- Buy the first shoes for a child who is just starting to walk independently, with a small preventive arch support (a special insert in the shoes that gently helps form the correct arch of the foot).
- Spend some time doing specific leg exercises. For example, a child may walk alternately on his toes and heels, on the inside of the foot and on the outside. Another exercise is to stand still and roll from your toes to your heels (when rolling onto your heels, lift your toes up). The most common and effective exercise is with a sports stick. You need to put the stick on the floor, put the baby on it (barefoot or in socks, most importantly - without shoes), and perform side steps on it. In this case, you need to ensure that the stick is strictly across the foot at all times.
Causes of the problem
Recent studies have demonstrated that some form of foot deformity occurs in 40% of patients. Not all of them go to the doctor: many simply cannot detect the disease in the early stages. According to statistics, children and adolescents most often suffer from flat feet. The disease predominantly affects girls, which is associated with weakness of the female musculo-ligamentous system.
Doctors identify the following causes of flat feet in children:
- Injuries. Suffered fractures, ruptures of ligaments and tendons provoke foot deformities. Surgery may be required in the future to treat the problem.
- Paralysis, which leads to weakening of the muscles of the foot and ankle.
- Past diseases, in particular rickets, which disrupts the structure of ligaments and bone tissue.
- Static factors. Practice shows that in more than 80% of cases of flat feet in children, the causes are associated with wearing the wrong shoes (the wrong size, worn out, hard, etc.), excess weight, and excessive physical activity.
All of these factors can cause flat feet in a child. Its congenital form is much less common in children. It is associated with genetic abnormalities and is most often accompanied by other problems of the musculoskeletal system.
Understanding the cause of the disease is an important condition for its cure.
Recommendations for parents
It is extremely important to choose the right shoes for babies. Choose only good and high-quality shoes.
Be sure to remember the following recommendations:
- The baby should not wear shoes that do not secure the ankle joint. Avoid flip-flops, house slippers, strappy sandals, and soft winter boots.
- All shoes a child wears must have a rigid, solid heel. Lace-up boots are recommended. For summer shoes, it is preferable to have a clasp.
- Never buy shoes for a child to grow into. In loose shoes there is a high risk of improper foot formation. Tight boots also lead to foot deformities.
- Don't let your child wear someone else's shoes. It is completely unsuitable for the baby, since it has already been trampled under someone else’s foot.
- Avoid rubber and synthetic boots.
May your baby's feet always be healthy!
How to tell if teenagers and children have flat feet
It is not easy to notice childhood flat feet in the early stages, because at first the baby does not express complaints about health and well-being. Therefore, many adults wonder how to understand whether their child has flat feet.
To notice the problem in a timely manner, you must:
- visit an orthopedist regularly: once a quarter with a baby up to one year old, and then once a year;
- monitor whether the baby walks correctly and whether his legs and back hurt.
Doctors give a lot of advice on how to find flat feet in children, how to identify it, and then how to cure it.
Particular attention should be paid to the first symptoms of the disease:
- the child reports pain and heaviness in the legs after walking;
- he is worried about his feet, ankles, knees or lumbar region;
- the child’s shoes wear out from the inside, the heel wears down unevenly;
- the baby began to limp on one leg;
- posture has changed.
There is a simple test on how to determine flat feet in a child at home. To conduct it, you need to smear the soles of your baby’s feet with watercolors or greasy cream and ask him to stand on a white sheet of paper. Let the baby not move his legs for 1-1.5 minutes. After this time, take the sheet in your hands and examine the prints left on it.
Ideally, the “traced” foot should have the shape of a bean: there is a recess on the inside, occupying at least 50% of the width of the print. If it is too small or missing completely (the entire sole of the foot is shown), there is cause for concern. If the child who received this test result is already six years old, if he regularly complains of pain in the legs, be sure to consult an orthopedic doctor to clarify the diagnosis.
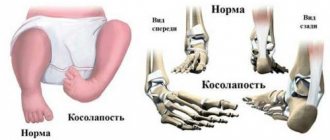
Degrees of flat feet in a child
Doctors distinguish the following types of flat feet in children, depending on the severity of the disease:
- First stage (mild flat feet)
There may be no deformity of the foot, but after a long walk, children experience pain and heaviness in the legs, and swelling may appear. Only a doctor can find out that a child has flat feet. Already at this stage you need to think about how to correct flat feet in adolescents and children.
- Second stage (combined flatfoot)
The longitudinal and transverse arches of the foot are weakened, the deformation is noticeable even by eye. The child constantly complains of pain in the ankle, knees, and lower back, swelling occurs, a change in gait is observed, and joint damage is possible.
- Third stage (severe flat feet)
Foot deformation is noticeable even to a layman; the disease provokes curvature of the spinal column and deterioration of posture, gait becomes forced and unnatural, and lameness may appear. The adverse consequences of advanced flat feet in children are arthritis and arthrosis, which are difficult to treat.
Physiotherapeutic treatment
Such procedures are prescribed for any stage of the disease. They allow you to restore mobility in joints and improve metabolism in tissues.
The following physiotherapy procedures may be recommended:
- Shock wave therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- paraffin-ozokerite application.
Electromyostimulation is quite popular. In this procedure, electrodes are applied to problem areas. Then a weak current is applied. “Forced” training of muscle tissue occurs.
Features of diagnosing flat feet in children
The definition of flat feet in preschool children has its own characteristics compared to the diagnosis of adult patients. In children aged 1-2 years, the foot is absolutely flat, and its anatomically correct shape develops gradually as the baby begins to walk independently. Until the age of three, the deepening of the arch of the foot is filled with fatty tissue and is therefore not noticeable. It is extremely difficult to see the disease before 3-4 years of age; only a professional orthopedic surgeon can do this.
By the age of five, the baby walks a lot, and therefore the longitudinal and transverse arches of the foot are formed, and the tone of the ankle muscles increases. In children at this age, flat feet can be noticed, especially if it has developed to degree 2-3.
The symptoms of the disease are especially pronounced in school-aged children. Foot deformity is noticeable “by eye” or can be easily determined using a home test. Characteristic symptoms appear: children report fatigue and pain in their legs in the evening, swelling is possible.
Is it possible to cure flat feet in children? Yes, because until the age of 14-15 the foot is still developing and can be corrected. To eliminate the disease at 5-6 years old, gentle measures are enough: baths with salt or medicinal herbs, physiotherapy, exercise therapy.
By the age of ten, a child’s foot is practically no different in structure from an adult’s. At this age, excessively intense physical activity or excess weight can provoke foot deformation. The clinical picture of the disease is well defined, so diagnosis is not difficult.
To diagnose flat feet in children, you need to visit an orthopedist in a timely manner. He uses methods such as external examination, studying the phases of walking, calculating the biomechanics of walking and other methods.
Orthopedic massage mat
It is recommended for the baby to go barefoot. However, the surface on which the baby steps must be uneven. For example, it could be land or grass outside the city. This event will allow you to exercise your foot muscles in a variety of ways.
You can use a special orthopedic mat for flat feet for children for such purposes. You can perform all physical exercises on it. Such a mat causes irritation of the receptors on the baby’s foot. As a result of the provoked impact, the foot is formed correctly. In addition, it has a beneficial effect on the nervous system.
How to deal with the disease, can it be cured?
Doctors recommend starting to treat the disease as early as possible. To recognize it in time, you need to monitor the child’s well-being and visit an orthopedist at least once a year. When the first symptoms of curvature appear, you should consult a doctor. It is advisable to start therapy before the age of 12-13 years.
Is it possible to cure flat feet in teenagers? Yes, but it will be more difficult to do than in childhood. After 14 years, the foot hardens and is difficult to treat. In advanced cases, surgery may be required to achieve improvement. However, do not despair; we must fight this disease in any case.
Treatment of flat feet in children involves the need to eliminate the root causes of the deformity, otherwise the result will not be achieved. For therapeutic measures to be effective,
you need to follow these steps:
- Relieve increased stress and eliminate the risk of injury
During the period of treatment it is necessary to abandon sports training. It is especially important to stop participating in sports such as dancing, weightlifting, skating and jumping.
- Review your child's diet
If the baby is overweight, a low-calorie diet is recommended. For children with normal body weight, a diet rich in vitamins, calcium and phosphorus is recommended.
- Choosing the right shoes for your baby
The system of measures on how to treat flat feet in teenagers or preschoolers always requires the right choice of shoes. It is unacceptable for a child to walk around in old, worn-out shoes, tight shoes or boots “for growth”, models “inherited” from older brothers or sisters. The “correct” shoe should have a heel of 1-1.5 cm, a hard back and a soft top.
If the child is severely deformed or the disease is severe, surgical treatment is indicated. It may involve cutting and lengthening tendons, securing bones in the correct position with implants or knitting needles. All of these methods are traumatic and require a long period of rehabilitation, so doctors try to resort to them as a last resort if conservative therapy does not produce results.
How to cure an illness: basic methods
The medical approach to treating flat feet in children involves a complex effect.
The following main techniques are used:
- Taking medications
This method is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease, not its root cause. It involves taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics to help relieve pain.
2.Healing baths
This procedure improves blood circulation and tissue nutrition, increases muscle tone, relieves discomfort and swelling.
The following recipes are effective:
- You need to prepare two basins: one with hot water, the other with cold water. First, you need to put your feet in the first for a couple of minutes, and then in the second for 15 seconds. This manipulation should be repeated several times.
- Add a tablespoon of sea or table salt to a liter of heated water and stir thoroughly. Lower your legs for a quarter of an hour. After the procedure, cover with nourishing cream.
- Add ½ teaspoon of fir oil to a liter of warm water. Dip your feet into this mixture and hold for 30 minutes. As the contents of the basin cool, add hot water.
Baths are recommended to be done in the evening. They relax the child and are a physiological method of relieving stress and fatigue.
3.Wearing orthopedic shoes
Treatment of flat feet in adolescents and children always involves the use of orthopedic
devices that help keep the leg in an anatomically correct position. There are insoles for the front and back of the foot, heel supports and other devices.
4.Therapeutic exercise
This is a method recognized by doctors on how to correct flat feet in a child. It helps strengthen the muscular-ligamentous system, raise the arches of the feet and correct the gait. To achieve results, exercises must be performed daily for at least 20-30 minutes. Preschoolers should be supervised by parents to ensure that all exercises are performed correctly.
The following activities are useful for flat feet:
- walking on toes and heels;
- drawing figures in the air with a toe;
- rolling balls with feet;
- walking on a massage mat, sand, grass, etc.
In preschool age, gymnastics, selected by an orthopedist, is considered the most effective method of foot correction.
5.Massage
If children have flat feet, treatment necessarily includes manual therapy. Massage helps strengthen muscles, restore lost functionality of the foot, and get rid of pain and heaviness in the legs.
Physiotherapy includes rubbing, pinching, bending and straightening fingers, stroking the ankle and other manipulations. It is better to perform a massage after a relaxing herbal bath.
The answer to the question “The child has flat feet, what should I do?” should be given by a qualified doctor based on the results of the diagnosis.
Self-medication is not only useless, but can even worsen the situation. To recognize the disease in a timely manner, you need to be attentive to your child and notice the first symptoms.
Exercises while sitting on the floor
1. Alternately and simultaneously pull the toes of your feet towards you and away from you.
2. Bend your knees and place your feet on the floor. Spread your heels to the sides and return to i. P.
3. Bend your knees and place your feet on the floor. Alternately and simultaneously lifting the heels from the support.
4. The legs are bent at the knee joints, the hips are apart, the feet are in contact with each other along the plantar surface. Abduction and adduction of the heels with emphasis on the toes.
5. Sliding movements of the foot of one leg along the shin of the other, while simultaneously covering the surface of the shin. Same with the other leg.
6. Sitting, legs bent at the knee joints, feet parallel. Raising your heels together alternately.
7. Flexion and extension of the feet, squeezing and unclenching of the fingers, circular movements in a maximum circle in both directions, turning the feet with the soles inward.
8. Raising the heel of one leg while dorsiflexing the foot of the other leg.
9. Grabbing small objects with your toes and moving them to the other side. Also with the toes of the other foot.
10. Sitting on the floor, legs straight, hands resting behind, spread your knees, pulling your feet until the soles of your feet touch each other.
11. Capturing and holding a ball (medium size) with two feet, moving it from place to place.