It is quite difficult to say how much a baby should weigh at 3 months. The development of each baby occurs individually, depending on its gene pool. However, there are generally accepted standards that pediatricians rely on. Deviation from the norm requires the close attention of parents. Even if nothing bothers the baby, underweight can be caused by various diseases. However, there is no need to worry too much. Trust your pediatrician, who can more objectively assess the baby’s health condition.
Norms of weight and height of babies up to one year
A table of height and weight for children under 12 months is used more often, since in infancy it is most important to track growth in indicators. The norm for boys is:
| Month | Height (cm) | Weight, kg) |
| 1 | 52-57 | 3500 – 5000 |
| 2 | 55-60 | 4500 – 6000 |
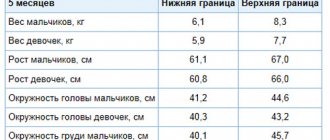
| 3 | 59-64 | 5500 – 6900 |
| 4 | 61-66 | 6100 – 7700 |
| 5 | 65-69 | 7000 – 8400 |
| 6 | 66-70 | 7900 – 8950 |
| 7 | 67-72 | 8000 – 1050 |
| 8 | 69-73 | 8200 – 10400 |
| 9 | 70-76 | 8700 – 11050 |
| 10 | 71-77 | 9200 – 11500 |
| 11 | 72-77 | 9300 – 11500 |
| 12 | 73-79 | 9400 – 11900 |
For girls, these standards will look like this:
| Month | Height (cm) | Weight, kg) |
| 1 | 51-56 | 3500 – 4600 |
| 2 | 55-59 | 4300 – 5500 |
| 3 | 58-62 | 5300 – 6400 |
| 4 | 60-65 | 5800 – 7100 |
| 5 | 62-67 | 6200 – 8000 |
| 6 | 64-69 | 7000 – 8800 |
| 7 | 65-70 | 7200 – 9100 |
| 8 | 68-72 | 7200 – 9400 |
| 9 | 68-73 | 8100 – 10000 |
| 10 | 69-75 | 8200 – 10800 |
| 11 | 71-76 | 8900 – 11000 |
| 12 | 72-77 | 9000 – 11300 |
Height and weight gain may slow down one month and speed up the next. The indicators depend on the baby’s maturity, type of feeding, and overall health. The influence is exerted by the lifestyle of the parents and the activity of the newborn. It is important to remember that the numbers are averaged and are assessed by the pediatrician only as part of the child’s general medical history.
What are “height and weight standards” and how to relate to them
In order to draw conclusions about underweight or overweight, as well as about lagging or too rapid growth in each individual child, doctors need guidelines. Such guidelines are the standards defined by the World Health Organization. These standards were created on the basis of long-term observations of the anthropometric development of children and represent a kind of “corridor” from the lowest limits of height and weight to the highest. All children whose anthropometric data fall into this “corridor” are considered to be developing normally.
If height or weight indicators deviate slightly from the lowest or highest “corridor” values, then doctors pay special attention to such a child, more carefully monitor his development and watch for any alarming symptoms. If the height and weight data deviate significantly from the boundaries of the “corridor”, then such children are additionally examined
Parents who carefully monitor the health and development of their child should pay attention to whether their child’s data falls within the “corridor” of normal indicators and whether the height and weight indicators correlate with each other
Development of girls under 14 years of age
The height and weight of girls between one and three years does not change so rapidly. By school age, after 6 years, a significant increase in height is observed. The second jump occurs in the range of 8.5 – 12 years. At first, the main growth occurs due to the elongation of the limbs; from the age of 11, the torso elongates more. The most intensive growth in adolescence is observed from 10 to 13 years, this is associated with puberty. The total increase of this jump is 36 -38 cm.
In preschool and school children's institutions, students are annually checked for compliance with standards; if they deviate from them, the child is sent for a medical examination, and recommendations are given for correcting nutrition. Tables approved by WHO have the following meanings:
| Age | Height (cm) | Weight, kg) |
| 1 | 72-77 | 9 – 11 |
| 2 | 83,2 – 89,6 | 10,2 – 13 |
| 3 | 91,2 – 98,9 | 12,2 – 15,8 |
| 4 | 98,4 – 107 | 14 – 18,5 |
| 5 | 104,7 – 114,2 | 15,8 – 21,2 |
| 6 | 110 – 120,2 | 17,5 – 23,5 |
| 7 | 115,3 – 126,3 | 19,3 – 26,3 |
| 8 | 120,8 – 132,4 | 21,4 – 29,7 |
| 9 | 126,4 – 138,6 | 24 – 33,6 |
| 10 | 132,2 – 145 | 27 – 38,2 |
| 11 | 136,2 – 153,2 | 30,7 – 38,9 |
| 12 | 142,2 – 159,2 | 36 – 45,4 |
| 13 | 148,3 – 163,7 | 43 – 52,5 |
| 14 | 152,6 – 167,2 | 48,2 – 58 |
Development of boys up to 14 years of age
After a year, the child’s weight and height gain becomes uneven and less intense. Between the ages of one and three, a boy gains approximately 10–30 mm every 3 months. The first acceleration in the rate of physical development in male children occurs at the age of 5 years; the norm during this period is considered to be an increase of 1–3 cm every six months.
From 7 to 13 years of age, growth rates stabilize. At the age of 14, hormonal changes occur in the body and puberty begins. At this age, a boy can grow by several cm in 2–3 months. At the end of this period, a person’s growth approaches the final mark.
| Age | Height (cm) | Weight, kg) |
| 1 | 73 – 79 | 9,4 – 11,9 |
| 2 | 81 – 93,5 | 9,7 – 15,3 |
| 3 | 85 – 99 | 11,3 – 18,3 |
| 4 | 88 – 103 | 12,7 – 21,2 |
| 5 | 99 – 111 | 14,1 – 24,2 |
| 6 | 100 – 120 | 15,9 – 27,1 |
| 7 | 106 – 126 | 17,7 – 30,7 |
| 8 | 111 – 127 | 19,5 – 34,7 |
| 9 | 116 – 138,5 | 21,3 – 39,4 |
| 10 | 120,5 – 144,5 | 23,2 – 45 |
| 11 | 125 – 150,5 | 28 – 44,9 |
| 12 | 134,5 – 152,9 | 30,7 -50,6 |
| 13 | 145,7 – 166 | 33,8 – 56,8 |
| 14 | 152,3 – 172 | 38 – 63,4 |
Important!
During a growth spurt, it is necessary to closely monitor the health of a teenager, since the body often does not have time to gain muscle mass in accordance with the growth rate.
Heterochrony or heterogeneity in the development of organs and systems of the body
At different ages of the child, body weight will increase depending on which part of the body receives the greatest development. So, at the age of 10-12 years, the child will intensively develop lymphoid tissue, which practically did not work in previous years. And after 12 years, the genital organs and the formation of reproductive function begin to develop. In girls this is clearly expressed. Because under the influence of female sex hormones, fat is deposited in the body and body weight increases. In boys, under the influence of testosterone, muscle mass will increase, and as a result, overall weight will increase.
Rules for assessing anthropometric indicators
Only a pediatrician should assess the height and weight of boys and girls. According to the norms, he conducts an examination every month during the first year of life, every 4 months from the age of one to three, and then annually. The assessment is carried out taking into account the following rules:
- Weighing is carried out in the morning, the interval after feeding should be at least 2 hours. Children under one year old are weighed lying down, in a clean diaper or naked. Children aged two years and older are measured in a standing position.
- Height up to 1.5 years is measured while lying on a special table, then in a standing position. Your heels should touch the measurement scale and your legs should be straight.
- For up to a year, head volume and chest girth indicators must be monitored.
The pediatrician checks the data obtained with centile tables. They are the result of many years of measurements, showing optimal values, upper and lower limits, and possible deviations from the norm.
Important!
Child development standards may differ in different countries, so it is useful to check not only the WHO tables, but also the indicators for your region of residence.
Your Child Is Not Meeting the Standards: When to Worry
If a child does not meet optimal developmental milestones, parents become concerned. However, deviations are not always symptoms of pathology. The weight and height of children are affected by:
- Genetic factors. If one or both parents are miniature, you should not expect above average performance from the baby.
- Quality of food, standard of living. Deviation from the norm may be associated with poor nutrition, its deficiency or excess, low standard of living (poor living conditions, rare walks, sedentary lifestyle, lack of vitamins and minerals).
- Week of birth. It is important when assessing the height and weight of infants, since premature infants are weaker than their peers and require several months to “level out.”
- Age. During adolescence, the increase occurs in spurts, so within six months a child can be below the normal limit, and then reach optimal levels in 1-2 months.
For children over two years of age, body mass index (BMI) is also taken into account. Its definition provides an assessment of the harmonious development, the relationship between bone growth and body weight.
What does a baby's growth depend on?
The growth of children is carried out due to the production of a special hormone - somatotropin. This mainly happens when they are sleeping, namely between 22 and 24 hours. Another fact in favor of following the regime!
Thematic material:
- What toys does a 1 year old child need?
- What to give a 1 year old boy on his birthday
In addition to the above-mentioned hereditary prerequisites, the physiological development of the baby can be affected by the following:
- Mom's pregnancy. The fetus grows fastest from 3 to 6 months. At this time, the mother’s diet and her absence of bad habits are especially important.
- Nutrition. Breastfeeding is the best prevention against rickets. And also long walks and sunbathing!
- Place of residence. Nationality, natural conditions and ecology also affect the growth of a child. For example, the Dutch are considered quite tall - 170-185 cm (women and men), the Chinese, on the contrary, grow up to 155-165 cm.
Since the times of the Soviet past, Russians have “grown up” a little, the female half of the population is on average up to 165 cm, the male half is up to 175.
If the baby is sick, his growth may slow down a little, but he will definitely return to normal after recovery.
In some cases, growth canalization is observed. This happens when the reason that was holding back the baby's growth is eliminated. For example, premature and or low-weight babies by 12 months are catching up and even ahead of their peers.
Thematic material:
- What should a 1 year old child be able to do?
- How much should a 1 year old child weigh?
BMI calculation
Calculating body mass index allows you to determine whether a child is underweight or obese. To calculate the indicator, body weight is divided by the square of height in meters. For example, height 95 cm, weight 16 kg, the formula is:
16:0.95²= 17,78
This indicator is checked against BMI percentage curves; they are separate for boys and girls. The blue area of the table is exhaustion, green is normal, yellow is overweight, red is obesity. If you fall into the green and red zones, you should consult your doctor about correcting your diet. The red zone requires diet and additional treatment.
What are the norms for height and weight and how to relate to them?
About nine thousand children brought up in favorable conditions took part in the WHO study. Based on the information received, graphs were drawn up that determined the norms of physical development, which show:
- absolute values under ideal conditions;
- deviations caused by diseases and other unfavorable factors;
- the relationship between body length and weight, which determines the degree of harmonious development.
This is a kind of guide for parents, helping them calculate the proportions of their child, according to available tables and formulas, and if necessary, seek advice from a pediatrician.
Useful tips for parents
A child’s normal weight is the key to his future health, so it is important to maintain it. You can prevent obesity by adhering to a healthy lifestyle and nutritional culture. Some useful tips will help with this:
- The whole family should have a healthy diet; parents are an example for the child, the norm by which he or she is guided in life. Give preference to low-fat foods; vegetables and fruits should be included in the diet in sufficient quantities. Try to minimize the consumption of fast carbohydrates and “harmful foods” (chips, soda, fast food).
- Physical activity should be an integral part of life. Even under heavy loads, find time to exercise or jog.
- Let children be involved in planning and preparing meals to keep them interested.
- Do not reward good behavior or merit with sweets, they should not be an incentive.
- Remember that your child may be full; do not force him to finish eating if he says he is full.
- Do not try to put a complete ban on everything sweet and harmful, this will lead to child rebellion. Set the measure.
Recommendations by age
If you see that the child does not correspond to normal weight, your pediatrician confirmed your fears, then you should not hesitate, but begin to correct the indicator. Otherwise, the situation may worsen, and in addition to excessive stress on the body, the child will develop psychological problems: complexes, self-rejection, isolation, and a depressed state.
When correcting weight, it is important to approach the issue taking into account the age characteristics of the child, namely:
- Before 12 months, people rarely talk about obesity, but bottle-fed babies have less control over their hunger and may gain more than they need. Control the amount of formula you eat, do not overfeed your baby, and do not give enriched formulas unless necessary.
- Before the age of five, eating habits are formed; they depend on the approach of the parents. Offer a variety of healthy foods, light snacks in the form of fruits, bread, and dairy products. Encourage your children to be active, try to find a sporting hobby for them that they like.
- At school age up to 12 years, the main tools for weight loss are sports sections and proper nutrition. Try to keep track of what your child eats outside the home, engage in physical training, exercise should be daily.
- After 13 years, children are dependent on social opinion; they are drawn to walks with fast food and soda. Try offering healthier alternatives such as homemade sandwiches or wraps, baked potatoes, etc.
- At any age, remember that you are an example. If you play sports, eat healthy and varied foods, and spend little time on the computer or TV, your child will adopt your habits. And the likelihood of being underweight or overweight if you live a healthy lifestyle is minimal.
When assessing weight, remember that all children are individual. Do not blindly follow the tables, because exceeding the norm may be explained by the presence of high-quality muscle mass, not fat. Do not put pressure on your child, adjust your diet and habits carefully, without offending your child or instilling in him weight-related complexes. The right example and healthy habits will quickly yield results.
The role of heredity
The growth of a child is a program that is included in the DNA. The genetic program ensures the life cycle of the child, controls the change in periods of development in appropriate conditions of nutrition and upbringing of the child.
The genetic program plays a very important role in the child's adaptation. Thus, under the influence of the external environment (starvation, infection), a profound restructuring of the body’s metabolic processes occurs, which will help the child survive.
The hereditary apparatus will help produce the necessary hormones, biologically active substances, everything that will help the child improve his immune reserve and resist the disease.