated with Cefekon suppositories. Depending on the age of the baby, the dosage of the drug is selected. This antipyretic drug is completely safe for the child, so it can be used immediately after the birth of the baby.
Candles are given to the child at intervals of 2–3 hours. It is very important not to overdo it. If the body temperature begins to rise, it is strictly forbidden to wrap the child in a warm blanket and put warm clothes on him. There is no need to cover a sleeping child with a blanket; a light sheet will be enough.
To achieve normal body temperature in a child, antipyretic suppositories are used.