First aid for acute urticaria
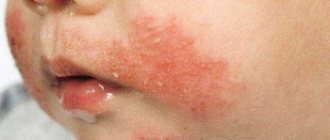
Skin manifestations of an acute allergic reaction in an infant
It is important to take action quickly so that the reaction does not spread and cause complications. First you need to stop contact with the allergen, rinse the skin with water, remove all irritating factors, and provide fresh air.
Drinking plenty of fluids is necessary. And to stop the allergic reaction, you need to take a safe antihistamine that is approved for children. The main problem with such an acute attack is severe itching. It can be removed with a non-hormonal cream. You can make a cool compress from a tablespoon of vinegar dissolved in a glass of water.
Prevention measures
Prevention is especially important in chronic forms of the disease, autoimmune pathologies, and hereditary predisposition. But even if a child has had one episode of hives, it can happen again. Therefore, the following measures need to be taken:
protect it from contact with the allergen; avoid hypothermia and overheating; use only natural fabrics for clothing and bedding; purchase hypoallergenic detergents, reduce the use of cosmetics to a minimum; follow a diet; for infants it is important to introduce complementary foods correctly; take medications prescribed by your doctor; strengthen immunity; treat infectious diseases in a timely manner; Do wet cleaning at home more often.
Urticaria is an unpleasant disease, but it can be easily cured if you take the necessary measures in time. By protecting your child from allergens, infections, hypothermia and stress, you can save him from discomfort. And if a rash occurs, you should not self-medicate; be sure to consult a doctor.
Many parents do not perceive urticaria as a serious illness and let its course take its course. This should not be done, since banal rashes can cause bronchospasms, anaphylactic shock, and Quincke's edema. These symptoms can threaten the life and health of the child and require immediate elimination.
To prevent the initial or repeated manifestation of urticaria, it is worth taking a number of preventive measures:
Follow a hypoallergenic diet; Detect and prevent the child from coming into contact with allergens; Pay attention to the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. If necessary, normalize its functions; Protect the child from stress and any moments that may affect the functioning of the nervous system; Treat all diseases in a timely manner; Timely elimination of inflammatory and infectious foci; Examine the child’s endocrine system; Pay attention to autoimmune conditions.
Diagnosis and treatment methods
Before starting treatment for urticaria, various studies are carried out. An experienced specialist will make a diagnosis based on external signs. In addition, a conversation with the baby’s mother is necessary to find out her diet. The baby is given allergy tests, blood and urine are examined, and, if necessary, an ultrasound examination is performed.
Urticaria must be differentiated from other similar diseases. Based on the results of the examinations, the most appropriate treatment is selected.
How to treat nettle fever in an infant? Urticaria in a small child requires a careful approach and comprehensive treatment. All therapy includes several points, compliance with which will restore the child’s health.
Items:
- Eliminate exposure to the allergen. In the acute form, identifying a harmful substance is quite simple. A young mother is advised to reconsider her diet and pay attention to cosmetics. If necessary, change the brand of diapers, ventilate the room more often, check the quality and composition of fabrics in contact with the baby’s delicate skin.
- If allergic urticaria has a food cause, then you can give your baby an enema to speed up the release of the irritating substance from the body. The use of sorbents is allowed, but before use, carefully study the instructions. In childhood, Enterosgel and Polysorb are allowed.
- Linex and Bifiform are used to restore microflora in the intestines.
- Moderate and severe forms of urticaria require drug treatment. The pediatrician may prescribe the use of antihistamines - Tavegil, Suprastin. Medicines are given to the child at night to reduce unpleasant symptoms and normalize sleep.
- To get rid of inflammatory processes on the skin, it is allowed to use external agents - Gistal and Epidel creams, Zinc ointment. Bepanten cream has received good reviews; it is used quite often and has no side effects. Medicines have a moisturizing effect on the skin, relieve swelling, and reduce itching.
- In very severe cases, Advantan cream is prescribed. But the drug is hormonal, so its use is permissible only as prescribed by a pediatrician and only for a specified period of time.
The appearance of signs of Quincke's edema requires immediate assistance in a medical facility. Self-treatment in this case is unacceptable.
Traditional medicine for the treatment of urticaria in infants is rarely used due to the fact that such remedies can often provoke an exacerbation of the baby’s condition. Any traditional medicine is allowed after consultation with a pediatrician.
First aid for acute urticaria in a child:
When the disease is triggered by the action of an allergen, it is necessary to take measures to eliminate it. If the pathogen is consumed with food, the child’s stomach should be rinsed and sorbents should be given.
If you are stung by a bee or wasp, carefully remove the sting from the wound, rinse it and apply a cream that relieves allergy symptoms. For children, non-hormonal local preparations are allowed; it is also possible to use sunburn cream and a vinegar compress. The rash should not be scratched to avoid secondary bacterial infection.
To avoid scratches, you may need to trim your child's nails. If there is significant itching of the skin, third and fourth generation antihistamines can be used. If a child exhibits alarming symptoms - difficulty breathing, dizziness, tachycardia, fainting, repeated vomiting, you need to call an ambulance. These signs may occur with intoxication syndrome, cardiac or respiratory failure. After elimination procedures, you need to provide the child with plenty of warm drinks; slightly alkaline mineral water or oral rehydration solutions from a pharmacy are suitable. You can make your own drinking solution by adding a gram of baking soda per liter of water.
Urticaria symptoms in children with photos, first signs
The mechanism according to which this phenomenon develops is that the body gives a certain reaction, which lies in an increase in vascular permeability. Swelling forms in these places and a rash appears on the face and body. As the negative influence of these factors increases, the situation worsens and other signs appear.
Blisters appear within the skin, with clear boundaries, similar in appearance to bite marks.
- Itching of the skin and rash on the body are localized in any places that are most heavily exposed to the main causative factors.
- As the disease begins to progress, a fusion of individual elements occurs, and all blisters, interestingly, are symmetrical in nature.
- The presence of full reversibility of diseases, since after their influence on the skin, pigmentation, scars and cicatrices are eliminated.
But there are allergic reactions and types of symptoms in which it is necessary to urgently call a doctor.
- Manifestation of a feverish state in the joints and muscles;
- Spread of external elements, formation of a swelling factor;
- Difficulty breathing and swallowing;
- Increased heart rate and beat;
Such phenomena can occur in children 5 years old, as well as in children under 3 years old, because urticaria can affect children of all ages.
Types and varieties of the disease
An acute disease occurs due to an irritant entering the body and lasts from a couple of days to a two-week period. The chronic form of the disease has a long course and relapses that occur every day. Based on the mechanism of action and damage, the disease also has its own classification - immunological and non-immunological type. In the first case, the rash, a photo of which can be seen below, develops due to problems with the immune system. In the second, development occurs against the background of pathologies. Considering the disease - urticaria in children, symptoms and treatment, photos, we can conclude that it can develop in various forms and characteristics.
Consequences of the disease
- The disease itself is safe, but it can be a signal of problems with the functioning of the body - liver, stomach, endocrine system. So the manifestation of a sign is a signal to contact a doctor for qualified support at a good level.
- The disease is a reflection of the position of the immune system and other mechanisms of the body, in particular this statement concerns a disease that is clearly expressed in the chronic type.
- The danger of the disease lies in the fact that it acts as the beginning of a condition that threatens the baby’s life, and can also be dangerous for the functioning of the body. So it is necessary to prevent exposure to factors that hide the danger.
- If a disease is suspected, symptoms should be monitored if the child's condition worsens. You need to urgently call a specialist to make a diagnosis.
Urticaria in children, symptoms and treatment, photos - all this has its own characteristics, so it is necessary to competently approach the diagnostic process and eliminate the disease.
Characteristic
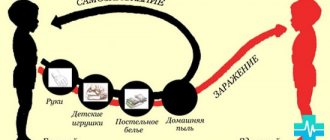
Urticaria got its name because of the appearance of the rash: the baby’s skin turns red and swells with blisters, extremely reminiscent of nettle “bites.” After a short time they pass, and then appear again in a different place. The disease is not contagious and cannot be transmitted even through close contact .
Many young mothers do not consider hives to be a serious illness and do not consult a doctor. But seemingly harmless rashes can lead to extremely serious consequences.
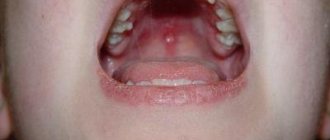
After all, blisters appear not only on the baby’s skin, but also on the mucous membranes of the eyes, mouth, nose, and even internal organs. At the same time, the mucous membrane swells, the baby’s breathing becomes difficult and is accompanied by a corresponding whistle and a dry “barking” cough. There is a danger of the baby developing Quincke's edema - angioedema, which can lead to damage to the nervous system and brain.
At the first signs of skin redness and blistering, you should consult a pediatrician. He will assess the severity of the situation, make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the treatment necessary for the baby.
Idiopathic urticaria in children
According to the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, the incidence rate of urticaria among children under 18 years of age is 3-7%. At the same time, the following trend is clearly visible: with increasing age of the child, the duration of the disease increases. Thus, in children under 2 years old, only cases of acute urticaria are recorded, in children from 2 to 12 years old - both acute and chronic, in adolescents from 12 to 18 years old - mainly chronic forms.
The cause of chronic urticaria in children is very difficult to establish due to the difficulties of diagnosis. In order to distinguish one form of urticaria from another, special diagnostic tests are performed. However, the results obtained can be interpreted in different ways, since there are no uniform assessment criteria for children. Therefore, in most cases of long-term disease in children, idiopathic urticaria is diagnosed and the fight against symptoms begins.
The main causes of chronic idiopathic urticaria in children are:
- unreasonable use of medications, in particular treatment of viral diseases with antibiotics;
- physical factors, reaction to cold, solar radiation, water;
- autoimmune diseases.
The variety of clinical manifestations of idiopathic urticaria in children is shown in the photo; the symptoms are the same as in adults.
When a diagnosis of chronic idiopathic urticaria is made in children, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. The patient should be monitored not by a pediatrician, but by an allergist-immunologist. If the disease is mild, you need to visit the clinic once every 3-6 months to monitor the condition and once a year for a full medical examination.
In the following cases, urgent hospitalization is indicated:
- in severe forms of the disease;
- lack of response to the proposed therapy;
- addition of edema of the respiratory tract.
The hospital stay can last from 7 to 14 days. The selection of medications, treatment regimens, and dosages is carried out by the attending physician.
In general, idiopathic urticaria in children can be successfully treated. However, parents should be aware of possible risks:
A fatal complication is swelling of the respiratory system. If you notice signs of facial swelling, you should urgently call an ambulance. If cold urticaria is detected, you should not bathe your child in cold water. Instant death can occur from a sharp drop in pressure and swelling of the larynx.
Treatment of urticaria in children
After determining the cause that provoked the disease and eliminating it, an allergist, pediatrician or dermatologist prescribes symptomatic therapy.
Algorithm of actions:
- Eliminate the allergen or cure the pathological root cause (chronic disease).
- Stop the inflammatory process with antihistamines.
- Smooth out swelling with diuretics.
- Deactivate the effect of toxins with enterosorbents.
- Prescribe drugs with menthol locally - as an antipruritic.
- Recommend a therapeutic and preventive diet.
If there is a child living in the house who is prone to body reactions to irritants, and signs of urticaria periodically make themselves felt, special attention should be paid to sanitation and the environment. For the sake of the physical well-being of children, parents not only focus on cleanliness and climate in the house
Often, in order to prevent the appearance of a chronic form, families are forced to change cities and even countries.
Treatment of infants
Urticaria in newborns causes serious concern for mother and baby. Babies refuse to eat, are capricious, and sleep is disturbed. Since medications for this age group are sharply limited, after consultation with a doctor, measures can be taken to alleviate symptoms. Treatment of allergic urticaria in children is carried out under the strict supervision of a leading specialist.
Treatment of urticaria in infants:
apply a cool compress to the affected area; apply sunburn cream for urticaria on the face of infants and older children (pay attention to o); give an antihistamine prescribed by a doctor; wear only clothes made from natural fabrics; completely exclude allergenic foods from the diet of mother and baby.
Changing your usual foods to healthy ones quickly relieves blisters, itching, and nervousness. The introduction of each new component to the menu requires special attention. To treat urticaria in children under 3 years of age, dietary adjustments are sufficient.
Treatment of children from 3 years old
Self-medication and dosage changes when treating patients diagnosed with urticaria are prohibited. Doctors select medications taking into account age, causes, clinical picture, and concomitant pathologies.
For external use the following is prescribed:
- Fenistil;
- Hydrocortisone;
- Gistan;
- Skin Cap;
- Advantan;
- Elidel.
In case of clearly developing symptoms, for the treatment of urticaria in children, Prednisolone is prescribed intramuscularly. In this way, you can quickly relieve inflammation, signs of allergies, and improve your psycho-emotional state.
For internal use the following are acceptable:
- histamines (Suprastin, Diazolin, Cetrin, Zirtek, Tavegil, Erius);
- calcium to strengthen vascular walls;
- immunostimulants;
- sorbents (Smecta, Enterosgel).
Homeopathy also offers a number of remedies with natural composition for the treatment of urticaria in a 3-year-old child (Apis; Pulsatilla, Prymula, Rhus toxicodendron, Urtica urens (molluscs, crustaceans), Rescue Remedy, Natrium muriaticum, Arsenicum album).
Basic principles of treatment
The main condition for successfully getting rid of urticaria is complete exclusion of contact with the irritant. A pediatrician or pediatric allergist who diagnoses and treats skin diseases in infants may prescribe medications and traditional therapies.
Medicines
To eliminate painful itching, external agents are used: ointments Fenistil, Advantan, Bepanten, creams Elidel, Gistan.
The doctor may prescribe oral administration of the following groups of drugs:
- antihistamines - Fenistil, Zodak, Suprastin, Erius, Diazolin;
- enterosorbents - Smecta, activated carbon, Polysorb;
- calcium preparations to increase vascular tone;
- immunostrengthening agents - Interferon.
Only a doctor should prescribe pharmacological drugs to a small child. In this case, in no case should you exceed the prescribed dosage and replace some medications with others yourself!
Folk remedies
Treatment of urticaria in infants can also be carried out using traditional medicine recipes. Before using this or that remedy, you should make sure that it will not aggravate the course of the disease. After all, many herbs, honey, and bee products are themselves strong allergens.
In order not to harm the baby, the use of home remedies should be agreed with the attending physician.
The most popular folk recipes for urticaria include the following:
- Herbal baths to relieve skin irritation. Brew a tablespoon of string herb with 2 cups of boiling water and leave for half an hour in a water bath. Dilute with warm water and keep your baby in it before bed. Bathing with chamomile, nettle, sage, calendula or a mixture of herbs is done in the same way.
- Wash the chicken eggs thoroughly and boil them. Peel the shells from the films and grind them using a coffee grinder. Give the child 2 g of powder daily, soaked in 3 drops of lemon juice. The course of treatment is 30 days.
- You can wipe your baby's skin with a piece of fresh cucumber or an aloe leaf, cut lengthwise and with the flesh turned outward.
- Starch bath. Brew two tablespoons of potato starch with 1 liter of boiling water. Cool and add to bathing water.
If the baby does not sleep well, you can add a decoction or lavender oil to the bath. They not only soothe, but also reduce redness and swelling of the skin.
Malaria
An infectious disease of viral origin, cyclical in nature. Transmitted by Anopheles malaria mosquitoes. They are found in tropical forests, on the coasts of Thailand, and become active in the dark. Most often you can meet them in Pattaya and Phuket. Symptoms of malaria resemble the flu, which does not go away for a long time, and acute attacks are repeated every 48-72 hours.
- heat;
- weakness, chills;
- shiver;
- excessive sweating;
- drowsiness;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- pain in muscles, joints;
- nausea, vomiting.
In Thailand, the disease is unlikely to be cured. Unless they bring medicines illegally from their home country. Often, upon returning to their native land, the symptoms are relieved, but the disease is not completely cured without therapy. There are no vaccinations against malaria. You can defeat the disease with drugs that are used for the flu.
As a preventive measure, a week before traveling to Thailand and during your stay in the country, you can take Doxycycline or Malarone. Or, when visiting the tropics, use mosquito repellent during evening walks.
Treatment of urticaria in a child
Having discovered characteristic rashes on the body of their baby, many parents are interested in: “How to treat hives in a child and not harm him”?
We proceed in order:
- First of all, it is necessary to determine the cause of the pathology by considering all possible factors. If for some reason this is difficult, go to the clinic and take a blood test for allergens. Immediately isolate the baby from the irritant.
- It is necessary to cleanse the child's body with the help of absorbent drugs. The drug “Polysorb” will effectively and safely rid the body of the allergen (dosages strictly according to the instructions). The little patient should be provided with a drinking regime: give as much liquid as possible. If hives are triggered by food, cleanse the child's intestines with an enema to rid the gastrointestinal tract of allergen remnants.
- Drug therapy. These are drugs with antihistamine properties (Diazolin, Suprastin, etc.) that relieve itching or eliminate rashes. Since these medications cause drowsiness, they should be given before bedtime.
- A strict diet in which all provoking foods are excluded from the diet of the nursing mother and child. The diet lasts 14-28 days.
If your child has hives, do not bathe him in hot water and keep him away from sunlight to avoid complications. Take treatment with full responsibility, because urticaria ranks second after bronchial asthma among fatal allergic conditions.
Advertisement
Diet for mom
Substances from the food that a breastfeeding woman eats, together with the milk, enter the baby’s body and can cause hives. Therefore, mothers during lactation should follow a special diet.
Prohibited products include:
- citrus fruits, bananas, brightly colored fruits;
- chocolate, coffee, cocoa;
- white bread and sweet pastries;
- fried, pickled, canned, salted and smoked foods;
- milk;
- yoghurts;
- products containing dyes and preservatives;
- fast food;
- seafood;
- fatty meats.
The diet should include:
- low-fat fermented milk products;
- yeast-free bread, biscuits;
- chicken and turkey meat;
- porridge cooked in water;
- light vegetables and fruits.
It is strictly forbidden to consume sweetened gas, water, beer and other alcoholic drinks for the entire period of lactation.
Causes
Children's urticaria is mostly formed as a result of an allergic reaction occurring in the body. A large number of mast cells and other inflammatory mediators are released into the blood, they cause swelling of the vascular wall and increase its permeability.
Intercellular fluid easily penetrates through these walls into the upper layers of the epidermis and forms blisters, bubbles, compactions and other external characteristics of the disease.
Main reasons for development:
- food;
- environmental factors (cat hair protein, plant pollen, household chemicals, etc.);
- medications (antibiotics, antiviral drugs, ointments, sulfonamides, multivitamins, vaccinations);
- poison obtained as a result of an insect bite (wasp, bee);
- bacterial infections;
- medical procedures (blood transfusions, etc.);
- congenital autoimmune diseases and other pathologies of the immune system;
- helminthic infestations;
- liver diseases.
Depending on the nature of development, its different types will appear (more details will be shown below in the photo).
Food
Foods that can cause allergic urticaria in children include:
- honey (bee products, products containing honey);
- whole milk;
- eggs (chicken, quail);
- seafood (if the child is breastfed, an allergic manifestation can be triggered by the mother’s consumption of seafood);
- cheeses;
- smoked meats;
- red vegetables and fruits (tomatoes, beets, bell peppers, etc.);
- pineapples and other “overseas” fruits;
- some types of nuts;
- fish;
- citruses.
Medications
Other causes of urticaria in children are medications. Among them, the most allergenic are:
- penicillins (“Ampicillin”, “Benzylpenicillin”, etc.);
- sulfonamides (“Biseptol”, “Co-trimoxazole”, etc.);
- vaccines and serums;
- anti-inflammatory drugs (Nurofen, Ibufen, etc.);
- analgesics (which are taken by the mother during breastfeeding);
- B vitamins (as part of multivitamin complexes that are given to the baby or taken by the mother);
- ointments and other products for external use.
If the period of development of redness coincides with taking medications, you should urgently report such a reaction to your doctor. He will reconsider the prescription, and if the baby’s allergy was caused by this, then, after stopping the medicine, it will go away on its own.
Other Possible Factors
The causes of its appearance are the result of serious pathologies, such as autoimmune processes. If we are talking about a baby, then in most cases they are hereditary in nature.
The functioning of the immune system is disrupted - cells that should attack foreign inclusions (microbes, bacteria, etc.) attack the tissues of their own body, constantly causing unhealthy activity of all parts of the immune system.
Edema develops in the same way as with regular allergies. Only in case of autoimmune processes, treatment should be aimed at correcting excessive immune activity.
These diseases include:
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- some pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- autoimmune attack of the intestinal walls.
Another serious factor in redness and itching can be infection. The mechanism of development of symptoms is also closely related to the constant work of the immune system at an accelerated pace. The following infections are especially dangerous:
- cytomegalovirus;
- hepatitis;
- herpes;
- streptococcus;
- staphylococcus;
- parasites: roundworms, etc.
Food causes of skin rashes
Urticaria in infants is considered a consequence of an inadequate response of the immune system to provoking factors. There are many such factors around a little person: when he first enters the world of bacteria and microorganisms, viruses and allergens, the baby learns to live with them.
Urticaria during breastfeeding, as a rule, can manifest itself in response to the mother's consumption of certain foods, since it has long been known that the baby eats the same things as the mother. Provocateurs of an allergic response in the form of urticaria can be:
- citrus;
- chocolate and chocolate products;
- red berries, such as strawberries or raspberries;
- smoked sausage, fish, meat;
- tomatoes and tomato juice;
- bee products, including honey;
- some types of nuts.
Food urticaria can appear on any part of the body, regardless of contact of the baby’s skin with clothes and underwear
It is not difficult to determine the allergen if the mother remembers what new items she allowed herself from the food range before the last feeding. If such products do not exist, the reasons should be looked for in other provoking factors. If the baby has been introduced to complementary foods, then the reason most likely lies in the new diet.
If no new products have entered the little person’s body, then the reason can be looked for in the new world surrounding the child.
Diagnostics
An experienced doctor will always be able to recognize urticaria by sight, but an accurate diagnosis is made only on the basis of laboratory tests. Parents cannot always remember what the child ate, drank, or had contact with during the last 24 hours, and therefore allergological tests, which are considered the most accurate method of establishing the fact of sensitization of the body, can help in the search for an allergen.
Allergy tests will not always answer the question of what exactly a child develops urticaria to, because they take the most common, so-called standardized allergens, and a particular child may have a reaction to another substance that is not on the list of standardized ones.
The essence of the tests comes down to the reaction to different allergens. Whatever the reaction will be is the “culprit” of nettle fever.
For total immunoglobulin E
IgE is detected in the blood if sensitization occurs. At the same time, the level of immunoglobulin indicates its extent. Blood is taken from a vein. Parents should know that it is impossible to feed and water the child before such an examination, and if the child is taking some medications as prescribed by the pediatrician and it is not possible to stop them, the allergist should also know about this fact before the blood is taken for analysis.
For specific immunoglobulins
Such a blood test is performed on a child if the fact of an allergy has already been established, but a specific allergen has not. The blood serum of a small patient is mixed with various allergens, for example, plant pollen, animal saliva, house dust, etc. The reaction allows us to judge which group of allergens can cause a negative reaction in the child.
Immunocap
This test is carried out if none of the previous ones could give a clear answer to the question about the origin of the allergy. The study requires a larger amount of blood, and therefore this test is not prescribed for children. Most often, you can count on prescribing such an examination only from adolescence.
In addition to blood tests, skin tests may be recommended for a child with hives. Their passage may take time: in one session, the doctor can apply no more than 20 types of allergens to the skin of a small patient, and there are thousands of them. Samples are recommended for children aged three years and older. The doctor’s task is to find the substance to which the skin will give a positive reaction. Typically, allergen solutions are applied to the forearms, but the procedure can also be performed on the skin of the back. For kids, drops of solutions are applied to the skin, and for teenagers, they can make a few scratches and drop the solutions there.
Urticaria in children: causes of the disease, main symptoms, treatment and prevention
It is an acute skin reaction of allergic origin, characterized by the development of urticarial rashes.
Causes
Urticaria in children can be either an independent nosological form or a syndrome that develops under various pathological conditions. Most often, acute urticaria in young children occurs against the background of food allergies, which are caused by the consumption of cow's milk, fish, seafood, eggs, nuts or citrus fruits.
In children over two years of age, the disease can be caused by a viral infection, for example, hepatitis B and C viruses, cytomegaly, herpes type I, Coxsackie A and B, and less commonly by parasitic infestation caused by infection with roundworms or echinococcosis and bacterial infection.
Transient urticaria in children develops after infectious mononucleosis, mycoplasma infection or rubella.
Chronic urticaria in children can occur due to exposure to physical factors, infections, allergies to food and food additives and medications.
Symptoms
Acute urticaria is caused by the sudden appearance on the child’s skin of very itchy spots and blisters of a pale pink color, which are mainly localized on the torso, arms and buttocks.
The blisters rise above the surface of the skin and are rounded formations with a matte tint and a rim of hyperemia and can merge into fairly large areas. The baby may experience chills, body hyperthermia, headache, diarrhea and vomiting.
It should be noted that rashes on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, nasopharynx and larynx are detected very rarely. In acute dermographic urticaria, itching is most often absent.
Chronic urticaria occurs with prolonged sensitization and is characterized by paroxysmal progression and minor rashes. Such patients exhibit weakness, low-grade fever, headache, arthralgia, nausea and diarrhea.
If severe itching occurs, neurotic disorders may occur.
Long-lasting urticarial elements of the rash can pass into the stage of papules with the development of the papular form of urticaria, which is sometimes accompanied by the development of hyperkeratoses and acanthoses.
Cold urticaria occurs a few minutes after exposure to cold or immediately after warming chilled skin, and when large areas of skin are affected, it can be combined with anaphylactoid reactions. Even eating cold food in such babies can be accompanied by oropharyngeal edema and gastrointestinal symptoms.
The papular form of the disease manifests itself in children with the appearance of small blisters at the site of an insect bite, which can persist for more than 24 hours. With repeated bites, systemic allergic reactions may develop. With serum sickness, urticaria may be accompanied by the development of fever, swollen lymph nodes and joint pain.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of urticaria in children is carried out on the basis of existing clinical symptoms and the collected medical history, results of physical and laboratory tests. Among the laboratory tests, the child may be prescribed a general blood test, a biochemical blood test, determination of general IgE and allergen-specific IgE antibodies, a general urine test and a stool test for helminth eggs.
Treatment
To obtain the maximum therapeutic effect in the treatment of urticaria in children, it is necessary to eliminate the pathogenetic factors that caused the development of the disease.
In acute and chronic forms of the disease, drug therapy is based on the use of antihistamines. Sometimes, for chronic urticaria, a combination of H1 and H2 blockers - histamine receptors - is prescribed, and for treatment-resistant forms of the pathology - adrenaline and glucocorticosteroids.
Prevention
Prevention of exacerbations and relapses of urticaria in children is based on diet, avoiding contact with allergens and limiting exposure to provoking factors.
Urticaria in babies, symptoms and treatment, photo
The characteristics of this disease may vary. Their disposition depends on the personal characteristics of the child’s body, its susceptibility to the allergen and the duration of the effect of negative causes on the small organism. The same reasons influence the doctor’s choice of effective methods of therapy and suitable medications.
The appearance of the disease can be provoked by:
- Food (eg fish, berries, eggs, fruit)
- Medicines
- Infectious viral or bacterial diseases
- Cosmetics used to care for baby's skin
- Physical factors: water, heat and cold
- Insect bites
- Substances moving in the air: pollen, dust, fluff
Urticaria in babies, photo
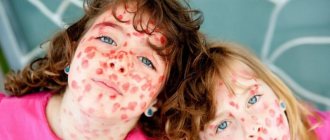
blisters of various shapes and sizes appear on the child’s skin .
Their color can vary from light pink to bright red. They often rise greatly above the surface of the body and have rims along the edges. When combing these spots, they spread and merge with each other .
Most often, these signs appear on the surface of the arms and legs, buttocks, folds of skin, body, head and neck. The spots can remain on the body for just a couple of hours. Later they disappear without a trace, and after a short gap of time, they appear in another place.
It may also be that the rash does not go away for more than a day.
So that the ancestors had no doubts and could clearly see what urticaria looks like in children, a photo of the rash was taken in its most vivid manifestations. This will allow you to immediately resort to the help of specialists if similar manifestations are detected.
What urticaria looks like in babies, a photo of it is presented in this section, also depends on the scale of spread and the effect of the disease on different layers of the skin. In the case when the swelling seeps deep, covering the mucous membranes and subcutaneous tissue, Quincke's edema can form .
Symptoms of urticaria in children
The process of progression of the pathology consists of the body’s response to the release of histamine into the blood, excess production of serotonin, and prostaglandins.
In accordance with this, what urticaria looks like in children depends on how much of these substances enters the body.
Thus, there are several forms of the disease, each of which is characterized by certain symptoms.
- Mild form (typically the absence of itching and intoxication. The child feels normal. Once the rash appears, it quickly passes without leaving any traces)
- If the disease is of moderate severity, then in addition to the rash, children experience a general malaise: increased temperature, vomiting, chills (areas of increased swelling appear on certain parts of the body, quickly spreading throughout the body)
- The severe form is characterized by strong severity of symptoms ( rashes are accompanied by intoxication, disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Severe swelling is also noted. When it appears in the respiratory tract, the child experiences difficulty breathing, blue discoloration of the area around the nose and lips, and frequent coughing. In some cases, when swelling disrupts the mucous membrane of the digestive tract, severe vomiting, diarrhea, high fever are noted. Damage to the inner ear or meninges contributes to the child developing headaches, dizziness, vomiting, loss of consciousness)
How to cure hives in children
Before choosing a treatment for a small patient, the doctor needs to conduct a diagnosis.
It usually includes the following activities:
Search for the prerequisites that influenced the development of the disease. The doctor will also find out if family members have any allergies.
Visual inspection. A study is being conducted of the nature of the rashes, their prevalence and size. The time for the blisters to disappear is determined. The doctor also notes the presence of pigmentation remaining after the rash, if any.
A special scale is used to determine the activity of the disease.
Laboratory activities. These include: blood and urine testing, tests with autologous blood serum and with atopic allergens, determination of immunoglobulin levels.
Different types of provocative tests are also used:
- Mechanical action (carried out when urticaria occurs due to contact with any object)
- Phototesting (it is prescribed if it is thought that the rays of the sun could have been a provocateur for the occurrence of pathology)
- Exposing the skin to an aqua compress (this test is used to confirm the occurrence of signs from water)
- Applying an ice cube helps monitor how your baby's skin reacts to cold.
- Test with hanging a vertical load (allows you to find a delayed type of pathology, formed several hours after prolonged pressure on the surface of the skin)
An extensive examination carried out to identify possible infections.
Additional procedures: Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, x-ray of the chest and nose.
Only when the causative agent of urticaria is identified, the doctor chooses how and with what to cure urticaria in children.
The main ways to help eliminate this disease are:
- Elimination (consisting in eliminating or reducing the effect of irritants on the child’s body)
- Prescribing pharmaceuticals
- Therapy of various pathologies contributing to the onset of the disease
- Cleansing the body
- Compliance with established nutrition
When urticaria is caused by a product consumed with food, it is excluded from the diet and a diet is prescribed .
Cleansing of the body is also required. It is carried out by prescribing plenty of fluids. A cleansing enema may also be prescribed. In this case, the use of sorbents is widespread, for example, activated carbon, Smecta, Enterosgel . If there are animals in the apartment, they should be given away for a while.
Treatment with medications is often used for therapy as an effective remedy that can quickly eliminate the signs of the disease.
The doctor should prescribe these drugs, taking into account the child’s previous illnesses and his personal intolerance to the components of the product. Only this approach will help avoid adverse reactions and safely restore health.
For the treatment of acute forms of the disease in children, the following are prescribed:
- Antihistamines (Suprastin, Tavegil, Erius. They will perfectly relieve itching and rash)
- Calcium supplements (help increase capillary tone)
- Topical medications (for example, zinc ointment, Fenistil gel, Advantan cream (hormonal). They help relieve itching, rashes, spots, moisturize the skin, eliminate irritation)
↑
Solar urticaria in children
Solar urticaria in children manifests itself in the same way as in older people. Pathology can be detected even in infants.
In addition to the main symptoms, the child may experience:
- nervousness, severe anxiety;
- attempts to scratch the growths (can lead to irritation or infection);
- cry;
- temperature increase (no more than 38°C).
For childhood solar urticaria, only a doctor can determine the symptoms and treatment. As a rule, only external sedatives are prescribed.
The most common causes associated with the development of rashes in children are advanced viral diseases, food allergies and hypersensitivity to certain medications.
Consequences of the disease
The disease itself is not dangerous, but it may indicate serious disruptions in the functioning of vital organs and systems. In addition, if treatment is not timely, complications may develop, the most serious of which are Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock.
Therefore, parents need to study all the available information regarding what urticaria looks like in children - photos, descriptions of symptoms, possible consequences and first aid methods. It is also necessary to protect the child from exposure to provoking factors, and if the first signs appear, carefully monitor the course of the disease so that, if necessary, immediately consult a doctor.
Read how to treat hives in children at home
Kinds
Depending on the cause of the disease:
- Allergic urticaria occurs as a reaction of the body to some external irritant.
- Psycho-emotional, appears as a result of stress and experiences of the child.
- Cold urticaria is a skin reaction to frost, a significant or sudden drop in temperature.
- Mechanical - a consequence of skin irritation due to contact with something (clothing, diaper, saliva).
- Urticaria pigmentosa (mastocytosis) is a consequence of the pathological proliferation of mast cells in the body tissues due to disorders in the immune system, so called because it leaves behind brown spots on the skin, similar to pigmentation.
Depending on the mechanism of development, 2 types of urticaria can be distinguished - immunological and non-immunological. The first type of disease develops due to disorders in the child’s immune system of an allergic (due to allergens entering the blood) or non-allergic nature (for example, a reaction to cold or insolation).
The second type of urticaria develops in connection with pathologies in the functioning of the child’s organs and systems. According to the course of the disease:
- Acute urticaria sharply manifests itself with a clear clinical picture, is diagnosed by parents independently at home, is quickly treated and resolves within 6 weeks.
- Chronic is practically untreatable and is characterized by regular recurrence again and again, although the symptoms are calmer and less pronounced.
According to the form of the disease:
- Mild: characterized by a satisfactory condition of the patient, mild symptoms (no swelling, mild itching). Passes within 24 hours.
- Moderate: the child’s condition is poor, there are symptoms of intoxication, possible fever, Quincke’s edema, quickly spreading throughout the body, starting from the eyelids and lips, respiratory distress.
- Severe cases are fraught with death for the child as a result of swelling of the larynx, which is why he cannot breathe normally.
Each type of urticaria on a child’s body is characterized by a special clinical picture, although in general it is approximately the same for this type of rash. So it doesn’t cost parents anything to diagnose the disease themselves.
Acute urticaria
Symptoms of acute urticaria usually appear abruptly (within 1-2 hours from the moment the body is exposed to the allergen), so it is often quite simple to determine what caused it. In this case, symptoms of the disease will appear every time after direct contact with the allergen. The duration of most acute cases is usually 24-48 hours. The disease is easy to treat.
Chronic urticaria
If the rash lasts more than a few weeks, it is worth talking about the chronic form of the disease. In children, it is quite successfully treated and in approximately 50% of cases the disease disappears on its own within 6 months.
However, it also happens that the disease is resistant to treatment, as a result of which it can persist for many years. Fortunately, chronic urticaria is quite rare. In this case, it is imperative to contact a pediatrician or dermatologist for further consultation.