Common sense should be a mother's main advisor when carrying out daily hygiene procedures for newborns. Despite this, parents are often at a loss when it comes to the required frequency of washing, and talking about phimosis or synechiae causes horror for most. To dispel fears and shed light on caring for a newborn girl, cicatricial phimosis in a newborn baby and other issues, we have prepared some tips for you.
At the end of the article we have prepared additional material for you. Watch a detailed video from an expert on how to properly care for your newborn's genitals.
Morning hygiene for infants
In the morning, when the baby wakes up, he needs to wash his eyes, clear the nasal passages of accumulated mucus, and wash. Before starting manipulations, mother needs to wash her hands with soap. A long manicure will greatly interfere with caring for a newborn baby. In addition, the baby can be accidentally injured . Therefore, nails should be cut short and the corners filed.
Hygiene items required for procedures are laid out on the changing table.
Morning eye hygiene
You need to pour boiled water into a clean small container, roll up cotton swabs in advance or stock up on sponges (cotton pads). Pieces of cotton wool are not suitable for such a scrupulous process. They leave behind lint on the child’s eyelashes, which can get into the eyes and cause discomfort.
A swab soaked in water, wring out a little, and wipe the eyes from the outer edge to the nose. Each eye requires its own separate swab, which is immediately discarded after use.
If a newborn baby accumulates a lot of discharge, you can use a decoction of herbs or weak tea leaves for eye hygiene.
Hygiene of the nasal passages of a newborn
Crusts and mucus accumulate in the baby's nose overnight, preventing him from breathing freely. Under no circumstances should it be removed with cotton swabs. This is extremely dangerous for the child . At any time when cleaning your nose, it can twitch, turn, sneeze and get injured. For the procedure, thinly wound cotton tubes (flagella) with a long tail, soaked in baby oil, are used. You can use ordinary vegetable oil rather than pharmaceutical oil. It is boiled in a water bath for 20 minutes. To care for a baby, 100 g is enough for a whole month.
The tube is carefully inserted into the nostril with screwing movements, and immediately taken out. When rotated, the cotton wool collects mucus and moistens the frozen crusts. They are removed using a new tube soaked in oil. There is no need to insert the flagellum deeply. A separate flagellum is used for each nostril. If you cannot get rid of the crusts, you can soften them by adding drops based on sea salt. They are hypoallergenic and non-hazardous.
Additionally : Read more about cleaning the nose of babies - read in detail here
Ear hygiene
You only need to clean the newborn's ear. The ear canal is not touched during treatment - it is very vulnerable. Any careless movement can lead to serious consequences for the child. It is better to clean your ears with sponges moistened with warm water.
Facial hygiene
The face of a newborn baby is wiped with sponges soaked in boiled warm water, close to the baby’s body temperature, so that he is not afraid. Be sure to wipe the baby’s forehead, chin and cheeks.
Everyday hygiene procedures after sleep include washing the butt and genitals. The procedure is carried out using warm water. The body is carefully wiped and lubricated with cream or powder. It is not recommended to use wet wipes for these purposes. They cause an allergic reaction and do not completely remove dirt. You can use a napkin only in an emergency, when mother and baby are away from home - a list of wet wipes for a newborn.
Processing folds
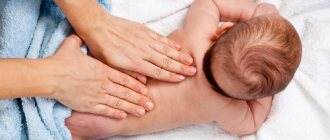
Wipe the folds with a sponge lightly dipped in oil. Be sure to pay attention to all places, including the folds behind the ears. Remnants of epithelium, villi and cream, which are used to lubricate the baby, often accumulate there.
Treatment should begin with the head: first the ears, then the neck, armpits, arms, palms, interdigital spaces, inguinal and popliteal folds. It is advisable to change tampons regularly. You only need to lubricate the folds, but not the entire body of the child. Oil worsens the respiratory function of the baby, clogs pores, and provokes inflammatory processes.
Additionally: Article about the treatment of skin folds in a baby
Special care for the navel
To do this, there should be cotton swabs, sponges, 40% alcohol, pharmacy 3% hydrogen peroxide, and a pink solution of potassium permanganate on the changing table. Not all doctors recommend using brilliant green, since the navel swells under it.
The sticks are soaked in peroxide and the navel, slightly spread apart with your fingers, is moistened. It is advisable to wait until the peroxide reacts, bubbles and softens the crusts. Then use a cotton swab to remove the remaining peroxide and crusts. Wipe the wound again with a clean cotton swab dipped in alcohol. Dry the navel and lubricate it with potassium permanganate. It is necessary to dilute potassium permanganate daily, as it is destroyed in the light.
There is no need to lubricate the area around the navel with an antiseptic. If the color of the skin around it has changed or redness has appeared, you should immediately see a pediatrician. Often the belly button heals within one week. Slight bleeding from the wound at this time is considered normal.
Additionally: Proper care of the umbilical wound of an infant
Personal hygiene of a newborn
20.Aug.2020
Calm, just calm
You just came from the maternity hospital, in your arms there is such a tiny and fragile baby, and, oh horror, you have to wash him. And then the grandmothers add fuel to the fire: “The first time is very important: if you get scared, you will then be afraid of water!” And so you, with shaking hands, carry the baby into a bath with potassium permanganate, make the water hotter so that the newborn does not freeze... Stop. First of all, calm down: newborn babies read the emotions of close adults in a matter of seconds, and your panic and fear will definitely be transferred to the baby. Inhale and exhale, we leave the child to dad and go prepare a bath for the baby. By the way, for the first time you should definitely enlist the help of relatives: watch the newborn while you pour water, give a towel or help throw it on the baby - it will be better if dad or grandmother are on hand for these actions. This will make everyone calmer and more comfortable.
What should be on hand:
• Bath. • A slide with a diaper or a hammock for bathing a newborn. This is a very convenient and irreplaceable invention. You don't have to bend over and hold your baby in the bathtub. The baby will just need to be placed on a soft slide. Your hands are free - you can wash your baby in peace. • Water thermometer. • Baby soap. • Soft towel. • Special children's bathing products and herbal sets are at the discretion of the parents.
First bath of a newborn: where to start
Bathing for a newborn is not only and not so much a way to become clean, because such a baby simply cannot be heavily soiled.
This is, first of all, a pleasant, soothing procedure that reminds the baby of the glorious days in the womb, where the child was in an aquatic environment for nine months. He feels comfortable in the water; bathing has a positive effect on the physical and emotional development of the baby. The first and most important thing you can’t do without when bathing your baby is a bath. Sometimes parents prefer to immediately accustom their newborn to an adult bath, but at least for the first couple of months it is better to use a small baby bath. Firstly, it is safe and hygienic. Secondly, the baby will be more comfortable in a small bathtub than in a large space. Don’t forget that he lived for a long time in his mother’s cramped tummy and the space still scares him. Thirdly, it will be more convenient to fill a small bathtub with warm water, even if the hot water supply is turned off. The bathtub must first be washed with regular baby soap: you should not use various “adult” cleaning products. Then you need to fill it with warm water: 35-37 degrees. The water should be comfortable, not hot. If a child becomes flushed while swimming, it means that the water temperature was too high, and this can have a bad effect on the baby’s well-being and mood. To measure temperature, if you don’t have a special thermometer at hand, use the “elbow method”: determine by touch how comfortable the water is. Do I need to boil water and add potassium permanganate to it?
Just a few decades ago, the correct answer to these questions was clear: yes. Modern pediatricians are more loyal: it is not at all necessary to boil water. This is only appropriate for bathing children whose umbilical cord has not yet fallen off. By the way, doctors previously advised to wait until the navel falls off and only then wash the baby. Today, opinions on this issue vary: some experts advise waiting until the navel falls off, others argue that there is nothing wrong with bathing a newborn with an unhealed umbilical wound. Adding potassium permanganate to water is also considered a relic of the past: the product greatly dries out the delicate skin of children, and an excessive concentration of the solution can even cause a burn. As for all kinds of means for bathing children: it is quite possible to do without gels and foams, especially in the first months of a baby’s life. Many parents rush to fill the house with dozens of bottles and tubes with the inscriptions “no tears” and “0+”, but at first it is enough to wash the baby with regular baby soap 1-2 times a week. The rest of the time, bathe in plain tap water. Later, of course, you can buy aromatic foaming products: with the right approach to purchase and careful study of the composition, they will not cause harm. Some pediatricians advise bathing a newborn in a decoction of herbs - valerian, motherwort and chamomile - so that the child sleeps better and is calmer. You need to be careful with seemingly harmless herbs: they can cause an allergic reaction, especially in very young children who are not even a month old. If allergies do not manifest themselves, sometimes you can practice bathing in herbs. Most likely, there will be no magical effect from valerian or string, but it will not cause harm either. But, in any case, this issue should be discussed with the baby’s attending physician.
How often and for how long to swim
The very first bath of a newborn should be short - 5-10 minutes is enough. The older the child gets, the more time he can spend in the bathroom: the baby becomes more and more interested in what is happening around him, so he happily flounders in the water, looks at the toys, is surprised by the splashes and is delighted that they can be made by actively moving his arms and legs . There are no clear limits on how much time a baby should spend in water procedures: focus on the child’s well-being and make sure he doesn’t freeze. Children up to six months are recommended to be bathed every day. Then - every other day. At the same time, you should not wash your child’s hair with soap often: it is enough to do this a couple of times a week. Relatives of the old school sometimes advise young parents to warm up the air in the room where the newborn will bathe. It gets to the point where moms and dads put a heater in the bathroom so that the baby “keeps warm.” Of course, you can't do that. Small children don't handle heat well, and at best you'll end up with a lethargic, sad, red-faced baby. And in the worst case, you risk developing health problems for the baby and forever discouraging his desire to swim.
When to bathe: in the morning or before bed?
The answer to this question is purely individual and depends on the characteristics of a particular child. For some children, bathing invigorates: in this case, water procedures should be carried out in the morning. For other newborns, spending time in the bath is a way to calm down and relax, some babies even fall asleep during pleasant minutes in warm water. Of course, in this case it is better to wash the baby in the evening, before bed. An important point: under no circumstances leave your child alone in the bathroom for even a second. Even if it seems to you that the child is still very small and will not be able to roll over. Children are often unpredictable, and their skills sometimes appear suddenly, and it only takes a few seconds for them to choke. Alas, there are many cases where children died in bathrooms when left alone there. We don’t want to scare you, we just urge you to make it a rule: while your newborn is in the bath, do not leave him unattended.
Another common question parents ask is: does a newborn need a washcloth? It is better to wash a very small child simply by hand. A baby's skin is very delicate, so it is better not to use a washcloth, even a special one for children, at first. Later, as the child grows up, you can try to gently wash him with a washcloth-mitten. In this case, you should not use force or rub the baby’s skin. Movements should be light and neat.
Child care during the day
Newborn hygiene does not only consist of mandatory morning procedures. The child needs to be looked after all day. After feedings, the area around the lips is wiped with a damp swab or sponge. Residues of milk or formula irritate the baby’s delicate skin, and various rashes appear on it.
Nail hygiene
Many new mothers are terrified of trimming the nails of their newborn babies for fear of hurting their tiny fingers. You can cope with this task easily and quickly using several recommendations:
- You need to buy scissors with rounded ends or special tweezers designed for newborns. They have a built-in magnifying glass that allows you to clearly see the nail. Using such a tool, you can safely begin the pruning process.
- Experienced mothers know that it is better to cut a newborn’s nails when he is sleeping soundly. The baby will not feel anything, and will not twitch at the most inopportune moment.
- You need to trim your nails regularly, paying attention to the edges. They grow back quickly, and the baby may accidentally scratch his face or stomach, since he is not yet able to control himself.
Additionally: See the article about nail treatment for babies -
Washing
The child should have individual hypoallergenic soap, clean napkins and a towel. Wash babies after each diaper change. Hygiene for a newborn girl is slightly different from washing a boy. When washing the genitals, you must adhere to the following rule: rinsing movements are made from the front back towards the anus. Residues of feces should not get on the mucous membrane, otherwise inflammation will occur. For the same reason, it is better to wash girls in a sink under running water, rather than in a basin.
There is no need to intensively soap, rinse and wipe the baby’s labia. This can provoke the development of synechia - fusion of the labia due to injury to the mucous membrane due to constant contact of the genitals with a towel and soap. After rinsing, the genital slit is blotted with a soft diaper, then the labia, inguinal folds and anus are wiped.
The vaginal mucosa of newborn girls is extremely sensitive. Therefore, you need to use hypoallergenic hygiene products. It is prohibited to wipe the labia from the inside. This can lead to infection and inflammation. At first, the baby may experience bleeding from the vagina. They pass quickly without requiring special treatment. You should immediately contact a pediatrician if there is redness of the labia, purulent-bloody or purulent-mucous secretion with an unpleasant odor. The child should have other secretions other than natural white mucous.
Boy hygiene includes washing the penis, scrotum and anus with warm running water. Afterwards, the child’s body is dried, lubricated with cream, treated with liquid talcum powder or powder. See our tips for cleaning
Bathing
Bathing your child becomes the most important ritual before bedtime. This procedure cannot be ignored. In the first month, the newborn should be bathed every day, then, if it is a cold season, bathing can be done every other day. It cleanses the skin of toxins, epithelial residues, and sweat. Warm water has a calming effect on the baby, since he spent 9 months in this environment before birth. After the washing procedure, the baby will sleep peacefully and for a long time.
First you need to choose a room. If the bathroom is uncomfortable, you can bathe your newborn in the room. To do this, close all windows and doors, eliminate drafts, and turn on the heater if necessary so that the air is not too cold and the baby does not catch a cold.
For bathing you need a bathtub, water heated to 37 degrees, a thermometer to measure the water temperature, hot water to regulate the warmth of the water in the bath, warm water in a rinse bucket, a diaper and a soft large towel. The newborn is first wrapped in a thin diaper so that he is not afraid of water. The baby’s legs are lowered into the filled bath, gradually pouring a little onto the chest and back from a ladle.
Then they carefully dip the whole body and make sure that no water gets into the eyes and ears. To prevent the baby's head from accidentally being under water, bathing should be carried out by two adults. One will hold the head, the other will carefully water it in a thin stream and wash it. When the baby gets used to the water, the diaper is removed.
The first time the bathing process lasts no longer than 7 minutes. Later the time is increased to 15 minutes. For washing, you can use special hygiene products for a newborn - shampoo that does not irritate the eyes and baby soap. At the end of the procedure, the baby is washed from the ladle, wrapped in a diaper, and then in a towel. When the water is absorbed, the baby is lightly wiped off drops of water. The groin area, folds, eyes, nose and umbilical wound are treated.
Useful to read:
- First bath of newborns - what needs to be prepared;
- Using various herbs for bathing.
Caring for a newborn: advice from a pediatrician
The neonatal period, as the early period of extrauterine existence, is calculated from the moment of birth to the 28th day of life. This is an important stage in the child’s adaptation to new conditions: an extrauterine type of blood circulation is established, the bronchopulmonary system and digestive tract begin to function, the blood supply to the liver changes, the functions of the skin and mucous membranes become more complicated, the immune system is activated, and independent thermoregulation is established. However, due to the functional immaturity of organs and systems characteristic of this period of development, it is at the age of the newborn that a number of borderline conditions appear that must be taken into account in organizing child care.
Due to the immaturity of most organs and systems, including the central nervous system, from birth a child exhibits only unconditioned reflexes (swallowing, sucking, proboscis, searching, grasping, etc.), and it is the presence and severity of physiological reflexes, their preservation for a certain period time and subsequent decline, along with the dynamics of body weight, are one of the main criteria for the normal development of an infant and his physical health [1].
The proportions of a newborn's body have their own characteristics. The head is large, the limbs are relatively short. The midpoint along the length of the body is located in the navel, while at an older age it shifts to the level of the pubic joint. By the time of birth, the skin is completely histologically structured, all appendages are developed (hair, nails, sebaceous and sweat glands), but there is a relative failure of a number of important functions, primarily barrier and thermoregulatory. There are intertriginous areas - axillary, cervical, popliteal and inguinal folds, which are the main areas of natural occlusion, and the area under the diaper is an area where artificial occlusion can occur. The dermis layer of a newborn child is structurally underdeveloped and is thinner compared to the dermis of an adult. More pronounced dry skin is noted; the sweat glands in full-term newborns are formed at the time of birth, but only after a few weeks of life they are fully involved in the process of sweating. In breastfed children, the sebaceous glands are more actively exposed to androgen stimulation, which often leads to the development of neonatal acne. Full-term newborns have a neutral or slightly alkaline skin surface reaction (pH > 6.0), which during the first day of life can decrease to 5.0, while in premature infants the skin pH is > 6.0 and only approaches the end of the first month of life to 5.0. It is in optimal conditions of an acidic environment that non-pathogenic saprophytes on the surface of the skin control the growth of opportunistic and pathogenic microorganisms. A prolonged alkaline reaction can cause the growth of foreign bacteria and fungi with the development of an inflammatory process [2].
There are characteristic features of the anatomical structure and functional activity of the digestive organs. The mucous membrane of the oral cavity and gastrointestinal tract is thin, dry and easily wounded. The secretory function of the digestive glands is reduced, which is manifested by a small amount of digestive juices and low enzyme activity. This greatly complicates the movement and digestion of food if the latter is not appropriate for the child’s age. The stomach of a newborn is located horizontally, the esophagus is relatively short, and the Gubarev valve (a fold of the mucous membrane that prevents the reverse reflux of food from the stomach) is almost not pronounced. There is a physiological weakness of the cardiac sphincter, while the muscular layer of the pylorus is well developed, which predisposes to regurgitation and vomiting. In addition, this may cause regurgitation of gastric contents, aspiration and the development of aspiration pneumonia.
Intestinal motility in newborns is more active, which contributes to frequent bowel movements. In the first three days, meconium (original feces) is passed - a thick, viscous mass of olive or dark green color. The next 2–4 days, the stool is characterized as transitional: it is more frequent, unevenly colored (dark green, yellow-brown), inhomogeneous with inclusions in the form of lumps and mucus. Subsequently, the stool becomes homogeneous, mushy, and yellow in color. The frequency of bowel movements depends on the nature of feeding and, as a rule, corresponds to the frequency of feedings. It is important to remember that high motor activity of the intestine in combination with insufficient fixation of its loops, morphofunctional immaturity of peripheral innervation and central regulation, low enzymatic activity promoting increased gas formation, the period of formation of microbiocenosis determines the tendency to frequent manifestations of functional disorders (infantile colic, dyschezia), and also a high risk of intussusception.
During the newborn period, a number of characteristics of the child are observed, due to mechanisms of adaptation to new conditions of existence, which are borderline (transient). These include physiological jaundice, melena, sexual crisis, physiological loss of body weight, uric acid infarction, physiological erythrocytosis, transient deficiency of vitamin K and K-dependent blood coagulation factors, etc. However, it is necessary to evaluate the severity and duration of manifestation of these conditions, as this may be an important criterion for the presence and progression of various abnormalities in the child’s health. The issue of carrying out appropriate treatment and preventive measures needs to be decided only individually.
Adequate and regular care for a newborn, taking into account the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the child’s body in this period of the postnatal period, is an important condition for maintaining the healthy state of the child and preventing various diseases; it is an element of hardening and hygienic education, as well as the formation of adequate psycho-emotional contact in the family. The main components of daily care include bathing, daily washing of the face, toileting of the eyes, nose, ears, care of the perineum and perianal area. Important components of the normal development of a baby are walks in the fresh air, compliance with temperature conditions, indoor humidity, control of feedings and bowel movements.
The optimal temperature in the room is 22 °C with a humidity of 50–70%; it is necessary to regularly ventilate the room, since the need for oxygen at this age is 2.5 times higher than in adults. It is advisable to remove carpets and bedspreads, sofa cushions, soft toys and other objects on which dust can accumulate from the child’s room. Children under 6 months should be bathed daily; after six months, you can bathe every other day. The water temperature should be 37–37.5 °C, the duration of the procedure is 5–7 minutes.
When organizing care for a newborn, a number of rules must be followed:
- The child should not be dressed in tight-fitting clothes that have a large number of frills, fasteners, folds, etc.; do not wrap up - a newborn is very sensitive to overheating, clothes and diapers should consist of natural cotton or blended fabrics, soft, with good breathability;
- use diapers with high absorbent properties, which helps maintain the required skin pH and prevents microbial colonization, reduce the time of skin contact with a wet diaper, change them in a timely manner (on average every 2-3 hours during the day and 1-2 times during night sleep ), immediate diaper change is necessary after defecation;
- It is better to dry the skin by blotting movements using paper towels or soft cotton diapers, avoid the use of alcohol-containing products: disposable baby wipes containing alcohol, fragrances or preservatives can cause skin irritation and increase the risk of allergic contact dermatitis.
The morning toilet of a newborn consists of wiping the face and washing the eyes with a cotton swab moistened with boiled water. Each eye is washed with a separate swab in the direction from the outer corner to the bridge of the nose. The baby's nasal passages have to be cleaned quite often. To do this, cotton swabs made from sterile cotton wool can be used, which are lubricated with sterile petroleum jelly or vegetable oil and carefully moved with rotational movements 1.0–1.5 cm deep into the nasal passages. Each nasal passage is cleaned by separate flagella. Toilet of the external auditory canals is carried out similarly as needed. The oral cavity is treated only in case of thrush. It is strictly forbidden to use dense objects (cotton swabs, matches with twisted cotton wool, etc.).
Creams, ointments, lotions and sprays are used as external products for baby skin care, but when using them, a number of important features must be taken into account: safety and effectiveness; no side effects; possibility of application to large surfaces of affected skin without systemic exposure; ease of use; possibility of long-term use; affordable price. It is important to follow a number of rules: do not change the dosage form of the official drug, as this will change its physicochemical and pharmacodynamic properties; do not mix ointments and creams of different compositions; remember that the effect of using external agents appears after some time and is consolidated with regular use [3, 4].
Quite often one has to deal with such a manifestation of motor dysfunction of the digestive tract as hiccups, which is characterized by convulsive contractions of the diaphragm and is most often caused by an overfilling of the stomach with gases. If hiccups occur immediately after eating, it is necessary to place the baby in an upright position for more convenient passage of gases. If it appears between feedings, you should carefully turn the baby either to the left or to the right side. In a number of infants, air leaves the stomach well when lying on their stomach.
Often, in order to remove gases from the child’s intestines, parents resort to gas tubes or enemas, which can be unsafe, especially in newborn children with easily wounded mucous membranes. At the same time, some babies get rid of gas quite easily on their own, while in others, excessive gas formation contributes to the development of colic.
Currently, to ensure the healthy growth and development of a child, parents have in their arsenal modern baby hygiene items, electronic scales, children's ear thermometers, smart toys, children's toothbrushes with a limiter, bottles with a heating indicator, pacifiers with an anti-vacuum effect, nasal aspirators, baby scissors with a rounded end, diapers, diaper panties, baby monitors, etc. Modern baby care products include Windi® disposable gas tubes (rectal catheters) and the NoseFrida® nasal aspirator.
The Windi® gas outlet tube is intended for one-time use to relieve babies of excess gases. This rectal catheter has no loose parts or components. The specially calculated length of the catheter allows it to be inserted to the desired depth to the sphincter, the spasm of which prevents the spontaneous removal of gases from the intestines, and its special configuration with a limiter helps to avoid too deep insertion. The Windi® catheter is quite soft and flexible, has a smooth rounded end, which ensures maximum safety and eliminates trauma to the rectal mucosa.
Before using the Windi® Gas Tube, massage your baby's tummy by gently moving your hand from the right side to the center of the tummy and then downwards to direct the gases towards the anus. Then do a similar massage on the left side. It is recommended to repeat the massage 3 times on each side. It is necessary to lubricate the catheter with baby cream, oil or petroleum jelly before insertion. You should lift the legs of the child lying on his back and carefully insert the catheter into the anus, similar to a thermometer. The release of gases is accompanied by a characteristic sound. A small amount of feces may be passed along with gas. Sometimes it is necessary to repeat the procedure several times to achieve the desired result. During one procedure, it is possible to use the same catheter several times, but after its successful completion, the catheter should not be stored and reused: its reuse after some time may be unsafe. It is recommended to use the catheter no more than three times a day, which does not affect the development of addiction and does not reduce the baby’s natural reflexes.
Quite often, to ensure adequate breathing and hygiene of the nasal cavity of a newborn child, especially during respiratory infections, the use of a nasal aspirator is recommended. Due to the fact that the openings of the nostrils and nasal passages at this age are relatively narrow, and the mucous membrane is abundantly supplied with blood capillaries, when there is a runny nose, pronounced swelling occurs and mucus secretion increases, which contributes to difficulty in nasal breathing. In addition, the Eustachian tubes connecting the nasal and ear cavities are relatively short, wide and horizontal, which often leads to translocation of infection with the development of otitis media.
There are a large number of aspirators: mechanical, electric, bulb aspirator, etc., however, mechanical aspirators have an undeniable advantage, as they are effective, simple and easy to use and, unlike electric ones, do not create unnecessary noise that can frighten a child.
The NoseFrida® nasal aspirator has a long suction catheter. The tube into which the mucus will flow is quite voluminous, this allows the child to treat two nasal passages in succession. The tip of the aspirator has a special narrowed atraumatic shape. It fits tightly to the nostril, which prevents trauma and irritation of the sensitive mucous membrane. The hygiene of the procedure is ensured by the presence of a replaceable filter in the NoseFrida® aspirator, which completely prevents the possibility of aspirate getting into the oral cavity of the person performing the procedure.
Literature
- Preventive Pediatrics / Ed. A. A. Baranova. M: Union of Pediatricians of Russia, 2012. 692 p.
- Gregory K. Microbiome aspects of perinatal and neonatal health // J Perinat Neonatal Nurs. 2011, 25: 158–162.
- Blume-Peytavi U., Lavender T., Jenerowicz D., Ryumina I., Stalder JF, Torrelo A., Cork MJ Recommendations from a European Roundtable Meeting on Best Practice Healthy Infant Skin Care // Pediatric Dermatology. 2021, 33(3): 311–321.
- Skin care for a newborn baby. Scientifically based methodological recommendations. 2021. Available https://www.pediatr-russia.ru/sites/default/files/file/uhod_za_kojey.pdf.
T. A. Bokova, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor
GBUZ MO MONIKI named after. M. F. Vladimirsky, Moscow
Contact Information
Caring for a newborn: advice from pediatrician T. A. Bokova For citation: Attending physician No. 6/2018; Page numbers in the issue: 40-43 Tags: children, babies, hygiene, removal of gases
Baby hygiene products for babies
Baby hygiene involves the use of special products for caring for small children. Required tools:
- bar of baby soap;
- liquid talc, which neutralizes moisture and does not clump;
- mild shampoo labeled “no tears”;
- cream or ointment for redness, rashes, irritations and rashes - Bepanten, Panthenol, Desitin.
When buying hygiene products for a child, it is advisable to look at the expiration date, quality of the product, integrity of the packaging and composition. It’s easy to determine which products are high-quality and which are not. The label will indicate the manufacturer, list the composition, instructions for use, written without errors or typos.