Nasal polyposis is a common upper respiratory tract disease among children under 10 years of age. It is expressed in the formation of small growths on the nasal mucosa, which, although benign, can cause a lot of trouble to their owner. The shape of neoplasms can be different - round and oblong, flat and pedunculated. Polyps like to “settle” not only in the nasal passages, but also in the frontal, maxillary, ethmoid and sphenoid sinuses.
You can find out what the symptoms of nasal polyps are from the article.
What causes
Modern medicine does not have an exact answer to the question “why do polyps occur?” But among the factors that can contribute to their formation are the following:
- frequent allergic diseases (bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, dermatitis, hay fever);
- cystic fibrosis is a genetic disease that causes functional disorders of the respiratory, musculoskeletal, endocrine systems, as well as disorders of the body’s secretory activity;
- chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract – sinusitis, sinusitis, rhinitis;
- anatomical features of the structure of the nose: curvature of the nasal septum, too narrow nasal passages;
- hereditary predisposition;
- Churg-Strauss syndrome is a disease that affects the small vessels that supply blood to the nose;
- fungal infection.
How to treat nasal polyps with celandine can be found in the article.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The main problem of polyposis is that in the early stages the disease does not make itself felt. When a child’s nose is blocked, he begins to sniffle, sneeze, and breathe with his mouth open. Most parents take this for a cold and begin to carry out the appropriate treatment on their own - rinse and put drops in the nose. But the treatment does not help, and the symptoms not only do not go away, but also intensify. After some time, sleep disturbances, headaches, and decreased tone are added to these problems.
During the examination, the doctor discovers growths in the baby’s nasal passages and makes a diagnosis of nasal polyposis. If tumors cannot be visually detected, an x-ray may be prescribed for diagnostic purposes. Also, when making a diagnosis, endoscopy is used - it most objectively helps to determine the scale of the lesion, its “landscape” and the degree of patency of the nasal passages. A CT scan is used to see if the paranasal sinuses are affected by the disease.
The patient is prescribed the following laboratory tests:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- test for cystic fibrosis;
- in rare cases - cytology (to exclude suspicion of a malignant neoplasm).
What happens if the disease is not diagnosed on time and left untreated? Nasal polyposis has three stages. In the first, growths block the upper part of the nasal passage. With the second, there is a gradual proliferation of tissues that cover most of it. The third, most difficult stage is complete healing of the cavities. The earlier treatment begins, the faster and easier it is to defeat the disease without consequences. Otherwise, the lack of oxygen will begin to affect the child’s mental development and academic performance, and constant difficulties with nasal breathing and a slightly open mouth will provoke inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx - tonsillitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis, etc.
Over time, the disease will affect the patient’s appearance: polyps contribute to displacement of the nasal bones and widening of the nose, nasolabial folds are smoothed out, and a constantly open mouth gives the patient a characteristic “polypous” expression. The voice will become dull and nasal, and hearing will suffer. In the most advanced cases, polyposis can have a negative impact even on the development of the child’s chest, the same applies to the dental system.
The reasons for the presence of mucus in the nasopharynx are indicated in this article.
The photo shows the location of the polyps:
Depending on the degree of the disease, polyps can be removed conservatively or surgically. At the initial stages of treatment, it is important to establish the cause of the disease and eliminate it. If this is not done, the disease will most likely recur.
Therapeutic methods include:
- salt inhalations , the purpose of which is to cleanse the mucous membranes of pus and allergens, as well as reduce swelling and inflammatory infiltration;
- ultraviolet light (dries out the mucous membrane and neutralizes foci of inflammation);
- turundas with stretching and healing ointments;
- laser therapy , which helps normalize lymph and blood flow and restores tissue nutrition;
- nasal corticosteroids : Triamcinolone, Fluticasone, Mometasone, Budesonide;
- drugs that suppress allergies : Aleron, Erius, Lortadine;
- cauterization at a temperature of 60-70 °C (after this method of exposure, polyps disappear within a few days and are easily removed by blowing your nose or using a cotton swab).
You can find out what to do when a child has blood crusts in his nose by reading the article.
What to do if conservative treatment did not help at all or did not have sufficient effect? In this case, surgeons are called to help and will perform a polypectomy, or a minor operation to remove polyps . It is performed using a polypous loop (Lange hook), laser or endoscope. The last method is the most accurate and effective; complications and relapses occur much less often after it. Parents should not be afraid - the times when growths were removed alive are, fortunately, far behind us, and today the operation is performed under general anesthesia.
In order for the postoperative period to pass without complications, the patient should rinse the nasal cavity with sprays for 10-14 days:
The use of self-prepared solutions during this period is contraindicated due to the need to maintain sterility. After each rinse, the bottle spout is treated with hydrogen peroxide. Anti-relapse treatment consists of taking corticosteroid drugs for three months. Once every three months, the child should be shown to an otolaryngologist.
What are the causes of nasal swelling without a runny nose can be found out by reading this article.
Symptoms
Nasal polyps can present in different ways in children. The severity of clinical manifestations depends on many initial factors, as well as the stage of growth of these formations in the baby. Children at an earlier age tend to have more significant problems with nasal breathing than teenagers.
Massive formations in the nasal cavity are accompanied by the development of the following symptoms:
- Severe congestion. This symptom can develop in a baby at any time of the day. The growth of formations contributes to the increase in congestion. The use of standard vasoconstrictor drops to eliminate this symptom usually does not have a significant effect.
- Increasing runny nose. Usually accompanied by the release of a small amount of mucous discharge. When a secondary bacterial infection occurs, the discharge from the nasal cavity becomes yellow or greenish and thick in consistency.
- Impaired sense of smell. In severe situations, there may even be anosmia, a condition in which the perception of smells is impossible. In many cases, an impaired sense of smell can cause a decrease in appetite in a sick child.
- Itching around the eye area. This symptom is quite rare, but it brings severe discomfort to the child.
- Feeling of pressure in the projection of the paranasal sinuses. The child begins to feel severe bloating, which also leads to impaired nasal breathing.
- Increased shortness of breath. This symptom usually appears during the third stage of polyp development. Severe shortness of breath occurs mainly in children with concomitant respiratory tract diseases.
Some experts note that babies with polyps in the nasal passages are more susceptible to developing allergic reactions to various allergens that enter the body through airborne droplets. Such babies are also very susceptible to various odors and chemicals that irritate the epithelial cells of the nose.
Pediatric otolaryngologists have long established that in children with polyps, the risk of developing chronic diseases of the paranasal sinuses increases several times. In this case, the course of the disease is usually chronic. In some cases, babies suffering from nasal polyposis have a high tendency to develop drug allergies.
The initial manifestations of this pathological condition are in many ways similar to the symptoms of a cold. The pronounced difference, as a rule, is that with polyposis of the nasal passages the body temperature does not increase and there are no symptoms of intoxication. The appearance of severe nasal congestion in the case of the appearance of polyps is largely due to changes in the anatomical architecture of the elements of the nasal cavity. As they grow, polypous formations strongly compress the blood vessels, which leads to severe congestion.
Impaired sense of smell with polyposis can either be transient or persist for quite a long time. With a prolonged course of the disease, this symptom can become persistent. In some cases, even surgical treatment cannot return the sick child to normal perception of various odors.
The strong proliferation of polypous tissue contributes to compression of the openings of the auditory tubes. This anatomical disorder causes the baby’s voice to change and become duller and rougher. In some children, this contributes to hearing loss.
In small children, large polyps can be detected independently. The abundant proliferation of polypous tissue contributes to some change in appearance. A sick baby usually opens his mouth, and the nasolabial folds are greatly smoothed out. Difficulty in nasal breathing leads to the child actively breathing through the mouth. If polyps appear in a baby at a very early age, this also contributes to a change in the shape of the nose.
Impaired oxygen supply due to impaired nasal breathing leads to the fact that over time the baby develops symptoms of tissue hypoxia. This condition is usually manifested by an increase in headache. In the first stages of the disease, it is expressed insignificantly, and then gradually increases.
ethnoscience
At an early stage of the disease and only with the permission of the doctor, therapeutic treatment and traditional methods can be combined. For this, herbal infusions, honey, and propolis are used. We offer you several recipes:
If a cold has become a constant companion for your child, a runny nose does not go away after the other symptoms disappear, the baby complains of difficulty breathing and prefers to breathe through the mouth, this should be an alarm bell for parents. It is possible that benign growths called polyps have appeared in the baby’s nose.
If a child has constant nasal congestion, it makes sense to check the nasal sinuses for the presence of polyps.
What are polyps, and for what reasons do they appear in children?
Among doctors, opinions about what exactly causes the appearance of polyps differ. Some consider them to be a consequence of allergic diseases, while others claim that asthma is to blame. The reasons can be grouped into three main groups:
- allergic diseases: bronchial asthma, rhinitis;
- inflammatory diseases of the respiratory tract: sinusitis, sinusitis;
- anatomical features of the structure of the nose: narrow nasal sinuses, congenital or acquired curvature of the nasal septum.
Nasal polyps can grow as a result of some kind of trauma. Children with weakened immune systems are also at risk. Possible causes also include individual intolerance to certain medications: aspirin, salicylic acid and drugs that contain them.
Condyloma formation: treatment and 3 effective drugs
A growth in the nostril may appear after mechanical stress, as a result of decreased immunity and a number of other reasons. Such a neoplasm can grow anywhere on the mucous membrane. Some form at the entrance to the nostrils and on the outer surface.
The septum consists of bone and cartilage tissue. In some cases, neoplastic inflammatory processes may occur here. Patients complain that their sense of smell has decreased and they have a runny nose. To get rid of this disease, surgical correction is required. A bone growth on the septum is called osteoma.
A chondroma forms on the cartilage - a benign tumor that grows slowly. It is gray in color and small in size. Without treatment, a deviated septum and a feeling of discomfort are likely. A purulent abscess can occur on the septum - a piece of tissue enclosed in a capsule, pedunculated polyps that bleed, a hematoma - a type of hemorrhage. All diseases of the septum lead to nasal deformities, so in most cases they are corrected surgically.
Nasal septum hematoma
Types of polyps
There are three types of nasal polyps:
- chronic nasal polyps - look like red bumps evenly covered with mucous membrane;
- adenocarcinomas - balls strewn with large cysts and mammary glands;
- combined polyps, which look like a mixture of polyps of the previous two types.
One type of polyp is worth mentioning separately. It occurs due to an inflammatory process in the sinus of the upper jaw and gradually grows into the nasal cavity. Its size is so large that it can even spread to the throat.
Stages of polyp development and their symptoms
The first manifestations are confused with a simple cold:
- mild nasal congestion;
- slight difficulty breathing;
- frequent sneezing.
In newborn babies and children under one year old, parents may notice:
- previously absent snoring;
- refusal to eat in the same amount because the child cannot breathe while eating;
- moodiness, problems sleeping.
If you do not consult a doctor with these symptoms, the growths will continue to grow and gradually cover the entire nasal septum, making breathing significantly more difficult. By the beginning of the third stage, the entire cavity is blocked by polyps. When they are present in both nasal passages, the ability to breathe normally is completely blocked. Children are usually diagnosed with polyposis of one nostril.
With polyps, the child complains of constant nasal congestion and pain
At this stage, additional symptoms appear:
- the child’s breathing is difficult, but attempts to blow his nose or rinse his nose do not improve the situation;
- the baby complains of a change in taste sensations; food seems tasteless to him;
- due to the inability to breathe normally, especially at night, the child develops constant headaches caused by oxygen starvation of the brain;
- memory, concentration, performance decreases, mood deteriorates;
- polyps put pressure on the vessels of the nose;
- night snoring appears;
- the baby complains of pain in the nose;
- there are problems with sleep, the baby has trouble falling asleep and often wakes up;
- as the cones grow, the voice changes, becoming nasal, as if you have a cold;
- further growth of tumors leads to hearing impairment;
- gradually internal changes lead to external ones: the nose looks swollen, the mouth is constantly slightly open;
- Some patients experience disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract: indigestion, vomiting, nausea.
Night snoring and restless sleep are faithful “companions” of polyps
Diagnosis of polyps
A child's nasal voice and constant nasal congestion should alert parents. Of course, polyps are not the only cause of such symptoms, but in any case they cannot be ignored. At the first examination, an experienced specialist will be able to see tumors in the nasal passages using a rhinoscope.
To clarify the diagnosis, a computed tomography scan of the sinuses may be prescribed. This is a mandatory analysis before surgical removal of polyps, which the surgeon needs to assess the complexity of the upcoming operation and the tactics of the procedure for getting rid of growths. If CT is not possible for a number of reasons, radiography should replace it.
Additional diagnostic methods are pharyngoscopy, otoscopy, smear from the mucous membrane of the pharynx, bacterial culture of nasal discharge. The patient will need to undergo a general blood test to assess the level of leukocytes and ESR. If the cause of the tumors is an allergy, a series of allergen tests are performed.
Features of treatment
Treatment of polyps in children and adults is no different. The key to successful treatment is timely and competent diagnosis and the prescription of comprehensive treatment. You cannot rely only on traditional medicine and self-medicate, this can only worsen the patient’s health condition.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment is effective only in the early stages; in other cases, it serves only as an aid to the main treatment. Medicines are used to eliminate the cause that led to the formation of growths. With their help, the following is carried out:
- treatment of the nasal cavity from the inside with disinfectants;
- drying;
- if necessary, treat allergic rhinitis;
- therapy aimed at restoring the normal functioning of the nasal passages;
- restoration and maintenance of immunity.
Drug treatment must be agreed upon with an ENT specialist
Drug therapy involves the use of the following means:
- ultraviolet sanitation;
- tampons soaked in ointment that sucks pus from the sinuses;
- salt inhalations;
- hormonal sprays.
Surgical intervention
Modern medicine knows several methods of surgical treatment of polyps:
- Removal with a special loop. It is considered the most traumatic type of surgical intervention: polyps are captured with a loop and pulled out along with the part of the mucous membrane to which they are attached. After the operation, a fairly long recovery period is expected, and often the growths recur.
- Laser removal. During the operation, the liquid from the polyps is evaporated using a laser, after which the dry membranes are removed manually.
- An endoscopic intervention, in which an instrument and a microcamera are inserted into the nasal cavity, the picture of the operation is reflected on a computer monitor.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine should be used as an aid to basic therapy and only in consultation with a doctor.
To treat polyps, infusions of the following herbs are used:
Nasal polyps are a fairly common problem among children, but, unfortunately, they are not always diagnosed on time, because in the early stages of development there is no clinical picture. Parents often begin to ring the bells only when the child has a characteristic appearance - an open mouth, smoothed nasolabial folds, and a drooping lower jaw. And untimely detection of this pathology in childhood can lead to serious consequences that will torment a person throughout his life: disturbances in the formation of the facial skull (deviated nasal septum), malocclusion; hearing loss, loss of smell.
Polyps are benign neoplasms that rise above the mucous membrane of the nose and (or) paranasal sinuses: maxillary, frontal, ethmoid and sphenoid. Located in the nasal passages, they can have a stalk, due to which they acquire a drop-shaped shape, or sit tightly on the mucous membrane, in which case they have a round shape. Polyps in children most often form before the age of 10 years.
Treatment
Polyps in children can be treated using surgical intervention or a conservative method. It all depends on the stage and cause of the disease. If the growths in the nose are small in size, then they can be treated with medication.
Cetirizine and Loratadine will help cure the cause of polyps, such as allergic rhinitis. Chronic inflammatory processes in the nasal sinuses will be eliminated by the antibiotics Ceftriaxone and Macropen.
If you have aspirin intolerance, you must follow a diet that is based on excluding from your diet foods containing large amounts of salicylates. Taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is also prohibited. Note! The presence of symptoms such as:
- Diarrhea, loose stools;
- Bloating, nausea, vomiting;
- Rumbling, belching;
- Alternating diarrhea with constipation;
- Bad breath, fatigue, general lethargy; They indicate intoxication of the body by parasites.
Treatment must begin now
, since helminths that live in the digestive tract or respiratory system...
Doctors' opinion..."
Medicines such as Mometasone and Beclomethasone will help relieve swelling in the nose and eliminate inflammation of the mucous membrane. These drugs are very effective, but long-term use of them leads to serious side effects.
Immunotherapy has gained enormous popularity in modern medicine. It consists of restoring immune functions through bacterial preparations, such as “Multicomponent vaccine”, “Ribomunil”.
Reasons for the formation of polyps
There are no clear causes for the occurrence of polyps; this is a polyetiological disease. Factors influencing the occurrence of polyps are:
- Anatomical features of the nasal cavity (narrow nasal passages, deviated nasal septum);
- Chronic diseases of the nose and paranasal sinuses (rhinitis, sinusitis, sinusitis);
- Allergic diseases (allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, allergic dermatitis, hay fever);
- Cystic fibrosis is a hereditary genetic disease characterized by disruption of the secretory activity of the exocrine glands and functional disorders of the respiratory, digestive, and musculoskeletal systems;
- Churg-Strauss syndrome is a rather rare disease that affects small-caliber vessels, namely those that supply blood to the nasal cavity;
- Hereditary predisposition.
Symptoms that should alert parents
There are no clinical manifestations for a long time. The initial symptoms are very similar to a cold: sneezing, difficulty breathing, nasal congestion, which over time leads to headaches, decreased mental performance, and sleep disturbances. The reason for this is the constant pressure that polyps exert on the blood vessels of the nasal cavity, which leads to a deterioration in the blood supply to the tissues; they become more susceptible to the penetration of various types of viruses. This is the cause of frequent inflammation of the palatine tonsils with a clinical picture of endless sore throats and chronic tonsillitis, pharyngeal tonsils with the development of adenoids. When the polyps reach an impressive size, the symptoms become more significant and varied: increased headaches, snoring at night, possibly pain in the paranasal sinuses, the sensation of a foreign body in the nose, which brings constant discomfort.
Children often complain of impaired sense of smell, up to its complete loss, and changes in taste sensations due to the fact that polyps block part of the mucous membrane responsible for the perception of odors. If you allow the disease to become chronic, you can say goodbye to your sense of smell forever.
You may also notice that your child has developed a nasal tone to his voice, and all because overgrown polyps block the auditory canals and lead to hearing loss, and in very young children, even to impaired speech development.
Children with nasal polyps usually have a characteristic appearance: they always breathe through their mouth, so it is always open, they have smoothed nasolabial folds, and a drooping jaw. Difficulty breathing and large polyps lead to disturbances in the formation of the facial skull and dental system, which is manifested by malocclusion and cosmetic defects. And in children of the first year of life, this is even more dangerous, since infants do not yet know how to breathe through their mouths. In them, difficulty in nasal breathing causes sucking and sleep disorders, which leads to malnutrition, weight loss (hypotrophy), and pathology of the bronchopulmonary system.
Types of adenoma in the nose and their diagnosis
Adenoma is a benign tumor. Localization area – lower, middle nasal concha; ethmoid, maxillary sinuses. Adenomas of the lateral wall develop rapidly, while adenomas of the medial wall slowly spread into the nasal cavity.
The neoplasm may be pink or white-gray in color. Such shades are considered the norm.
Attached to the inner walls of the nasal sinuses using a stalk. Despite the fact that the adenoma is benign, it can degenerate into malignant at any time. Therefore, removal of the tumor is recommended.
Types of adenoma in the nose
- Bleeding polyps. Placement area: nasal septum. It looks like a round, regular-shaped formation, has a red smooth surface. Characterized by frequent bleeding and significant difficulty breathing.
- Osteomas.
At the initial stage it develops asymptomatically. The localization area is the posterior wall of the nasal sinuses. An increase leads to headaches, difficulty breathing, and increased intracranial pressure. The enlargement of the tumor leads to protrusion of the eyeball. - Chondromas.
The localization area is the septum and walls of the nasal sinuses. More often diagnosed in children and teenagers. The size of the tumor can reach 6 cm in diameter. It grows slowly over several years.The growing tumor makes it difficult to breathe through the nose, impairs the sense of smell, and a sensation of a foreign body appears.
Adenomas in the nose in children
Nasal adenomas cause discomfort for children
Children most often develop polyps, which cause regular bleeding and cause breathing problems.
The causes are inflammatory processes of the nasal mucosa, which are typical for children. Even a small mechanical impact causes severe nosebleeds.
In childhood it measures about 2-3 mm. Such a tumor is surgically removed, and then the base of the tumor is cauterized. An incompletely removed leg contributes to the recurrence of the pathology.
Osteomas are not common in children. The tumor is localized in the paranasal sinuses. It is a bone tumor. In children, they most often appear during a period of intensive growth of the facial skeleton.
The tumor may begin to grow or, on the contrary, stop growing during adolescence, against the background of intense hormone production.
If there is a rapid increase in size, surgery is prescribed to remove the tumor.
Chondromas in children develop in places where disturbances occurred during the formation of cartilaginous tissue during embryonic development. Localized in the main and maxillary sinuses. The tumor impairs blood circulation, squeezing blood vessels.
Symptoms of nasal adenoma
Benign tumors in the initial stages of development grow asymptomatically. They can only be identified through examination of other pathologies by an otolaryngologist. Symptoms appear as the size of the tumor increases.
The first signs of a developing adenoma in the nose, both in children and adults, are difficulty breathing; impaired sense of smell; sensation of a foreign body in the nose. Children complain about “some kind of ball” in their nose. If the adenoma is bleeding, then children will experience frequent bleeding. It is common for children to breathe through their mouth. That's why it's always open.
Photos of symptoms of nasal adenoma:
Impaired nasal ventilation leads to the addition of a secondary infection - rhinitis and rhinosinusitis develop. In this case, pure mucus or with admixtures of pus is released.
Chondromas and osteomas grow in the area of the paranasal sinuses, pharynx, eye orbits, and brain. This leads, accordingly, to breathing problems; swallowing; narrowing of visual fields; limited mobility of the eyeball; headaches. Osteoma and chondroma, growing into the bones, especially in children during the formation of the skull bones, cause facial deformation.
Diagnosis of adenomas in the nose
To identify an adenoma in the nose, you should contact an otolaryngologist. Parents need to watch their children.
Even if nosebleeds do not occur frequently, it is necessary to consult a doctor in any case. An open mouth, difficulty breathing are also reasons to visit a specialist.
Diagnosis of adenoma is carried out by rhinoscopy (a method of examining the nasal cavity using special mirrors; visual examination of the vestibule of the nose, nasal cavity). This eliminates the presence of scleromas and foreign bodies. A biopsy (sampling of biomaterial for research) is mandatory.
The extent to which adenomas have grown into structures adjacent to the nasal cavity is determined using:
Photo gallery of nasal adenoma diagnosis:
In almost all cases, if an adenoma is present, an ophthalmological examination is prescribed. Pathogenic microflora is detected using a smear of the throat and nasal cavity.
Throat and nasopharynx swab
Nasal adenomas treatment in children and adults
Drug treatment of nasal adenoma is carried out if the child has a type of adenoma - nasal polyps. The need for drug therapy is determined by an ENT doctor. You can familiarize yourself with methods of treating polyps without surgery in this article.
The tumor is removed to prevent it from becoming malignant.
There are the following types of operations to remove adenomas:
- Electrocoagulation loop.
It is a special instrument that heats up to 4000 C. After pressing the pedal, the loop removes the adenoma. Due to the high temperature, the blood vessels stick together. There is no bleeding. Polyps are removed in this way. Electrocoagulation loop for adenoma removal - Coblation – cold plasma tumor removal. After the procedure, adjacent tissues are not damaged, there is no bleeding or swelling.
- The chondroma is removed by the endonasal route.
Minimally invasive, non-traumatic procedure. Performed with an endoscope. Endoscopic removal of adenoma in the nose
To prevent the development of tumors, immunomodulatory therapy is prescribed.
Source: https://nos-zdorov.com/dobrokachestvennye-opuxoli/adenomy
Diagnostics
If you notice any of the above symptoms in your child, contact your local pediatrician or otolaryngologist to start treatment as early as possible and not waste precious time.
Polyps located in the nasal cavity near the nostrils can be visible to the naked eye, but if they are located deep, the doctor performs a rhinoscopy (examination of the nasal cavity using special equipment) and identifies specific drop-shaped or grape-shaped growths of the mucous membrane. In some cases, a biopsy of the polyp is performed to exclude its malignancy.
To assess the extent of polyp growth, radiography and CT or MRI of the paranasal sinuses are performed. It is necessary to take a general detailed and biochemical blood test, which will allow the doctor to determine the degree of the inflammatory process; allergy tests are taken in patients with a history of allergies (performed only during stable remission of the underlying disease).
If there is a predisposition to cystic fibrosis in the family, it is advisable for the child to undergo a test to determine this disease.
Treatment of polyps
Treatment of polyps is divided into conservative and surgical.
It is very important to identify the root cause and eliminate it, but this is not always easy, so it is recommended to eliminate all factors that can trigger the occurrence of nasal polyps. These include eliminating exposure to infectious and food agents and allergens on the body; rehabilitation of foci of chronic infection and treatment of inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx with antibiotics; antiallergic therapy, including the use of antihistamines (Loratadine, Aleron, Erius), corticosteroids in the form of nasal sprays (Budesonide, Fluticasone, Mometasone and Triamcinolone).
Method of thermal influence on
polyps are also considered conservative. As a result of heating to a temperature of 60–70 C, after a few days the polyps fall off from the nasal mucosa, after which the patient blows his nose out on his own.
If conservative treatment does not produce positive results for several months, they resort to a surgical solution to the problem.
Indications for surgical treatment are: too large polyps, purulent-inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx, impaired sense of smell, deviated nasal septum, frequent attacks of bronchial asthma.
Removing polyps using surgical instruments is called a polypectomy. The procedure is also carried out using a laser or endoscope. The most effective is endoscopic removal of polyps due to higher accuracy, lower likelihood of relapses and complications. In children it is performed under general anesthesia, in older adults – possibly under local anesthesia.
Since nasal polyps tend to recur, postoperative and anti-relapse therapy is mandatory. After the operation, you need to rinse your nose with saline solution Aquamaris, Humer, etc. for 7-10 days.
For anti-relapse purposes, after polypectomy, three months of local treatment with nasal corticosteroids in the form of a spray is prescribed.
To identify recurrent nasal polyps, observation by an otolaryngologist is recommended for at least 1 year, consultation once a quarter.
In children of preschool and primary school age, polyposis is often found - benign growths on the nasal mucosa. The disease is not detected immediately; at the initial stage it occurs without visible symptoms. If the disease is not cured in a timely manner, then polyps begin to grow not only in the nose, but also in the maxillary and frontal sinuses, which causes a lot of trouble.
Traditional methods
Treatment using traditional medicine is very effective. Especially if you combine it with other methods.
Recipes for preparing effective remedies:
Anise drops. Pour half a glass of alcohol 20 g. dry anise herb and refrigerate for a week. Shake before use and dilute with water in a ratio of 1:3. Place 10 drops into each nostril three times a day. The procedure must be repeated for two weeks, then take a break.
Inhalation. Pour boiling water over a mixture of 2 tablespoons of celandine and 2 tablespoons of chamomile. Bring to a boil over low heat, then remove from heat and ready to use. You need to breathe steam twice a day for 2 weeks.
In order not to have to resort to drastic methods of influencing nasal polyps, parents need to closely monitor the health of their child. If you have the slightest suspicion of illness, you should not delay visiting a doctor and treating the problem that has arisen.
More articles on this topic:
The mucous membrane of the nasal passages is constantly exposed to the environment. Chronic inflammation leads to the formation of soft polyps or hard crusts. Large growths in the nose can cause breathing problems and reduce the sense of smell. Frequent infections, allergic reactions, and immune disorders contribute to pathological changes. Conservative and surgical treatment of the disease is possible.
How and why do polyps appear?
Nasal polyps in a child are small growths on the mucous membrane (see photo). They may look like a droplet on a stem, branch like a tree, or be shaped like a cone or ball. Color varies from white to pink or red with a bluish tint. The formation has its own nerves and blood vessels, so if the polyp is damaged, the child experiences pain, and liquid exudate flows from the wound site. Polyposis can be unilateral or bilateral. Some polyps can grow, others remain small and unnoticeable.
Stages of the disease
Polyposis goes through three stages of its development:
- First. The neoplasms are invisible, cover less than 50% of the nasal passage, and breathing is not difficult.
- Second. Polyps filled more than half of the nasal passage. It is difficult for the baby to breathe through his nose; he increasingly tries to breathe through his mouth.
- Third. The air opening is completely blocked. Breathing through the nose is impossible.
Causes and risk factors
Long-term observation of the clinical picture of polyposis has not revealed the cause of the disease. Experts only know a number of factors that can provoke the disease. The most common of these is considered to be the presence of chronic infectious processes in the nasal mucosa and sinuses. It is assumed that by forming polyps, the mucous membrane seeks to increase its surface area in order to increase resistance to infection. Risk factors include chronic rhinitis, sinusitis, and sinusitis.
Provoking factors also include features of the anatomical structure of the nose, in which the load on the epithelium is increased, which leads to frequent inflammation in the nasal passage:
- the lumen of the nasal passage is narrow, insufficient for normal breathing;
- the nasal septum is deviated.
Risk groups are identified among children who are most susceptible to polyposis. These are children suffering from diseases:
- bronchial asthma;
- aspirin intolerance;
- chronic rhinitis, sinusitis, sinusitis;
- allergy;
- cystic fibrosis;
- Churg–Strauss syndrome;
- fungal infection of the nasal cavity;
- heredity.
Why are they dangerous?
Overgrown polyps damage the child’s health and can lead to serious consequences:
- In infants, respiratory function is impaired, which leads to eating and sleeping disorders, pathology of bronchial tubes, and weakened hearing;
- in older children, diseases of the respiratory system become chronic, adenoids enlarge, sore throats and tonsillitis become more frequent (we recommend reading: how to recognize adenoids in the nose in children, their photos and symptoms);
- sense of smell worsens;
- polyps can block the auditory canals from the inside, which leads to deafness;
- respiratory failure causes hypoxia - oxygen starvation of the body;
- penetrating into the frontal sinuses, polyps cause changes in the structure of the skull, and associated infections cause meningitis and encephalitis;
- Polyposis is benign in nature, but can degenerate into malignant tumors.
Symptoms
Signs of the development of a sore appear based on an infection that has affected the nasal passages. The symptoms of the disease are varied:
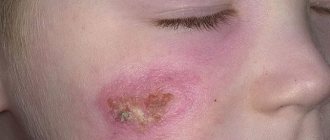
- Furuncle - the child’s body temperature rises, the skin is inflamed, hurts, and when touched, gives off increased pain. After a short period of time, an abscess with a purulent blister forms on the affected area. There is an increase in lymph nodes located close to the sore.
- Sycosis - the skin near the wings of the respiratory organ is strewn with small papules with purulent content, covered with dry crusts on top. During exacerbation, swelling and redness are observed.
- Eczema - in the acute course of the disease, there is swelling all over the face, small pimples appear near the nasal sinuses, which open up and form weeping ulcers. The upper layers of the epidermis are covered with dry crusts, under which cracks and redness can be seen.
- Erysipelas - the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity acquires a reddish, inflamed tint, there is severe painful discomfort, and sometimes fluid-filled papules appear. Lymph nodes enlarge, an increase in body temperature and all signs of intoxication are detected.
- An allergic reaction – an inflammatory rash forms that is constantly itchy. The baby periodically scratches it, which leads to the growth of the affected area due to scratching of the blisters.
Soreness occurs not only due to inflammation of the tissues, but also due to the tension of the skin during the maturation of the boil.
Symptoms of the disease
At the first stage, it is quite difficult to detect polyps in a child’s nose. Most often, the disease is detected when some kind of growth or lump appears almost outside the wings of the nose. The following symptoms should cause concern and suspicion in parents:
- frequent headache;
- snore;
- deterioration of sense of smell;
- nasal voice;
- hearing impairment;
- pain in the paranasal sinuses;
- discharge of blood when blowing nose;
- Constantly stuffy nose and mouth breathing.
Symptoms
Dacryocystitis of the eye has a variety of symptoms. In children, the disease can be suspected if the corner of the eye turns red or tears periodically roll out, or the eye begins to sour. Do not self-medicate; immediately show your baby to an ophthalmologist.
As for adults, we list the symptoms as they increase:
- the appearance of wet eye syndrome, constant tears in the eye;
- lacrimation in the cold;
- deterioration, blurred vision;
- excessive lacrimation, inflammation, redness of the lacrimal caruncle (corner of the eye near the nose);
- inflammation spreads to the lacrimal canal and lacrimal sac, symptoms include the appearance of swelling and purulent discharge;
- significant swelling, soreness of the eyelids or places of projection of the lacrimal canal;
- Possible enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes, increased body temperature.
One of the indirect signs of beginning obstruction of the lacrimal canal is lacrimation in the cold. Cold additionally narrows the outflow channels and increases tear production, and in the presence of disturbances, profuse lacrimation is observed, which may not have existed before.
Treatment of the disease
After identifying polyposis in a child, it is necessary to begin treatment immediately, since polyps grow very quickly. If the formations are insignificant, then conservative therapy is applicable, which consists of taking medications. In the second and third stages of the disease, surgical intervention is necessary.
Conservative therapy
The medication treatment regimen involves solving the following problems:
- eliminate the factor that provokes polyposis (infections, allergies, concomitant diseases);
- cleanse the mucous membranes and sinuses;
- relieve swelling and restore breathing;
- stop the growth of polyps;
- strengthen the immune system.
To eliminate the infection, antibiotics (for bacterial infections), antiviral and antifungal agents (for other types of pathogens) are prescribed. For allergies, antihistamine therapy is necessary. For polyposis, second-generation antihistamines that are safe for the child’s body are used (Fenistil, Zodak, Zyrtec).
To cleanse the mucous membrane, irrigation of the nasal cavity with saline solutions (Aquamaris, Humer) is used. You can learn to do this procedure yourself, or you can sanitize the nose and sinuses and remove purulent deposits in a clinic. It is important that saline rinsing is carried out continuously and after completion of treatment.
In addition, when taking steroids, the growth of polyps stops. For children, drugs without significant side effects are used (Beclomethasone Orion, Triamcinolone, Nazarel and others).
To combat polyps with the aim of their destruction, keratolites are used: solcoseryl ointment, Collomak, lapis pencil. These drugs soften the growths, as if “dissolving” them. To strengthen the immune system, immunomodulators, vitamin complexes, and a special diet are prescribed.
Surgical intervention
If conservative treatment for 3 months is unsuccessful or the disease is at a deep stage, then surgery is performed. Modern clinics do it using an endoscope or laser. Endoscopy is preferable because it is more accurate. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. Postoperative therapy consists of rinsing with saline solution for 7-10 days.
After discharge from the clinic, the attending physician prescribes the child three months of anti-relapse treatment, since in most cases, after surgical removal, the polyps grow again. To prevent this phenomenon, a course of treatment with hormonal nasal medications is carried out. Throughout the year, the operated patient should be regularly examined by an otolaryngologist.
Various neoplasms can appear on any part of the body. Papilloma in the nose appears as often as on the arms and neck.
They are usually benign, but the fact that they can block the nasal passage and make it difficult to breathe is very dangerous. Such formations must be removed, but always under the supervision of the attending physician.
How and with what to treat growths in the nose on the septum?
When a patient complains that a growth has appeared in the nose, the otolaryngologist conducts a visual examination. Papillomas are easily diagnosed by external signs . To determine the etiology of the disease, differential studies are supplemented with a biopsy, polymerase chain reaction, and vinegar test. To confirm polyposis, the doctor is guided by x-ray photos, rhinoscopy data, MRI, CT.
Conservative therapy
There is no universal method for getting rid of a growth on the nasal septum. The recovery scheme for each clinical case is determined by the characteristics of the pathology and the patient’s physiology.
Advice! To enhance the absorption of nasal medications, before irrigating the mucous membrane, it is necessary to irrigate the nasal cavity with saline solution.
The goal of drug treatment is to prevent relapses of the disease, reduce growths in the nostrils, and activate the defense mechanism. To achieve positive dynamics, the specialist prescribes medications of different pharmacodynamics:
- corticosteroids : Nazarel, Nasonex, Triamcinolone, Flixonase, Beclomethasone Orion. Local nasal sprays exhibit anti-inflammatory and antiallergic activity and have a vasoconstrictor effect. They improve external respiration functions by reducing spasm in smooth muscle muscles. The duration of treatment is regulated by an ENT doctor. The therapeutic effect develops on days 5-7 ; if necessary, the course is extended, gradually reducing the dosage;
- antihistamines : “Cetirizine”, “Loratadine”, “Cetrin”, “Erius”, “Fenistil”, “Zodak”. They have an antipruritic effect, reduce the intensity of allergic reactions until symptoms are completely relieved. Peripheral H-1 histamine receptor blockers are not prescribed if the body is hypersensitive to individual components. Side effects are manifested by disorders of the central nervous system, cardiovascular system, and gastrointestinal tract.
In addition to the complex technique, nasal rinsing, inhalations, and compresses are performed.
Growths in a child’s nose cause discomfort and create a feeling of the presence of a foreign object in the sinuses
Drug treatment
Neoplasms respond well to pharmacotherapy, so timely medical intervention and well-chosen techniques will ensure active regression of the pathology with minimal risk of their re-formation. Treatment of papillomas is aimed at eliminating the infectious agent and eliminating the growth . For this purpose, the following medications are prescribed:
- antiviral : “Vartek”, “Kondilin”, “Verrukatsid”. Accelerate the process of necrosis of affected tissues, reduce inflammation, resist the penetration of pathogens into the tissue structures of the body;
- keratolytic : “Lapis pencil”, “Kollomak”, “Salipod” patch, “Lekker Superclean”, “Solcoseryl” ointment. Used for the destruction of epithelial tumors, calluses, warts, and hyperkeratosis. The main action is complemented by antimicrobial and local anesthetic activity. The course of treatment does not exceed 7 days , with a daily frequency of treating the hypertrophied area twice a day ;
- immunomodulatory : “Oxolinic ointment.” The main component oxolin has antiviral activity and promotes the formation of the barrier function of the immune system. In the absence of positive dynamics, the doctor is forced to conduct minimally invasive therapy.
Surgery
Modern medicine offers many atraumatic methods for excision of benign tumors in the nose; only in rare cases is traditional removal performed.
Important! Open surgery is not recommended for children due to damage to the integrity of the skin and long and difficult postoperative recovery.
There are several types of operations to eliminate papillomas and polyps:
- Endoscopy . Special optical equipment is inserted through the natural nasal opening for visual control. The image from the video camera is transmitted to the monitor, which allows the operation to be performed more delicately and eliminates the need for a large incision. The advantages of this method include a short hospital period (up to several hours), absence of postoperative pain, and low trauma. The endosurgical procedure requires the use of expensive equipment, which is reflected in the price range.
- Cryodestruction . Surface treatment of papillomas with liquid nitrogen. By flash freezing, epithelial growths are destroyed. In otolaryngology, this method is considered to be the most effective at the lowest cost. The event is well tolerated by patients, most often the therapeutic result does not require repeated actions.
- Electrocoagulation . The essence of the technique is thermal damage to tissue structures by electric current. All layers of tissue are exposed, so the blood clots well, thereby preventing the risk of infection and nasal bleeding.
- Laser removal . The latest non-contact technology. The procedure does not require special preparation or rehabilitation period. Elimination of neoplasms in the nasal cavity occurs due to coagulation of soft tissues and ablation (evaporation) of soft tissues. Session duration varies up to 5 minutes . Manipulation is a one-time procedure; in rare clinical cases, there are indications for several stages.
- Radio knife . Non-contact excision of growths on the nasal septum is carried out with high-frequency waves, which dissect and simultaneously sterilize the cells and stop the bleeding. They are used for active growth of growths, after which benign defects do not tend to re-grow.
For reference! Drops and infusion of celandine are effective in the treatment of papillomas.
, local decongestants (Nazivin, Noxprey, Xylometazoline) and glucocorticosteroids (Nasobek, Flixonase) are prescribed for a short course of up to 5 days to restore natural breathing
Complex treatment of growths in the nose complements the use of moisturizing drops, hormonal and antiviral drugs. The latter group has anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, antitoxic effects, and increases resistance to antigens.
Reasons for appearance
Papilloma in the nose appears in the same way as other formations on the body, when the human papillomavirus (HPV) is activated. This virus enters the skin of a healthy person and may not cause any manifestations for a long time. Typically, growths occur after a decrease in the body's protective function.
Immunity is reduced if:
- The presence of chronic or acute gastrointestinal diseases.
- Frequent colds.
- Poor nutrition.
- Low physical activity.
- Long-term use of medications.
- Regular stress and nervous breakdowns.
- Hormonal changes
- The presence of bad habits in a person’s life (alcohol, tobacco, drugs, overeating).
Very often the virus is transmitted sexually. But in order for papilloma to appear in the nose, you can get this microorganism in another place. For example, during tactile contact with a carrier of the virus, in a public bath, sauna, swimming pool, water park.
Localization of nasal polyps
Inflammation, which leads to the formation of growths, occurs in the mucous membrane of the nose and sinuses. Polyps can appear at any age, although the disease is more often diagnosed in young people. Nasal growths form inside the nasal passages and sinuses, which are located around the nose, towards the eyes and cheekbones. The risk of developing polyps increases with frequent colds, chronic inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, and allergies. Doctors confirm the negative role of factors such as general inflammation and narrowing of the airways in asthma, allergic reactions to microorganisms, and cystic fibrosis. A possible complication is obstructive sleep apnea, which occurs when breathing stops for more than 10 seconds up to 10 times per hour. The spread of infection from the sinuses causes swelling of the eyelids, blurred vision and the inability to move the eyes, and meningitis.
Type of growths
Nasal papilloma can be of several types. Firstly, they can form in the nasal cavity and in its vestibule.
- New growths usually appear in the nasal cavity itself in older people. For children, such a growth is very rare. Such formations look like a small mushroom on a stalk or a head of cauliflower. They can be grayish or flesh-colored.
- The formations that appear on the threshold of the nasal passage are quite dense and covered with tubercles. Such papillomas in a child’s nose can occur if personal hygiene is not maintained. Picking your nose with dirty hands will lead to nothing good.
In addition, there is another classification of formations in the nasal cavity:
- Exophytic . Formations most often appear in front of the nasal passage or on the septum. They are usually reddish in color, very dense and lumpy. Such papillomas quickly change size and cause difficulty breathing.
- Invented . Growths of this type appear in older people on the wall or septum in the nasal cavity. Papillomas are attached to a thin stalk, so they are easy to injure. This impact on the growth can cause severe bleeding. Inverter formations often degenerate into malignant tumors.
It is important to say that papilloma on the nose appears extremely rarely. Thanks to its placement, it is very easy to detect and at the first manifestations you should consult a dermatologist. It is he who will advise how to get rid of the tumor.
Crusts in the nose in the form of small growths
Hard growths appear in the nose due to excessive dryness of the nasal passages, atrophy of the mucous membrane due to hormonal disorders. The causes may be pathologies of the nasal sinuses, degeneration of the mucous membrane due to exposure to negative external or internal factors. The breakdown of the epithelium occurs with the formation of bloody or gray-green crusts. Apply essential oils of eucalyptus, tea tree, bergamot to soften hard growths, disinfect and heal mucous membranes, adding them dropwise to fatty oils. It is useful to rinse and irrigate the nasal passages with infusion of chamomile, calendula, and sage. You can apply ointments to the nasal passages - “Rescuer” and Fleming. The products have a softening and healing effect. When hard growths appear in the nasal cavity, it is recommended to lubricate with oxolinic ointment to dissolve crusts and prevent viral infection. Lubricate the nasal cavity with olive and sea buckthorn oils, diluted calendula tincture, and oil solutions of vitamins A and E. An infusion for rinsing the nasal cavity is prepared from chamomile, sage and plantain (take a tablespoon of each herb). Add the raw material to 400 ml of boiling water and leave for half an hour, use warm. A solution of sea salt with the addition of one of the vegetable oils (olive, sunflower, flaxseed) is suitable for rinsing the nasal passages.
Treatment options
Before treating papillomas in the nose, the causes and strain that caused the appearance of neoplasms must be determined first. To do this, you must undergo the necessary laboratory tests. A referral for diagnostics should be given by a qualified specialist.
After the strain of the virus is determined, the doctor will prescribe treatment that will help remove papilloma in the nose. This will include both medications and hardware removal of nasal papillomas. Unfortunately, a medicine has not yet been invented that will help remove HPV from the human body once and for all. What should doctors do in this case? After all, people need help.
Then exclusively antiviral drugs are used in combination with vitamins and immunomodulatory agents. If a wart has grown in the nose, then such measures will reduce the activity of the virus and help the human immune system cope with the pathogen much more easily.
The next step will be to eliminate the external manifestation. Although the tumors are almost invisible, they cause some discomfort, so they are always removed. How to remove papilloma? A dermatologist will answer this question when he prescribes medications. Most often, one of the following procedures is prescribed:
- Excision with a scalpel. The most ancient method, but due to severe trauma, it is chosen very rarely.
- Laser correction. quite a popular method. It can be used both in a clinic and in a beauty salon. Papillomas in the nose, the removal of which is mandatory, are removed very quickly and the recovery period is minimal.
- Radio knife.
- Electrocoagulation.
- Cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen.
The last four removal methods are the most modern, fast and virtually painless. In some cases, when the procedure is performed on a delicate area of the body or a low threshold of sensitivity, local anesthesia is used.
If a formation has grown in the nose, drug treatment can also remove the external manifestations. These can be ointments, creams and other drugs, which are presented in a huge assortment in pharmacies. But you can’t prescribe them for yourself.
Patients often ask the question, how to remove growth at home? Doctors recommend not resorting to traditional medicine methods. Typically, such medications contain aggressive substances, and they can have a bad effect on the mucous membranes of the nose. Before getting rid of papilloma in the nose in an unconventional way, you need to analyze whether the person will lose their sense of smell.
Types of growths in the nasal cavity
Depending on the morphology, the following types of papillomas are distinguished:
- Mushroom type: occurs in 50% of cases, localized in the vestibule and on the nasal septum. The age of patients is from 6 years. Fungal papillomas are not prone to malignancy.
- The inverted type is typical for older people - from 50-60 years old. Localization - walls and septum of the nose. Visually, the pathology resembles ripe mulberries or cauliflower. The inverted type is accompanied by nosebleeds, unilateral obstruction and, as a consequence, difficulty breathing. The possibility of malignancy of inverted papilloma is 5-10%.
- The cylindrical type of pathology is quite rare: only 5-8%. Localized on the walls of the nose and paranasal sinuses. Middle-aged and elderly people (usually over 50 years of age) are more susceptible to damage. Papillomas of the cylindrical type provoke unilateral nosebleeds (depending on the location of the growths). Quite a high incidence of malignancy: 19-20%.
Doctors rarely detect papillomas in young children. Children of older preschool and school age who attend sports clubs, swimming pools and other places where contact with patients is possible are more susceptible to this disease. A large number of contact persons and a humid environment contribute to the rapid penetration of the virus into the body.
If a child has a papilloma in his nose, parents should definitely consult a doctor to determine the type of tumor and develop treatment tactics. Under the influence of the virus, epithelial cells multiply very quickly, forming small neoplasms on the mucous membrane and skin, which can not only cause complexes about appearance, but also cause serious illnesses in the future.
Regarding the removal of papillomas in children and adults, the opinion of doctors is ambiguous. Some argue that growths must be removed immediately after detection, while other experts are confident that it is necessary to take an individual approach to the treatment of each patient and resort to radical methods only in cases where conservative therapy has not had the desired effect.
Due to the disruption of normal respiratory function, the risk of malignancy and proliferation, benign tumors of the nasal cavity are an indication for surgical treatment. A limitation to surgical intervention may be the patient’s advanced age and the presence of chronic decompensated diseases (heart failure, coronary artery disease, severe hypertension, respiratory failure, bronchial asthma, diabetes mellitus, renal failure, cirrhosis of the liver, etc.).
A bleeding nasal polyp is excised along with a section of the nasal septum at its attachment site. To prevent relapses, the base of the tumor is cauterized by cryotreatment or electrocoagulation. Large benign tumors of the nasal cavity are excised with a scalpel, radio wave knife or using a laser. To clearly differentiate tumor cells from surrounding tissues during surgery, a surgical microscope is used.