Author's rating
Author of the article
Shutofedova Ksenia Yurievna
General practitioner
Articles written
578
about the author
Children periodically suffer from colds. They are accompanied by nasal discharge and inflammation of the mucous membrane of the throat with a pink or red painful lesion - signs of pharyngitis. Despite the fact that it is not considered a dangerous disease, treatment of pharyngitis in children is best done in the initial stages. Untimely intervention can develop from an acute form of the disease into a chronic one.
Pharyngitis is characterized by seasonality. Children suffer en masse from acute respiratory viral infections in winter, autumn, and the off-season.
At the age of up to one year, due to limited contact, babies are less susceptible to the disease, and from one to two years it is necessary to be vigilant and stop the disease at the first minor symptoms. Children of any age suffer from pharyngitis, and quite often there is a logical explanation for this - the body’s fragile immune system.
More about the disease
Acute pharyngitis is called inflammation of the back wall of the pharynx; the cause of the disease can be respiratory infections or stomatitis. The chronic form of the disease is often associated with the state of the digestive system, especially the stomach. Treatment of such an ailment is successfully carried out using traditional methods that relieve sore throat and soften cough.
In children under two years of age, the disease is very severe; in addition to the throat, inflammation spreads to the entire nasopharynx and is often accompanied by catarrhal rhinitis. The cause of the disease can be:
- hypothermia;
- inhalation of gases that irritate mucous membranes or dust;
- eating food that is too cold;
- stomatitis;
- viruses.
Acute pharyngitis is immediately manifested by a sore throat and a severe dry cough. The chronic form is milder - sore throat and cough, but with exacerbation the symptoms intensify.
Classification of pharyngitis in children
Types of pharyngitis in patients:
- Traumatic.
- Allergic.
- Infectious.
- Manifested due to contact with an irritating factor.
Therapy is selected based on the diagnosis of a specific type of pharyngitis.
The disease can be acute or chronic. If a child gets pharyngitis in the acute stage, the mucous membrane immediately becomes inflamed.
In chronic pharyngitis, inflammation is sluggish and lasts a long time with changing stages. Chronic pharyngitis often occurs due to improper treatment of the acute stage, but can also occur as an independent disease.
The severity of inflammation affects the nature of chronic pharyngitis:
- Catarrhal form. A sign is hyperemia of the mucous membrane.
- Atrophic. Inflamed tissues dry out and become thinner.
- Hypertrophic. The inflammatory process grows, spreading to the tissue.
- Mixed form.
Signs of the disease
According to the form of manifestation, inflammation can be:
- sharp;
- subacute;
- chronic.
As mentioned above, acute pharyngitis is either an independent disease or a direct consequence of other diseases; often its cause is stomatitis, tonsillitis, tonsillitis or adenoiditis. In this case, the symptoms of one of the listed diseases go along with the signs of pharyngitis itself. In such cases, treatment should be comprehensive.
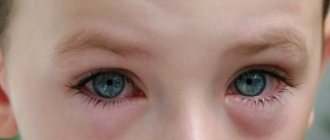
Older children may talk about a dry and sore throat, all this goes along with a high temperature - 38 ° C. Newborns cannot tell about pain, so a baby’s illness can be determined by external signs. The baby becomes lethargic, sleeps and eats poorly - this is how the acute form of the disease manifests itself. In any case, only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis after examining the pharynx. Acute pharyngitis makes itself felt by redness of the back of the throat and swelling. The viral form of pharyngitis is usually observed in the presence of acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections.
In severe cases, the oral mucosa becomes covered with blisters and red dots. In addition to poor sleep and appetite, children may experience other symptoms characteristic of diseases associated with pharyngitis - runny nose, high temperature, cough, conjunctivitis. The younger the child, the more severely he suffers from the disease. A newborn may also experience the following symptoms:
- breathing problems;
- mucus and pus from the nose.
The appearance of such discharge usually indicates that an acute form of rhinitis occurs along with pharyngitis, which somewhat complicates treatment.
Stomatitis, if it is the cause of pharyngitis, manifests itself in the appearance of ulcers in the baby’s mouth. The child may also develop bad breath and a white tongue due to plaque.
Causes of pharyngitis
Even if the baby’s mother behaves like a real mother hen and tries with all her might to protect her child from the disease, it is not a fact that pharyngitis will pass by. There may be several reasons for the onset of the disease at such a young age:
- Rare walks. A growing child needs to spend at least several hours a day in the fresh air - this is a guarantee that the immune system will develop correctly and no pharyngitis will be scary for him in adulthood.
- Constantly being in a room with dry air and a temperature above 25 degrees. It would seem that in such conditions it is not at all possible to get sick, however, in fact, dry air very much irritates the mucous membrane and pharyngitis develops quite quickly. To avoid the need for treatment later, you should ventilate the room as often as possible, and if necessary, purchase a device for humidifying the air.
And pharyngitis itself can be caused by various pathogens, and self-medication depends on the nature of the disease. In infants, pharyngitis can be of the following types:
- Bacterial. It practically never occurs in infants. The cause is pathogenic bacteria – streptococci and staphylococci.
- Viral. But this, on the contrary, is the main cause of sore throat in children under one year old. Transmitted by airborne droplets.
- Pharyngitis caused by exposure to irritating factors. This is exactly the disease that occurs from dry air and other conditions unfavorable for babies. Treatment should begin with the elimination of those same irritating factors.
How to treat pharyngitis and can it be done with folk remedies?
Treatment is prescribed by a local pediatrician or otolaryngologist. Depending on the presence or absence of concomitant diseases, treatment of pharyngitis is carried out in different ways - from drug treatment to traditional medicine methods.
If the disease develops on its own, it is enough to eliminate the symptoms - do foot baths, apply warming compresses, give the child milk and honey, gargle and do inhalations. Such measures are usually sufficient. If the cause of pharyngitis is another ailment, for example, stomatitis, then you first need to cure it.
For children under two years of age, any treatment is suitable. In such cases, Dr. Komarovsky advises limiting yourself to dry neck compresses, drinking plenty of fluids and restorative medications.
The worst situation is for infants and children under 1 year old - they are difficult to treat at home, too many common folk remedies are not suitable as therapy. The maximum that is available to you is compresses and massage. Warming compresses should never be used if the child has a high temperature.
Prevention
It is impossible to cure granulosa pharyngitis completely, but you can extend the period of calm . To do this, parents need to follow a number of preventive measures :
- Constant wet cleaning and air humidity control. Sleeping in a dry room for a child with a predisposition to chronic hypertrophied pharyngitis can be dangerous.
- Protect your baby from harmful factors. For example, tobacco smoke or dust.
- Timely and complete treatment of any disease.
- Hardening and strengthening the immune system in general.
Source
What compresses are suitable for treatment?
Honey and mustard
This compress perfectly removes symptoms of the disease such as cough and tickling. To make a medicinal cake, mix honey, dry mustard, any vegetable oil and vodka in equal proportions. The fabric is coated with the mixture, one half is wrapped around the breast, the other on the back.
The compress is secured with a bandage, and pajamas are put on top. If the child is too small, then you can leave the compress on for a maximum of 2 hours. If after this time no allergic reactions have occurred, and the baby himself tolerated the procedure normally, then the warm-up period can be increased.
Honey and fat for cough
Mix honey (2 tablespoons), vodka and pork or goose fat in approximately equal proportions - you will have to experiment a little until you get a creamy mixture. You need to rub this ointment on the baby’s back, chest and feet. Put on warm socks, wrap (only!) the torso with film and put the baby to bed.
Potato compress
This type of compress is the simplest and most gentle; it consists only of warm mashed potatoes. Place the pulp in a bag, distributing it evenly, wrap the whole thing in several layers of cotton cloth and place it on the baby’s chest. Make sure that the compress is not too hot - it should be warm. The temperature is regulated by the cloth - as soon as the compress begins to cool, remove one layer. Warm-up time is an hour.
Classification and forms
Granular pharyngitis can be primary or secondary.
In the first case, the disease occurs in an acute form and is an independent pathology .
The secondary type of granulosa pharyngitis is a complication of previous diseases. Both forms of the disease are characterized by a chronic course and a tendency to frequent relapses.
This type of pharyngitis can accompany every cold in a young patient.
Granular pharyngitis can develop in three forms of the inflammatory process:
- acute type (rapid development of symptoms and disease duration on average one month);
- protracted form (symptoms of the disease persist longer than one month);
- chronic variant (relapses of the disease can occur at short intervals, the period of exacerbation lasts on average six months).
How to cure a cough
Acute pharyngitis can be cured not only with the help of compresses; there are several other methods that Komarovsky advises:
- The baby must move, do not forbid him to do so. The more active the child is, the better the bronchi will be cleared of mucus;
- You can periodically gently pat the baby on the back, this will also help mucus and phlegm move away from the bronchi faster;
- Give your baby warm water more often.
Massage your baby's feet with honey as a warming agent. You can also use plain sunflower or olive oil and special baby creams for therapeutic massage.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is based on the results of pharyngoscopy. If there is a possibility of a bacterial etiology, a swab is taken from the back of the pharynx.
Visual examination of the pharynx and larynx by an otolaryngologist - pharyngoscopy
In the acute form of pharyngitis there are:
- redness, swelling, infiltration of the throat;
- uneven surface of the mucous membrane of its posterior wall;
- various types of inflammation of the palate, ridges on the sides of the pharynx;
- inflammation of the follicles in the larynx in the form of red grains,
- in rare cases, the appearance of pinpoint hemorrhages on the back of the larynx.
When suffering from chronic pharyngitis, symptoms are observed: the laryngeal mucosa is loose, not completely inflamed, but partially inflamed.
Pharyngitis must be distinguished from other types of nasopharyngeal diseases. Often, in its chronic course, an examination by an allergist, immunologist and gastroenterologist is necessary.
Mustard wraps
Mustard plasters are not suitable for babies under 1 year of age - their effect is too aggressive. But there is an alternative - mustard wrap, which is much safer. For wrapping, dilute 1 spoon of mustard in 0.5 liters of water. Soak gauze folded in several layers in the liquid and apply it to the baby’s back or wrap the cloth around the entire torso. Wrap the child in a blanket or cover with a warm towel. Do not keep this compress for more than 5 minutes. After removing the gauze, wipe your baby with plain warm water. Usually it is enough to do this procedure four times for acute pharyngitis to go away.
Reviews from parents
Most parents who have experienced their children getting sick with pharyngitis declare the significant danger of this disease for the child’s body. Moreover, there is a peculiar pattern that the younger the baby, the greater the likelihood of severe complications. It is possible to avoid any consequences, but only if you seek help from a pediatrician from the very first days of symptoms. It is much easier to prevent the initial stage of acute pharyngitis than to treat the disease when the disease is at its peak.
Fighting stomatitis
If the cause of pharyngitis is stomatitis, then it must be treated first. Children are prescribed Shostakovsky ointment, which needs to be used to treat ulcers 5 times a day, and Solcoseryl. These drugs have a healing effect.
Dr. Komarovsky categorically does not recommend treating infants with Fluconazole, Cholisal gel, Metrogyl denta and Lidochlor gel. These products are suitable for children over 1 year of age, but Metrogyl denta can only be used from 6 years of age.
Treatment of the disease is effectively carried out using folk remedies that are safe for the baby. Stomatitis can be treated with calendula - just soak a cotton swab in the solution and treat the wounds in your mouth with it.
Baking soda is also an excellent healing agent and helps eliminate the symptoms of stomatitis. Dilute 1 tsp. soda powder in 1 tbsp. warm water (necessarily boiled). Treat ulcers with this solution in the same way as with calendula.
Some people advise feeding your baby blueberries, but it’s better not to risk it - the berry can cause allergies.
General information
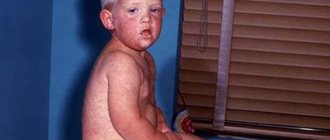
Granular pharyngitis in a child - photo:
In a broad sense, pharyngitis is an inflammation of the pharynx , which is a characteristic symptom of diseases such as acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, tonsillitis or bronchitis.
In some cases, the disease turns into an independent pathology and becomes chronic. If the inflammatory process does not extend beyond the anatomical boundaries of the pharynx, then in medical practice the term “granular pharyngitis” is used to designate this pathology.
Unlike the simple form of the disease, this type of pathology does not end with the child’s complete recovery, and therapy is characterized by a long process.
Possible complications
In the case when children experience symptoms of acute pharyngitis, treatment should begin immediately, but it also happens that parents self-medicate, which is why the disease progresses and can lead to certain complications.
First, the disease becomes chronic, and then side diseases develop:
- hearing loss;
- purulent otitis;
- inflammation of the retropharyngeal space;
- purulent mediastinitis.
With the bacterial form, other diseases can develop, including rheumatism and kidney disease.
Symptoms of the disease in infants
Pathology in infants can be recognized by the following signs:
- temperature rises to 39 degrees ;
- the baby often cries and is capricious;
- regurgitation occurs ;
- the child loses appetite and may refuse to feed;
- sleep is disturbing and constantly interrupted;
- the baby behaves restlessly ;
- There is often a slight cough .
The disease is combined with acute inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx and nose, a runny nose , and the baby’s general condition can be described as weakened.
Treatment options
In the process of treating a disease in children, it is important to constantly give infants plenty of warm drinks .
This will help warm the throat and help wash away pathogenic microorganisms from the surface of the mucous membrane.
The air in the room where the sick baby is located must be sufficiently humidified - dry air is an additional irritant for the mucous membranes.
The main treatment involves taking medications.
But since many of these medications may have contraindications for infants, the pediatrician should conduct a preliminary examination that will show which medications the child will tolerate normally.
Important! Hospitalization for pharyngitis at this age is not required and treatment is performed on an outpatient basis, at home. The entire process usually takes several days.
Infants with illness in the absence of complications are prescribed complex treatment including the following drugs:
- compositions for lubricating the laryngeal mucosa (Lugol's solution);
- immunomodulators (aflubin, viferon, immunoflazid, laferobion);
- antibacterial agents (the drug depends on what pathogen was identified);
- inhalation solutions (saline, decasan);
- ibuprofen or paracetamol as antipyretics (if the temperature rises above 38 degrees);
- antihistamine drops and syrups (zodak, zyrtec, fenistil, cetirizine, erius).
For the treatment of pharyngitis in newborns, sprays, aerosols and lozenges are not used, since when treating the larynx with sprays, laryngospasm may occur in infants, and children at this age simply cannot dissolve lozenges and tablets.