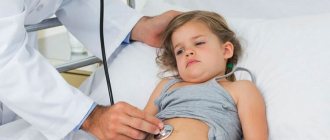
Causes of dehydration in infants
The term dehydration or rehydration means a stage of lack of fluid in the human body, at which it enters the body in much smaller quantities than is excreted.
The result is a violation of the water-alkaline balance of the body and a decrease in the total volume of red blood cells in it. In addition, there are hemodynamic disturbances in the body. Dehydration in infants is especially dangerous because it occurs rapidly and has quite unpleasant consequences. It is for this reason that it is extremely important to have a good understanding of what exactly causes dehydration in infants. In a child under one year of age, dehydration may occur for the following reasons:
- poorly adjusted drinking regime. Due to his age, a child cannot yet inform his parents about the thirst that torments him, and parents, due to inexperience (if this is their first child), may simply not be aware of it;
- overheating of the baby. Due to the heat exchange process that has not yet been established, a child can easily overheat, which will result in the evaporation of the liquid he drinks along with sweat;
- diseases accompanied by an increase in the child’s body temperature. In this case, a loss of water occurs, and if the baby has a sore throat, he may simply refuse to drink, which results in a disruption in the process of replenishing fluid in his body;
- manifestations of diarrhea or vomiting due to the penetration of a bacterial infection into the child’s body. In this case, the child loses a significant volume of fluid that cannot be restored;
- features of the child’s physiology. If you compare it with an adult, the loss of fluid in a baby’s body occurs much faster. Rapid evaporation of water occurs due to the permeability of the cell membrane of a small child. The body of an infant contains four-fifths of water, while the body of an adult contains only three-fifths.
What should you not do if your baby is dehydrated?
Because dehydration is potentially life-threatening for an infant, the following actions are not recommended:
- If you treat your child independently, if his condition raises concerns, it is better to consult a doctor for help.
- Trying to select a drug, increase the dosage of a medication, start taking antibiotics - such actions are unlikely to be within the competence of parents.
- Immerse the baby in water, trying in this way to compensate for the lack of fluid in his body.
- Give your child plenty to drink, as this can cause vomiting and worsen existing problems.
- Undress the baby, trying to correct his condition using this method.
- Giving various herbs may have a diuretic effect, which will lead to the opposite effect.
- Use traditional methods of treating dehydration - they will not bring any effect.
- Giving sugary water, juice or other drinks high in sugar will only make you thirstier.
In an attempt to help a baby, parents can unknowingly cause serious harm to the baby’s body. A timely visit to the doctor will help to avoid this; the doctor will cope with the problem faster, will be able to adequately assess the condition of the small patient and, if necessary, will refer him for hospitalization in a hospital.
Recommended video:
Signs of dehydration in a baby
Knowing the signs of dehydration in an infant will help parents recognize their baby's condition in a timely manner and provide him with all the necessary assistance in a timely manner. These signs can be monitored; it is generally accepted that there are three main degrees of dehydration in infants:
- A mild degree of dehydration in a child’s body almost always goes unnoticed. Its main indicator is the thirst experienced by the child. The child himself cannot yet publicly announce his condition, but by carefully observing him, one can note some signs that indicate this condition. The baby begins to lick his lips frequently, his urination becomes difficult and he too often begins to reach for water when he sees it;
- the average degree of dehydration is accompanied by an acceleration of the child’s pulse; his lips may become dry, some shortness of breath may appear slightly, and the fontanel will sink. His tongue will dry out and begin to stick, saliva will acquire a certain viscosity, the child will begin to show anxiety, and less often than earlier he will begin to urinate;
- a severe degree of dehydration of an infant's body is accompanied by the cessation of his bowel movements, and changes in his pulse occur. This can manifest itself both in acceleration of pulsation and in its deceleration. The pulsation slows down, the fontanelle becomes retracted, and the skin becomes dull and sagging. All the child’s actions are accompanied by some inhibition.
In this case, parents should pay attention to the increase in the child’s body temperature, the darkening of his urine, as well as the dryness of his diaper when waking up in the morning.
The first signs of dehydration in infants
It is not always easy to quickly identify dehydration in infants, since the child himself cannot express his condition out loud, and parents, especially if this is their first child, tend to attribute the situation to other factors. In order to be able to quickly determine the condition of your baby, it is advisable to be able to quickly identify the first signs of such a problem. There are several of them:
- confluence of the fontanel of an infant and his eyes;
- sudden dryness of the skin, its inflammation and a feeling of intense warmth when touching the child’s skin;
- the skin becomes less elastic and even rough to the touch;
- The child begins to show anxiety and cries loudly.
If diarrhea and vomiting are added to all of the above symptoms, the child needs immediate medical attention. The situation should not be left to chance, since dehydration in infancy is very dangerous; it is best to place the baby in a hospital setting to quickly resolve the problem.
Signs of dehydration in a baby with diarrhea
Symptoms of nausea, diarrhea and vomiting are characteristic of a large number of diseases. First of all, this applies to painful conditions characterized by the penetration of various infections into the body. If diarrhea is of a significant degree of intensity, we can talk about the possible loss of a significant amount of fluid in the body, which can become one of the reasons for the development of dehydration.
The most characteristic symptom indicating dehydration of an infant's body due to diarrhea is the child's weight loss. We are talking about reducing the baby’s weight by four kilograms within three days. Severe dehydration involves a child losing one-tenth of his or her original body weight. It is the lack of moisture in the baby’s body that can be the most important sign of dehydration during diarrhea. The result may be disruptions in the child’s water balance, disruption of the functioning of his kidneys, as well as other unpleasant situations that threaten the health of the little person.
Causes of water shortage
Dehydration in infants occurs when the required amount of fluid is not regularly supplied to the body. It is important to recognize the situation in time and take all measures to eliminate the negative consequences. The causes of this condition:
- Quite often, vomiting and diarrhea remove all fluid from the body. The situation is dangerous because additional minerals are removed from the body.
- Infectious diseases often resolve with elevated body temperature, which helps remove all fluid from the body.
- Taking diuretics.
- Diabetes causes a large amount of urine to be produced. Its production requires spending additional water from the body's resources.
- Excessive sweating, which is a consequence of various pathologies.
- The baby may also refuse drinks due to poor health. For example, the symptom often appears during teething. The baby sometimes completely refuses mother's breast milk.
The manifestation of dehydration occurs against the background of changes in the functioning of some organs and systems or the lack of supply of a necessary component for a long time. Dehydration is dangerous when severe, so it is important to respond to the first symptoms in a timely manner. Mommy must provide the baby with the necessary amount of drink.
Common symptoms of dehydration in infants
When the process of dehydration of an infant begins, a gradual development of a certain clinical picture takes place, which is characteristic of this particular condition of the baby. At the same time, general symptoms have significant variability in manifestations. There are several characteristics by which this condition can be identified:
- the child begins to suffer from thirst, which is noticeable by changes in his condition, additional nervousness, irritability, and a constant craving for water, which he notices;
- The child experiences drying of his skin, and the oral mucosa also becomes dry, which is especially unpleasant for him. His skin loses its firmness and elasticity;
- the child becomes lethargic, inactive, and begins to fall asleep more often than usual;
- when a child starts crying, there are no tears in his eyes;
- The child’s urine darkens significantly and its smell becomes much more pungent. Similar symptoms are easily detected in a baby under one year of age by the change in color and smell of his diapers;
- urination becomes very rare compared to what was noted earlier. The break during urination can be up to eight hours;
- When you apply your hand to the area where the fontanel is located on the child’s head, it is noted to be significantly retracted. This is also one of the common signs of dehydration in children under one year of age. In the normal state of affairs, there should be no swelling of the fontanel in this area, nor its retraction;
- The child's eyes are sunken.
Dehydration in infants: treatment
It is best to immediately consult a doctor when dehydration begins to develop in a baby to prescribe specific treatment. It should include an enhanced drinking regime, including abundant consumption of milk or milk-based formulas. In this case, it’s not bad even if the child starts drinking less milk than before, but starts doing it more often. For a child who is bottle-fed, it is important not to dilute the formula he consumes. For children who are both artificially and naturally fed, and at the same time eat solid complementary foods, there may be an excess of fluid in their body. You should not give your child large amounts of juice if dehydration was caused by vomiting or diarrhea.
If a child’s body is dehydrated, the baby may consume an oral rehydration solution, but small portions should be given to him; it is also possible for the child to consume a mixture of milk and water. Such methods make it possible to qualitatively replenish the loss of fluid in the baby’s body, as well as the sugar and salt he has lost.
The use of children's varieties of Paracetamol and Ibuprofen is indicated in cases where the child has difficulty swallowing and for this reason he cannot drink. It is best to consult a pharmacist or pediatrician if you are not sure that the use of these medications can help your child.
During hot times of the day, it is best to keep the child in a cool place, away from the sun, and at the same time give him plenty of fluids. When breastfeeding, this may not be necessary, since the baby may not need additional fluid. This measure is justified in cases where the child is bottle-fed or eats solid food.
Dehydration in an infant
Dehydration is the process of complete dehydration, which is very dangerous for the baby.
The body of any person consists of 80% water, so its loss is very dangerous and can lead to negative consequences. Against this background, irreversible pathologies that are dangerous to the child’s health develop.
Dehydration in a baby should be stopped in time, so parents should know the first signs of this condition.
Causes of water shortage
Dehydration in infants occurs when the required amount of fluid is not regularly supplied to the body. It is important to recognize the situation in time and take all measures to eliminate the negative consequences. The causes of this condition:
- Quite often, vomiting and diarrhea remove all fluid from the body. The situation is dangerous because additional minerals are removed from the body.
- Infectious diseases often resolve with elevated body temperature, which helps remove all fluid from the body.
- Taking diuretics.
- Diabetes causes a large amount of urine to be produced. Its production requires spending additional water from the body's resources.
- Excessive sweating, which is a consequence of various pathologies.
- The baby may also refuse drinks due to poor health. For example, the symptom often appears during teething. The baby sometimes completely refuses mother's breast milk.
The manifestation of dehydration occurs against the background of changes in the functioning of some organs and systems or the lack of supply of a necessary component for a long time. Dehydration is dangerous when severe, so it is important to respond to the first symptoms in a timely manner. Mommy must provide the baby with the necessary amount of drink.
Severe consequences of the process
Dehydration in newborns leads to negative changes in a large number of metabolic processes. First of all, it negatively affects the absorption of chlorine and potassium. The components are necessary for the proper growth and development of the central nervous system. If the pathology is not eliminated in time, the baby’s risk of kidney failure increases.
Severe illness puts the baby into shock, so he may lose consciousness. The situation is aggravated by seizures. They indicate the beginning of negative changes in the brain.
During this period, it is necessary to provide medical assistance. Otherwise, the risk of death increases.
Only a doctor can correctly assess the condition of a small patient and prescribe the necessary therapy.
Degree of manifestation of the disease
Depending on the volume of fluid lost, the degree of dehydration in an infant is determined.
A mild manifestation is diagnosed if no more than 5% of the substance is lost from the total body weight.
In this case, the following symptoms of dehydration of this nature are distinguished:
We recommend reading: Diarrhea in newborns
- The baby is constantly thirsty.
- Bright flashes of vomiting are observed periodically.
- Stool occurs two to five times a day.
- The condition and character of the mucous membranes change noticeably.
The manifestation can be recorded at the first stage of dehydration development.
The balance can be restored independently, provided that fluid is regularly supplied to the body.
The average degree is diagnosed in the absence of 6 to 9% of the required volume of water in the body. The following signs of dehydration in an infant at this stage of development of the pathology are identified:
- Stool occurs several times more often. For children older than six months, the frequency may be more than ten.
- Excessive salivation and vomiting.
- Lack of mucous membrane in the nose and mouth.
- Poor palpation of pulse.
- The skin has a characteristic blue color.
- The skin becomes less elastic.
A severe degree poses a real threat to the child’s life. A sign of its presence is considered to be the removal from the body of more than 10% of fluid from the total body weight. The symptoms are similar, but more pronounced.
Children become cranky and have difficulty sleeping when dehydrated
The frequency of attacks also differs:
- Profuse diarrhea.
- Complete drying of the mucous membranes.
- The child has no facial expressions.
- You can additionally record the retraction of the fontanel and eyeballs.
- In some situations, the baby cannot close his eyes completely.
- The skin becomes blue.
- Complete absence of urination.
- A marble pattern is noticeable on the epidermis.
- The limbs are completely cold.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Heart beats too fast.
The manifestation is dangerous because it occurs with complete leaching of potassium cells. In their absence, there is a deterioration in the functioning of the central nervous system, which becomes pathological.
Parents also need to know how to recognize that their child is extremely dehydrated. In this case, he can lose up to 20% of his own body weight.
The changes are irreversible, because disruption occurs in the functioning of organs and individual cells of the skin.
That is why mothers should be extremely attentive to their babies and, if they detect the first symptoms of the disease, immediately seek advice from a doctor.
How to properly treat dehydration?
It is also important to determine the degree of development of the negative situation. Not all parents will be able to cope with the process on their own. To do this, you should consult a pediatrician. He will carefully analyze the nature of the manifestation and select the necessary course of treatment. To eliminate severe forms, a mandatory hospital stay is required.
If parents notice the first signs of dehydration in their baby, then they should give him solutions that can replenish the fluid deficiency in the baby’s body. It is necessary to be extremely attentive to this manifestation if the situation is caused by diarrhea or vomiting.
Dehydration often occurs due to a sore throat. After all, during this period the child cannot drink. It is advisable to use antibiotics to treat rotavirus infection.
If a child has diarrhea for a long time, it is also recommended to use special drugs to restore stool.
Regidron helps cope with dehydration in infants
The situation cannot be left to chance, because it can only get worse.
- If a child has a bowel disorder in the form of diarrhea, it is recommended to give him plain boiled water to drink. You should completely avoid juice, compote or tea, because these drinks can only worsen the general course of the disease. Even water should be given in small portions. Thanks to this, it will be possible to achieve maximum digestibility.
- Vomiting is characterized by other manifestations. To eliminate it, you should give your baby special solutions every five minutes. A large volume is dangerous because it can lead to severe irritation of the stomach or esophagus. In this case, vomiting can only intensify, and with it the general picture of dehydration.
- To improve the process of moisture absorption, Regidron should be used. The drug is available in powder form, which must be diluted in ordinary boiled water. It should also be given to the child in small quantities, but often. Thanks to this, it will be possible to achieve a stable state within a short period.
Pediatricians recommend always having Regidron in your first aid kit. However, if it was not available at the required time, then a composition with similar properties can be made independently.
To do this, you will need to add 0.5 tsp to one liter of water. salt and soda. To improve the properties of the mixture, 4 tbsp is also added to it. l. granulated sugar. You will also need to take one fourth of the ampoule of potassium chloride.
This substance is used in the process of homemade curds.
At the first sign of dehydration, seek medical attention
Preventive actions
- The baby must receive enough fluids for proper growth and development. On average, this volume per day ranges from 100-150 ml per kilogram of weight.
- The child drinks much more water in the hot season. He should not be limited in this.
- Fluid from the body may also be excreted through sweat. The situation can only be prevented if you do not wrap up the baby.
- If during treatment it is necessary to take diuretics, then during this period it is important to provide the child with sufficient fluids.
- Parents are recommended to always have Regidron in their first aid kit. It can only be used if its expiration dates are within the acceptable range. The drug helps cope with the consequences of vomiting and diarrhea. Thanks to this composition, it will be possible to prevent the development of complete dehydration of the body.
Dehydration is a dangerous manifestation for the fragile body of an infant.
Parents should be extremely attentive to his state of health and, if there are characteristic symptoms, quickly seek advice from a doctor. In this case, they will not allow the development of negative manifestations and serious consequences.
Source: https://floragaz.ru/zdorovye/obezvozhivanie-grudnogo-rebenka
Causes of lack of fluid in the baby’s body
The causes of dehydration in infants can be different. This applies mostly to a child under one year old who cannot speak and cannot express his desires in words.
- Physiological features. An infant loses fluid much more rapidly than an adult. It is for a baby that the statement that a person consists of 80% water is true. In adulthood, this percentage decreases to 60. A child has thinner skin, the baby's cell membranes are easily permeable, so water evaporates at a faster rate.
- Fluid loss due to vomiting or diarrhea during gastrointestinal infections. Uncontrollable vomiting or debilitating diarrhea quickly disrupts the precarious water-salt balance in the child’s body and does not allow it to be restored through the fluid consumed, especially if every sip taken results in a new attack of vomiting.
- Fever or high temperature during acute respiratory viral infections and sore throats is a common cause of dehydration. The baby has problems swallowing due to an inflamed throat, so he drinks less and does not have time to replenish the volume of lost fluid.
- When overheating, a child loses a lot of fluid through sweat and breathing. Overheating in young children is common. Imperfect thermoregulation can lead to such consequences even if the temperature in the environment is slightly exceeded.
- Unbalanced drinking regime. A newborn may feel thirsty, but cannot let its parents know. Inexperienced parents have no idea how much water to give their baby per day, or are not even aware that they should be given extra water at all.
Risk group for dehydration
Some babies are at higher risk of dehydration. If parents are aware of this, they can significantly reduce it.
Premature babies and infants with digestive disorders are at risk. In the first category, the metabolism is much faster than in children born at term, so during breathing, as well as with urine and stool, they lose more fluid than necessary. Such babies need to be offered water as often as possible and from the very first days, preferably every 10-20 minutes. With lactase deficiency, sugar is not broken down by enzymes, absorbs water and is excreted along with the stool, which because of this becomes liquid and abundant. Cow's milk intolerance causes not only diarrhea, but also vomiting. For such digestive disorders, the child will need treatment to eliminate the root cause of dehydration.
How often does a child of the first year of life get sick?
For any mother, a baby’s illness becomes not only a reason for violent unrest, but also a source of troubling questions. The most common of them is: how often can a child get sick in the first year of life? Read more
15 feats of a newborn
Wise nature has provided newborn babies with a whole arsenal of innate reflexes that help them quickly adapt to new life circumstances. By checking these reactions, you can judge how the nervous system is developing, and by eliminating failures, you can level out disturbances at an early stage. Read more
Children's drinking water
In order for water not only to quench thirst, but also to enrich the baby’s body with essential minerals, you need to give preference to a product specially created for baby food. What is the difference between children's drinking water and adult drinking water? Read more
Degrees and signs of dehydration
Dehydration can be mild, moderate, or severe. Each degree of this condition has its own symptoms.
Mild degree
Mild dehydration in a baby is almost invisible. Only attentive parents of a baby can understand that the baby is thirsty. He behaves restlessly, licks his lips, reaches for water if he sees it next to him. A sign of mild dehydration is urinating less frequently. The diaper fills more slowly than usual.
Average degree
The middle degree looks a little different:
- accelerated pulse;
- dry lips;
- shortness of breath on exertion;
- slight but noticeable retraction of the fontanelle;
- sticky, dry tongue;
- viscous saliva;
- noticeably less frequent urination;
- anxiety, “causeless” crying.
Strong degree
This stage of dehydration is characterized by even more serious symptoms:
- stopping urination;
- pulse disturbances: severe slowing or acceleration;
- slow breathing;
- severe retraction of the fontanelle;
- lethargy, sagging skin;
- lethargy.
A fever and dark urine can also be signs of dehydration, as can a diaper that remains dry for a long time, especially after sleep.
Treatment of dehydration
If the fact of dehydration is established (by a doctor or the parents themselves), then it is necessary to immediately begin to remove the child from this state.
A slight degree of dehydration can be eliminated by simple supplementation. Determining whether a baby is drunk is very simple: he simply stops drinking and turns away from the bottle or cup as soon as he quenches his thirst.
Moderate dehydration is usually the result of an infection accompanied by diarrhea and vomiting, so simply drinking water will not help. It is necessary to supply the body not only with water, but also with salts, the loss of which occurs at a catastrophic rate. In this situation, the baby is given Electrolyte or Regidron instead of water. If it is impossible to give the child something to drink due to vomiting, the water-salt balance is adjusted through infusion therapy (droppers with saline solution).
Severe dehydration can only be treated in a hospital. Doctors monitor such a child around the clock.
The more severe the degree of dehydration, the more dangerous the condition and the more difficult it is to get out of it. Therefore, in any potentially dangerous situation (high temperature, hot weather, intestinal infection), it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the baby and prevent severe loss of water from his body.
Signs of dehydration in a baby
Signs of Dehydration in a Baby: How to Identify Dehydration in Your Baby.
For a new mother, it is simply necessary to be able to identify signs of dehydration in a child. In this article we will talk about this in detail. Dehydration
- this is a banal lack of water in the body. In medical terms, it is the loss of water from the cells of the human body through sweat, urine, vomiting and diarrhea, which is not compensated for.
The child may be too ill to drink, or water may not be available.
Dehydration occurs very quickly in infants and young children as a result of gastrointestinal illness or fever. This is very dangerous, even life-saving measures may be required, since a violation of the water-salt balance leads to a severe imbalance in metabolism.
Dehydration in infants
We often encounter dehydration in everyday life. But if to eliminate the problem it is enough for an adult to quench his thirst, then dehydration in an infant requires special control and special measures of assistance, because he is not used to drinking water. How to help the baby?
March 1, 2013 · Text: Svetlana Lyuboshits · Photo: GettyImages
Lyubov Kharitonova
pediatrician
Nina Lerner
pediatrician at the European Medical Center
Dehydration in a baby occurs when the body experiences an acute lack of fluid. Unlike adults, very young children are at higher risk of dehydration due to several factors. Despite the fact that the tissues and organs of babies contain much more water than adults, their cell membranes are highly permeable, so it evaporates faster. A water molecule “lives” in a baby’s body for no longer than 3-5 days, while in an adult’s body it lasts an average of 15 days.
Children actively lose moisture not only during bowel movements and urination, but also through the lungs during breathing and through the skin through sweat. The second feature of babies is that their water-salt metabolism is much more intense than that of their parents. But it also consumes a lot of fluid, and if its volume decreases and is not replenished, the level of potassium and sodium decreases, which can lead to malfunctions of the kidneys and brain.
Dehydration in infants most often occurs if the mother is young and inexperienced. The first warning signs may be present already upon discharge from the maternity hospital. The reason for this may be difficult childbirth. If the baby was born weakened, he may be reluctant to suckle at the breast and become very tired from sucking it. In the maternity hospital, they sometimes solve this problem by supplementing the baby with formula instead of teaching an inexperienced mother breastfeeding skills.
To avoid such troubles, parents need to make sure that the child receives a sufficient amount of fluid with food and drink. The volume of liquid that a baby should consume per day depends on its age and weight. The daily norm for a baby up to one year is 100 ml of liquid per kilogram of weight. This includes not only water, but also breast milk, and liquid contained in porridge, purees, etc. Please note that an increase in temperature outside or in an apartment by 1°C above what is comfortable for a baby 20°C -22°C requires the consumption of an additional 100 ml of liquid.
For this reason, pediatricians recommend offering water to all children, without exception, in addition to the main diet from the first day of life. If the baby refuses, there is no need to force him, and if he agrees, he should not be limited: he knows his own norm.
The first signs of dehydration in infants
Signs of dehydration in infants and young children:
- sunken fontanel and eyes,
- hot, dry and inflamed skin,
- loss of its elasticity,
- loud crying.
Dehydration in a child
is a disease that is not so easy to identify, and many parents attribute it to other diagnoses without understanding the signs. We should talk about dehydration in children when less fluid enters the baby’s body than comes out of it. And as statistics show, newborn children are more susceptible to this than adults. It is clear why. After all, when an adult wants to drink, he will go and drink, but a baby cannot tell his parents about his desire to drink. But those mothers who carefully monitor that the child drinks often will never face the problem of baby dehydration.
Signs of baby dehydration:
- urine is concentrated, colored and has a characteristic odor;
- wet diaper 2-4 times a day,
- flaccid skin that does not straighten immediately after pulling;
- sunken fontanel;
- long sleep and lethargic behavior;
- dry mucous membranes (mouth and eyes);
- increase in body temperature.
A child who exhibits such signs must be supplemented with food and see a doctor as soon as possible!
The danger of dehydration lies primarily in the fact that with the loss of fluid, the body leaves reserves of salts and microelements, therefore, in case of severe dehydration, it is not water that is offered, but saline solutions.
Top 5 tips: how to survive the heat for a child when it’s +30 outside
Signs and causes of dehydration in newborns
There can be many reasons for a child’s dehydration, but the most basic one can be called a virus that enters the baby’s body, whose immunity is weak. Another cause of dehydration is a sore throat, when it is difficult for a child to even drink. Another common cause is hot weather and frequent urination. Parents need to identify the causes of this disease as soon as possible and take appropriate measures.
There are also many signs of dehydration; below we will discuss the most obvious ones:
- Temperature increase;
- appetite;
- Diarrhea;
- Dry mouth;
- Lethargy and drowsiness;
- Sunken fontanel;
- Sunken eyes;
- Lack of tears while crying;
- The child rarely pees.
Signs of dehydration in a baby with diarrhea
A symptom such as diarrhea requires special consideration. And any parent will be able to notice something wrong in the baby’s behavior. Signs of dehydration during diarrhea include the following:
- Chapped lips;
- Unusual skin color of the baby;
- Sunken and tired eyes;
- Long sleep;
- Weakness;
- Dry skin;
- Dry diaper, i.e. the child does not urinate;
- Lack of salivation;
- Cold hands and feet.
All of the above symptoms are very serious, especially for an infant, and if some of them occur, you need to consult a doctor so that he can establish the correct diagnosis. And first of all, before the doctor arrives, you need to replenish your child’s water balance. If intoxication occurs, there can be very disastrous consequences.
If a child has diarrhea, then he needs to be given a saline solution; this will improve the child’s condition, at least for a while.
Diarrhea can occur due to infectious and non-infectious causes. During the first months of a baby’s life, his diet should be treated with care in order to improve intestinal function and avoid the occurrence of colic and other diseases. If we are talking about non-infectious causes, then there is no need to take special treatment, because this can occur against the background of teething.
Symptoms of dehydration in infants
- First degree. Weight loss (4-5% of total body weight). At this stage, urination occurs much less frequently, the color of urine is brighter than usual, and the smell of urine is pungent. The lips are cracked and the baby's skin color has changed. The duration of sleep has increased. The baby feels weak.
- Second degree. Weight loss (5-9% of total body weight). Lack of sweating, salivation, the child does not urinate, shortness of breath appears, rapid pulse (especially when crying), the fontanel slightly sinks.
- Third degree. Weight loss (more than 9% of total body weight).
It is very important to promptly identify dehydration in a child, since the more severe the stage, the longer and more problematic the treatment will be. Therefore, it is necessary to avoid the risk of disease and carry out regular preventive measures.
Nutrition and treatment for dehydration
If a few years ago, if you were dehydrated, doctors recommended not to feed your child. But today pediatricians loudly insist that a sufficient amount of microelements must enter the baby’s body. When feeding a newborn baby, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- You should not force feed your child. Even if on the first day of illness he ate less than half the amount he was supposed to eat, that’s good.
- It is necessary to feed the child with the foods that he has eaten recently; there is no need to introduce anything new.
- It is better to eat formula or milk, refusing adult food.
If we are talking about babies who are fed formulas, then there should not be a break between feedings of more than six hours. You may even have to change your diet. For example, switch from one brand of mixture to another. At this time, you need to treat the child with the drugs prescribed by the doctor.
Advice from pediatricians
As pediatricians advise, a newborn baby’s temperature should be brought down only when it reaches thirty-eight degrees. During diarrhea, it is not recommended to take antibiotics, as they will only worsen the situation. If the microflora is disturbed, you need to take medications that help restore it, which only a doctor can prescribe.
The signs of dehydration in a child under one year old were described above, which can be noticed by any parent who is caring and sensitive to their child and his health.
Video - Komarovsky about child dehydration
Next, we recommend watching an educational video: how to determine signs of dehydration in a child using a blood test, the famous pediatrician Komarovsky:
The main causes and signs of dehydration in infants
The body of any person consists of 50-80 percent water and its derivative liquids. If in adults this indicator is unstable and may well fluctuate, then in newborns and infants it must be at a high level - at least 70-75 percent. Even a slight deviation from it threatens the baby with serious health problems, which, under the most unfavorable circumstances, can take the child’s life.
You shouldn’t be surprised by this state of affairs, because moisture plays a significant role in the human body. The correct functioning of internal organs and all systems depends on the fluid. Due to lack of water, the brain and heart suffer, which is especially dangerous for infants. Given this, all mothers should know the signs of dehydration or even a slight lack of moisture in newborn babies. We’ll talk more about them, the dangers of this phenomenon and ways to normalize fluid balance in today’s article.
Signs of dehydration in a baby, dangerous symptoms and first aid
The body of any person consists of 50-80 percent water and its derivative liquids.
If in adults this indicator is unstable and may well fluctuate, then in newborns and infants it must be at a high level - at least 70-75 percent.
Even a slight deviation from it threatens the baby with serious health problems, which, under the most unfavorable circumstances, can take the child’s life.
You shouldn’t be surprised by this state of affairs, because moisture plays a significant role in the human body. The correct functioning of internal organs and all systems depends on the fluid.
Due to lack of water, the brain and heart suffer, which is especially dangerous for infants. Given this, all mothers should know the signs of dehydration or even a slight lack of moisture in newborn babies.
We’ll talk more about them, the dangers of this phenomenon and ways to normalize fluid balance in today’s article.
Why does dehydration develop?
Dehydration is a lack of water in the body
Its development occurs frequently for a large number of reasons. It's no secret that the human body is half or even two-thirds liquid.
Naturally, its role is great for the functioning of all internal organs, and a lack of moisture provokes serious consequences.
Dehydration is especially dangerous for newborns, whose bodies are made up of as much as 80 percent water.
There are truly many reasons for the development of dehydration in humans. Most often, pathology is provoked by:
- Vomiting and diarrhea, in which liquid and many useful minerals are washed out of the body along with the contents of the stomach.
- Infectious lesions that occur with elevated body temperature and provoke profuse sweating.
- Incorrect use of many medications (mostly diuretics).
- Diabetes mellitus, always accompanied by excessive urination.
- Frequent and intense sweating for any reason (congenital anomalies, temporary disruptions in the body, etc.).
- Insufficient fluid intake.
That is, the development of dehydration occurs in situations where the child experiences an imbalance between the incoming fluid and its secretions from the body.
In infants, a similar problem is observed especially often during the period of teeth growth or throat diseases, when the baby eats little and rarely.
Regardless of the cause of dehydration in a child, parents must respond to violations in a timely manner and prevent the most dangerous stages of the pathology. To eliminate the problem, it is enough to identify and eliminate the cause of dehydration, supporting the baby with plenty of fluids during therapy.
Degrees of violations and their signs
In medicine, there are mild, moderate and severe degrees of dehydration.
In modern medicine, dehydration is divided into three degrees. Each of them has its own specificity, severity and course characteristics. For optimal treatment of pathology, it is important to know the essence of each degree.
Mild dehydration is a type of dehydration that does not have significant manifestations. It proceeds almost unnoticed and is not accompanied by a serious lack of fluid. As a rule, with a mild degree of pathology, moisture loss does not exceed 5-10 percent of the norm. Signs of its course are:
- child's anxiety
- constant manifestation of thirst on his part
- licking teeth
- infrequent urination accompanied by slow filling of diapers
Moderate dehydration is characterized by more severe fluid loss. Often deviations are at the level of 10-15 percent from the norm. With moderate dehydration, the following symptoms are observed:
- heart rate acceleration
- dry lips, mouth and tongue
- increased viscosity of saliva
- slight shortness of breath
- incorrect position of the fontanelle
- child's severe anxiety
- very infrequent urination
will introduce you to the first signs of dehydration:
Severe dehydration is the most dangerous, since its development is associated with a severe lack of moisture in the baby’s body. Deviations are above 15 percent of the norm. The development of severe disease is provoked by:
- almost complete cessation of urine formation
- abnormal pulse
- breathing problems
- severe deviations in the position of the fontanel
- sagging and unnatural skin color
- clear manifestations of lack of fluid (dry mouth, mucous membranes, etc.)
With severe dehydration, the temperature often rises and the baby's urine becomes dark in color. It is unacceptable to hesitate in situations with the noted signs, since their development is a real harbinger of trouble.
Why does dehydration develop?
Dehydration is a lack of water in the body
Its development occurs frequently for a large number of reasons. It's no secret that the human body is half or even two-thirds liquid. Naturally, its role is great for the functioning of all internal organs, and a lack of moisture provokes serious consequences. Dehydration is especially dangerous for newborns, whose bodies are made up of as much as 80 percent water.
There are truly many reasons for the development of dehydration in humans. Most often, pathology is provoked by:
- Vomiting and diarrhea, in which liquid and many useful minerals are washed out of the body along with the contents of the stomach.
- Infectious lesions that occur with elevated body temperature and provoke profuse sweating.
- Incorrect use of many medications (mostly diuretics).
- Diabetes mellitus, always accompanied by excessive urination.
- Frequent and intense sweating for any reason (congenital anomalies, temporary disruptions in the body, etc.).
- Insufficient fluid intake.
That is, the development of dehydration occurs in situations where the child experiences an imbalance between the incoming fluid and its secretions from the body.
In infants, a similar problem is observed especially often during the period of teeth growth or throat diseases, when the baby eats little and rarely.
Regardless of the cause of dehydration in a child, parents must respond to violations in a timely manner and prevent the most dangerous stages of the pathology. To eliminate the problem, it is enough to identify and eliminate the cause of dehydration, supporting the baby with plenty of fluids during therapy.
Degrees of violations and their signs
In medicine, there are mild, moderate and severe degrees of dehydration.
In modern medicine, dehydration is divided into three degrees. Each of them has its own specificity, severity and course characteristics. For optimal treatment of pathology, it is important to know the essence of each degree.
Mild dehydration is a type of dehydration that does not have significant manifestations. It proceeds almost unnoticed and is not accompanied by a serious lack of fluid. As a rule, with a mild degree of pathology, moisture loss does not exceed 5-10 percent of the norm. Signs of its course are:
- child's anxiety
- constant manifestation of thirst on his part
- licking teeth
- infrequent urination accompanied by slow filling of diapers
Moderate dehydration is characterized by more severe fluid loss. Often deviations are at the level of 10-15 percent from the norm. With moderate dehydration, the following symptoms are observed:
- heart rate acceleration
- dry lips, mouth and tongue
- increased viscosity of saliva
- slight shortness of breath
- incorrect position of the fontanelle
- child's severe anxiety
- very infrequent urination
The video will introduce you to the first signs of dehydration:
Severe dehydration is the most dangerous, since its development is associated with a severe lack of moisture in the baby’s body. Deviations are above 15 percent of the norm. The development of severe disease is provoked by:
- almost complete cessation of urine formation
- abnormal pulse
- breathing problems
- severe deviations in the position of the fontanel
- sagging and unnatural skin color
- clear manifestations of lack of fluid (dry mouth, mucous membranes, etc.)
Degree of manifestation of the disease
Depending on the volume of fluid lost, the degree of dehydration in an infant is determined.
A mild manifestation is diagnosed if no more than 5% of the substance is lost from the total body weight.
In this case, the following symptoms of dehydration of this nature are distinguished:
We recommend reading: Diarrhea in newborns
- The baby is constantly thirsty.
- Bright flashes of vomiting are observed periodically.
- Stool occurs two to five times a day.
- The condition and character of the mucous membranes change noticeably.
The manifestation can be recorded at the first stage of dehydration development.
The balance can be restored independently, provided that fluid is regularly supplied to the body.
The average degree is diagnosed in the absence of 6 to 9% of the required volume of water in the body. The following signs of dehydration in an infant at this stage of development of the pathology are identified:
- Stool occurs several times more often. For children older than six months, the frequency may be more than ten.
- Excessive salivation and vomiting.
- Lack of mucous membrane in the nose and mouth.
- Poor palpation of pulse.
- The skin has a characteristic blue color.
- The skin becomes less elastic.
A severe degree poses a real threat to the child’s life. A sign of its presence is considered to be the removal from the body of more than 10% of fluid from the total body weight. The symptoms are similar, but more pronounced.
Children become cranky and have difficulty sleeping when dehydrated
The frequency of attacks also differs:
- Profuse diarrhea.
- Complete drying of the mucous membranes.
- The child has no facial expressions.
- You can additionally record the retraction of the fontanel and eyeballs.
- In some situations, the baby cannot close his eyes completely.
- The skin becomes blue.
- Complete absence of urination.
- A marble pattern is noticeable on the epidermis.
- The limbs are completely cold.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Heart beats too fast.
The manifestation is dangerous because it occurs with complete leaching of potassium cells. In their absence, there is a deterioration in the functioning of the central nervous system, which becomes pathological.
Parents also need to know how to recognize that their child is extremely dehydrated. In this case, he can lose up to 20% of his own body weight. The changes are irreversible, because disruption occurs in the functioning of organs and individual cells of the skin. That is why mothers should be extremely attentive to their babies and, if they detect the first symptoms of the disease, immediately seek advice from a doctor.
Basic principles of helping a child
To restore fluid, infants can be given electrolyte solutions.
Fighting dehydration is a responsible procedure that should be organized together with a professional doctor. This approach is most important in the treatment of newborns and young children, since they are most susceptible to the adverse consequences of pathology. At a minimum, a visit to a doctor is required to determine the degree of dehydration.
In modern medicine, the rule is that the elimination of mild and moderate dehydration is carried out at home, and the fight against severe illness is carried out in a hospital. Regardless of the form of dehydration that the baby has developed, at the first signs of pathology, it is important for parents to:
- First, try to normalize the body's fluid balance by drinking plenty of fluids.
- Secondly, show the baby to the doctor as quickly as possible.
After a high-quality diagnosis, treatment of the child is organized. As mentioned above, in mild and moderate stages of the disease, therapy is carried out at home, in more severe cases - in an inpatient setting. The general approach to getting rid of dehydration comes down to three steps:
- Normalization of the moisture balance in the baby’s body (soldering, increased nutrition, etc.).
- Elimination of the root cause of disorders (therapy of vomiting or diarrhea, infectious pathologies, etc.).
- Relief of symptoms of the disease and its complications (if necessary).
Since each case of dehydration in an infant is individual, it is irrational to consider the treatment of the pathology in more detail. Our resource strongly recommends treating children with a similar illness together with a specialist and at the first signs of a lack of fluid. Only this approach to treatment will allow you to overcome dehydration with the greatest effect and in the shortest possible time.
Features of inpatient treatment for children
If the child is severely dehydrated, the child will need to be hospitalized for long-term intravenous fluid therapy.
Many parents are very concerned when their child is admitted to the hospital for inpatient treatment due to dehydration. In fact, there is no need to worry here - such measures are important, first of all, for the condition of the baby himself. The principles of inpatient treatment of dehydration are not much different from those discussed earlier.
In any case, the therapeutic course is aimed at eliminating:
- the very fact of dehydration
- the root causes of its development
- developed symptoms and complications
Only those children diagnosed with severe dehydration are treated in the hospital. It occurs when serious fluid losses exceed 15 percent of normal. The need for treatment in a hospital is caused by the danger of such a disease, since a threshold of 25-30 percent of lost moisture is fatal.
Severe dehydration develops due to serious disorders in the functioning of the body. In infants, pathology occurs for three basic reasons:
- severe infectious diseases accompanied by high fever
- severe vomiting or prolonged diarrhea
- the presence of congenital diseases such as diabetes mellitus, various types of anomalies, and so on
Treatment of dehydration in a hospital is based on taking quite strong drugs. As a rule, they are managed through injections or IVs. In any case, when placing a baby in a hospital, his parents should not worry. Such measures are taken solely for safety purposes and are always beneficial for the child.