Our kids get sick much more often than adults, because the respiratory system of children has a slightly different structure. A child has rather narrow openings in the respiratory tract due to the fact that its sections are located at a short distance from each other. If, God forbid, a baby develops some kind of inflammation or becomes infected with a viral infection, then the airways immediately become swollen and narrow to a dangerous size. Diseases in children are much more complex, and therefore mothers and fathers need to monitor their course very carefully.
Very often, parents come to see the pediatrician and say that their child has a fever and is coughing.
Many diseases are characterized by a cough, so the doctor needs to make an accurate diagnosis based on the severe symptoms. Cough, due to its nature and characteristics, makes it possible to identify the disease.
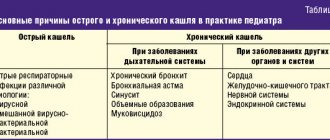
Types of cough associated with various diseases
From a physiological point of view, coughing is an unconditioned reflex that appears in a child from birth. It is simply necessary for the normal functioning of the body. When you cough, the airways are cleared naturally, that is, the trachea, bronchi, and lungs secrete mucus and other foreign bodies. If a baby clears the airways by coughing up to 13 times a day on average in the absence of illness, then this is normal. Children usually cough in the morning to clear out mucus that has accumulated during the night. The child often begins to cough to attract the attention of his parents. But a normal physiological cough without fever does not bring any discomfort to children and ends quickly.
Any disease has its own characteristics, and if you listen carefully, then with the correct diagnosis you can easily get rid of a child’s cough.
There are two types of cough: dry and wet, and is observed with the following diseases:
- ARVI;
- pharyngitis;
- laryngitis;
- tracheitis;
- bronchitis;
- pneumonia;
- pleurisy;
- flu;
- rhinovirus infection;
- whooping cough;
- bronchiolitis;
- measles.
With ARVI, there is usually a strong and sharp cough, as well as other symptoms such as runny nose, lethargy, and fever. With laryngitis, the cough in children seems to be barking, quite loud, turning into a whistle. If a diagnosis of “tracheitis” is made, then the cough is chesty, strong, deep. With bronchitis, a paroxysmal cough with sputum production is observed, a very loud cough. The disease “pneumonia” gives a deep and wet cough with prolonged painful attacks.
With pleurisy, the cough is dry and painful without sputum, and shortness of breath occurs due to the accumulation of fluid inside the pleural cavity. The flu causes a very high fever and a sudden, dry and persistent cough. With rhinovirus infection, a dry, barking and whistling cough is observed mainly at night. Whooping cough is very difficult to tolerate if the baby is not vaccinated on time. The child coughs painfully with a dry cough, sometimes with vomiting.
There may be several dozen attacks during the day. Vaccination makes the course of the disease easier; the cough is dry, but not severe. With bronchiolitis, the cough is frequent and dry with low fever and shortness of breath. Another serious childhood disease is measles, when the cough appears before the rash. High temperature, possibly conjunctivitis. After several days of illness, the cough becomes rough, sharp, and hoarse.
Helping babies up to one year old with the treatment of wet, dry cough: possible methods
Every person (both adults and even infants) is familiar with cough, which is one of the main manifestations of most diseases of the respiratory system.
This unpleasant phenomenon, exhausting both the patient and his environment, serves as a defense mechanism.
With the help of spasms that occur as a result of irritation of the nerve endings of the mucous membrane of the larynx, trachea or bronchi, the body tries to get rid of foreign bodies. Therefore, you should not fight the cough as such, but the cause that caused it.
Cough is a fairly common ailment in children.
What types of cough are there?
There are different classifications of cough. For example, according to duration it is divided into:
- acute (paroxysmal, lasting a couple of weeks);
- protracted (from half a month to a month);
- subacute (lasts up to one and a half months);
- If the baby coughs for a long time, it is a chronic cough (duration – more than two months).
You can compare the intensity: light coughing and hysterical cough. Also, the baby may begin to seem to bark; such coughing sounds often accompany laryngeal stenosis with croup or false croup.
How to recognize cough symptoms yourself
Cough to the point of vomiting in a child - what to do if a baby is vomiting
It is not so difficult to determine the type of cough and its symptoms yourself; you need to carefully monitor the child.
Thus, with a viral infection of the respiratory system, the usual cough reflex is triggered in response to irritation of the pharyngeal mucosa by nasal discharge. When you have a runny nose, a cough is accompanied by sputum production.
With false croup, the mucous membrane is affected and swells, as a result of which the lumen of the larynx narrows, and a barking cough with wheezing inhalation occurs.
Additional Information. If the inflammation affects the bronchi and alveoli, the baby begins to cough constantly, he experiences shortness of breath, and the temperature may also rise. During asthmatic attacks, mucus accumulates as a result of exposure to allergens, which provoke coughing.
How is a wet cough different from a dry cough?
The most popular division of cough types is dry and wet. If a cough attack does not produce sputum, it is called dry; otherwise, it is called wet. Most often, a dry cough accompanies the first days of the development of viral diseases, and also occurs with:
- laryngitis;
- tracheitis;
- pleurisy;
- tumor diseases of the bronchi.
This type of coughing is considered unproductive, since it only further irritates the mucous membrane of the larynx (as well as the nerves of the patient and everyone at home), but does not lead to cleansing.
If sputum is released (it is very advisable to expectorate it), the cough is characterized as wet. Phlegm is mucus that is produced on the walls of the bronchi. It is one of the symptoms of respiratory system diseases.
Important! Sputum separation is a phenomenon that is designed to help cleanse the lungs of pathological microorganisms and destroyed epithelial cells, therefore such a cough is cured with expectorants.
Thick sputum is a very difficult substance to cough up; the more there is, the “scarier” and rougher the child coughs.
Common causes of cough in infants
Wet or dry cough in the morning in a child - possible causes
The causes of coughing attacks in children are varied:
- the presence of a foreign body in the larynx;
- pharyngitis - an inflammatory process in the pharynx, a characteristic onset of a cold, accompanied by a sore throat, runny nose and fever;
- laryngitis is an inflammatory process in the nasopharynx, cough with laryngitis in a child affects the ligaments, it is dry and very sharp; the mucous membrane in this place is subject to rapid swelling, attacks occur mainly at night;
- tracheitis - inflammation reaches the trachea, the cough is unproductive, it happens with acute respiratory infections and any childhood infections;
- whooping cough – attacks are caused by the action of toxins on the cough center in the brain; it is a long, debilitating illness;
- acute bronchitis - accompanied by a dry cough, which then turns into a wet one, as well as an increase in temperature to 38 degrees, sweating, the child is constantly shivering;
- chronic bronchitis - a “chest” cough with discharge of green sputum can last up to three months;
- pneumonia - a dry cough that characterizes the onset of the disease, goes away within a short time, inflammation of the bronchi may occur;
- bronchial asthma - accompanied by bronchospasm, in which exhalation becomes difficult and inhalation of air becomes intermittent.
Cough with fever
When a child has a cough and fever, but the nose is clean, without snot, it is similar to a sore throat, which at first occurs without symptoms, and only the appearance of fever signals an illness. Then the dry cough is accompanied by redness of the throat and swelling of the tonsils.
With a sore throat, a cough is accompanied by redness of the throat
Another reason that a child has a fever and coughs heavily are complications after an untreated acute respiratory viral infection, when infectious agents enter the respiratory system and the disease develops into pneumonia or bronchitis. If the baby also has rashes, this may be symptoms of chickenpox or rubella.
Cough without fever
Children under one year of age and older experience coughing attacks without fever (maximum - 37-37.5 degrees). For example, if you have an allergy, after contact with an allergen, your baby’s throat may feel sore for a long time. Chronic cough at normal body temperature occurs with bronchial asthma; it is whistling and hacking.
Night cough
It happens that during the day the child does not complain about anything, but at night he is “covered” by coughing attacks that interfere with the baby’s proper sleep. This can be either due to a serious pathology of the upper respiratory tract, or because mucous nasal secretions enter the throat and irritate it. This usually happens upon waking up.
Note! Dust and dry air can intensify the urge to cough at night.
Cough with vomiting
Sometimes coughing attacks are accompanied by vomiting. This is a rather alarming symptom; it may be a sign of whooping cough, which is especially dangerous not only for newborns, but also for six-month-old children.
Sometimes even a simple “runny nose” cough and sneezing can trigger a gag reflex. Doctors advise feeding such babies little by little, but often.
Caring for a baby from birth to one year with a cough
Rough, dry, hard cough in a child under one year old
The first condition for complete care is consultation with a doctor, especially when the child has a severe cough. The ability to determine its type “by ear” will greatly help the pediatrician when making a diagnosis. A sick baby (be it two months old or already one year old) needs to be provided with rest and try to follow the doctor’s recommendations.
How to stop an attack
In order to stop a dry cough, you need to:
- if a child coughs, before treatment, he must be calmed down and the baby held in his arms;
If you have a coughing attack, you need to hold your baby in your arms.
- give warm drinks to soften mucous membranes;
- drop saline solution into the nose;
- increase the air humidity in the room, you can sit with your little one in the bathroom;
- carry out inhalation with saline solution or mineral water.
You can help relieve an attack with medication only after consultation with your pediatrician.
General recommendations
The main recommendation for coughing in newborns and children under one year of age is bed rest for the whole day. It is advisable to wrap the patient in a blanket, maintain the temperature in the room no higher than 22 degrees and maintain high humidity.
It is necessary to maintain a fluid balance: give your baby plenty of water, tea, juice, fruit drinks, and you can make homemade compote. Food should be easily digestible: soups, purees, you can grate fruits and berries.
What not to do
One of the strict prohibitions is self-medication - you cannot decide on your own how and with what to treat a baby’s cough, because there is no universal remedy, and the wrong treatment can harm the baby.
It is undesirable to “stuff” a child with medications as soon as he starts coughing, because the cough can be caused by a natural cause. For example, infants up to three months of age may cough when a drop of milk enters the trachea.
It is not recommended to put mustard plasters on either a four-month or a six-month-old baby - they can cause burns. It is also advisable to exclude sweet and sour foods and dry crumbly foods from the diet.
Which doctor should I contact?
As soon as the baby shows the first signs of the disease, parents must decide which specialist to show it to. First of all, this is a pediatrician who will determine the main causes of the cough and prescribe further directions.
To clarify the diagnosis, the child will be examined by an ENT specialist and an allergist. If the cough is associated with diseases in the gastrointestinal tract, a gastroenterologist will come to the rescue. When coughing attacks occur at night while lying down, it is better to show the child to a cardiologist.
Sometimes the pediatrician may refer you to a pulmonologist, TB specialist or oncologist.
Diagnostic methods
The first method is listening with a stethoscope. Further, depending on the cause, diagnostic procedures such as:
A child with a cough may need an x-ray
- physical examination;
- allergy tests;
- bronchoscopy;
- computed tomography of the lungs.
High-quality and timely diagnosis is the key to further effective treatment.
Features of therapy in children under one year of age
In order to cure a cough in children as soon as possible, you should not delay visiting a doctor, because in children six months old and older, inflammation very quickly brings an acute condition. The key to successful treatment is strict adherence to the pediatrician’s instructions.
Drainage massage
A very effective remedy for relieving children from several months to a year of cough is drainage massage. During this procedure, the child's head is lowered below the body. Movements are carried out gently and carefully. The back is first smoothed, then tapped. Then the sides are rubbed, the third stage is breast drainage. After the massage, it is better for the patient to sleep, maybe until the morning.
Drainage massage
Use of inhalers, nebulizers
Steam inhalation (to moisturize sputum) has a good effect. However, if there is no dried mucus in the throat, such procedures are not at all useful. Inhalation of fine particles of strong drugs using nebulizers provides relief from lesions of the upper respiratory tract.
Medications
how to treat a cough in a one-month-old baby ; he can prescribe the following medications to the baby:
- mucolytics to get rid of phlegm;
- suppresses the cough reflex;
- expectorants;
- antiallergic;
- antibiotics in severe cases.
Dr. Komarovsky about severe cough in infants
The famous pediatrician Komarovsky believes that expectorants should not be given to children under five months of age and a little older, they only increase the amount of mucus. To quickly get rid of attacks, the doctor advises high humidity and low temperature in the room, as well as the child drinking plenty of fluids.
Doctor Komarovsky
Prevention measures
It is easier to carry out preventive measures than to go through all the stages of subsequent treatment. Such measures include:
- healthy lifestyle;
- strengthening the child’s immunity;
- elimination of potential allergens.
Even ideal conditions do not provide good health, so every child experiences a cough. It can be wet or dry, and differ in the reasons that caused it. Considering the nuances of treatment for young children, it can only be started after visiting a pediatrician.
Source: https://kpoxa.info/zdorovie-pitanie/vylechit-kashel-bystro-effektivno.html
What to do if a child’s wet cough turns into dry
It is no secret that it is easier to cure any disease at the initial stage, rather than after complications. Therefore, you should not delay the illness if you have a wet, much less a dry cough, as this is fraught with complications in the future. It is much easier to recover from a wet cough than from one that has become severe and already causes chest pain.
Tips for treating dry cough in a child:
- Plenty of fluid intake is required;
- systematic humidification of indoor air;
- when coughing at night, place two pillows under your head;
- When cleaning premises, do not use aerosols or caustic cleaning agents.
The most important thing is not to self-medicate under any circumstances, but be sure to show the baby to a doctor and take the necessary tests immediately after the initial signs. Only a specialist can determine the reason for the transition of a cough to another stage, since a dry cough after unsatisfactory treatment will lead to pneumonia and other serious diseases.
When the pediatrician has found out the true cause of the cough, treatment should be started immediately. Natural herbal remedies work best. The most important thing in this case is to use the necessary general-purpose drugs for treatment in combination. Usually, treatment is difficult, so during the cold season the child must be protected, ensure that the diet contains as many vitamins as possible, and dress warmly enough so that illnesses do not overtake your baby. Medicinal herbs that can help treat dry cough in children have long been known as folk remedies, these are oregano, coltsfoot, chamomile, thermopsis, licorice root.
Inhalations are very effective, but they can only be given to a child after three years. It’s a good idea to give your baby natural buckwheat honey in small quantities. You need to wash it down with warm milk with 1 teaspoon of baking soda. It is also appropriate to give juice from squeezed black radish and honey in a 1:1 ratio, but provided there are no allergies. After two years of age, a child can drink warm tea with 2-3 teaspoons of raspberry jam. If you brew tea from the herbs marshmallow, wild rosemary, coltsfoot, and elecampane, then the concentration should not be strong.
An excellent effect is obtained from the extract of anise and thyme fruits; they not only alleviate the child’s condition, but also have good expectorant properties. Very often, carrot juice is used, diluted with sugar syrup in equal proportions. It is given to children 5 times a day, a teaspoon. Sugar syrup can be replaced with warm milk, and carrot juice can be obtained using a juicer or from squeezed grated carrots. A decoction of milk and sage herb is excellent for dry coughs. Add 1 spoon of sage to 200 grams of milk in an enamel pan, bring to a boil, then filter the mixture, cool and give it to the child warm. After this they are put to bed.
A doctor may prescribe additional treatment options for a child with a dry cough:
- mucolytics for expectorant effect and thinning of sputum;
- resorptive drugs for thinning and expectoration of mucus (sodium bicarbonate, sodium and potassium iodide, ammonium chloride);
- drugs with a secretomotor effect for the rapid outflow of sputum.
In addition to drug treatment, proper care for the child during his illness is of great importance, which will alleviate the condition and speed up recovery.
When a child develops a cough, it may be due to either a cold or a natural reaction of the body. This means that a child’s body, like an adult’s, reacts to dust or chemical elements. When they get on the mucous membrane, they irritate it. As a result, the body naturally cleanses parts of the respiratory system.
Treatment of dry cough with medications
If the transition of a wet cough to a dry form has begun, then its treatment is carried out in this direction. Prescribed medications help relax the smooth muscles of the respiratory organs, reduce viscosity and thin the sputum. Untimely and improper treatment leads to the spread of infection to the lower respiratory tract, causing bronchitis, pleurisy, and pneumonia.
In this regard, the patient is prescribed the following medications, which have proven to be the most effective:
- Stoptussin. Antitussive syrup with a combined effect. Provides mucolytic and expectorant activity, successfully fights nocturnal attacks, thins mucus and activates its removal to the outside.
- Bronholitin. Anti-cough syrup with antiseptic and bronchodilator effects. Stops painful attacks and prevents infection from spreading through inflammatory processes in the respiratory tract when sputum accumulates in them.
- Ambroxol. A mucolytic agent that thins sputum and reduces the adhesive properties of mucus. Under the influence of the drug, the secretory activity of the bronchi returns to normal, and sputum is easily removed.
- Prothiazine. Antitussive syrup that has antiallergic, sedative and secretomotor effects. Prescribed for spasmodic cough accompanied by spasms in the larynx. Suitable for adults and children from two years of age.
- Erespal. Anti-inflammatory tablets. They help to increase the internal lumen of the bronchi, remove sputum and transform a non-productive cough into a wet state.
The viscosity of mucus is noticeably reduced by taking resorptive drugs - ammonium chloride and sodium bicarbonate. After the debilitating dry cough becomes wet, syrups and expectorant tablets are prescribed. These include ACC, Bronchosan, Libexin Muco, Fluditek and others. Their action is aimed at stimulating the mucociliary system and accelerating the removal of mucus from the respiratory tract.
Children, in case of difficulties with sputum separation, are prescribed herbal medicines - Alteyka, Thermopsol, Codelac Broncho with thyme. They rarely cause side effects and do not put much strain on the kidneys and liver. Inhalation procedures using nebulizers help well, especially effective for prolonged illness. They are carried out with the following drugs intended to eliminate painful dry cough:
- Ambrobene. Improves the functions of the mucociliary apparatus, facilitates the removal of sputum.
- Berodual. Provides expansion of the lumens in the bronchi, thereby activating the outflow of mucus from the lower respiratory tract.
- Berotek. Stops severe coughing attacks, increases the lumen of the bronchi.
Dry cough
Very often in children, coughing is associated with colds and infectious diseases, although it can also be a consequence of an allergic reaction.
Moreover, this symptom has its own sequence of development:
- First, the child develops a sore throat.
- Then the cough becomes dry, and copious sputum production is completely absent.
- Only after a few days does it become wet.
As a rule, the process described above is the progression of a symptom of the influenza virus. But a dry cough is not always associated with this disease. There are quite a few reasons for this. The following are considered key:
- allergic reaction;
- strong chemical odors;
- if the room or premises has dry air;
- Often a cough is associated with a foreign body getting into the throat. In this case, it is accompanied by suffocation.
Moist cough
In addition to the dry appearance, the child may cough and produce mucus and sputum. This type is also called “wet”, “wet” or “productive”. It is very important, since during such a cough the bronchi are cleared of mucus. Otherwise, there will be complications, since microbes multiply in this viscous consistency of sputum. If treatment is not started in time, this can lead to other diseases, including sore throat. But at the same time, we note that there is also a cough that is associated with genetic lung diseases, such as cystic fibrosis.
When a child has a wet cough, it is very important to observe the color and consistency of the sputum produced. Every parent and adult should know that if a wet cough turns into a dry one, then this is a sign of a speedy recovery for the child.
You should also know how to treat this type of cough. It must be remembered that it is difficult for children to clear sputum. This is due to high mucus viscosity and weak muscle function. It is for this reason that you need to start drug treatment.
Treatment for cough depends on the diagnosis. It is mandatory to visit a doctor, who, according to the tests performed, will determine the pathogenesis and select the correct treatment!
Reasons for the occurrence of the violation
Often parents do not pay enough attention to a wet cough that turns into a dry one. They are sure that this indicates that all the mucus has come out and the baby is recovering. However, it is not. Such a lingering cough may indicate the presence of various diseases.
If a child’s wet cough turns into a pronounced dry cough, one can suspect the presence of:
- bronchitis;
- pharyngitis;
- colds with complications;
- pleurisy (with this disease there is also elevated body temperature and difficulty breathing);
- tuberculosis.
A dry cough can occur after a wet one if there was no treatment for the cold or it was incorrect. In this case, the infection spreads and enters the lower parts of the respiratory system. As a result, bronchitis occurs. The cough may become unbearable. If you suspect bronchitis, you should immediately take your child to the doctor. There is a risk that an acute type of disease will become chronic. In this case, the baby will constantly have a cough.
Children with bronchitis need properly prescribed drug treatment. With this disease, they become lethargic and complain of a significant loss of strength. If left untreated, bronchitis can cause complications. Possible appearance:
- pneumonia;
- bronchial type asthma;
- lung abscess.
You cannot do without consulting a doctor. It is impossible to cure bronchitis in a child on your own, and self-medication can result in serious complications.
A wet cough turning into a dry cough is often observed in children who have had a cold. Incorrect treatment or lack thereof can cause inflammation of various types. Often a passing cough is present with pharyngitis. In this case, the baby complains of pain in the throat. Treatment should be started immediately.
A dry cough after a wet one is often observed with tuberculosis. Many people mistakenly believe that such a disease occurs only in those people who have an extremely low standard of living and do not take care of their health. However, this is not at all true. This disease is transmitted by airborne droplets. It can be contracted in any crowded place or through direct contact with a sick person. Everyone is at risk of developing the disease.
How to relieve coughing attacks
In infectious diseases, coughing attacks are a natural occurrence. As a rule, they occur infrequently, but over the course of several days. But if attacks last more than 2 weeks and are accompanied by headache, sore throat and fever, then this should cause concern in adults. If you start the process and do not start treatment on time, the child may develop the most dangerous childhood disease - whooping cough.
Coughing attacks with this disease are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- severe cough occurs at night;
- with severe attacks there is vomiting;
- there is redness or cyanosis of the skin on the face;
- body temperature rises;
- appetite decreases sharply;
- In some cases, infants experience respiratory arrest.
It is difficult to get rid of coughing attacks in children, but you still need to prevent the disease from progressing and start treatment on time.
There are also some measures to relieve an attack:
- If the baby starts coughing at night, he needs to be woken up, raised and given warm milk and honey.
- You should give the child pharmaceutical syrups to drink and rub his chest and back with warming agents.
The main reasons for the degeneration of a productive cough into a dry cough in children
Most likely, a complication of acute respiratory infections occurred, and the child began a new stage of the disease.
Mainly as a result complications develop: These diseases affect the pharynx and larynx of the child. The mucous membrane of the pharynx or larynx becomes inflamed, which causes pain and a dry barking cough. Coughing attacks can be prolonged and usually occur at night. The first thing parents should do is give the child a warm drink and organize an impromptu steam room. Bring the child into the bathroom and fill the bath with hot water. The steam filling the bathroom will relieve a barking cough attack. His breathing will calm down.
And in the morning you need to call the local pediatrician at home. You shouldn’t drag your baby in this condition on public transport to the clinic.
Other types of childhood cough
In addition to the main types of cough - dry and wet, children may have other types.
The most common are the following:
- cough without fever - also called a physiological cough. It is not dangerous for children and even infants. Moreover, it is considered normal if children cough several times a day. In this case, the upper respiratory tract is simply cleared of accumulated mucus;
- allergic cough - most often this cough has a paroxysmal character. It occurs only when there is an irritating factor nearby - an allergen;
- reflex night cough - begins when the child is in a horizontal position and mucus accumulates in the nasopharynx, forming congestion.
Healthy and happy children are what every mother dreams of. The smaller the baby, the more difficult it is for him to tolerate various diseases due to the unformed nervous, muscular, and immune systems of the body. Viruses, bacterial pathogens, allergens, infections can become a source of illness. The wisdom of Mother Nature is so great that with various symptoms the body hints to doctors and parents about the causes of problems. What does a wet (productive) cough in a child indicate and how dangerous is it?
Cough as a symptom of illness
But, nevertheless, most often a child’s cough occurs as a result of an onset of illness or pathology. Every parent should know and be able to distinguish between dry and wet cough. A dry or unproductive cough does not bring relief; the child coughs, but there is no discharge of mucus or sputum. Such a cough cannot be controlled even by an older child, it is debilitating, and can contribute to vomiting, muscle pain, chest pain and other consequences. Coughing attacks can last quite a long time depending on the disease, most often at night.
Causes of wet cough in babies
A cough is an increased exhalation through the mouth caused by factors irritating the respiratory tract receptors. The physiological processes that occur in this case - contraction of the muscular tissue of the larynx, increased tone of the muscles of the bronchial system, tension of the abdominal muscles - are reflexive. The cough reflex is unconditional and acts as a protective function of the body, allowing the removal of foreign bodies and other irritating objects.
The presence of a cough in a baby with sputum discharge in most cases is not a dangerous symptom that threatens life and health in general. Doctors call this type of mucus expectoration productive: the muscles of the bronchial tree contract, getting rid of interfering foreign bodies - sputum, dust particles, allergens. Pulmonologists and pediatricians insist that neither wet nor dry cough can be treated! It is necessary to identify the cause of the occurrence and act on it.
So, the reasons for the productive removal of sputum are:
- Colds, viral and other diseases.
- Various respiratory tract infections.
- Bacterial complications.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Chronic diseases.
- Oncology.
- Allergy.
- Runny nose or snot.
- Physiological reasons (often found in infants when milk enters the respiratory tract).
- Teething. From 8 months, most babies begin to have their first teeth. Excessive salivation and inflammation of the mucous membranes become “provocateurs”.
In what cases should the appearance of a wet cough in a child prompt an emergency response from parents and the presence and supervision of a doctor:
- Child's age (1 year). A cough with sputum in an infant is dangerous due to the underdevelopment of body systems and the inability to cough effectively. While the baby cannot sit up, phlegm accumulates in the bronchi. A wet, gurgling cough can lead to vomiting and cause breathing problems.
- Having a temperature above 38 for three or more days.
- Sudden prolonged attacks.
- The presence of shortness of breath with a frequency of: more than 60 breaths – in infants up to 3 months;
- more than 50 breaths per minute - in a one-year-old baby;
- from 40 or more breaths in a child aged 2 years and older.
Causes of dry and wet cough in the morning in adults and children
Both adults and children can wake up with a morning cough. In most cases, it is a common occurrence and you should not immediately panic about it. You need to monitor your condition for several days. At this time, you can give up bad habits, sleep longer and not be nervous. But if this does not help, the intensity of the cough will increase. Then you should consult a doctor and, together with him, identify and eliminate the causes of the morning phenomenon. The main thing now is not to delay treatment, not to wait 2-3 months or more, so that it does not turn into an acute form.
Causes
The human respiratory system is designed in such a way that a cough can occur from the slightest changes in the environment or due to various diseases of the body.
Wet
In a non-smoking person, a cough with phlegm may occur as a consequence of a common cold or chronic illness. At the very beginning, its symptoms are hoarseness and dry bouts of blubbering. And then the wheezing becomes stronger, and thick mucus is released along with the cough. It can be assumed that with such symptoms the main culprit is bronchitis. It can be chronic and is often accompanied by the discharge of pus.
A wet cough can also appear with ARVI. If particles of dust or paint were inhaled during the leak, they became mucus intensifiers. This phenomenon often occurs in people suffering from chronic sinusitis or allergic reactions.
A cough that produces mucus streaked with blood may indicate pneumonia. The color of the sputum will play an important role here; it can be used to determine the type of bacteria present.
How to cure adenoids in a child using folk remedies?
Reviews about the use of amoxicillin in the treatment of angina: https://prolor.ru/g/lechenie/amoksicillin-pri-angine.html.
Here you can find instructions for using Ascoril cough syrup.
Dry
This type of morning cough, possibly severe, can occur for several reasons:
- Due to a genetic disease - asthma . Even if her treatment is intensified and the attacks recede. A morning cough can linger and be difficult to treat. Even the use of strong inhalers does not always work; most of them give a temporary effect.
- Nasal congestion . But after it is cleansed, the cough may go away within a few minutes. And after complete recovery from rhinitis, you can leave completely. It occurs when mucus flows onto the back walls of the larynx. The discharge irritates their mucous membranes. During night sleep they accumulate, and when you get up in the morning they begin to flow into the nose and cause a coughing attack.
- Reflux disease . The injection of acidic stomach contents into the oral cavity always occurs suddenly. And as soon as this disease begins, a morning cough immediately appears.
- Humbling can also be caused by taking medications such as ACE inhibitors. Their side effect is precisely this symptom. You can contact your doctor to change your hypertension medication to a less potent or safer one.
- With obstructive pulmonary disease, the first sign is a cough in the morning, after sleep. This disease may be associated with emphysema and chronic bronchitis. With the latter, an increase in the glands of the mucous membrane is observed, which causes a narrowing of the airways. Emphysema causes the destruction of lung tissue and reduces access to oxygen.
- Dehydration . If a person drinks little liquid during the day, this can also cause a dry morning cough. If this phenomenon occurs, then monitor yourself over the next day and try to drink at least two liters of water. It also doesn’t hurt to install a humidifier in your sleeping area.
With attacks of nausea
There is no need to ring all the bells at once. This phenomenon indicates a common cold. But it is not worth starting its treatment, so that a more severe disease does not develop against this background. The causes of this cough can be convulsive attacks, which are accompanied by contraction of the diaphragm. It can also be caused by the accumulation of mucous secretions in the nasal passages. There is not enough space for them and they begin to flow, irritating her and causing her to vomit. A completely untreated or neglected cough can also turn into a frequent morning accompaniment. Sometimes the gag reflex can be caused by accidentally getting sputum during its release along with a cough. This cough can also be caused by some diseases not associated with a cold:
- heart failure . When it occurs, a lack of air may occur, and if it is spontaneously captured, vomiting may occur;
- Lung cancer or tuberculosis are deadly diseases. But they can be distinguished not only by vomiting, but simply by terrifying convulsive coughing attacks. They have a fever, and the sputum that comes out often contains blood;
- bronchial asthma . With this disease, vomiting is also accompanied by suffocation;
- allergy. It is accompanied by intense sneezing and runny nose, and when the muscles of the diaphragm contract, a gag reflex may occur. The symptoms of allergic cough in adults are described in detail here.
If it doesn't take a long time
The main reason for prolonged treatment may be asthma. Its frequent companions are: dry wheezing, heartburn, nasal congestion, bloody sputum, sour belching and discomfort in the nasopharynx.
Long-term treatment of cough may be associated with a recent acute respiratory infection. After this, sluggish infectious processes may occur in the body at the final stage. And the appearance of a morning cough is purely reflexive in nature.
The video talks about the causes of cough in the morning in an adult:
For smokers
This phenomenon is widespread, and coughing in the mornings and sometimes in the evenings quickly becomes chronic. Over time, in heavy smokers it is accompanied by bleeding.
Causes of morning cough in children
In children, including infants, this type of bubbling is divided into pathological and physiological. The latter occurs due to the nightly accumulation of mucus and sputum in the baby’s respiratory organs. In the morning he gets rid of them by coughing. The first type can be caused by gastric mucus. During sleep, the contents of the stomach flow into the baby's throat and lead to morning attacks. They are accompanied by white regurgitation. If the baby has such signs, treatment should begin with a visit to a gastroenterologist.
If a cough appears in the morning, you need to monitor the baby’s condition for a couple of days. And if it does not go away, but rather becomes more frequent, you should contact your pediatrician.
If the bubbling is infrequent and is accompanied by the removal of sputum, then it is quite possible that this is a normal phenomenon. Healthy children can cough up to a dozen times a day, thereby their body cleanses itself of ingested germs. But if the symptoms are strong and frequent, you should visit a doctor.
Wet
The reasons for its occurrence may be:
- acute manifestations of respiratory diseases caused by viral or bacterial infections. These include: bronchiolitis, laryngitis, tracheitis, and pharyngitis;
- gastroesophageal reflux . When it occurs, the contents of the stomach suddenly enter the oral cavity. This phenomenon can provoke the appearance of pneumonia or bronchitis;
- allergic diseases (bronchial asthma and obstructive bronchitis, here we describe how to treat the disease);
- chronic pneumonia or its acute form . If a morning cough is accompanied by sputum, this indicates the beginning of recovery;
- diseases that are accompanied by moist discharge from the nasal passages. These include sinusitis, viral runny nose, sinusitis and allergic rhinitis. They are often accompanied by a reflex cough.
The link describes what to do if a child’s wet cough does not go away for a long time.
Dry
This type occurs without sputum production. It causes severe attacks that cause pain. Dry cough occurs as a result of colds. Their first signs are dry throat, causing coughing. The main reasons are: strong odors, the flu virus, and possibly heavy air in the child’s bedroom.
Also, a dry morning cough can be accompanied by whooping cough, measles and laryngitis (read how laryngitis manifests itself in children). Or worms have settled in the baby’s body. To check this, you need to pass the appropriate tests. Inflammatory processes that develop into chronic respiratory diseases can also affect its appearance. The link describes the treatment of dry cough in a 3-year-old child. Treatment of dry cough in infants is described here.
Komarovsky's opinion
The doctor associates the occurrence of a morning cough with the child or the place where he sleeps. If you change the room or position of the baby during the night's rest, he stops bubbling. In this case, the baby has a fairly common disease - posterior rhinitis. This is an inflammation of the posterior sections of the nose, which is allergic in nature, because the viral course cannot last long. Along the back walls of the nose, the mucus that accumulates overnight flows into the throat and the baby swallows it. In another case, if mucus forms only at night, it is necessary to analyze what could provoke it. This could be new furniture in the child’s room, a recently purchased toy, or the powder that was used to wash his bedding. To eliminate such a cough, it is necessary to ventilate the room, remove the source and consult a doctor.
In the video, Dr. Komarovsky talks about a child’s cough in the morning, what to do, how to treat it:
Timely treatment and correct identification of its cause will help to overcome a morning cough. It is necessary to reconsider your living conditions, drink enough fluids, engage in the prevention of chronic diseases and give up bad habits. Then the frequency of diseases accompanied by cough will noticeably decrease.
ProLor.ru>
Folk remedies
When treating with a variety of methods, one should focus on the age of the child and the nature of the disease. The absence of fever and the presence of appetite, accompanied by a cough after an illness, should not cause acute concern for parents. Babies under one year old require special attention and care. If your baby develops a cough, be sure to call a doctor at home! Severe attacks, including vomiting, can be provoked by:
- Whooping cough stick. This is one of the few cases when the symptom goes away after taking drugs that inhibit the cough center in the brain. Self-medication is strictly prohibited, and to make a diagnosis through laboratory tests, it is necessary to confirm the presence of whooping cough in the baby’s body.
- Laryngeal stenosis (laryngotracheitis). In this case, urgently call an ambulance: you and your baby will need hospitalization! While you are waiting for the doctor, fill the bathroom with hot water after closing the door. Keep your baby in a humid, warm microclimate, trying to calm him down as much as possible.
Other cases of cough with phlegm in infants under one year of age, as well as in older children and adolescents, can be easily treated with physiotherapy - inhalations, chest massage; breathing exercises; light physical activity; spending time in the fresh air.
Inhalations are an excellent way to “translate” a cough from dry to wet, affecting the upper respiratory tract with warm air, essential oils, saturated vapors of soda, salt, and iodine. Do you remember from childhood how to treat colds “breathe over boiled potatoes”? So, our grandmothers and mothers were right: warm air, warming the trachea and nasopharynx, thins the mucus, improving the motor function of the ciliated epithelium. This method is ideal for those who have phlegm accumulating in the throat and upper tract.
Modern medicine, for the convenience of children and parents, suggests using special inhalers:
- Cheaper and simpler versions are represented by a bath and a tube with nozzles.
- A nebulizer is a medical device for use at home. By inhaling aerosolized liquids (medicines, soda water, etc.), the child's viscous sputum is perfectly liquefied.
Expectorant massage
Chest massage performed at home by parents or a specialist is effective in relieving the child of a wet cough. Light tapping movements; wide sweeping strokes with pressure on the chest, performed from top to bottom; kneading and pinching will increase blood flow to the bronchi and lungs, stimulating the thinning of mucus and the removal of phlegm.
Other effective remedies
Herbal decoctions and berry tinctures have long been known as effective cough remedies. To turn a dry cough into a wet one, brew 4 tbsp in 0.5 liters of water. breast collection. Rosehip tincture (100 g of dry berries per liter of water) will improve tone, saturating the body with vitamin C; Linden decoction will strengthen the expectorant component, thinning the sputum; Chamomile tea, being a natural antiseptic, will help get rid of bacteria and viruses faster.
Breathing exercises are good for children. Helps relax the cough center, reduces the frequency of urges, and helps normalize the functioning of the ciliated epithelium of the respiratory organs. To improve lung function by “pumping” larger volumes of air, buy inflatable balloons for your child. By combining the game with breathing procedures when inflating the latter, you will help your baby.
A child’s cough is a natural reaction of the body that allows the parts of the respiratory system to be cleared of dust, mucus, accumulated sputum, foreign matter or chemical elements that irritate the mucous membrane.
All children, like adults, cough sometimes. But you need to be careful, because a cough may be the first symptom of any disease.
To cure a child’s cough, you cannot engage in symptomatic treatment; you should approach the problem comprehensively, and treat the disease, and not just one of its symptoms. And here it is very important to consult a doctor in time.
When answering the question of how to cure a child’s cough, you must first determine its nature: dry or wet. After all, the wrong treatment can cause complications.
A dry cough is not accompanied by sputum production. It can be strong, hysterical, and cause pain.
Dry cough in a child: causes
The cause of a dry cough may be a cold or infection of the respiratory organs. If a child has a cold, a sore throat and a dry cough appear. After a few days, the body begins to produce sputum, and the cough becomes wet. When mucus production slows down, the cough becomes dry again. A child may develop a dry cough if they are infected with the influenza virus, due to tobacco smoke, too dry air in the room, or a strong smell of chemicals. If the child has no symptoms of a cold, the temperature has not risen, and he began to cough sharply, with signs of suffocation, this may indicate that a foreign body, for example, a small part from a toy, has entered the throat.
If a dry cough is barking in nature and occurs many times a day, it may be a symptom of laryngitis, whooping cough, or measles.
A barking dry cough caused by “false croup” is of great danger, since with this disease the larynx and trachea swell. There are also a number of diseases of the respiratory tract, which are accompanied by a dry cough and chest pain when sighing - these are tracheitis, pleurisy, pharyngitis, and allergic diseases.
Dry cough in a child: features
1. Most often, a dry cough is paroxysmal in nature. It begins and ends abruptly, sometimes reminiscent of the barking of a dog or the croaking of a crow. 2. The attack occurs suddenly, creating the impression of a foreign body entering the respiratory tract. 3. The attack can last several minutes, during which time it is difficult to breathe and it is impossible to inhale oxygen. 4. A dry cough prevents you from falling asleep and prevents you from sleeping at night. 5. A coughing attack can provoke vomiting. 6. During a cough, mucus is not released, so the cough does not bring relief. 7. During and after an attack, your chest may hurt.
Often, the main goal of treating a dry cough is to transform it into a wet cough so that mucus can begin to be removed from the body. Among the home methods for treating dry cough, inhalations are effective.
Moist (wet) cough in a child: causes
If the baby begins to cough up phlegm, such a cough is called productive. As a result, the bronchi are cleared of mucus.
This cough occurs with acute respiratory viral infections, bronchitis, allergic reactions, and even a common runny nose. Sputum itself has a viscous consistency, so it is very important that the mucus leaves and does not remain in the bronchi for a long time.
If the discharge from a wet cough has a cloudy tint, this means that an inflammatory process has begun. Sputum with a green tint may indicate bronchitis, sinusitis; with a rusty tint - an allergy.
Copious sputum may indicate tracheitis. If a wet cough replaces a dry cough as a result of treatment, this is a harbinger of recovery.
Wet cough in a child: features
1. A wet cough is also called productive because it brings relief to the patient and the result of the cough reflex is visible.
2. As a rule, a wet cough does not last long and is not paroxysmal.
3. After the cough stops, a lump of mucus appears in the mouth, which comes out of the bronchi.
4. There should be no pain when coughing.
5. With a wet cough, wheezing is heard, especially during sleep, and sometimes shortness of breath appears.
6. Body temperature may rise.
To cure a wet cough, you need to use mucolytic agents with an expectorant and thinning effect. They help reduce the viscosity of thick mucus and promote its removal.
Dear readers, we all know that no one is immune from coughing, especially when there are colds. It is important to know when and how to transform a dry cough into a wet one in time so as not to provoke the disease into a more serious persistent disease.
Both children and adults get sick. To help the body recover, you need to know what causes this unpleasant and often painful symptom and, depending on the cause, choose the right treatment. Next, we will look in more detail at the differences between a wet cough and a dry one, the causes of its occurrence, and how to treat dry and wet coughs with folk remedies and medications.
Residual cough in a child
Why does the child have a residual cough?
A residual cough is observed in a child after suffering from bronchitis, pneumonia and tracheitis. It is observed after all the symptoms have gone away, the temperature has returned to normal, and all the main signs of the disease have passed. In this case, the child periodically coughs without spitting out sputum. Such manifestations are called residual cough.
A residual cough may appear for up to two weeks. In this case, children's immunity becomes decisive. If a child has ARVI for the sixth time a year, a residual cough can be observed for up to three weeks.
The causative agent of an infectious disease causes a residual cough. The mucous membrane of the bronchi and trachea is damaged by the virus, and it does not recover too quickly. A certain amount of time must pass for its complete recovery. This is what constitutes the period of observation of residual cough.
Residual cough after bronchitis in a child
A residual cough after bronchitis causes a lot of trouble for the child and requires appropriate treatment. Despite the fact that coughing after bronchitis does not pose any immediate danger, there are two circumstances that force you to take it seriously.
First of all, it is often confused with the symptoms of bronchitis itself or its complications. In this case, the duration of the cough and the nature of its course are important. After bronchitis, it makes sense to periodically show the child to the doctor. If a child has been coughing for more than three weeks, and the cough is dry and occurs in attacks, the possibility of whooping cough should be excluded.
The duration of a cough after bronchitis indicates that there are problems with the immune system. The pathogenic microbes that cause the disease are perfectly deposited on the irritated bronchi of the child. He could catch the infection again if it is present in his team, be it a kindergarten group or a class. It is better to keep the child at home until his cough is completely eliminated.
Residual cough in a child after ARVI
A cough can be a residual phenomenon after an acute respiratory viral infection suffered by a child. It is observed because there is a disruption in the normal functioning of the child’s respiratory system and sputum in the form of mucus is formed in his bronchi. It is the presence of a residual cough after an acute respiratory viral infection that guarantees the protection of the bronchi and trachea from sputum.
Residual cough after a respiratory infection can be either dry or with sputum. In this case, the sputum released is thick and viscous, with mucus admixtures.
A child's cough can manifest itself in different ways. Coughing can be either inconspicuous or develop into a strong, persistent cough. In the latter case, the child may develop a fever and feel worse. Residual cough after acute respiratory viral infection most often occurs in preschool children.
Residual cough in a child after tracheitis
The main symptoms of tracheitis in a child are fatigue, weakness, and fever. In their outward absence, the child may experience a cough, which is one of the residual symptoms of the disease. This is observed in almost every second case. Residual cough in a child after tracheitis occurs due to weakened immunity or the individual characteristics of the child’s body. Once on the mucous membranes of the trachea and bronchi, the virus begins to actively multiply. Residual cough does not require any additional treatment, but recovery time is necessary.
How long does a child's residual cough last?
A residual cough after illness in a child is considered normal. In approximately half of the reported cases, it lasts up to a month or longer. It all depends on the condition of the child’s body and the disease he suffered. If it is observed after bronchitis, special attention should be paid to the nature of the discharge when coughing. They should be light, body temperature should not rise, and in general, the cough itself should tend to decrease.
Children of preschool age themselves cannot monitor the frequency of sputum secretion and spit it out normally. In addition, they need more time to restore the bronchial mucosa. If you do not resort to additional treatment methods, the sputum disappears in about a month.
Children of primary school age are characterized by a shorter amount of time required to eliminate the symptoms of residual cough. If no additional treatment is used, their cough goes away within ten days on average. Treatment can reduce this period by half.
Residual cough in a child: how to treat?
To treat residual cough in a child, a number of preventive procedures are required to facilitate the treatment process itself. Often this is enough for the residual cough to stop, especially if it occurs after bronchitis. Preventive measures include ventilating the room in which the child lives, preventing exposure to acute allergens, protecting the child from smoking in his presence, maintaining the temperature in the child’s living space at a certain level, without changes.
In residential premises, it is necessary to regularly carry out wet cleaning and monitor the general condition of the microclimate. It is recommended to use an air humidifier, the operating principle of which is based on the use of ultrasound. This is more effective than hanging wet towels in the room and placing containers of water on the floor. An air humidifier is capable of not only maintaining air humidity at a given level, but also purifying it of harmful impurities.
How to cure residual dry cough in a child
A dry cough is one of the types of residual cough that occurs in a child after he has suffered from various diseases. Like any type of cough, it requires the use of a certain method of treatment.
First of all, it is necessary to place the child in a comfortable and calm state. Most often, parents are well aware that a dry cough is often caused by the child’s exposure to noise or strong light.
Pediatricians recommend the following remedies for the treatment of dry cough:
- a teaspoon of fresh honey without adding anything else;
- a glass of boiled milk with the addition of a teaspoon of baking soda;
- using tea with raspberry jam to water the child before going to bed.
Steam inhalations can significantly alleviate a child’s dry cough. To do this, use drinking water with a baking soda concentration of four tablespoons per liter.
If self-administered treatment does not produce any desired results, you should seek help from a doctor. He will be able to correctly determine the cause of a dry cough in a child and prescribe adequate treatment.
How to remove residual wet cough in a child
A child's residual cough is most often explained by phlegm accumulated in his lungs. In such cases, pediatricians generally advise first of all to ensure the child’s room is ventilated. In addition, you can rinse his nose with saline solution placed in a jar. This measure is more suitable for prevention so that sputum does not dry out in the child’s nasopharynx.
Be sure to give your child plenty to drink. Rosehip decoction is best suited for this; it contains a large amount of vitamins and microelements. For example, it contains more vitamin C than all mineral and vitamin complexes. When preparing the solution, you should follow the dosage of its use. One tablespoon of rose hips is poured into a glass of water, after which the entire volume must be brought to a boil. After boiling for an hour, all the liquid must be cooled for two hours. After this, approximately a tenth of the solution is diluted with water to a volume of 200 milliliters. Should be used every other day. After about a week and a half, a weakening of the dry cough is observed, and by the end of the month it completely stops.
How to treat residual cough according to Komarovsky
Dr. Komarovsky’s main recommendations boil down to the following: the child’s residual cough should not be suppressed by using various cough suppressants. This is dangerous, since coughing is nothing more than the consequences of previously suffered seasonal illnesses. In this way, the child’s body cleanses itself. If the cough stops, the lungs will not produce enough mucus. This entails impaired ventilation of the lungs and increases the risk of pneumonia and bronchitis.
Dr. Komarovsky believes that a child’s body needs a cough. Of course, it needs to be treated, but treatment should not be based on eliminating the cough, but on relieving it. The alleviating effect on the child’s lungs should be quite effective. The use of medications should primarily be aimed at eliminating sputum. Everyone knows that the thicker the sputum, the more difficult it is for it to leave the child’s body.
Residual cough in a child, how to treat with folk remedies?
These folk remedies are recommended for the treatment of residual cough in a child.
Pine buds in water or milk give a good effect when used to treat residual cough in a child. Preparing a medicinal infusion involves adding a tablespoon of pine buds to half a liter of boiling milk. The fire is turned off and the infusion is carried out for an hour. To solder the child, a warm infusion is used once every two hours in a volume of 50 milliliters. In this case, milk can be replaced with water, and pine cones with spruce shoots.
Badger fat is considered a good traditional medicine for treating residual cough in a child. For preschoolers, only external use is recommended. The fat is rubbed onto the skin on the child’s back, stomach, shoulders, chest and legs. After this, the child must be covered warmly and put to bed. After he has sweated well, you need to change his underwear.
For children over seven years old, badger fat can be recommended for oral use, a teaspoon three times a day. You can dissolve it in warm milk and give it to your child with honey, it will be healthy and tasty. If your child is allergic to such drinking components, you can buy him badger fat at the pharmacy.
In addition to badger fat, you can also use sheep fat, as well as goose fat. The intake of such fats follows the same principle as the use of badger fat for medicinal purposes.
kashelb.com>
Why does a dry cough appear?
Because the body thus develops a protective reaction to the irritant. The most common causes:
- Smoking.
- Infection.
- Tuberculosis.
- Cold.
- Entry of a foreign body.
If the cough is not accompanied by fever and no compelling reason is found, then most likely it is caused by an allergy to an external irritant.
If it appears at night, then most likely it is a reflex due to a horizontal position during sleep or changes in room temperature (at night the temperature and humidity drop, this provokes attacks).
If the cough is either dry or wet, this indicates a temporary cessation of sputum production. If a child has a dry cough after a wet one, you should quickly contact your pediatrician so that he can prescribe age-appropriate medications that promote the formation and removal of sputum.
It is imperative to consult a doctor to find the cause of the appearance, as treatment for a more serious disease may be required.
Treatment of pathology
Treatment for a cough that has changed from wet to dry should be prescribed by a specialist. It is impossible to choose effective and safe therapy on your own. When choosing a medicine, the specialist takes into account all the individual characteristics of the patient and his underlying disease. Only in this case will the treatment become as effective and harmless as possible.
First of all, during therapy you need to follow simple recommendations, thanks to them the baby’s condition will improve. To do this you need:
- give the little patient plenty of fluids;
- give your child as many fresh fruits and vegetables as possible;
- radically change your diet, giving up all unhealthy foods;
- take your child for a walk every day in the fresh air.
Humidify the air in the room where the small patient is located daily. It also needs to be wet cleaned every day. You need to take your child for a walk outside every day. You can only stay at home if you have a high body temperature. At night, the baby needs to place another pillow under his head. This will prevent excessive mucus formation. The risk of seizures will decrease.
For a cough that has changed from wet to dry, the baby may be prescribed:
All medications have contraindications. You should visit a doctor before using them. Most often, Gerbion is recommended for children. This medicine consists mainly of natural ingredients. It can only be purchased in the form of syrup. The medicine has a sweetish taste, so children use it without objection. Moreover, the drug does not contain sucrose.
Treatment can be carried out using traditional medicine. Natural components with proper treatment cannot cause complications. Experts often recommend giving preference to inhalations. You can add essential oils, onions or garlic to the solution.
At night, the baby needs to wear warm socks and pour mustard powder into them. This method of treatment can only be used in the absence of individual intolerance. Traditional medicine should also not be used without consultation with a specialist.
Wet cough during teething will be discussed in the video:
How to distinguish a dry cough from a wet one?
With a dry cough, the sputum becomes viscous and thick, which is why it stops being released. Bacteria contained in mucus accumulate; an excess of secretion can lead to disruption of the respiratory system.
Features and differences:
- after an attack of dryness, a painful effect remains in the chest area;
- moist makes breathing easier;
- when wet, a person feels accumulated mucus, which causes wheezing;
- How to determine whether a dry or wet cough is determined by the duration of the attack - a wet cough does not last long.
How to make a dry cough wet?
Treatment depends on the cause of the appearance and can be aimed at mitigating symptoms, suppressing cough, or at the appearance and expectoration of sputum.
Folk remedies
Before starting treatment with folk remedies, be sure to consult a doctor and coordinate home therapy with him, because improper treatment can aggravate the situation and cause serious harm to the body. So, how to make a dry cough wet?
If the cause is a cold or ARVI, then honey in combination with other products will be an effective remedy for expectoration.
- heat a glass of milk, take a teaspoon, add 1-2 tablespoons of honey, half of soda (promotes the appearance of phlegm), a small piece of butter, drink at least 4 times a day. Such a drink will quickly relieve the “scratching” effect, soreness, thanks to its enveloping, antiviral effect;
- radish (black) in combination with honey is simply an amazing natural medicine, and also very tasty, children will be happy to be treated with natural syrup. For colds, respiratory tract diseases (upper), bronchitis, the infusion will have an antitussive, expectorant, anti-inflammatory effect, and the remedy also helps to liquefy and remove sputum.
It is especially recommended to take syrup if a child or adult had a wet cough and suddenly became dry. Cut out a third of the pulp from the black radish and fill the hole a third with honey, leaving room for healthy juice to form. Wait until the syrup forms (preferably 12 hours). Take before meals 4-5 times a day. After 3 days of use, change the root vegetable.
Plantain
The well-known plantain is not only a natural antiseptic, but also an effective remedy for respiratory diseases. It is used even in severe cases such as tuberculosis, lung cancer, whooping cough (read how Icelandic moss helps with such serious diseases in this article).
If a wet cough has turned into a dry one, then decoctions and syrups from plantain will help; they increase the secretion of mucus in the bronchi, thin it, and have a general antimicrobial and calming effect.
Using fresh plantain leaves will have a faster healing effect than dried ones. It is necessary to grind fresh leaves, add hot water (proportions 1:3), bring to a boil, add a little honey. Let it brew for at least 3 hours, take a teaspoon every hour.
You can use dry leaves to make tea. Pour 2 tsp. leaves with a glass of water brought to a boil. Add a spoonful of honey, drink like tea 4-5 times a day.
A few hours after using plantain infusion, you can notice improved breathing and a slight expectorant effect.
Potato inhalation and compress
Many of us will remember this procedure from childhood. The method really works because... hot steam helps warm the respiratory tract, soften the cough reflex, form and dilute sputum, and eliminate the inflammatory process. This is a cure for dry and wet cough at the same time.
Attention! If you have diseases of the heart, blood vessels, problems with blood pressure, temperature, or pneumonia, it is strictly not recommended to use it.
You need to boil the potatoes, place the pan on a chair, sit next to them, lean over the steam and cover yourself with a blanket. You need to breathe deeply and through your mouth over the steam, but not harshly. If you have a runny nose, try to breathe through your nose. The procedure should not take more than 20 minutes.
Then the potatoes can be used as a compress on the bronchi. Crush, add a couple of tablespoons of alcohol, place the mixture in a bag and wrap in a towel, apply to the bronchi or throat for 10-15 minutes.
When phlegm appears, it is recommended to drink a lot of fluid so that it is not thick and comes off easier. The mucus must be spat out. Moist air in the room will make breathing easier. You can find out more about traditional medicine for upper respiratory tract disease here.
What is dangerous and how is dry cough in a child treated?
All children cough, but the reasons for this phenomenon may be different. The most unpleasant thing is a child's dry cough. It can occur for several reasons, on which further treatment depends. During a dry cough, sputum is not produced, for this reason it is often painful for the child. To decide on treatment, especially for a newborn child, you need to visit a doctor to find out the cause of the cough.
How to treat a cough?
Coughing is a protective reaction that occurs due to irritation of the respiratory tract and removes foreign particles or mucus from the throat. Including a child may cough due to a virus or bacterial infectious disease.
The main causes of cough are:
- foreign particles;
- irritation of the respiratory organs, that is, their walls, with excessively dry air, chemical vapors or cigarette smoke;
- presence of allergies;
- diseases associated with the respiratory system;
- bacterial infections;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- helminthic penetrations;
- beginning of teething.
Dry cough as a manifestation of various diseases
Based on intensity, coughs are divided into mild, moderate, or just coughing. In children it can be either short-term or permanent. Over time it can happen:
- in acute form – up to 3 weeks;
- subacute – up to 8 weeks;
- in chronic form – more than 8 weeks.
Such a cough can signal diseases associated with the respiratory, circulatory, and digestive systems. For different diseases, cough has a specific character. It can be paroxysmal, suffocating, whistling and barking. It may appear in the morning or in the evening. Other symptoms may appear: snot, general weakness. Coughing is often accompanied by a high temperature, but it can also occur without it.
Diseases that are accompanied by a dry cough
Often a dry cough in a child occurs before the age of 1 year; it helps clear the airways of mucus and occurs most often in the morning.
A dry cough after an acute respiratory viral infection occurs due to the release of accumulated sputum and means that the disease will soon end.
During the flu, the child coughs violently and violently, feeling pain in the chest. Body temperature rises.
With persistent narrowing of the lumen of the larynx, a dry cough occurs in the baby before sleep or coughing attacks occur at night. The cough during whooping cough is paroxysmal, dry, strong, accompanied by a specific buzzing sound. The attack ends with the discharge of sputum. Often, with whooping cough, cough in children turns into vomiting. The disease is protracted.
Cough may be present with some gastrointestinal problems. It occurs as a result of a reaction to irritation by stomach juices. In this case, attacks occur when changing body position, during or after eating. If a dry cough appears only at night, the presence of heart failure can be suspected. Moreover, this cough occurs in fits and starts during sleep.
Cough combined with wheezing occurs in bronchial asthma. Not accompanied by an increase in body temperature. If the cough is strong, obsessive and is not combined with other manifestations, then perhaps a foreign body has entered the child’s respiratory tract, and it occurs in the form of attacks and is regular. Occurs with chest pain and suffocation. If the baby coughs with a dry cough all the time, and no other symptoms are observed, the help of a doctor is needed.
A dry cough with fever can be a symptom of measles, pleurisy, the onset of bronchitis and other diseases. Usually it does not last long and then turns into wet. A lingering, constant, long dry cough often indicates tumors of the respiratory tract or tuberculosis. When helminthic penetration occurs in a child, a rare and prolonged dry cough occurs.
The dangers of dry cough
Dry cough can have complications:
- deterioration in sleep quality;
- vomit;
- loss of consciousness;
- tears of the mucous membrane;
- unexpected leakage of urine;
- hemoptysis.
In newborn babies, an attack can lead to a short-term cessation of breathing. If a child develops a dry cough, it should be shown to a doctor.
Methods for detecting the disease:
- X-rays of light;
- magnetic resonance imaging of the respiratory system;
- blood analysis;
- other functional methods.
If respiratory tract disorders are not identified, additional examination methods are prescribed.
Medicines, warming compresses, rubbing and preparations
Medicines that can be given to your baby for a dry cough:
- Mucolytic agents (ACC, Bromhexine, Lazolvan, Ambrobene).
- Expectorants (Gedelix, Doctor Mom, Pertussin).
- Antitussives (Glaucine hydrochloride, Codeine).
- Combined effect agents (Ascoril, Bronholitin).
Rubbing should not be done on children under two years of age. In addition, the procedure is not recommended for suspected false croup and bronchial asthma.
The products used for rubbing are Doctor Mom, Pulmex and Eucabal.
Warming compresses, as well as mustard plasters, give a local effect and help in the removal of accumulated mucus. These manipulations must not be done at high temperatures. As for compresses, they are made in the area between the shoulder blades and the cervical area and left overnight. Mustard plasters are applied to the subscapular area.
Breast preparations, which are sold in pharmacies, are excellent drugs for dry cough. They are used for inhalation or as a decoction or tincture.
Treatment with traditional medicine and the use of antibiotics
There are many traditional medicine recipes for dry cough:
- A compress based on sunflower oil: cotton material soaked in oil is applied to the chest, covered with polyethylene, then with a dry cloth, towel, and left overnight.
- Soda inhalations using garlic: pre-chopped garlic is placed in boiling water, boiled for several seconds and removed from the hot stove. Next, add one teaspoon of soda. You need to inhale this mixture while covering yourself with a blanket. The bactericidal properties of garlic will also help resist infection.
- Burnt sugar with milk: heat the sugar on the stove until it turns dark brown. The syrup is poured into a bowl of milk. The resulting lollipop is placed in the mouth until completely dissolved.
Antibiotics are prescribed for bacterial coughs, such as pneumonia or bronchitis, which are accompanied by fever. In the case of a viral cough, antibiotics will not relieve this symptom.
During an attack, it is necessary to first create certain microclimatic conditions in the room. The air must be moist and slightly cool. You need to open the windows and use air humidifiers. If you don’t have one, you can hang wet towels in the room. To make breathing easier, the child needs to inhale warm, moist air. You can take your child to the bath and turn on the hot water tap. However, there should be no foreign odors in the room.
For distraction therapy, when an attack begins, it is allowed to use hot baths on the feet. If the child does not have an allergic reaction, you can apply eucalyptus ointment to the skin in the wrists or temple area. The child should be given plenty of fluids to drink. It is best for your baby to drink linden tea, warm milk, cranberry juice, tea with a spoon of honey, and warmed alkaline mineral water.
Preventive measures against dry cough
A preventive measure against cough is considered, first of all, to prevent the cause of its occurrence (viral diseases, infections, allergic reactions).
Maintaining the microclimate in the nursery at an optimal level plays an important role. Normal room temperature is no more than 24 °C, and humidity is 60%. It is necessary to protect the baby from passive smoking and inhalation of suspensions of household chemicals.
respiratoria.ru>