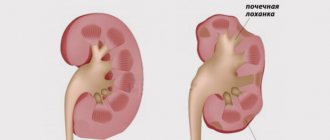
Glomerulonephritis with nephrotic syndrome is a serious disease accompanied by an inflammatory process affecting the renal glomeruli. This form accounts for about 20% of cases of the pathological condition. Usually the lesion is bilateral. Glomerulonephritis of this form is of an immunoinflammatory nature.
In some cases, there is a completely asymptomatic course of this pathological condition, often lasting more than 15 years. Renal function is fully preserved throughout this long period of time. However, everything is not as good as it might seem.
This disease is extremely insidious and requires increased attention from a specialist.
In the absence of targeted treatment, a number of severe complications may develop, including chronic renal failure.
Etiology and pathogenesis of the disease
In the vast majority of cases, the inflammatory autoimmune reaction that affects the glomeruli is the result of infection of the body by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus. Pathogenic microorganisms do not directly affect the basement membrane area. In response to an increase in the number of these bacteria, an antigen-antibody reaction is triggered and cyclic immune complexes are formed.
Thus, when staphylococcus enters the body, it causes the activation of defense mechanisms.
With the formation of cyclic immune complexes, they begin to settle in the glomerular membranes, which causes nephrotic syndrome, characterized by the rapid removal of proteins from the blood.
Such a disorder of kidney function may be associated with damage to the body:
- herpes;
- enterococcus;
- cytomegalovirus;
- hepatitis B virus, etc.
Quite rarely, nephrotic syndrome with glomerulonephritis is caused by taking certain medications. Such drugs include antibiotics, NSAIDs, etc. A particular danger is the presence of individual intolerance to these drugs, as well as other renal pathologies.
Among other things, the presence of glomerulonephritis, accompanied by nephrotic syndrome, is often noted in children who have recently suffered infectious diseases such as tonsillitis, tonsillitis, diphtheria, mumps, chickenpox, etc. In addition, the formation of this pathological condition is often the result of the influence congenital anomalies of the urinary system. In rare cases, glomerulonephritis is diagnosed against the background of severe poisoning with elements such as mercury, arsenic, and lead. These substances have a pronounced toxic effect on the renal glomeruli.
Causes of glomerulonephritis
What factors contribute to the development of the disease? Who acts as the causative agent? Infections entering the body are the main problem, since they cause inflammatory processes. Stimulators of the development of the disease include primarily streptococci, which also provoke sore throat, pharyngitis, and scarlet fever. After three weeks from the moment of contracting one of the colds, an acute form of glomerulonephritis is detected.
Not only because of harmful microorganisms, internal organs can suffer, so the initiators are noted:
- allergic reaction to various pathogens such as pollen, insects, household chemicals, etc.;
- Some medications contain toxic substances that cause unnatural processes that disrupt the stable functioning of internal organs. As a result of poisoning, the functioning of the body system also gets out of a single rhythm, and side effects from the illness begin;
- insect bites;
- vaccination carried out.
When faced with any of these pathogens, the child may feel unwell and experience discomfort. At such moments, it is important to exclude the influence of cold or hot air, and not to be in the sun for too long.
A sharp change in climate, increased physical or emotional stress also does not bode well, and an exacerbation of the disease is observed. Due to a malfunction of the kidneys, the filtration process is disrupted; this occurs due to the accumulation of water and food surpluses that remain in the body without removal.
Classification of glomerulonephritis with nephrotic syndrome
There are many approaches to describing this pathological condition. Depending on the form of the course, glomerulonephritis can be acute, rapidly progressive or chronic. This is one of the most important classification parameters.
The most often diagnosed is the acute variant of the disease, in which symptomatic manifestations increase over 3 months.
The subacute or rapidly progressive form is characterized by the presence of impaired renal function over a period of 3 to 12 months. Glomerulonephritis becomes chronic when morphological changes in the kidneys increase over more than 1 year. This may cause kidney failure.
Most often, the disease occurs with protracted periods and remission. Usually, with the onset of characteristic manifestations of renal dysfunction, no signs of renal dysfunction are observed. Then they become noticeable. Severe damage to the renal glomeruli causes the cessation of their work. Among other things, depending on the type of morphological changes present, proliferative and non-proliferative variants of the disease are distinguished.
How is glomerulonephritis treated today?
Since this is a fairly serious disease, therapy is possible only in a hospital setting, especially in the phase of pronounced symptoms or in the presence of renal failure. Modern treatment of glomerulonephritis is a complex of measures, of which the most important is given to drug therapy, which, depending on the characteristics of the course of the disease, includes:
- antibacterial drugs to fight streptococci or other infections that provoke the development of inflammation of the renal glomeruli;
- antifungal medications if the disease is caused by a fungal infection;
- anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce inflammation in the kidneys;
- symptomatic medications - antihypertensives, diuretics, immunosuppressants, anticoagulants, etc.
Severe renal failure requires hemodialysis. If the kidney is seriously damaged, a transplant may be needed.
One of the powerful therapeutic factors is a special diet for glomerulonephritis, which reduces the load on the kidneys, allowing the tissues to recover. It is based on the limitation:
- table salt – no more than 3-5 grams per day;
- proteins – no more than 80 grams per day;
- carbohydrates – no more than 350 grams per day;
- fats – no more than 90 grams per day.
The main dishes are cereal soups with potatoes, cereal porridges, pasta, herbs and vegetables, low-fat dairy products, low-fat fish, meat and poultry. Pickles and smoked foods, fried foods, sausages, chocolate, legumes, and canned food are completely excluded. In the hospital, patients receive food as part of diet No. 7, but even after discharge it is recommended to adhere to food restrictions.
Symptoms of glomerulonephritis with nephrotic syndrome
Clinical manifestations and the degree of their severity differ significantly in acute and chronic forms of this disease. Glomerulonephritis is inflammatory in nature. It gradually leads to the appearance of atrophic and dystrophic changes in the kidney tissues. This causes functional nephrons to rapidly die and be replaced by connective tissue. The presence of a pronounced inflammatory process and cell death provoke the appearance of signs characteristic of this disease.
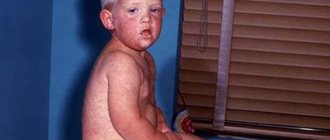
All signs of glomerulonephritis with nephrotic syndrome can be divided into urinary and general. The first include the appearance of blood in the urine, as well as a decrease in daily diuresis, etc.; General symptoms include severe swelling due to insufficient removal of fluid from the body and a stable increase in blood pressure.
Typically, the symptoms of glomerulonephritis that disturb the patient and force him to see a nephrologist include nagging pain in the lumbar region. In addition, general weakness and a feeling of malaise may be present.
Due to existing symptomatic manifestations, a person experiences a decrease in performance. In the future, as the kidney tissue swells, oliguria, dysuria or anuria may develop.
The accumulation of fluid in the soft tissues of the body occurs, as a rule, unevenly. Edema cannot be eliminated completely in this form of glomerulonephritis, even when taking diuretics. In addition, a person is significantly bothered by shortness of breath with minimal physical exertion. In severe cases, pale skin, complete loss of appetite and dizziness are noted.
After the disease becomes chronic, the intensity of symptomatic manifestations decreases. Lower back pain disappears, and the person’s condition stabilizes. In addition, tissue swelling is significantly reduced and diuresis is almost completely restored.
At the same time, arterial hypertension steadily progresses, which often leads to the development of heart failure.
Such a secretive course is interspersed with rare periods of exacerbation. Despite the fact that this form of the disease does not lead to disability or serious deterioration in health for a long time, the inflammatory process that affects the nephrons can cause renal failure and severe uremia in just 3–5 years. Typically, at the terminal stage of development of this pathological condition, signs of severe intoxication of the body with the constituents of urine appear.
Causes and factors for the development of glomerulonephritis in children
In acute glomerulonephritis, there is a clear relationship with the infection 2–4 weeks before the onset of symptoms of the pathology:
- streptococcal, staphylococcal, pneumococcal infections, which occur in the form of: sore throat;
The consequence of a sore throat in a child can be glomerulonephritis.
- scarlet fever;
- streptoderma;
- endocarditis;
- pneumonia;
- malaria;
Chronic glomerulonephritis appears after acute glomerulonephritis. But more often it occurs as primary chronic with:
- excessive antigenic load on the body (incorrect vaccination, administration of immunoglobulins);
- chronic foci of infection and untimely sanitation (tonsillitis, caries, gastritis);
Caries is a source of chronic infection, from where bacteria can travel through the bloodstream to any other organ.
- taking nephrotoxic drugs;
- congenital malfunctions of the immune system.
The following factors can influence the occurrence of the disease:
- hypothermia;
- stress;
- climate change;
- physical stress;
- prolonged exposure to the sun.
Video: causes of glomerulonephritis
Diagnosis of glomerulonephritis with nephrotic syndrome
At the first signs of kidney damage, it is very important to contact a nephrologist for a comprehensive examination. The nephrotic form of glomerulonephritis can be easily identified by conducting a urine test. This determines the presence of massive proteinuria. The main part of the proteins in the released protein fractions is albumin. Among other things, a decrease in the excretion of the daily dose of urine along with an increase in its density, due to a steadily progressive loss of protein, is indicative.
Microscopic examination reveals the presence of hyaline cylinders.
Since glomerulonephritis is accompanied by increased permeability of the glomerular membranes, altered red blood cells can also be seen in urine.
This is usually determined by the doctor when taking a medical history. On external examination, severe swelling is indicative. The patient's complaints about the presence of arterial hypertension are the reason for additional examination under the supervision of a cardiologist.
In addition, the nephrologist will order a blood test. This study allows you to determine the increase in ESR. Among other things, there is an increase in cholesterol and lipid levels. A biochemical blood test determines a decrease in protein elements, including albumin.
Considering that in this pathological condition large quantities of potassium are excreted in the urine, an electrolyte imbalance occurs.
Additionally, an ultrasound scan of the kidneys and blood vessels running in them is prescribed. In some cases, when the doctor remains in doubt about the diagnosis, a fine-needle biopsy and histological examination of the resulting tissue may be performed. It is very important to distinguish between this pathological condition and collagen nephropathy, diabetic glomerulosclerosis, myeloma and amyloidosis.
Treatment of the disease
Timely detection of pathology allows treatment with conservative methods. In this case, hospital therapy is required. To suppress the autoimmune reaction, a course of immunosuppressants is prescribed. Typically, cytostatics, glucocorticosteroids and selective immunosuppressants are used. Among other things, diuretics are used to stabilize the condition and reduce swelling. Additional medications may be prescribed to correct symptoms that have developed against the background of the underlying disease.
Throughout the entire period of treatment, the patient must remain in bed.
During treatment for this pathological condition, it is very important for patients to support the body with a special diet, primarily aimed at increasing the daily dose of protein.
It is very important that food contains at least 1.4 g of this substance per 1 kg of human weight. Animal proteins should make up at least 2/3 of the total. Typically, patients are recommended to follow diet plan No. 7 with the consumption of egg whites, cottage cheese, lean fish and meat. If, against the background of such a diet, a decrease in kidney function is observed, it is necessary to reduce the amount of protein intake. It is very important that the patient avoids high-fat foods throughout the treatment period. Against the background of the disease, an increase in the level of triglycerides and cholesterol is observed in the blood.
As a rule, for this disease it is recommended to consume about 80 g of fats, and vegetable fats should account for about 35%.
To compensate for potassium deficiency, potatoes, bananas, honey, legumes, and greens are introduced into the diet. Given the severity of edema, salt intake should be completely eliminated or limited. Patients suffering from glomerulonephritis with nephrotic syndrome should not consume marinades and salty sauces.
Among other things, to reduce swelling, it is necessary to significantly reduce the daily dose of water consumption; it is recommended to consume no more than 1 liter. Throughout the entire period of treatment, patients suffering from this pathological condition are strictly prohibited from consuming mushroom broths, bread, offal, fatty meats, spicy and salty dishes, smoked meats and cheeses. A gentle diet should be followed until complete remission occurs.
Prognosis and development of pathological complications
This disease is an extremely dangerous condition, since if the course is unfavorable, it can cause severe complications.
With timely and comprehensive therapy, the prognosis is usually favorable. After a long recovery period, people return to normal life and have no further restrictions.
However, if the disease was detected too late or therapy did not produce the desired effect, kidney failure may develop. In this case, patients need to undergo hemodialysis procedures to purify the blood using an artificial method. In the future, to stabilize the condition and prevent the development of complications associated with the treatment of renal failure, the patient needs a kidney transplant, which will allow the person to return to a full life.
In some cases, when patients do not follow the doctor’s recommendations, other dangerous complications may develop. Against the background of tissue swelling, pneumonia is often diagnosed, which significantly worsens the general condition. In addition, if tissue swelling reaches its peak, cracks in the skin may appear, which must be treated with strong disinfectants to prevent infections.
In addition, nephrotic crisis poses a particular danger. Against this background, severe pain syndrome and a sharp drop in blood pressure are observed. Often such attacks pose a mortal danger to the patient.
Treatment of glomerulonephritis in children
A major role in the treatment of glomerulonephritis in a child is given to:
- Bed rest with possible further transfer to semi-bed rest if the condition improves.
- Following a diet. The products are carefully boiled and mechanically processed. Soups with vegetable broth, dairy products, stewed vegetables, and cereals are allowed. When the process subsides, well-processed meat and fish are added.
- Fluid restriction, which is prescribed based on diuresis of the previous day (on average 3-4 glasses per day).
- Eliminate salt. After increasing diuresis and normalizing blood pressure, it is allowed to add a little salt to food.
- Limit foods containing protein (meat, fish, dairy products, eggs are completely excluded). The calorie content of food is maintained by carbohydrates and fats (boiled vegetables, fresh fruits, small amounts of milk in cereals or tea).
In case of severe glomerulonephritis in a child (presence of toxins in the blood, yellowing of the skin, smell of acetone in the mouth), hemodialysis is prescribed - blood purification using an artificial kidney machine.
Video: foods dangerous to the kidneys
Drug therapy
Medicines are prescribed by a doctor based on the form of the disease and the characteristics of its course in a particular child:
- corticosteroids (anti-inflammatory effect) are prescribed for rapidly progressing variants of the disease (Prednisolone);
- antibacterial therapy (in the presence of a bacterial infection) with drugs with low nephrotoxicity (penicillins, cephalosporins, macrolides): Penicillin;
- Erythromycin;
- Empiox;
- Eufillin;
- Reserpine;
- Furosemide;
Photo gallery: drugs for inflammation of the glomeruli in children
Prednisolone helps quickly reduce inflammation
Curantil improves blood supply to the kidneys
Furosemide helps fight swelling
Captopril is prescribed for high blood pressure
Erythromycin fights bacterial infection