Swelling of the nasal mucosa in a child can be caused by allergies or other diseases. Sometimes eliminating contact with the allergen is enough to alleviate the condition, but vasoconstrictor drops may be required.
If, after taking the drugs, breathing remains noisy and heavy, this indicates that inflammatory processes are developing in the adenoids. In this case, antibacterial drugs are often used for treatment.
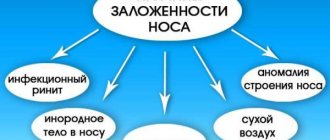
Causes
Cells of the mucous membranes are necessary to protect the internal environment from the penetration of various substances that have a pathogenic effect.
They are the first line of defense against the penetration of various bacterial infections into the child’s body. Nasal breathing disorders develop in children at any age. Almost every mother faces this situation quite often.
Any allergies lead to swelling of the nasal mucosa in children. They occur when various allergens enter the body. Such situations usually occur seasonally.
Their peak development occurs in spring and summer. At this time, various flowers, herbs and shrubs begin to bloom. The settling pollen causes the child to develop allergic rhinitis (runny nose).
The peculiarity of the structure of the nasopharynx in infants and newborns means that their runny nose can be of a very physiological nature. This is especially common in children who spend a long time in very dry rooms. A decrease in humidity in the children's room provokes the baby to show signs of impaired nasal breathing.
of various polyps in the nasopharynx leads to the fact that the baby breathes worse through his nose. They can appear in the nose due to a variety of reasons. Most often, such pathologies appear in school-age children. It is quite easy to identify this manifestation - by the appearance of the child. The baby begins to constantly breathe through his mouth, since breathing through his nose is significantly impaired.
Bacteria or viruses, getting on the mucous membranes, also cause the baby to develop symptoms of a severe runny nose. The disease can occur in different ways. The severity of adverse symptoms largely depends on the age at which the child developed such an infection.
Many aggressive staphylococci cause severe swelling of the mucous membranes in the baby, which is accompanied by a prolonged and severe runny nose.
Swelling of the nasopharynx is quite common with adenoids. This pathology is manifested by the development in a child of excessive growth of adenoid tissue, which blocks the lumen of the nasopharynx for air passage. This condition develops mainly in school-age children.
The disease can progress in different ways. The initial stages of this disease, as a rule, do not manifest themselves in any way. Only when the adenoids grow quite actively does the baby develop specific manifestations of this pathological condition.
Traumatic injuries to the nose also lead to the baby developing severe swelling in the nasopharynx area. Boys who often get into fights are much more susceptible to this condition. The danger of nasal injuries is also that they can lead to damage to the nasal septum, which will only contribute to the progression of adverse symptoms in the child in the future.
Preventive measures
How to reduce the likelihood of swelling of the nasal mucosa in a child? Make sure to maintain normal indoor air humidity. Typically, the problem makes itself felt when heating radiators are turned on throughout the day during the cold season. To increase the humidity of the surrounding area to a comfortable level of about 60-70%, use a household humidifier. According to observations, the action makes it possible to significantly reduce the risk of swelling of the nasopharynx in children and speed up recovery in an existing pathological condition.
If your child is prone to developing acute allergic reactions, take care to limit your baby's exposure to potential irritants. During the spring period of exacerbation, send your child for street walks less often. Temporarily remove indoor plants and pets from your home. Use prophylactic antihistamines promptly.
Symptoms
Swollen mucous membranes can cause the child to develop some adverse symptoms. A sick baby looks normal. The appearance of the child practically does not change in any way , especially in the initial stages of the disease. Only when the course is advanced does the baby begin to actively breathe through his mouth, since breathing through his nose is very difficult.
Such breathing causes the child's lips to become very dry. The mucous membranes of the throat also begin to dry out greatly. This not only manifests itself as severe dry lips, but can also lead to the development of pharyngitis or other diseases in the child. This is usually caused by too cold air coming into contact with the mucous membranes.
All symptoms begin to appear in the baby sequentially and gradually increase. First, the baby develops congestion. The next symptom is the appearance of a runny nose. Nasal discharge is mucous, usually with a yellowish tint. With bacterial infections, a runny nose can be profuse with green discharge.
Severe swelling causes the baby to snore during sleep. This symptom manifests itself especially well if the child has various adenoid growths or polyps in the nasopharynx that interfere with normal breathing. Severe forms of the disease are also accompanied by a change in voice. A sick child begins to nasal or wheeze.
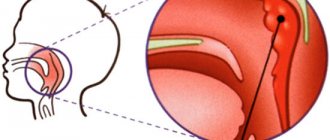
The bridge of a child's nose is swollen with a runny nose
Edema is usually called a subcutaneous accumulation of fluid, provoked by increased permeability of blood vessels, the presence of inflammatory processes, as well as mechanical damage, for example, after a bruise.
Situations where the bridge of the nose is swollen in a child or an adult can be accompanied not only by a change in the patient’s appearance, but also by a deterioration in nasal breathing, which in turn is dangerously increased by the risk of complications.
Only an otolaryngologist can determine the degree of risk and the need for treatment after a thorough examination of the patient.
A consultation and examination by a doctor of the bridge of the nose itself is considered mandatory if it is not only swollen, but also painful.
Development mechanism
Swelling of the mucous membrane of the bridge of the nose is possible as a consequence of the body’s protective reaction against the effects of irritating factors.
These could be foreign objects that got inside through negligence, harmful bacteria, the result of surgery, as well as infections.
In each case, there is a violation of the integrity (permeability) of blood vessels, which means an increase in blood flow.
Causes and corresponding symptoms
Since the causes of edema can be very different, the symptoms of their manifestation differ from each other. Thus, the pathology itself can be provoked by:
- Sinusitis, in which swelling is observed not only on the bridge of the nose, but also on the wings of the sinuses and near the eyes. When pressing on swollen areas, the patient may feel increasing pain. The main reason for this is the accumulating pus inside the sinuses themselves.
- Rhinitis (in the acute form of an infectious lesion), in which the nasal cavity may become completely swollen. In this case, the patient himself experiences pain in the nose, excessive lacrimation, sneezing attacks, and an increase in body temperature. Lack of timely treatment can lead to the formation of boils and painful cracks.
- The presence of formations (benign or malignant). These can be either hollow cystic formations with internal liquid contents or tumors producing cancer cells. Often, in addition to swelling, the disease is accompanied by pain only in the later stages of development of the pathology (when the tumor increases in size and puts pressure on neighboring tissues and organs).
- One or more boils , which are the result of inflammation of the sebaceous glands or hair follicles. In such cases, timely surgical intervention is necessary. The presence of boils may be accompanied by itching and pain when pressed.
- Excessive acne in the nasal area, accompanied by itching and pain.
- The presence of numerous herpes rashes , characterized by painful tingling in the affected area.
- The entry of a foreign object into the nasal sinuses, which in turn causes the accumulation of purulent discharge and pain when pressing on the swelling itself.
- Inflammations around the eyes, for example styes, which if left untreated can cause swelling.
- Syphilis, which is dangerous due to the risk of destruction of the bone base of the nasal cavity, accompanied by painful inflammation.
- Rhinosinusitis, which is characterized by loss of smell, increased body temperature and the presence of mucopurulent discharge from the nose.
- The manifestation of an allergic reaction of the body to cosmetics, pollen, flowering, which is complemented by increased tearfulness, difficulty breathing and redness in the eye area. The presence of an allergy to anything from the environment is not accompanied by pain, which is its distinguishing characteristic when diagnosing the disorder itself.
- Anatomical features of the structure of the nasal sinuses and bridge of the nose, as well as possible previous injuries, such as bruises and fractures. Often occurs precisely after a blow to the bridge of the nose. In such cases, pain in the damaged area is often observed, as well as the inability to breathe properly.
- Impaired kidney function. In such cases, changes in the color and volume of urine excreted, pain in the lumbar region, and an increase in body temperature are typical. The patient himself may also complain of lack of appetite.
Swelling can be caused by uncontrolled use of vasoconstrictor nasal drops, hormonal dysfunction, disturbances in the cardiovascular system, and excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Often, temporary swelling on the bridge of the nose is observed after rhinoplasty (plastic surgery to correct or restore the nose).
With this pathology, the patient may often complain of excessive dryness and burning in the nose and loss of sensitivity to smells.
Diagnostics
Only a correctly established cause of edema will allow the doctor to adequately assess the degree of development of the pathology and prescribe the most effective treatment. To do this, the specialist must examine the bridge of the nose and also refer the patient to:
- blood test (general and biochemistry);
- conducting allergy tests;
- conducting a nasal culture study;
- passing urine tests according to the method of Zimnitsky and Nechiporenko;
- tomography;
- ultrasound examination of the kidneys;
- rhinoscopy;
- radiography.
Only after receiving the examination results will the doctor be able to correctly diagnose the pathology and prescribe appropriate treatment. As a rule, additional tests can rule out the presence of more serious diseases. This is especially true for the presence of cancer, as well as disorders in the cardiovascular and renal systems.
Treatment methods
The selection of effective therapeutic methods directly depends on the reasons for which the swelling itself is observed. Before starting to take medications and perform procedures, the patient should consult with a traumatologist who can correctly assess the degree of damage to the soft tissues and the bone itself.
As a rule, painkillers and decongestants are additionally prescribed to the general treatment package. This will help alleviate the patient’s condition and speed up the recovery process.
In the presence of boils, rhinitis or sinusitis, swelling is relieved by taking special anti-inflammatory drugs in addition to antibiotics. In cases of diagnosing an allergic reaction of the body to irritating factors, Loratadine, Diazolin or Suprastin are considered to be effective drugs that relieve swelling.
To relieve swelling of the bridge of the nose due to herpes skin lesions, the doctor may recommend taking antiviral medications in combination with effective diuretics (improving kidney function) and anti-inflammatory drugs of herbal origin.
When treating barley, it would not be superfluous to rinse the nasal cavity with a solution of salt and clean water in the ratio of half a teaspoon of salt per 250 ml of liquid. If nasal swelling is a consequence of ARVI, the patient is prescribed vasoconstrictor nasal drops, for example, Naphthyzin, Otrivin or Noxprey.
Anatomical abnormalities in the structure of the nose can only be corrected surgically.
Swelling of the bridge of the nose in a child
Observing swelling in a child is a good reason to immediately consult a doctor. Among the main reasons for the manifestation of pathology are:
- the appearance of recurrent pimples and acne in the sinus area;
- the formation of hollow cystic formations and inflammatory granulomas, in which swelling spreads to the cheek);
- disturbances in the functioning of the adenoids.
Swelling can also be the result of an injury or frostbite after a long walk outdoors in severe frost. An allergic reaction to flowering or pollen is also no exception when diagnosing the cause of swelling in a child. Timely assistance will help to avoid complications and quickly restore full breathing.
Possible treatment
The use of any pharmaceutical drugs and traditional medicine, as well as their permissible dosage, should be discussed in advance with the attending physician.
This also applies to special decongestant gels and ointments, which are not allowed for use by children under 14 years of age.
Acceptable therapeutic methods include:
- rinsing the nasal cavity with antiseptic drugs (2 Furacilin tablets per glass of cooled boiled water), which will prevent the development of infection;
- applying cold compresses (ice wrapped in a clean towel) to relieve pain in the area of the bruise;
- cosmetic cotton pads, which must first be soaked in hydrogen peroxide and folded into a tube, and then inserted into the nostrils to stop bleeding.
If there is vomiting, nausea and dizziness, the child needs emergency medical attention, so it is necessary to call an ambulance as soon as possible. Treatment of rhinitis should fully comply with the recommendations of the attending physician.
Among antiallergenic drugs, a specialist may recommend taking Suprastin, Claritin or Tavegil.
The little patient himself must also eat healthy food, take a complex of vitamins, and undergo mandatory hardening procedures.
Treatment
After determining the cause that caused nasopharyngeal swelling in the baby, doctors prescribe an appropriate treatment regimen. Pediatric otolaryngologists treat various nasal diseases. To establish the correct diagnosis, they conduct research using special medical instruments. During such an examination, they can identify a variety of pathological changes that are present on the mucous membranes of the nasal passages.
Nasal swelling can be relieved by using various medications. The choice of such drugs is made by the attending physician , since many of these drugs have a number of restrictions for use.
Parents should remember that these medications should be used for a certain period of time, as they can cause the appearance and development of unwanted side effects in the child.
In order to remove swelling of the nasopharynx, doctors usually prescribe various antihistamines . They do a good job of eliminating inflammation and also have a restorative effect on damaged mucous membranes of the nasal cavity. The duration of taking such drugs is usually 5-10 days and depends on the severity of the child’s pathological condition.
Modern antihistamines practically do not cause side effects in children. The most unfavorable of them is severe drowsiness. However, in order to further reduce the likelihood of the baby developing such an undesirable manifestation of the drug, doctors recommend taking these medications mainly in the second half of the day before going to bed.
This condition should be observed by schoolchildren so as not to deteriorate their performance during school.
The form of release of antihistamines can be very different. To treat swelling of the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity, the most common medications are those available in the form of sprays . They perfectly irrigate the nasal passages and do not have any systemic effect on the baby’s body . "Cromosol" and "Cromoglin" will help reduce swelling in the nasopharynx and will promote better breathing in a sick child.
In some cases, local treatment is not enough. In such situations, doctors resort to the use of medications produced in the form of tablets. These drugs have a more pronounced therapeutic effect. They are usually prescribed 1-2 times a day. Take these medications with a sufficient amount of liquid.
Allergy
Allergic rhinitis develops not only during the flowering season, that is, in the spring. Plant pollen does cause such reactions, but not all potential allergens appear in the spring. Some plants still bloom all summer and 'take over' part of September. In addition, allergic rhinitis can be long-lasting and even year-round. In this case, irritants include book and house dust, animal hair, fluff, including from pillows and blankets, etc.
As a result of exposure to the allergens they contain, the child experiences swelling of the mucous membrane, hyperproduction of mucus begins, and as a result, the nasal passages narrow. And it is possible that allergic laryngitis or adenoiditis will be added to the swelling of the mucous membrane and runny nose.
In case of allergic rhinitis, it is impossible to use treatment regimens prescribed for acute respiratory viral infections. With allergies, nasal discharge remains clear, while with viral and bacterial ones it will be green. With a cold, only one nasal passage often suffers until the infection spreads to the other, and with allergies, both at the same time. ARVI and acute respiratory infections are accompanied by an increase in temperature, but allergies are not. Only a doctor can confirm the correctness of the diagnosis.
Vasoconstrictors are rarely used for allergic rhinitis. But if there is severe swelling, the doctor prescribes Otrivin. Treatment with corticosteroid drugs is also possible. There are also specially developed sprays - stabilizers of mast cell membranes - Cromoglin and Cromosol. The use of systemic antihistamines also plays an important role. For children, drugs like Suprastin and Fenkarol, that is, first-generation drugs, are not recommended, since they have many side effects. The second generation product - Fenistil drops - can be given to children starting from the age of two months.
Allergic rhinitis significantly impairs quality of life. Therefore, doctors advise using specific therapy, which will further reduce the risk of allergies returning. This treatment involves identifying a significant allergen and then introducing it - initially in a small dose, but gradually it will increase, increasing resistance to the irritant.
Another cause of swelling of the mucous membrane is cold rhinitis. It is treated in the same way as a regular allergy; antihistamines are used for this. In this case, you will have to do without vasoconstrictor drops, since they will only worsen the situation.
In case of edema resulting from a physiological runny nose in an infant, the main thing is to ensure a comfortable microclimate in the room, that is, fresh and sufficiently humid air. From time to time you can use drops like Aquamaris to normalize the condition of the mucous membrane.
What is swelling of the nasal mucosa?
Swelling of the nasal mucosa in a child occurs due to the action of both external and internal provoking factors on the body. This condition occurs due to a large flow of blood into the nasal passages. In this case, the mucous membrane of the nasal passages swells greatly, causing an inflammatory process.
Since the nasal mucosa is a kind of protective barrier from external pollutants, when they enter the nasal passages, the blood vessels begin to become more filled with blood and swell, which indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
What causes swelling of the nasopharynx in children?
Swelling of mucous tissues is a developed response of the body to an infection that has gotten inside. Together with the mucus that the nasal mucosa forms, harmful bodies are transported out without breaking the protective barrier. At the slightest disruption, the pathogen enters the respiratory tract. Main reasons for the failure:
- allergic syndrome;
- infectious diseases;
- penetration of chemicals into the nasal passages;
- mechanical damage;
- deviated septum;
- adenoid vegetations – enlargement of the nasopharyngeal tonsil;
- polyp growths.
It is not easy to find the cause that causes swelling of the nasopharynx: the younger the patient, the more difficult it is to recognize what the reaction is to. Natural protection against any pathogens is developed in the human body through direct contact with them, and in children under 1-3 months of age, the automicroflora is not organized at all. It is worth noting that newborns normally experience physiological swelling of the nose.
First aid for a child with nasal allergies
To quickly help your baby with swelling of the nasopharynx, you should follow a certain algorithm :
- rid the child of contact with the allergen if the problem is caused by its exposure;
- drip antihistamine drops into the nasal cavity;
- ensure normal drinking regime;
- take the child out into the fresh air;
- if you don’t have vasoconstrictor or antihistamine drops on hand, you can try to relieve swelling with aloe juice;
- seek advice from a specialist.
When using a herbal component, you should take a plant older than three years, it is in it that the maximum concentration of useful substances is observed. Place three drops of freshly squeezed aloe into each nasal passage.
The bridge of the child’s nose, the forehead between the eyebrows and the eyes are swollen - what is the cause of the swelling?
Swelling of the bridge of the nose and the area between the eyebrows is not a harmless phenomenon. This may be a manifestation of a hematoma after a blow, the spread of inflammation deep into the nasal sinuses during rhinitis, or a reaction to an allergen. Parents should take this symptom seriously, especially if the child is small and cannot explain what is happening to him.
Facial swelling in children is a cause for concern
The danger of swelling in the area between the eyebrows is the risk of breathing problems. Also, inflammation can spread from the frontal sinuses to the brain due to its close location. In addition, the inflammatory process can spread to the eyes with the appearance of severe symptoms and dangerous complications.
Pain and burning, breathing problems cause stress in the baby, which negatively affects the nervous system. A hysterical state aggravates the course of the disease. Breastfed babies have difficulty sucking and breathing at the same time when they are swollen, so they may become malnourished and not gain weight. A weakened child gets sick longer and has a harder time recovering.
Swelling is a consequence of injury
Damage to soft tissue and blood vessels can occur due to impact or fracture of the bones of the nose and upper jaw. Bone fragments further destroy them, preventing rapid healing and reducing swelling.
A comminuted fracture may require surgery. After this, the bones are fixed for several days by packing the nose. Sometimes, when the jaw bones are fractured, the lips are fixed with staples and the patient is given only liquid food.
For any injury to the nose, it is advisable to take an x-ray to check the condition of the bones. A fracture that does not heal properly will cause breathing problems and recurring swelling in the future. If the nose is injured, cold should be applied to the damaged area to prevent swelling.
Foreign body in the nose
When a small child explores the world around him, he “tastes” things - he tries to put them in his mouth or nose. These can be small parts of toys, peas and even tablets. In nature, insects, poplar fluff or dandelion seeds can get into the nasal passages.
When swimming, microorganisms living in the water can crawl in. The task of parents is to organize the space for children in such a way that small objects and medicines are out of their reach.
It happens that during medical procedures a fragment of a tampon or a piece of an instrument remains in the nose.
The presence of an object in the nose impairs the ventilation of the sinuses, leading to an inflammatory process (even suppuration) and swelling. If the object is not removed for a long time, polypous tissue growths, dysfunction of the lacrimal process, suppuration and swelling of the conjunctival sacs are possible. The presence of a foreign object can be indirectly determined by the release of exudate from the affected nostril.
Complication of conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis of viral or bacterial origin often occurs in children during seasonal epidemics. Children attending nurseries and kindergartens are especially susceptible to them.
They occur in combination with rhinitis and sinusitis, cough, and fever. Inflammation of the conjunctiva and nasal mucosa can cause swelling of the eyelids and nasal area.
The baby's condition is aggravated by a painful and uncomfortable eye condition.
Why does my forehead swell?
Swelling of the forehead often has the same etiology as swelling of the upper part of the nose. It occurs as a result of the penetration of inflammation into the frontal sinuses or as a reaction to injury to both zones. Swelling of the forehead without swelling of the bridge of the nose can be a manifestation of contact dermatitis, an insect bite, sunburn, or a pinpoint injury.
Allergic reaction
As a rule, contact dermatitis occurs when the surface of the skin comes into contact with an allergenic substance. If your forehead is swollen, it may be a reaction to creams, ointments, liquid repellents, or fabric headgear. The symptom is accompanied by itching and redness of the skin. It can be eliminated with the help of external antihistamines containing corticosteroids.
Kidney disorders
With renal failure, fluid retention in the body and changes in blood composition occur (decreased protein levels, increased concentration of Na ions, toxins). This leads to swelling of the upper torso, eyelids, and area around the eyes. With swelling of the upper eyelids, the swelling extends to the brow ridges.
Renal edema can be distinguished by its mobility (when pressure is applied, it moves), pale color and normal body temperature. Indirect signs: small amount of urine excreted, deviations in its composition, lower back pain.
Who should I turn to for help?
If swelling of the bridge of the nose and forehead rapidly progresses, you should immediately call an ambulance, because there is a risk of blocking the airways and stopping breathing.
The formation of a swelling after an impact requires a visit to a traumatologist and an x-ray.
In other cases, you should contact your pediatrician - he will prescribe the necessary tests and, if necessary, refer you to specialists.
Symptoms
Visually, swelling of the nose in a child or newborn is determined only by examining the nasal passages. At the same time, the mucous membrane swells and becomes redder. The person feels difficulty breathing and a feeling of heaviness in the nasal area.
Acute viral diseases, which are accompanied by swelling of the nasal passages, are characterized by headache, fever and the presence of greenish discharge from the nasal cavity. It is sometimes not possible to relieve such symptoms in a child and newborn unless appropriate treatment is carried out.
Comments (2)
Irina Viktorovna
06/10/2017 at 09:36 | I do the same, rinse my daughter’s nose. The doctor told us that swelling of the mucous membrane is relieved by Morenazal with chamomile, so we use it. This is calcined sea water with chamomile oil. A runny nose goes away quickly.
Answer
Igor
29.11.2019 at 20:38 |
A fairly effective way to relieve nasal swelling in a child is to rinse the nose with purified sea water, for example, Aqua Maris, there is no chemical in this solution and the child has never had an allergic reaction.
Answer
What does congestion without a runny nose mean?
Among the main reasons for possible swelling of the nasal sinuses without mucus production are:
the formation of polyps , which can completely block the nasal airways and cause swelling of the mucous membrane;
- severe dehydration of the nasal mucosa due to constant inhalation of tobacco smoke, harmful chemicals and dust;
- use of certain medications , most often such a disorder is caused by those medications that are taken through the nose;
- sinusitis and other forms of sinusitis , in which, due to the strong formation of pus, the nasopharynx can swell without a runny nose, sputum simply accumulates in the sinuses;
- excessive sugar consumption, which disrupts hormonal balance and causes congestion without a runny nose.
Despite the above reasons, most often the pathology is caused by an allergic reaction.It can be triggered by any irritant from house dust to cosmetics. The exact allergen can only be identified after a medical examination.
A runny nose is a clear sign of allergic rhinitis that accompanies the disease. It is he who speaks of the relatively safe development of allergies for the patient.
If it is not accompanied by sputum production, the disease can progress to a generalized stage, which is characterized by many severe complications. That is why it is worth making sure that your child does not have a hidden form of allergic rhinitis .
Swollen forehead what to do
The danger of swelling in the area between the eyebrows is the risk of breathing problems. Also, inflammation can spread from the frontal sinuses to the brain due to its close location. In addition, the inflammatory process can spread to the eyes with the appearance of severe symptoms and dangerous complications.
Pain and burning, breathing problems cause stress in the baby, which negatively affects the nervous system. A hysterical state aggravates the course of the disease. Breastfed babies have difficulty sucking and breathing at the same time when they are swollen, so they may become malnourished and not gain weight. A weakened child gets sick longer and has a harder time recovering.
Swelling of the forehead often has the same etiology as swelling of the upper part of the nose. It occurs as a result of the penetration of inflammation into the frontal sinuses or as a reaction to injury to both zones. Swelling of the forehead without swelling of the bridge of the nose can be a manifestation of contact dermatitis, an insect bite, sunburn, or a pinpoint injury.
As a rule, contact dermatitis occurs when the surface of the skin comes into contact with an allergenic substance. If your forehead is swollen, it may be a reaction to creams, ointments, liquid repellents, or fabric headgear. The symptom is accompanied by itching and redness of the skin. It can be eliminated with the help of external antihistamines containing corticosteroids.
A bite of an insect
Bites from large insects that inject venom into the wound cause particularly extensive swelling. These could be wasps, bees, gadflies. Multiple bites from mosquitoes and other mosquitoes, especially midges, can cause swelling of the entire face. Midges bite off part of the flesh and inject hemolytic poison into the wound with their saliva, which causes an allergy in many people in the form of simulidotoxicosis.
With renal failure, fluid retention in the body and changes in blood composition occur (decreased protein levels, increased concentration of Na ions, toxins). This leads to swelling of the upper torso, eyelids, and area around the eyes. With swelling of the upper eyelids, the swelling extends to the brow ridges.
Renal edema can be distinguished by its mobility (when pressure is applied, it moves), pale color and normal body temperature. Indirect signs: small amount of urine excreted, deviations in its composition, lower back pain.
Why is the bridge of my nose swollen?
Swelling of the bridge of the nose is usually a manifestation of an inflammatory process, which can have many causes:
- Inflammation of the nasal mucosa (infectious, vasomotor, allergic rhinitis). In the acute phase, swelling is noted, in the chronic phase, tissue growth occurs due to pathological cell division (proliferation).
- Sinusitis (inflammation of the paranasal sinuses). Its types are sinusitis (inflamed maxillary sinuses), frontal sinusitis (frontal sinuses are affected), their combination with inflammation of the ethmoid bone (frontoethmoiditis, maxillary ethmoiditis).
- Foreign body inside the nose. The area around it becomes inflamed, the body reacts with an accumulation of white blood cells (pus).
- Injury to the bridge of the nose. When struck, a hematoma (consequence of internal bleeding) and swelling with blue (sometimes black) under the eyes occur.
- Congenital or traumatic curvature of the nasal septum or anatomical narrowness of the canals. The breathing process is difficult, the mucous membrane easily becomes inflamed and swollen.
Damage to soft tissue and blood vessels can occur due to impact or fracture of the bones of the nose and upper jaw. Bone fragments further destroy them, preventing rapid healing and reducing swelling.
A comminuted fracture may require surgery. After this, the bones are fixed for several days by packing the nose. Sometimes, when the jaw bones are fractured, the lips are fixed with staples and the patient is given only liquid food.
For any injury to the nose, it is advisable to take an x-ray to check the condition of the bones. A fracture that does not heal properly will cause breathing problems and recurring swelling in the future. If the nose is injured, cold should be applied to the damaged area to prevent swelling.
When a small child explores the world around him, he “tastes” things - he tries to put them in his mouth or nose. These can be small parts of toys, peas and even tablets. In nature, insects, poplar fluff or dandelion seeds can get into the nasal passages. When swimming, microorganisms living in the water can crawl in.
The presence of an object in the nose impairs the ventilation of the sinuses, leading to an inflammatory process (even suppuration) and swelling. If the object is not removed for a long time, polypous tissue growths, dysfunction of the lacrimal process, suppuration and swelling of the conjunctival sacs are possible. The presence of a foreign object can be indirectly determined by the release of exudate from the affected nostril.
Conjunctivitis of viral or bacterial origin often occurs in children during seasonal epidemics. Children attending nurseries and kindergartens are especially susceptible to them.
They occur in combination with rhinitis and sinusitis, cough, and fever. Inflammation of the conjunctiva and nasal mucosa can cause swelling of the eyelids and nasal area.
The baby's condition is aggravated by a painful and uncomfortable eye condition.
Other causes (tumors, skin diseases)
Sunburn, frostbite, and exposure to hot air can also cause swelling on the forehead. It will pass when damaged cells are regenerated.
In adolescents, at the onset of puberty, the sebaceous glands produce excessive amounts of sebum. This often occurs on the face, especially the forehead. When the sebaceous gland cannot cope with the removal of fat, a cyst or atheroma (a bag of sebum) appears under the skin, which looks like swelling. Sometimes cysts transform into abscesses, and in their place boils filled with pus appear.
Swelling on the forehead and bridge of the nose can be caused by a bone growth (osteoma), a fatty deposit (lipoma), or a basal cell tumor on the skin of the forehead and nose (carcinoma). Tumors of various etiologies, cysts in the nasal area cause narrowing of the respiratory passages from the inside and swelling from the outside.
Treatment of edema
Many parents wonder: how to relieve swelling of the nasal mucosa in a child? How to alleviate the condition? What kind of treatment is needed in this or that case? Allergic swelling of the mucous membrane can be relieved if you immediately exclude all possible contacts with the allergen that provoked this condition in the patient. However, if this cannot be done, then drug treatment should be used. It includes:
special antihistamine sprays - Cromosol;
Swelling of a physiological nature can occur in newborns. In this case, special inhalations and rinsing with a hypertonic solution of weak consistency are used.
Infectious swelling can only be eliminated by using anti-infective drugs. Treatment for viral infection is nonspecific. For it they use:
- Interferon;
- rinsing the nasal passages with a hypertonic solution;
- nasal drops based on sea salt.
Treatment of a runny nose of a bacterial nature is carried out only with the help of antibiotics. Edema of a traumatic nature is relieved with cold. Ice is applied directly to the injured area. This procedure is repeated several more days after the injury. After removing severe external swelling, vasoconstrictor drops are used.
Treatment of polyps always begins with eliminating the cause that led to the swelling. There are some direct indications for surgical solution to the problem. Among them:
- chronic asthma;
- frequently recurring sinusitis;
- deviated nasal septum;
- heavy snoring;
- inability to breathe through the nose, as a result of severe congestion in both nasal passages;
- partial or complete loss of smell.
Adenoids that have not returned to normal over time are removed only through surgery, which is preferably done in childhood, since adults tolerate such surgical interventions much more difficult.
Thus, you should always remember that traditional methods of treatment are the most correct and effective. When the first symptoms of a runny nose appear, you should immediately take some therapeutic and preventive measures. And it would be best to contact a good doctor who will do everything to prevent further development of the disease.
However, there are also people who do not want to immediately seek help from a doctor. Then the long-known, simplest folk remedies come to the rescue. But when self-medicating, you should always take into account all the possible risks that you expose yourself to.
Rinsing the nose with salt solution
An excellent folk solution for relieving swelling of the mucous membranes in children is rinsing the nasal passages with a solution of sea salt. Carry out therapy according to the following scheme:
- Prepare 0.5 liters of boiled water.
- Dilute a dessert spoon of sea salt in the specified volume of liquid.
- Mix the composition thoroughly until the mineral grains are completely dissolved.
- Gently pour the product, which has cooled to room temperature, through one nostril and release through the other.
- Perform the procedure every time there is absolute blockage of the nasal passages.
- Exposure to sea salt helps relieve inflammation and release mucous masses accumulated in the nasopharynx to the outside.
Medications
In some cases, the rinsing procedure is sufficient to relieve swelling; in others, treatment with vasoconstrictor drops is required. Drugs in this group are divided according to their main active substances and have different durations of action. Let's look at some of them:
- Vibrocil is a drug that effectively relieves nasal swelling in respiratory diseases and allergic reactions. Prescribed to children over one year of age no more than 3 times a day.
- Sanorin is available in a dosage of 0.05% for children from 2 years of age and has a short duration of action. Using the drug for more than five days leads to the development of the opposite effect.
- A child over 6 years old may be prescribed the drug Nazol to relieve swelling of the mucous membrane. The medicine is used twice a day and no longer than three days.
How to relieve swelling in an infant:
- Otrivin - a product based on xylometazoline in a dosage of 0.05% is allowed for children from the first months of life.
- Nazol baby can also be prescribed from birth. It gives good results, but it is important to follow the prescribed dosage and use the drug to relieve swelling for no more than three days.
- Tizin acts quickly and retains its effect for 8 hours. Despite the fact that the manufacturer indicates a minimum age of 1 year, pediatricians prescribe it at an earlier age.
Infants should undergo treatment under the supervision of a doctor.
Onion
The use of a product prepared on the basis of onion juice allows you to eliminate pathological swelling of the nasopharynx. The recipe for preparing the medicine is as follows:
- Take a large onion and peel it.
- Divide the root vegetable into small slices.
- Place the pieces in a garlic press and squeeze out the juice.
- Remove the resulting liquid from pulp particles by passing through cheesecloth.
- Dilute onion juice with boiled water in a ratio of 1:2.
- Pour the mixture into a glass jar and seal tightly with a lid.
- Store the product in the refrigerator.
If nasal swelling occurs in a child, instill 1-2 drops of the medicine into each nostril using a pipette. Perform this procedure several times a day. As a rule, on the second day the degree of congestion in the upper respiratory tract decreases noticeably. If drops prepared from onion juice painfully burn the tissues of the nasopharynx, it is advisable to dilute the composition with additional water.
Allergic rhinitis: year-round and seasonal
The year-round form of the disease manifests itself regardless of the season of the year. Symptoms are caused by particles of fluff, fur, as well as dander, saliva and animal excrement. Allergies in children most often develop in the presence of those “little brothers” who live in houses and apartments with their owners. These are dogs, cats, rodents, birds, cockroaches. The so-called hypoallergenic breeds of pets are, in a sense, a publicity stunt. After all, the point is not in the animal itself, but in the reaction of the human immune system.
Symptoms of allergic rhinitis:
- nasal congestion, copious discharge of clear mucus from both nostrils;
- redness of the eyes, swelling of the eyelids, lacrimation;
- irritability, loss of appetite;
- itching in the nose, eyes, sore throat;
- difficulty wheezing in the throat;
- dark circles under the eyes;
- bouts of sneezing;
- dry cough.
Seasonal rhinitis is caused by an unusually strong reaction to the pollen of certain plants. This type of disease appears throughout the warm period of the year or only in those months when certain types of trees and grasses bloom. All types of ragweed, birch, alder, poplar, dandelion, and cereals have the most powerful allergenic properties.
Light pollen and plant spores are carried by wind over long distances. Therefore, symptoms of seasonal allergic rhinitis may appear in children living tens of kilometers from fields or parks. Dry, warm and windy weather promotes the transfer of pollen, and in rain the patient's condition improves.
Causes of swelling of the nasal mucosa and nasopharynx
Swelling of the nasal mucosa in a child, like swelling of the nasopharynx, accompanies a number of diseases in which the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract becomes the site of development of a pathological phenomenon. Several specific diseases can be identified.
Allergy
Allergic swelling of the nasal and nasopharyngeal mucosa is common among children. The mucous membrane has an abundant vascular network and a large number of mast cells, due to which a strong allergic response to communication with the antigen develops. Moreover, the nose is the entrance gate for any tiny particles in the air. Among the allergens that can cause allergic rhinitis are:
- plant pollen;
- animal hair and dander;
- house dust;
- cockroaches;
- mold;
- fluff, bird feather.
Allergic swelling of the nasal mucosa and nasopharynx has certain symptoms that distinguish it from other types of edema:
- In the immediate period after contact with the allergen, characteristic manifestations begin.
- The first symptom is itchy nose.
- Then mucus appears.
- Sneezing.
- Severe swelling of the mucous membrane occurs, which makes it difficult to breathe through the nose.
- The olfactory function is impaired, the voice becomes nasal.
A characteristic sign that speaks in favor of an allergic nature is the presence of a history of allergies. This could be previously occurring rhinitis, allergic dermatitis, asthma, urticaria, etc. This predisposition to various allergic diseases is called atopy. A newborn may also develop nasal swelling as a result of allergies to formulas and various foods consumed by the nursing mother.
Physiological runny nose
The cause of swelling of the mucous membrane in a newborn may be a physiological runny nose. The thing is that in a baby, the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx cannot fully cope with its new job, because in the womb the respiratory system does not function. And regulatory processes are not yet fully formed, which leads to nasal swelling in a newborn.
Infection
The predominant causative agents of rhinitis in children are viruses. In a newborn, it is a viral infection that causes swelling of the nose. But bacteria can also actively multiply on the mucous membrane. Viral rhinitis is characterized by the following features:
- the onset is not associated with the action of any allergen;
- the first symptom is profuse mucus from the nose, while the mucus is transparent;
- sneezing;
- after a few days, bacteria enter the damaged mucous membrane, causing bacterial inflammation, a characteristic feature of which is the yellow and/or green color of the mucus;
- swelling of the mucous membrane is slightly expressed;
- cessation of breathing through the nose occurs due to the accumulation of viscous mucus in the nasopharynx.
A bacterial infection can occur if the child’s hand hygiene is not maintained. You can carry various microorganisms into your nose with your hand.
Polyps
A polyp is a protrusion of hypertrophied nasal mucosa. And it hypertrophies as a result of frequent negative influences, for example, due to frequent infections or contact with an allergen, as well as as a result of anatomical imperfections. Thus, a polyp of the nasal mucosa can be called a protective mechanism of the body.
But the development of polyps is not a momentary process, so the symptoms of the disease increase with the increase in polyps. The onset of the disease in children is associated with the development of a runny nose, general malaise, and drowsiness, which are perceived as symptoms of ARI. Over time it develops:
- decrease and then loss of smell;
- loss of appetite;
- memory impairment and decreased attention (occurs due to chronic lack of oxygen);
- nasal breathing is impaired, as a result of which the child breathes through the mouth (typical appearance - the mouth is open, the lower jaw sags);
- there is noise in the ears;
- severe night snoring occurs.
Progression of the disease can lead to complete closure of the nasopharynx. And this will already affect food intake, the development of oral speech, etc.
Adenoids
Adenoids are called the tonsils of the nasopharynx. In children, this lymphoid tissue responds to the inflammatory process with edema and hypertrophy. After eliminating the cause, swelling of the adenoids goes away very slowly. Therefore, true hypertrophy can be judged some time after recovery from the underlying disease. Symptoms of enlarged adenoids:
- the child’s mouth is open due to the cessation of nasal breathing;
- snoring or snoring during sleep;
- runny nose that does not respond to treatment;
- night cough;
- nasal voice;
- hearing loss.
Injury
Trauma to the nose will lead to the development of swelling. Such injuries are quite common in children. It is not difficult to make sure that it was the injury that caused the swelling: it is enough to simply examine the child’s nose - blood from the nose, its deformation, abrasions, scratches, etc. will indicate an injury.
How can you relieve nasal swelling in a child?
Many mothers who are faced with this problem for the first time are concerned with the question: how to relieve swelling in the child’s nose. You can find many products on pharmacy shelves, but few know which one to give preference to. Not only ready-made medications will be effective, but also medications prepared with your own hands.
What Causes Swelling
The mucous membrane of the nasal cavities contains a large number of blood vessels that provide warming to the inhaled air. The ciliated epithelium, namely its cilia, help retain particles of dust and dirt, and the nasal secretion helps prevent their penetration into the bronchi.
Inflammation that begins to develop in the nasopharynx due to the penetration of viruses, bacteria, and allergens, as a rule, causes swelling of the mucous membrane of this area and the organs of the visual system. Swelling in the nasal passages is characterized by difficulty breathing, frequent sneezing, and the production of mucous fluid.
Nasal swelling in newborns is caused not only by colds, but often occurs against the background of other provoking factors: teething, overheating, pathologies in the anatomical structure of the nasal passages. A common cause of edema is dry air in the living room.
If the air in the room where the newborn lives is too dry, this often causes swelling. The nasal passages of a baby are narrower than, for example, those of a baby who has reached the age of one. In this regard, swelling of these can provoke pathology.
During the cold season (for example, in winter), many parents try to heat the room by turning on air heaters, but these contribute to drying out the room. Nasal swelling caused by this factor occurs without a runny nose and, as a rule, appears in the morning after waking up.
Why are the symptoms dangerous?
If swelling of the nasal membrane with or without a runny nose begins to bother you, you need to consult an otolaryngologist. Based on the results of the diagnostic measures, the doctor will select the most appropriate therapy. If you use the prescribed method of treatment and follow the doctor’s recommendations, you can hope for a favorable prognosis and a speedy recovery.
If you neglect going to a specialist and rely on self-medication, the risk of developing negative consequences increases, including inflammation of the sinuses. In other words, sinusitis, which can spread to nearby tissues of the jaw (development of osteomyelitis), eyes (development of conjunctivitis), and brain (development of meningitis).
As a result of the development of swelling of the nasal passages in a child, breathing through the nose becomes difficult and often stops altogether. This gives its owner some discomfort.
After penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the epithelium, a malfunction of the functions of ciliated cells begins. There is an increase in blood circulation and lymph flow to the affected area, which promotes inflammation and also causes severe swelling of the nose in a child or adult.
The reasons are various: from viral and bacterial infections to allergic irritants.
Symptoms of allergic damage to the nasal passages are clearly expressed. Clinical manifestations include the following:
- impaired breathing through the nose (partially or completely);
- cough and frequent sneezing;
- itching syndrome in the nose and throat;
- secreted mucous exudate;
- increased tear production.
It is not difficult to distinguish the signs of a bacterial or viral infection from an allergic rhinitis. In the first case, the mucous exudate quickly turns into purulent. Symptoms include: fever, headaches, general malaise.
In most cases, allergic swelling is eliminated quickly. It is enough to exclude the influence of a provoking factor (inhalation of dust, plant pollen). Elimination of rhinitis with a runny nose of allergic etiology is carried out with appropriate medications (drops, nasal sprays).
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DnSkrCrzAwI
Sources of swelling of the mucous membranes in babies may be associated with infection. Exposure to pathogens (bacterial or viral) causes this symptom and others that provoke physical discomfort in the child:
- sneezing;
- impaired nasal breathing;
- redness of the epidermis on the face;
- a feeling of heaviness and pressure in the bridge of the nose;
- pain in the bridge of the nose;
- production of mucous or purulent fluid and its secretion from the passages.
Among the initial symptoms of infectious nasal diseases are noise during nasal breathing (usually from one nostril), the appearance of mucous exudate from one passage and congestion.
Swelling of the nose in a child with enlarged adenoids is not the only symptom of the disease. The disease may be accompanied by the following clinical manifestations:
- difficulties in the process of nasal breathing;
- night snoring;
- symptoms of general intoxication: decreased attention and memory, rapid fatigue, delayed physical development, elevated temperature;
- discharge of mucous or purulent exudate.
The disease has a chronic course and, in the absence of necessary therapy, increases the risk of complications from other organs and systems. The cardiovascular system suffers: myocarditis and endocarditis develop. Visual function (conjunctivitis) and auditory function (otitis) are damaged.
If there is swelling of the adenoids, only a doctor can determine how to relieve it. Self-medication in this case is dangerous to health. During the development of pathology, the body's protective function decreases, which requires the use of immunomodulatory drugs.
Chronic nasal congestion often occurs due to the abuse of local drugs in the form of drops and sprays. The following symptoms are also associated:
- the sense of smell is impaired;
- there is pain in the head;
- the work and rest schedule is disrupted;
- irritability and blood pressure increase;
- pulse quickens;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia develops;
- heart pain occurs;
- a slight mucous exudate is released.
Swelling affects the entire nasal mucosa, which leads to blockage of the nasal passages and difficulty breathing. The intensity of symptoms increases in the evening.
Diseases of the upper respiratory tract due to the abuse of local drugs are difficult to treat.
First teeth
Swelling of the nose during teething in a baby is a natural phenomenon that does not require specific therapy. In this case, there is a discharge of mucous exudate from the passages and hyperemia of the inner walls of the nose. There are no other symptoms that bother the child.
Parents need to promptly remove accumulated exudate - a favorable environment for the reproduction and activity of pathogens.
In the first 10-14 weeks, the child’s body adapts to its new living conditions.
This also applies to the mucous membrane of the nasal passages, which begins to fulfill its functions: moisturizing, warming the air, and cleansing.
Due to increased activity of the mucous membranes, slight swelling may form and light mucus may be released. This should not unduly alarm parents, because the child’s condition is not impaired.
The disease occurs against the background of exposure to the mucous membranes of the nose and throat of various types of pathogens (viral or bacterial). Classic symptoms are swelling of the child’s nose, runny nose, stuffiness, and sneezing. Mucous or purulent exudate is released from the passages.
Due to difficulty in breathing, the baby becomes restless, irritable, and sleep is disturbed.
The development of nasal swelling without a runny nose in a child does not occur on its own. This condition is influenced by several factors, namely infectious or allergic:
- vasomotor rhinitis caused by infectious pathogens or allergic irritants (narrowing of the nasal passages occurs, congestion and runny nose);
- constant exposure to medications, which contributes to the development of chronic swelling without a runny nose.
In addition, the causes of dry rhinitis are polyps in the passages, a deviated septum, and dry air that the child breathes. The doctor will tell you what to do if your child has mucus due to swelling of the nose, but without snot.
Therapy in children
You can remove swelling in a child’s nose using a comprehensive method, using medications and other therapeutic procedures (for example, physiotherapy). Among the medications, vasoconstrictors are actively prescribed, for example, Naphthyzin or Galazolin. These products should only be used after consultation with your doctor.
A universal treatment for nasal swelling without a runny nose in a child has not been developed. Methods of getting rid of a symptom depend on the root cause of this condition: with an infectious etiology they are the same, and, for example, with an allergic etiology, they are different.
It is important for a child to choose the safest and most effective remedy to alleviate the condition and quickly get rid of the pathology. Modern medicine has different groups of drugs that can quickly relieve swelling.
Nasal drops
Before determining how to relieve swelling of the nasopharynx in a child, the doctor finds out the cause of the symptom. If this is an allergic reaction, antihistamines are prescribed in the form of drops or spray. If the edema is infectious, vasoconstrictor nasal drops are prescribed, which have an anti-edematous effect on the body.
The drugs have a quick effect: already in the first minutes there is a decrease in swelling, congestion and the volume of mucous exudate produced. Despite this advantage, they are not able to eliminate the source of edema, and if the dosage is systematically exceeded, they will cause side effects: dryness, burning of mucous membranes, sneezing, increased blood pressure.
Many experts recommend treating nasal swelling and runny nose in a child with such remedies only at night. This method of therapy is prescribed for a period of no more than 7 days. Among the representatives:
- Naphthyzin;
- Sanorin;
- Xylene;
- Rhinostop;
- Tizin Xylo.
Other drugs in nasal form used to treat swelling of the nasal mucosa are moisturizers, which include sea water. Such products moisturize the mucous membrane, help thin the mucus and prevent it from drying out. This could be Rinostop, Aqualor, Aqua Maris spray.
Allergic rhinitis and the swelling caused by it require the use of antihistamines in local form. These are Histimet, Vibrocil, Cromosol. Antiseptic agents have an antimicrobial effect (Protargol, Sialor, etc.).
Treatment in children
When performing medical treatment for swelling of the nasal mucosa in children, it must be taken into account that all measures must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. This especially applies to infants, who may suffocate while sleeping or feeding. Most often, doctors prescribe a drug with a vasoconstrictor effect to their young patients.
This includes Vibrocil (the link describes how to use Vibrocil drops for children). It also has an antihistamine effect. During its development, phenylephrine was used, which relieves swelling. But what is better to use, Vibrocil or Nazivin for children, is described in detail in this article.
Vasoconstrictor drops cannot be used for a long time, as complications may occur.
When using Naphazoline, Ephedrine or Tetrazoline, you must stop treatment after 7 days. After this, even more swelling may occur. It is better to use drops that have a long-lasting effect to treat childhood nasal swelling.
Folk remedies
You can use folk remedies to treat swelling of the mucous membrane in children only if they are part of complex therapy. The following recipes are considered effective:
- You can get rid of swelling of the throat and nose with the help of a collection that includes the following herbs: calendula, marshmallow, chamomile and plantain . Take 40 g of raw materials, add 200 ml of boiling water. Leave for 30 minutes, filter and take 100 ml 4 times a day. But how to use chamomile for coughs for infants is described in great detail in this article.
- Take 200 ml of warm water, add a few tablespoons of sea salt . Using a syringe, rinse the nasal cavity with the resulting solution. Perform such manipulations 3 times a day. But how you can warm your throat with salt, and how to do it correctly, is described in this article.
- Place a glass of water and a few drops of fir, pine or cedar ether in a wide container. Lean over the container, covering yourself with a towel. Inhale the vapors for 20 minutes. Perform the manipulation 2 times a day. This information will help you understand how much a mixture of essential oils helps against colds and how they should be used.
- You can relieve swelling of the nasal mucosa with aloe, beet or Kalanchoe juice. For example, honey is combined with beet juice, and onion juice is best mixed with vegetable oil. Place drops into the nose 2 times a day.
- Take lemon juice and add water in a 1:1 ratio . Use the resulting solution to rinse the nasal cavity. Upon completion of the procedure, it is necessary to form a cotton swab and soak it in a saline solution. Such manipulations must be performed as often as possible. Lemon will eliminate germs, and salt will relieve swelling. But how to make honey with lemon for colds, and how effective this remedy is, is described in great detail in this article.
Safe and effective treatment
Treatment depends on why your child has a swollen nose.
Nasal drops
Several groups of nasal drops have been developed, the main ones being:
- Vasoconstrictors. The action is aimed at narrowing the blood vessels of the mucous membrane, relieving swelling, but they do not eliminate the cause of the disease. Used for no more than a week, it is important to carefully read the instructions before starting use.
- Antiseptic. In case of acute viral infections, antiseptic drops do their job well. Cleanse the mucous membrane of viruses. A common remedy is Miramistin spray.
- Antibacterial. Used for bacterial attack of the mucous membrane. These drops include: Sofradex, Polydex.
- Antihistamines. Prescribed for swelling due to allergies.
Before using any drops, it is necessary to rinse your nose from possible crusts, mucus and dust so that the medicine reaches the surface of the mucous membrane as much as possible.
Antibiotics
Sometimes, against the background of a viral disease, a bacterial infection will join, then antibiotic drugs come into play. Only a doctor can correctly calculate the dosage and select the right drug for a specific case.
Glucocorticosteroids
Children are prescribed only when it is not possible to cope with swelling with other drugs. There is no need to deviate from the dosage and course of use prescribed by your doctor.
Washing
Nasal rinsing is the most important point for the prevention and treatment of children's noses. Pharmacies offer many salt formulations from different manufacturers. They can be found in the form of drops and sprays, with a wide variety of excipients.
You can make saline solutions yourself; this does not reduce their effectiveness. To prepare, you need to dilute 1 teaspoon of salt in a liter of boiled water.
Rinsing with such solutions is used regardless of the cause of the swelling. If the first symptoms of a viral infection appear, the solution washes viruses out of the nose, softens the crusts, and rinses away mucous secretions. With the allergic nature of the edema, allergens that have entered the mucous membrane are washed away.
In case of bacterial complications, it is important to maintain nasal hygiene to avoid even greater complications. In such cases, the salt composition washes away the mucus, preventing it from stagnating in the sinuses.
If the cause of nasal swelling is an injury or foreign body, you should not use a solution with salt. If the nose is injured, it is necessary to put cold on the site of the injury and let the child lie down. If your baby puts something in his nose, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.