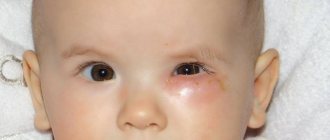
The position of the fetus during pregnancy determines how a woman’s birth will proceed. If the baby is in a normal position, the woman will be able to give birth on her own. If the baby is not located as nature intended, some manipulations may be required in the prenatal period or even a cesarean section.
How should the fetus be positioned depending on the week of pregnancy?
The position of the baby in the early stages depends on where the egg is implanted. Most often it is implanted to the back wall of the uterus; this position is considered the best, since the woman begins to feel movements earlier, and it is easier for the doctor to track the fetal pulse. Less commonly observed is the location on the anterior wall of the uterus; it is a variant of the norm and does not cause dangerous deviations.
A low position can be dangerous. If this option is noted for placing the baby in the stomach for weeks until 31-32 weeks, the doctor does not consider it a deviation: often the baby moves to the upper parts of the uterus. In cases where this does not happen, the doctor diagnoses placenta previa, which is an indication for a cesarean section.
The position of the baby in relation to the birth canal may also be different. In the early stages it can easily change; up to 32 weeks, the norm is a constant change in the position of the fetus. However, before birth, the baby should lie head down; otherwise complications will arise. It is better if the back is pressed against the anterior uterine wall, the position will be longitudinal (the line from the tailbone to the back of the baby's head is parallel to the uterine axis).
The oblique and transverse position is considered incorrect in the later stages.
At what time does the issue of presentation become relevant?
Since the fetus is constantly moving and changing its location in space, in the first and second trimesters you should not worry if the ultrasound results show that the baby is lying head up or perpendicular to the birth canal. The child will have time to move many times.
In the third trimester, the fetus increases greatly. The space in the uterus becomes insufficient for active movements. By week 34, the baby most often takes its final position. At this stage, it is important that the baby is positioned head down. If a pelvic or transverse presentation is noted, complications are possible; this phenomenon is observed in approximately 4-6% of cases. If the position of the baby in the stomach at this stage is incorrect, the doctor prescribes a caesarean section.
Pregnancy by week: fetal development and sensations
From the moment a woman finds out about pregnancy, it is necessary to take an extremely responsible approach to her health, listen carefully to her body and actively prepare for the upcoming birth. It is also important to understand what exactly happens inside the uterus: how the first weeks after conception pass, how the fetus develops in the second and third trimester, how the body prepares for labor in the later stages. We will try to answer all these questions in this article.
Pregnancy in the first trimester
If you are planning a pregnancy, then the last one can occur in any month of active attempts.
And since the first week will not manifest itself in any way symptomatically, then take a responsible approach to your health even at the planning stage. Firstly, give up all bad habits: drinking alcohol, smoking tobacco and hookah, taking illegal substances, etc. Also try to maintain a wakefulness and rest regime, be sure to get enough sleep. The diet should be dominated by vitamin foods (vegetables, fruits, berries), dairy and fermented milk products, and lean meat. At the planning stage, have all your teeth treated by a dentist, since during pregnancy their condition can rapidly worsen, but there will be no possibility of resorting to anesthesia. Week 2
Conception can be considered in the 2nd week of pregnancy.
Thus, the largest and healthiest egg with nutritional components leaves the ovary and is sent through the fallopian tube, where a sperm awaits it. At the site where the egg came off, a yellow spot appears, and if in the future fertilization is successful and the zygote attaches to the uterus, then as a result of the production of hormones by the spot, a feeling of dizziness, drowsiness, and nausea occurs. In the 2nd week, it is important to maintain normal vaginal pH - stop douching, do not use any gynecological suppositories. Wash with a special intimate hygiene product, herbal decoctions or baby soap. Week 3
The egg passes into the fallopian tube, where it is fertilized by sperm. As a result of conception, a zygote is formed, and this moment can be considered the birth of the fetus. The egg moves through the fallopian tube and attaches to the wall of the uterus. The corpus luteum (spot) produces progesterone, which supplies the zygote with the necessary moisture. In the 3rd week, women who listen carefully to their body may notice the first signs: pulling in the lower abdomen, nipples swelling and becoming sensitive.
4 week
The woman experiences slight malaise, lethargy and drowsiness - the body is actively adjusting to bearing the fetus.
Brown discharge may appear from the vagina. Some also report a nagging or aching pain in the lower abdomen. If all of the above symptoms are present, it is advisable to consult a gynecologist to rule out ectopic pregnancy. In the 4th week, cell division of the zygote continues and its second layer is formed, which acts as a kind of barrier from negative factors. Week 5
During this period, pregnant women may notice toxicosis: nausea and even sometimes vomiting in the morning, intolerance to certain smells, changes in taste and food preferences.
This period is accompanied by a radical change in hormonal levels, which may be accompanied by mood swings, increased nervousness and anxiety, lethargy and drowsiness. The embryo at the 5th week gradually transforms into a fetus in which the neural tube develops, and from it, in turn, the primary nervous system and spine. The first contraction of the fetal heart muscle also occurs at this stage. The formation of the gastrointestinal tract organs occurs. Week 6
There is an increase in toxicosis, and the need for proper rest increases.
Many pregnant women note dehydration and an increased need for fluid. During this period, body weight may decrease slightly. The development of the internal organs of the fetus continues. Week 7
The macula, which produced pregnancy hormones, disappears - the function is responsibly transferred to the placenta.
During this period, the threat of miscarriage increases, so women who have pathologies of the hormonal or endocrine systems need to be especially attentive to their health. Pregnant women who have different Rhesus blood levels with their husbands also need to beware. As for the fetus, on ultrasound it gradually straightens to its full height, which is up to 1 cm. Gradually, brain cells are formed, the stomach and lungs develop. Toxicosis in a pregnant woman may intensify. Week 8
The dangerous period of gestation is coming to an end.
Pregnant women note strange taste preferences, such as chewing a piece of chalk, drinking salty water, eating herring with cake, etc. Doctors recommend eating small portions up to 7 times a day. A woman’s uterus gradually enlarges along with the mammary glands. The child develops taste and smell receptors. At week 8, you can try to determine the sex of the baby. Week 9
The appearance of the pregnant woman changes slightly: veins become more visible, and the breasts swell significantly.
On an ultrasound you can see the first movements of the fetus. He also ends up developing the convolutions of his brain. Week 10
The uterus continues to actively expand.
Symptoms of toxicosis become less and weight begins to increase rapidly. The growing uterus puts pressure on the bladder, causing the urge to go to the toilet. The child grows up to 4 cm. Week 11
During this period, the risk of diabetes in a pregnant woman increases - control the consumption of sweets.
As a result of increased metabolism, you may feel hot and your nails and hair may grow stronger. The embryo develops an iris, an excretory system, and its own metabolism. Week 12
Pregnant women may experience digestive problems, in particular constipation. Also during this period, the belly continues to grow, which affects posture and puts strain on the lower back. An ultrasound will diagnose the presence or absence of Down syndrome in a child.
Pregnancy in the second trimester
Week 13
Digestive problems may continue: bloating, flatulence, constipation, etc. The rudiments of baby teeth are formed in the fetus.
During this period, the child’s intestines are already able to absorb food. Week 14
The pregnant woman’s health becomes a little better, but it’s harder to move - her legs and lower back get swollen and quickly get tired.
The baby's urine is released into the amniotic fluid. Week 15
The expectant mother notices a dark hormonal line that extends from the navel to the pubis - it will disappear some time after giving birth.
Ultrasound already suggests the likely date of birth. Problems with constipation are replaced by high blood pressure. The fetus can clench its fists and begins to move more actively in the uterus. Week 16
The active development of the fetus continues, its weight gain and growth increase.
Week 17
The load on the pregnant woman’s heart muscle increases, but the uterus stops squeezing the internal organs.
The fruit is about 16 cm long. It also develops its own immunity. Week 18
A woman gains an average of 0.5 kg per week.
Severe swelling and sodium deficiency may occur, which leads to problems with fluid outflow. The child's facial features are already visible and he is able to hear sounds. Week 19
As the uterus enlarges, the nagging pain in the lower back becomes more and more noticeable.
The body gradually prepares for childbirth by relaxing its joints. The fetus develops a central nervous system with a brain and a stomach. Week 20
The fetus may actively kick, causing slight discomfort to the mother.
The growing uterus puts pressure on the lungs, causing shortness of breath. During this period, false contractions sometimes occur, and mucus may be released from the vagina. 21 weeks
The expectant mother may complain of heartburn, so a special diet will not hurt.
The fetus begins to gradually store fat. Week 22
The pregnant woman notices severe swelling of the face, neck, and limbs.
At the same time, the skin becomes healthier, elastic and youthful, the hairline thickens. The baby develops eyebrows, weight can reach 0.5 kilos, and height up to 25 cm. Week 23
The uterus grows and expands, stretching the skin and leading to mild itching.
Colostrum may be released from the nipples. The bones of the sacrum gradually soften, which leads to disruption of the usual gait. There may be numbness and tingling in the extremities as a result of swelling. The baby develops a sucking reflex. Week 24
Already during this period, training or even real contractions may appear (the main thing is not to be nervous and avoid psychologically and physically stressful situations). The fetus begins to produce growth hormone.
Pregnancy in the third trimester
Week 25
The pregnant woman notices pink skin on her stomach - the uterus continues to expand on the sides.
The weight of the fetus reaches 0.7 kg, and the height is more than 20 cm. The heartbeat can be heard if you put your ear to the stomach. Week 26
The baby’s central nervous system and brain continue to actively develop.
27 and 28 weeks
The placenta begins to produce progesterone, which contributes to the normal course of pregnancy.
Week 29
It becomes difficult for a pregnant woman to walk and perform even basic physical exercises.
The baby is actively growing, his tummy becomes cramped, so his movements decrease. Week 30
During this period, pressure changes may occur.
The baby gradually turns in the tummy to a natural position with his head down. 31 weeks
The woman practically does not gain weight, but the swelling, unfortunately, does not go away, since it is difficult for the kidneys to cope with the increased load.
The fruit has formed by this time. Week 32
It's time to sign up for an ultrasound scan for a follow-up check.
The child gains weight up to 2 kilos and height up to 40 cm. Week 33
The expectant mother notices frequent urges to go to the toilet.
It is better to reduce drinking, making it easier for the kidneys. Week 34
False matches may occur again.
However, if your water breaks, you must immediately go to the maternity hospital. Week 35
The pregnant woman still complains of insomnia, since sleeping late in pregnancy is really uncomfortable.
During this period, the diet should contain foods with sodium and calcium. It's time to pack your bag for the maternity hospital so that it is always ready. Week 36
On average, by this period the weight gain of the expectant mother during pregnancy reaches 12 kg.
It is necessary to refrain from intimate relationships, as they can provoke labor ahead of time. The baby's weight reaches 2.5 kilos, and his height is about 45-47 cm. Week 37
Labor can begin any day.
The mammary glands have fully developed and stop squeezing the breasts - the pregnant woman can breathe easier. Colostrum may be actively released from the nipples. Week 38
At this point, the pregnancy is considered full-term.
The fetus is ready to be born, it turns over less often. The fewer movements the baby makes, the closer the day of birth. Gradually, discomfort appears in the lower abdomen - a nagging pain. Week 39
The baby's head passes into the birth canal, so the belly may visually drop down a little.
The baby’s weight is approaching 3 kg, and his height is 52 cm. Week 40
It’s time for the baby to be born, so be prepared to go to the maternity hospital at any moment. Excessive mucus discharge from the vagina is also a harbinger of imminent labor.
How does pregnancy go after 40 weeks?
41 weeks
It is necessary to understand that prolongation of pregnancy by 2 weeks can be considered normal according to medical standards, which is due to the individual characteristics of the body.
There is no need to worry - just wait. Week 42
According to statistics, only 10% of pregnant women give birth at this stage.
Doctors advise massaging the mammary glands to stimulate the production of oxytocin, a hormone that stimulates uterine contractions. 43 weeks
It is advisable for a pregnant woman to go to the hospital, since the baby’s stomach begins to work independently, digesting food and excreting feces - meconium.
The latter enters the amniotic fluid, which can cause intoxication of the body. 44 weeks or more
is the deadline for pregnancy - you can’t postpone it any further. The grown baby is very cramped in the uterus and lacks air, and the placenta begins to die, which can cause nutritional deficiency. Amniotic fluid contaminated with meconium and urine may enter the baby's gastrointestinal tract.
We tried to describe in detail what changes occur in the female body during pregnancy. It also became known how exactly the fetus is formed and develops week by week, what key points future parents need to pay attention to in order for pregnancy and childbirth to be successful and comfortable.
How to understand how the baby lies in the mother's belly
You can find out how the baby lies in the mother's belly using an ultrasound examination. In the early stages, when the fetus is too small, it is impossible to independently determine its location.
Determining the baby's position by heartbeat
The placement of the child can be determined by the contractions of the heart muscle. It is believed that a heartbeat below the mother's navel indicates that the baby is lying upside down. If the heart is heard at the level of the navel or slightly above, the baby is positioned head up. In the early stages, there is no need to worry, since the baby’s position can easily change. For such a study, you will need an obstetric stethoscope: with its help you can understand how the baby is positioned at home.
How to determine the location of the fetus yourself by kicks
Based on the characteristics of the movements, the expectant mother can independently determine how the baby is positioned.
If shocks are felt under the ribs, the baby lies with his back forward. In this case, most often the stomach and navel protrude forward. If the tremors are felt in the front part, the stomach has become flatter, the baby’s back is on the side of the mother’s back. To independently determine the position of the baby, a woman needs to pay attention to which part of the abdomen the baby is pushing into.
If the tremors are felt above the navel, the fetus lies head down; in the third trimester this is a good sign.
Determining the position of the baby using the abdominal map
A map of the abdomen also helps to understand the location of the fetus. It can be used from the 30th week: the baby at this stage does not become too active, his position does not change much. It is better to draw a map after a visit to the gynecologist: the doctor will determine by palpation where the baby’s pelvis and head are. A woman also needs to carefully monitor sensations: it is possible to determine the position of the child by movements.
Belly map
Non-toxic paint should be used for painting. The doll will help determine the position; It is better to use one that imitates a baby for greater accuracy.
First, determine the position of the head and pelvis. It is better to use data obtained from a gynecologist: this will increase accuracy. But you can try to determine it by some signs, your own feelings. Then the heartbeat is determined. You need to use paint to mark in which part of the abdomen it is heard. After this, the woman notes the movements: this will help to detect the location of the arms and legs. They may be bent or straightened, making them difficult to identify.
How a new life is born at 3 weeks
The egg is fertilized by a sperm outside the uterus: this can happen either in the abdominal cavity directly near the ovary or in the far part of the fallopian tube. Then it begins to divide, gradually moving towards its permanent location. While the morula (the so-called dividing embryo because of its external resemblance to a mulberry) is in free movement, its cells feed on the substances contained in the egg. By the way, at this stage the sex of your future baby has already been determined.
What happens next to the fetus, since in 3 weeks of pregnancy it should have depleted its entire food supply? Having reached the uterine cavity, the embryo already acquires a spherical shape and is called a blastocyst. Having gone through the stages of attachment to the uterine mucosa, adhesion to it, invasion and destruction, the blastocyst is implanted in the place where the placenta will subsequently form. And it is by the end of the 3rd week that the first chorionic villi are formed here, penetrating the mother’s capillaries and coming into contact with her blood. And here it is – free access to adequate nutrition and oxygen! Carbon dioxide and metabolic products of the fetus are released back into the mother's blood. It also sends immunosuppressive substances into the woman’s body at 3 weeks of pregnancy, suppressing the mother’s immunity against foreign protein. After all, the embryo is half composed of heterogeneous paternal material.
What does an embryo look like?
In fact, in our understanding it does not “look” yet, because its dimensions reach approximately 0.2 mm in diameter! Only a histologist under a microscope can assess the direction of development. This is where the fun begins. Embryologists are happy people: at the 3rd week of pregnancy they can see the formation of a new full-fledged life in 250 different cells, because the rudiments of all (!) vital organs and systems are laid precisely at this period, even if they are represented by 2-3-5 differentiating elements. We are talking about the nervous, cardiovascular, excretory system, gastrointestinal tract, osteoarticular skeleton, muscle tissue and primitive hematopoiesis. Visually, the embryo does not at all resemble a person, but, as you know, we are links in evolution, so our embryo goes through all the stages of high organization of matter. And only because of the external and internal similarity with other forms of life at different stages of embryogenesis, scientists cannot annul Darwin’s laws.
Do you want to know what will happen next to your embryo? Watch a short video:
Why you can’t determine your baby’s position in the womb on your own
In the early stages, independent determination of the location is difficult due to the small size of the fetus: the woman does not yet feel movements. Then, when the baby begins to actively move, detection becomes possible, but the high activity of the baby allows him to constantly move in the uterus. He constantly moves and does not stay in one position for long.
The position of the baby in the womb at home can be difficult to track even in the third trimester. Sometimes this can be difficult even for experienced gynecologists: doctors often confuse the baby’s butt and head.
The most accurate method is ultrasound examination.
How can the fetus be positioned before birth?
There are several options for positioning the baby before birth. Not all of them are considered physiological: some can cause dangerous complications. If the presentation is incorrect, you will have to resort to surgery to prevent dangerous consequences and complications during childbirth. The position of the baby in the womb remains almost unchanged after 32-33 weeks.
Longitudinal position
The correct position of the fetus assumes that its tailbone and the back of the head are extended in one line, parallel to the axis of the mother's uterus. It is better if the back is turned towards the mother’s stomach: this reduces the likelihood of complications. The norm is also a position where the baby’s back is located closer to the mother’s back, and the duration of labor may increase. The head should be at the bottom, the pelvis at the top.
Oblique position of the fetus
The baby in the womb may lie diagonally to the mother's birth canal. This option is not considered normal, it can be dangerous and pose a risk of complications during childbirth. In most cases, doctors prescribe a caesarean section.
Transverse position of the fetus
Transverse presentation of the fetus is an indication for obstetrics through surgery. The child is positioned perpendicularly.
Breech presentation
Before birth, the baby may be in a position resembling a sitting position. After 32-33 weeks, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes a caesarean section for obstetrics.
Causes of breech presentation
Malpresentation of a child is observed in the presence of various pathologies that provoke increased activity. Often diagnosed with microcephaly, anencephaly, hypoxia. Often children are born premature. Possible leg or breech presentation with polyhydramnios.
Women's pathologies can also become a cause. The baby often lies incorrectly if the pregnant woman has been subjected to severe or constant stress, is overly tense, or suffers from neuroses. If you have a history of difficult childbirth, multiple abortions and curettages, cervicitis, endometritis, then the likelihood of breech presentation increases.
Why is breech presentation dangerous?
If the position is incorrect, the baby often gets injured during childbirth. Possible injuries to the spine, craniocerebral, hip dysplasia. Hypoxia often develops during childbirth.
Childbirth is also more difficult for a mother whose child is in an incorrect position: ruptures of the vagina, vulva, perineum, and cervix occur more often. The pelvic bones are damaged.
Mental development of a newborn child
According to child psychologists, in addition to physiological needs, the main need of a baby during this period is the need to feel the presence of the mother, the warmth of her body, and the beating of her heart. The presence of an adult nearby who is able to understand his needs and eliminate troubles gives the newborn a feeling of security and forms in him a basic trust in the world - a feeling that the world is reliable and safe. Therefore, the most important thing for the full mental development of a child during the newborn period is the physical presence of parents, mainly the mother.
The emotional state of the newborn and the formation of temperament
Even before birth, the child is able to respond to the emotional state of the mother. All the mother’s experiences, both positive and negative (including stress), are immediately transferred to the child’s psychological state. Therefore, if the mother is constantly nervous or angry, the baby may become capricious and whiny.
The mother's temperament and mood also influence the development of the child's own worldview, attitude towards others and towards life in general.
A newborn's first experience of the world comes from his mother's milk.
Feelings and sensations of a newborn: crying
Mothers should know and remember that a newborn’s feelings and sensations are not differentiated from emotions. The baby communicates his needs to his parents in the only way available to him - by crying. Most often, it is caused by hunger or thirst, the need for warmth, wet or dirty laundry, and various physical inconveniences associated with a static body position or clothing. At first, parents do not distinguish the cry of a hungry child from the cry of a child who is cold or overheated. But the newborn does not yet know what he wants. The kid feels that “something is wrong” and reports it. Therefore, he willingly accepts everything that is offered to him: breasts, a warm blanket, stroking his tummy. After some time, the baby begins to understand that he will be relieved of unpleasant sensations. And then the next time he spits out the pacifier and throws off the blanket with his legs.
Incorrect presentation of the fetus. Types and reasons
Incorrect presentation is oblique. Its extreme form is considered transverse: the baby turns perpendicular to the birth canal. This arrangement of the fetus in the abdomen is possible with tumors of the uterus, with excessive stretching of the organ due to the too large size of the fetus or multiple births.
Breech presentation is divided into breech and leg presentation. The first is considered more favorable. It occurs due to pathologies of the fetus and a history of diseases of the mother’s reproductive system.
If fetal malposition is diagnosed
If there is any position of the child other than the head, you should consult a doctor. The decision on the method of delivery is made individually.
Transverse presentation is an absolute indication for surgery.
If pelvic birth is observed, the decision is made individually, taking into account the sex of the child (it is safer to give birth to a girl on your own than to a boy, since there is no risk of damage to the child’s genital organs), the woman’s age, the course of previous births, and the position of the baby (breech or leg presentation).
Location of the fetus in the uterus by week
Expectant mothers carrying a child remain curious about the correct position of the fetus.
Throughout pregnancy, the baby grows and forms in the woman’s belly. He carries out various movements, changing his position.
The success of the birth depends on what it will be like at the end of the gestation period.
It floats in the amniotic fluid and as the period expires, the embryo occupies one specific position.
This is how the baby prepares to be born. This occurs from 32 to 36 weeks, after which the baby no longer changes location in the uterine cavity.
When does an embryo become a fetus?
The formation of a baby in the mother's womb takes place in two successive stages. In general, during pregnancy, fetal development lasts 40 weeks, or 10 months by obstetric standards.
- Moreover, the first 8 weeks are the embryonic period, during which the most important embryogenesis processes occur. It is during these 8 weeks that the baby is considered an embryo and gradually acquires human outlines, and vital systems are laid down and formed inside its microscopic body.
- Then, starting from the 9th gestational week, the fetal stage of development begins, which lasts until delivery. It is from this moment that the child officially acquires the status of a fetus.
The development and growth of the baby develops systematically throughout pregnancy, week by week.
How to determine the location of the fetus yourself by kicks
In addition to accurately determining the position of the child using ultrasound, you can try to find out on your own where the fetus is.
This must be done carefully so as not to damage parts of the baby’s body. One of the ways to determine it is through the tremors that the baby makes while moving.
Every mother can feel the position of her baby's back by simply running her hand over her stomach. You can also feel the resting legs, and at the very bottom you can feel a certain bulge - the head of the fetus.
This period is characterized by hand tremors in the area of the sacrum or bladder. It is with the help of interpretations that it is possible to determine the approximate location of the child.
- The presence of the baby in the womb, head up, will be characterized by regular tremors above the womb. Where the inguinal folds are located, the movement will be felt most of all.
- The transverse arrangement is characterized by an unusually wide size of the abdomen. A woman may feel pain in the umbilical area due to its stretching. Painful sensations also occur when the baby straightens his head or moves his legs.
- The cephalic location of the presenting part is considered the most common. In this case, the baby will put pressure on the area of the mother’s lower ribs.
This phenomenon occurs at the end of pregnancy. If you run your palm along the anterior abdominal wall, you can feel the baby's head. A presentation that is too low will be accompanied by sudden movements of the baby's head, and the mother will feel the urge to urinate more often than usual.
Then it is recommended to wear a bandage if the placenta is low. It helps prevent premature birth by reducing pressure on the cervix.
After 31-33 weeks, the fetus no longer changes its position and can only move its arms and legs, as well as its head.
If doctors note that the fetus is not positioned correctly, they prescribe special exercises for pregnant women that will help the baby roll over.
Pregnancy Calendar
A woman’s happiness lies in children, therefore, when a pregnant woman receives incredible news about her imminent motherhood, she begins to look for signs of an interesting situation, sometimes gets scared when she doesn’t find them, and gets nervous, which is not very good for the child. The development of the fetus and the sensations of the woman throughout the gestational period are constantly changing, in accordance with the mechanisms laid down by nature itself.
To make it more convenient to navigate the stages of pregnancy and know what is happening to the baby at a specific stage, a pregnancy calendar was created. It examines in detail the entire pregnancy week by week: what changes occur with the baby, what sensations and transformations affect the mother, what is normal, what to be wary of, and other important points.
1st and 2nd obstetric weeks
In fact, there is no pregnancy yet; the processes of the female cycle proceed as usual. In the first week, active egg maturation and preparation for ovulatory processes occur. In the second week, the egg completes development and ovulation occurs, during which the follicle ruptures and the mature female cell leaves the ovary, heading into the fallopian tube.
If sexual contact occurs at this time, then the male sperm at this time is sent to the female uterus, where in order for fertilization to occur, it must meet a female cell.
You need to eat a varied and balanced diet
Third
In the third week, fertilization occurs and the egg is implanted into the uterine wall. After fertilization, the zygote is continuously formed, and the number of embryonic cellular structures increases hourly through continuous division. If on the third day after conception the zygote contains only 8 cells, then already on the next day it consists of 20 similar cellular structures.
They form into a small lump, similar to a blackberry, which moves into the uterine body and is attached to its wall to begin full embryogenesis. During implantation, there is a clear change in the mother's hormonal background; hormones are rearranged in such a way as to protect the embryo and prevent its rejection. In this case, mommy may have brown or pink discharge.
4 week
After implantation of the fertilized egg, the processes of grouping cellular structures begin:
- The inner layer of cells is intended to form the digestive, pulmonary and liver systems;
- The circulatory and skeletal system is formed from the middle layer of cells of the fetal egg;
- The outer cellular layer is responsible for nervous system development, hair or skin, etc.
The umbilical cord is actively being formed and the formation of nervous system and intraorganic structures is taking place. Meanwhile, the patient begins to show the first hints of an interesting situation, such as nausea and breast swelling.
Fifth week
Usually, during this period, women detect a delay and do a test that reliably shows 2 stripes. Pregnant symptoms become more pronounced, accompanied by toxicosis, constant fatigue and drowsiness.
All embryonic systems are actively developing; the baby itself does not exceed the size of a sesame seed. If ultrasound diagnostics is performed at this time, the specialist will be able to detect the number of fertilized eggs in the uterus.
Many people suffer from bouts of nausea during the first trimester.
Sixth
During this period, if pregnancy is already known, the woman should consult a doctor for obstetric registration. Now the baby’s neural tube is tightening and brain structures are forming.
At six weeks, the heart, which has already divided into two chambers, will improve, and the bronchopulmonary structures and features of a small face will continue to actively develop, and phalangeal formations will appear on tiny fingers.
Seventh
The patient experiences toxic ailments, the uterine body enlarges, which affects urination by a noticeable increase in frequency. The internal organ structures of the baby are actively developing, which already reaches a size of about 1.8-2 cm and two grams of weight. Both cerebral hemispheres have already formed, the skeleton and nervous system structures are actively developing.
The body and head have approximately the same parameters, and in place of the tailbone a tiny tail is clearly visible. Blood circulation is well established, and the placental tissues already supply the baby with oxygen and provide protection from the infiltration of infectious pathogens and toxic substances.
During the ultrasound examination, you can already notice that the small embryo bends its knees and elbows for a more convenient position. The lips and nose are already visible on the face, tooth buds are beginning to form, and the auditory system is forming. The baby is developing at an accelerated pace, which promotes the growth of the uterine body, which causes slight pulling sensations in the abdomen. The nipples on the chest begin to darken, and a dark line appears on the tummy from the navel.
Eighth
Even if a woman does not follow the cycle and regularity of her periods at all, then by this time she will definitely understand that she is carrying a baby. In especially thin girls, the tummy becomes more rounded due to the enlargement of the uterine body and the growth of placental tissue. But the mammary glands become rounded and swell in all mothers. Also, the following changes are typical for the eighth gestational week:
- The baby has already grown to 2-3.2 g and is about 2 cm;
- The formation of all intraorganic systems and organs has almost finished; now all they have to do is develop;
- The baby actively clenches and unclenches his fists, moves his fingers, and the tail process disappears.
- Bone and joint structures become stronger, improving every day.
- The embryo becomes more and more like a tiny little man. The eyes on his face gradually come closer together, the contours of his ears begin to appear, and facial expressions are already slightly visible on his small face.
Experts say that when the belly is touched, it is at this time that the baby begins to show a response to such an action. Mommy herself often experiences sharp taste desires, which are sometimes surprising, because women manage to combine pickled cucumbers with bananas, strawberries with pickled herring, etc.
Ninth
At 9 weeks, the embryo reaches a decent size and acquires the status of a fetus. Toxic symptoms become more and more pronounced, and women sometimes lose noticeably weight against this background. As for the baby, his limbs have already finished forming, but his head is still large and lies on his chest. In a small body, sexual characteristics begin to appear, however, ultrasound diagnostics cannot determine this.
The ninth gestational week is considered a dangerous turning point, at which miscarriages often occur. Therefore, a woman should take utmost care of her own health and monitor symptoms. If painful spasms and bleeding suddenly appear, you should urgently seek medical help or consult a gynecologist.
The growing fetus begins to put pressure on the bladder
10 week
A calmer period began, since mom’s body had already adapted as much as possible to the changes taking place and the new situation. The baby has already completed the formation of all structures, now they are simply developing and improving. The baby's weight becomes about 7 g, the head no longer lies on the chest, but rises slightly.
The fingers are gradually lengthening, however, there are still membranous connections between them. The development of intraorganic structures such as the respiratory and gastrointestinal tract, liver and kidney sections continues. Depending on the gender of the fetus, the synthesis of sex hormones - estrogen or testosterone - begins.
The pressure on the pelvic organs gradually increases as the uterine body continues to enlarge. Some patients may develop psycho-emotional disorders against the background of rounded changes in their figure, but you should not dwell on them. And updating your wardrobe will help you take your mind off this.
11 week period
At the eleventh week, the baby already reaches 10-11 g of weight, and his height is 5-6 cm. From this time on, doctors consider gestation according to the patient’s condition, the correctness and appropriateness of fetal development. When undergoing ultrasound screening, the doctor will accurately determine the correspondence between development and actual gestational age.
- During an obstetric examination, the doctor can listen to the fetal heart rate, which at this stage should correspond to 135-140 beats/min.
- The baby is developing rapidly, because his body especially needs the supply of nutrients, for which blood vascular structures begin to actively develop in the placental canal.
- At the same time, the formation of hair follicles occurs.
- The pregnant woman herself also begins to feel much better, since her toxic symptoms subside, but they do not completely go away.
- Mothers may still be bothered by frequent urination, which is considered normal.
- To reduce the load on the urinary system, it is recommended to increase the drinking regime, but be sure to exclude salt and any salty foods, as well as caffeine-containing drinks from the diet.
Already now, mommy should take care of the prevention of stretch marks, so it is recommended to apply natural oils to the tummy, hips and breasts. It is useful to start regular exercise for pregnant women to support the body and train the perineal muscles, which will help the baby develop correctly and facilitate delivery.
12 weeks
With the onset of 12 weeks, fetal development becomes more rapid. By the end of the third trimester, the risks of miscarriage are reduced as much as possible; it is believed that the turning point has passed, and the baby is now in no danger. Mommy herself has already become thoroughly accustomed to her new status, and given that toxicosis has practically disappeared, she can now completely relax.
It is useful to include natural juices in the menu
Usually the second trimester, which has just begun, is considered the calmest and most favorable period of gestation. Toxicosis has subsided, and the tummy is still so small that it is not able to disrupt the patient’s usual way of life. Moreover, right now women’s appearance is noticeably changing – their face brightens, their skin tone evens out, their hair shines and becomes thicker.
Although mommy feels great, there is no need to relax. Now it is important to monitor your diet to prevent constipation, which is typical for this gestational age. You should also exclude fast food, processed foods, foods with preservatives and dyes, and food additives. You should eat more protein foods, which will become a worthy source of nutrition for the baby.
By the way, the baby has grown a little, his height already reaches 6.5 cm, and his weight is about 13 g. Now the respiratory system, especially the lungs, is being actively improved, gastrointestinal functionality is stabilizing, and the head is rising more and more. The baby is already making attempts to taste his fingers. Now the baby especially reacts to his mother’s voice, stroking his belly, he is already able to feel pain.
Thirteenth
At this stage, it is worth continuing to follow the previously stated recommendations regarding diet and physical activity. The waist begins to gradually spread out, the chest can become larger by as much as 2 sizes. To maintain it, you should purchase a special bra. The active release of colostrum from the nipples begins, which looks like a clear or slightly cloudy liquid. The uterus rises a little, so the urge to urinate is normalized, which mommy feels as a noticeable relief.
- Now it’s worth paying attention to the discharge; it should be colorless or whitish, without odor or associated discomfort.
- The baby has grown another half a centimeter, now his height is 7 cm, and his weight reaches 20 g.
- Now the baby is rapidly developing emotional sensitivity, so he reacts vividly to loud sounds, changes in his mother’s mood, noises and bright lights, and pain.
- Already now he is able to see dreams, which are quite short-lived and do not exceed two minutes in duration.
At the same time, the fetus can use its limbs with might and main, raise its head and cross its small legs. Although for mommy these miracles of balancing act remain unnoticeable.
Week 14
By the 14-week gestation period, women usually completely get used to the new situation and move on to a new stage - waiting to meet the baby. Under the influence of active fetal growth, the mother's appearance is steadily changing, which is manifested in the expansion of the hips and breast enlargement. Now it won’t hurt to buy a few new wardrobe items “for growth”; clothes should be loose and not interfere with movements.
Any emotions also affect the baby in the womb.
Compliance with dietary recommendations continues, and the pregnant woman’s weight increases noticeably. Now it’s worth paying special attention to weight gain, avoiding overeating so as not to gain more than the required kilograms.
The baby has reached ten centimeters in height, and his weight has already reached 50 g. During an ultrasound examination, the baby clearly expresses facial emotions. The respiratory system continues to improve, the insulin hormone begins to be produced, and the baby begins to live according to a clear schedule of wakefulness and sleep. Mommy should monitor her emotions and not be nervous, because such moods cause the baby’s heart rate to increase.
Week 15
The baby’s cerebral cortex and nervous system structures are formed, intrasecretory glands and respiratory systems, as well as taste buds, are actively developing.
At this stage, mothers may experience frequent attacks of calf cramps, which warns of potassium, calcium and magnesium deficiency.
Sixteenth
The fetal liver and bladder system are already functioning, and the baby’s bloodstream contains all the necessary and important elements such as monocytes, lymphocytes or red blood cells.
At this stage, mothers often develop a runny nose and congestion in the nasal passages, which experts explain by estrogen activity, which causes swelling of the mucous tissues.
17 weeks
The baby's ears have finished developing, the myocardial conduction system has finished forming, the baby develops a swallowing reflex, and the finest hair fluff appears on the surface of the skin. The patient's weight gain reaches approximately 3-6 kg, which increases the load on the lower extremities, which is manifested by pain and hyperedema.
18 week period
The weight continues to creep up, which is why mommy experiences increased pain in her lower back and back, which is sometimes accompanied by vaginal discharge. The baby's heart and ears are actively working, and the immune system has formed.
Any new sensations should be reported to your gynecologist.
19 weeks
Now the baby especially needs calcium supplementation. If the micronutrient is not enough, it will pull out all the calcium from mommy’s teeth, so if the condition of the teeth suddenly worsens, you should urgently consult a dentist.
The baby continues to actively develop brain structures. The individual elements of the respiratory system with bronchioles, lung tissues and bronchi gradually unite.
Twentieth
The baby began to develop subcutaneous fat. The woman notes an increase in vaginal discharge, which sometimes causes the development of varicose veins. Around now, mommy will be able to feel the baby’s first kicks.
- The child already grows to 23 cm, and his weight reaches 300 g.
- He actively tumbles, yawns contagiously and plays.
- The correct formation of the limbs begins, which show a healthy proportion in relation to the parameters of the body.
- The head steadily decreases, acquiring its usual proportions, and nail plates or small hairs appear on the baby’s nails.
Until the end of gestation, the fetus will remain virtually unchanged, except that it will be several times larger.
21 weeks
Experts believe that now mommy can help the baby develop healthy taste priorities. If mommy regularly indulges in unhealthy food, then the baby is unlikely to eat only vegetables in the future.
A child at 21 weeks already gains up to 340 g, and his height is approximately 26 cm. Outwardly, the baby looks like an ordinary child, he just has to grow up. If the baby is not happy with the food, then the mother often suffers from poking and kicking the fetus.
Week 22
Now the tummy takes on more noticeable features; it can no longer be hidden under enormous clothing. All intraorganic structures of the fetus continue their coordinated activity, the liver synthesizes hormonal components.
Mommy acquires an awkward gait and sometimes suffers from hyperedema and varicose veins. Now a massage of the limbs and herbal baths will come in very handy.
Vitamins should not be taken on your own, it is dangerous
Week 23
Mommy can still afford to rest, because toxicosis has long passed, and heartburn has not yet begun. Now it is important to monitor weight gain and prevent excess weight. Usually, now the mother is gaining up to 7 kg in comparison with the state before conception.
The baby has already grown to 420 g of weight, and its surface looks wrinkled, but after the formation of the subcutaneous fat layer, this feature will disappear. The baby mostly sleeps or absorbs nutrients.
Week 24
At 24 weeks, there is a clear increase in the tummy, this will continue weekly. Don’t forget to lubricate your body with oils to prevent the formation of stretch marks.
Now the baby is trying to learn how to inhale and exhale, although the bulk of the oxygen supply penetrates to him through the umbilical cord. The formation of neural brain connections continues actively. The baby, while in the mother's womb, grimaces, frowns or sucks a finger. His weight has now reached 0.5 kg.
Week 25
At this stage, mothers often experience heartburn and constipation. For prevention, you should follow your doctor's recommendations on nutrition and, if necessary, take iron-containing medications. A prenatal bandage, which will help distribute the load and relieve excess tension from the back, will not hurt the mother.
Now the onset of premature birth is already possible, but it is extremely undesirable, although experts say that he is already quite viable and if placed in an incubator he is quite capable of surviving. It must be said that the baby’s height is already 35 cm, and its weight reaches about 700 g.
You need to monitor your feelings as closely as possible.
Twenty-sixth
The 26-week period has its own characteristics.
- The workload is steadily increasing, and sometimes mothers exhibit conditions such as forgetfulness or absent-mindedness.
- If we add to this excess weight, which for this period of gestation is normally an 8-kilogram gain, then it becomes difficult for the mother to walk, since there is a large load on the lumbar area.
- The baby grows to a kilogram weight, his skin becomes lighter due to subcutaneous fat deposits.
- The baby’s muscles become stronger, so when he pushes, the mother feels more pronounced discomfort, and sometimes even obvious pain.
Mommy needs to carefully monitor her feelings. If the uterus is toned, then bed rest is indicated, and if bleeding and contractions occur, you should urgently call an ambulance.
Week 27
By this time, mommy is finding it increasingly difficult to do housework. The baby is developing and growing rapidly, and the mother almost always feels tired, so she rests more and more. Now is the time to go on maternity leave. It is useful to engage in some favorite hobby that does not require physical effort. It's time to strictly focus on your diet so as not to gain excess weight.
Since the baby’s skeletal system is now actively developing, more calcium-containing foods should be included in the diet. The baby’s subcutaneous fat layer also continues to grow, and thanks to the placental structures, the baby develops immune protection.
Twenty-eighth
If mommy has gained more weight than she should, then her motor activity becomes more difficult, and the woman acquires characteristic clumsiness when walking. Mommy is becoming more and more sleepy and constantly tired, and may suffer from digestive problems.
The baby weighs more than a kilogram, and his height already reaches 38 cm. The skin is smoothed out, the skin membrane film disappears from the eyes, so they are already opening. The baby is already a little cramped in his mother’s tummy, but this does not have any negative consequences for ontogenesis.
Daytime naps will help you regain your strength.
29 week period
At week 29, the baby’s weight reaches 1.3 kg, and the height already reaches 40 cm. The baby is already actively preparing for birth. All the mucus comes out of the tiny nose, and the fluff on the body and the amount of vernix lubrication noticeably decreases. The baby receives a lot of antibodies from the mother's bloodstream, which provides him with additional protection.
Under pressure from the enlarged uterus, blood flow in the lower half of the female body is disrupted. This provokes constipation, varicose veins and hemorrhoids, and can also cause heartburn and shortness of breath. Nowadays it is recommended to do special yoga, but only after the doctor’s approval. It is also useful to train the perineal muscles using the Kegel technique.
Thirtieth
The patient's abdomen grows greatly, stretching the skin. Striae may also appear on the thighs. But with a properly adjusted diet, mommy will be able to avoid constipation and swelling. The baby is in a position favorable for birth.
31 weeks
This week the baby's weight reaches one and a half kilograms, and his height is 41 cm. The baby's pancreas produces the insulin hormone, and his liver effectively cleanses the blood of toxins. By this time, the baby’s brain makes up 25% of the organ size of adults. In girls, the clitoris begins to appear, and in boys, the testicles descend into the scrotum.
A woman can no longer rest on her back, since the enlarged uterus puts great pressure on the veins and intraorganic structures. In this situation, mommy begins to feel dizzy and her health worsens.
Week 32
The peculiarities of this period are the following changes:
- The baby continues to grow, but his skull is still quite soft.
- Intraorganic structures function fully, and the body actively produces immunoglobulin components that provide the baby with protection from bacterial and viral pathogens.
- The baby actively tosses and turns, causing mommy a lot of inconvenience. Many pregnant women are unable to sleep all night because of these baby marathons.
- The tummy becomes large and strongly pulls down, so mothers are strongly recommended to wear a prenatal bandage.
- The weight of the belly reaches 1.8 kg, and the height reaches 45 cm.
- The baby is now positioned head down, as it should be normally.
Experts believe that now is the time to start talking to the baby, reading books to him or playing classical music, which will have a beneficial effect on his overall development and mental abilities in the future.
Week 33
By this time, mothers usually gain up to 12 kg in weight, and some gain more. For 33 weeks, excessive hormonal activity, bleeding gums, and increased irritability are typical. Now it is useful to do gymnastics for pregnant women, which will help keep the labor and delivery processes under control.
The baby's height reaches 46 cm, and his weight is already about 2.3 kg. The baby's musculoskeletal structures are actively developing, and outwardly he already looks like an ordinary baby.
The approaching date of birth becomes more and more exciting
34 week
The baby is becoming increasingly cramped in the mother’s womb; several months ago his weight already exceeded 2 kg, and his height exceeds 47 cm. The mother’s total weight gain can exceed 15 kg, while the mammary glands continue to enlarge.
In a tiny body, the gastrointestinal tract structures are prepared for full functioning. If the baby decides to be born right now, he will be able to breathe on his own.
Week 35
It's time to prepare for childbirth, for which mommy is recommended to take preparatory courses. The tummy grows to its maximum size, so mommy gets tired from any exertion, even banal walking. Women are also concerned about swelling.
Now you especially shouldn’t overeat, otherwise the baby will continue to grow rapidly and will be born overweight, which is fraught with ruptures and other birth complications. The baby's respiratory functions, sucking and swallowing reflex reactions, immune, endocrine and nervous systems continue to improve.
Week 36
The baby's head center actively controls and coordinates the activities of the respiratory, cardiovascular and thermoregulatory functions. When the baby is born, they will immediately begin to actively function. Mommy often suffers from severe shortness of breath.
The placenta begins to gradually age, which can provoke fetal hypoxia. Due to excessive tightness in the mother’s womb, the fetus’s movements become constrained, and the baby’s turns, pushes and other somersaults become dangerous for mothers and extremely painful.
Week 37
The mucous plug in the cervical canal begins to drain. The baby continues to develop his nervous system structures. Mommy's cervix is also preparing to stretch.
The baby’s weight is now about 3 kg, and its length is 48-49 cm. The most important intraorganic functions such as the myocardium, motor structures, and respiratory activity are being improved.
The baby can arrive at any time
Week 38
The baby weighs more than 3 kg and has already grown to half a meter. His organs work perfectly and can function independently. The fetus descends into the pelvic structures, causing severe pain. The nipples also become much more sensitive, and the breasts become even more engorged.
Week 39
Painful sensations in the lumbar region and back continue to bother me, mommy suffers from heartburn and hyperedema, constipation also complicates life. Any day now the baby will be born. And now it continues to move down into the pelvic cavity.
Forty weeks pregnant
Ideally, birth occurs at this time. If they do not occur, then the uterine body has already completely descended into the small pelvis, so it becomes easier for the woman to breathe. The stomach begins to function fully, so cases of heartburn occur less and less often. A descending baby puts pressure on the genitals, which is why heaviness and pressure are felt in the perineum. The placenta has already aged, so it cannot provide the baby with everything necessary. Lack of oxygen is dangerous because it can disrupt the cerebral and intraorganic activity of the fetus.
If labor does not occur before 42 weeks, the patient is prepared for induction of labor and drugs are administered to induce labor. After which comes the long-awaited meeting between mother and baby. The first hug with a baby and latching on to the breast is the most unforgettable experience for any mother.
Correct and incorrect placement
A child who is in a head-down position, with the back of his head turned toward the stomach, has a normal position in the uterus.
With this phenomenon, there is no doubt that the birth will be successful. Since the upper part of the head exerts uniform pressure on the cervix, labor becomes easier.
But there are other types of baby positions, which are divided into correct and incorrect options:
- Longitudinal position of the child. It is characterized by cephalic presentation of the fetus and is positioned as correct.
If, with this arrangement, the ultrasound report indicates that the presentation is breech, then various pathologies may occur during childbirth.
This type is considered rare and is observed in only 5% of expectant mothers. If a woman gives birth on her own, childbirth is accompanied by difficulties, so a caesarean section is most often prescribed. Oblique location. The difference is that the axis of the uterus and the spine intersect at an acute angle. The baby's head and pelvis are located on both sides of the mother's abdomen - this is considered a deviation from the norm.
The phenomenon is observed in less than 1% of women, often having second births. The reasons for the oblique position of the fetus are high levels of water, a large child, and obstacles on the way out of the womb.
In multiparous mothers, this is due to a weakening of the anterior abdominal wall. The safest solution is a caesarean section.
- Transverse position. In this case, the fetus crosses the uterus transversely. It is considered incorrect and occurs due to congenital pathologies in the development of the uterus, a narrowed pelvis, and incorrect localization of the placenta. With this phenomenon, premature birth often occurs.
It is worth understanding that in the early stages of pregnancy the baby is fully mobile, and after 33 weeks he stops actively behaving and is preparing to leave.
The normal position of the fetus is longitudinal with a cephalic presentation; in other cases, it is worth carefully monitoring the pregnancy.
If incorrect presentation has been diagnosed, there is no need to panic; it is best to consult with a qualified obstetrician.
Useful video
What happens to mom at 3 weeks of pregnancy
Mom is expecting her period! This is what happens to her. That’s why she’s worried about the usual premenstrual symptoms:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- dull pain in the lower back;
- swelling of the mammary glands;
- irritability;
- frequent urination;
- transient dizziness;
- sometimes - nausea;
- drowsiness.
But these familiar premenstrual messages may be joined by others that do not quite correspond to the upcoming menstruation. What are these symptoms?
Belly growth
Well, if you consider that the blastocyst has a diameter of less than 0.5 mm, then there should be no talk of increasing the size of the abdomen. Yes, the uterus is preparing for the upcoming birth of a child, but at this stage it only becomes full-blooded and slightly swollen. And, believe me, its size does not change much because of this. Here the psychological attitude has a greater influence. At the first suspicion of pregnancy, women begin to eat heavily, not limiting themselves to sweets, intuitively become clumsy and are afraid of any physical activity. Hence the weight gain. In fact, during pregnancy - the belly begins to grow in later weeks - when the size of the fetus, uterus and amniotic fluid volume increases. But at that moment you will already know exactly about your situation. In the meantime, at 3 weeks of pregnancy, you cannot observe specific signs and feel any special “pregnant” sensations. But if you really want to hear it, then: “Yes, your belly has grown because you are expecting a child!” Do you want to feel like you're pregnant? Please! If this is the only thing that worries you, and not early toxicosis, then all your loved ones, colleagues, and most of all, your local obstetrician-gynecologist will be happy for you.
Weight gain
First of all, you need to study, or even hang on the refrigerator, a table of physiological weight gain during pregnancy by week. The fact is that excessive weight gain or, conversely, loss of kilograms leads to the threat of miscarriage. Therefore, you must monitor the amount of calories you consume and the quality of food more than ever. At 3 weeks, you could have gained weight only for psychological reasons. But we need to put an end to this! Now you are responsible not only for your health: you need to raise a healthy baby and provide optimal conditions for his birth. And, believe me, your and his weight plays a very big role in this. And it’s not just about the mechanical factors that influence the physiology of childbirth: as you get fatter, the baby gets fatter too. And a baby born with excessive weight (more than 4 kg) runs the risk of developing diabetes, even if such a pathology has not occurred in your family or among your husband’s relatives. Now you should tune in to proper nutrition and at least for a while forget about junk food. More details below.
Self-awareness
Premenstrual sensations in the 3rd week of pregnancy are accompanied by specific symptoms: unbridled or, conversely, decreased appetite, intolerance to certain smells or tastes. Moreover, this applies not only to ready-made food: in the early stages, the only sign of pregnancy may be an aversion to cigarette smoke, stuffiness in public transport, the smell in fish or meat pavilions, even the aroma of a beloved man can negatively affect the olfactory receptors of a pregnant woman. If you have not laboratory confirmed your “interesting position”, but intuitively insist on it, you begin to develop a pregnancy dominant: you become clumsy, afraid of sudden movements, on a bus or trolleybus you defend your even not enlarged belly, you are offended by the rudeness of others, which Ordinary life wouldn't even excite you. This also explains slowness, drowsiness, and absent-mindedness. But at 3 weeks of pregnancy these are only psychological aspects: neither the hormones of the fetus or placenta, nor other substances secreted by them or the ovaries, fundamentally affect your condition. Their concentration at this time is very low!
Pain
What can worry a woman in the 3rd week of a normal pregnancy: only something that pulls in the lower abdomen. Nobody knows why this happens! Most likely, the next menstruation is approaching, and this is one of the “dangerous periods of pregnancy.” Nagging pain may be accompanied by strange discharge: it seems that your period has not yet arrived, but brown mucus is discharged from the vagina. But this has never happened before! There is nothing stopping you from seeing a doctor: and don’t be shy - that’s his job!
Possible allocations
Brown discharge at 3 weeks of pregnancy indicates successful implantation (if we are really talking about pregnancy). They are usually accompanied by previous minor short-term pain in the lower abdomen. And, if the discharge is insignificant and does not last for several days, then everything is fine: your blastocyst has penetrated the endometrium and has already begun to receive nutrients. You should be alerted by copious discharge that is brown or red, or even worse, downright bloody. And if all this does not coincide with the date of your expected period, then you have a gynecological problem and only a specialist can solve it.
Psychological condition
Psychological symptoms of pregnancy at 3 weeks are on the brink: YES or NO. As soon as the woman found out about the delay, she is no longer interested in anything - neither work, nor the child, nor, especially, her husband - the culprit of her condition. She cares only about one question, which sits in her head around the clock. She is capricious, changeable in mood, her joy or sadness is exaggerated. But it all comes down to only one thing: she wants to finally make up her mind, and cheap pharmacy tests are powerless to confirm suspicions. What should she do?
Location of the fetus in the uterus by week of pregnancy
Throughout pregnancy, the baby develops and grows in the uterus. From the second month of pregnancy, it often changes its location and makes various movements. The successful course of labor depends on the position that the baby takes at the end of the gestational period.
If the pregnancy proceeds normally, then until the third trimester of gestation, the position of the fetus changes regularly over the weeks of pregnancy. It has no functional significance, since the baby moves during every waking period.
- Starting from the 24th week of pregnancy, the location of the fetus in the mother’s abdomen ceases to change. The child gradually increases in size and becomes inactive. It is no longer possible to move as before.
- For most women, from the 26th week of pregnancy, the position of the fetus no longer changes.
- Experts make a decision on the position of the fetus after 32 weeks, when it is finally established. The remaining time before birth, the fetus remains inactive and changes its position slightly.
- From the 36th week, when the position is favorable, the head descends into the birth canal. The fruit is now in a low position. Sometimes he takes this position earlier.
Ideas for mothers and babies
Back in 1965, Swedish photographer Lennart Nilsson was the first to photograph the stages of embryo development using a powerful macro lens. And since then, as it turned out, nothing new has been invented yet. Nilsson's photographs are ingenious - he placed a microscopic macro camera lens and an illuminator on the tip of a cystoscope tube (a device used to examine the bladder) and shot a unique 40-week long “report” of how a new life is born and develops.
Lennart Nilsson was born in 1922 on August 24 and is still alive, which is good news. In 2006, he released his latest book, Life. It will still be interesting to understand his books and photographs, but that will be ahead.
Now let's look at the stages of fetal development week by week. After all, pregnant women always want to know how the life emerging in them develops. What the future man sees, hears, feels.
7-8 hours passed...
The sperm practically digs into the egg.
Until eight weeks, the fetus is called an embryo.
1 Week
For the birth of a new life in the female body, ovulation occurs. At the same time, the temperature rises, the amount of vaginal mucus increases, and there may be slight pain in the ovarian area. Hormones are active in the body, causing a desire for intimacy. The fertilization of the egg by the sperm occurs.
2 week
The fertilized egg divides. The child inherits half of the parent's chromosomes. The sex of the unborn child depends on the sperm that fertilized the cell. After this, the embryo travels through the fallopian tube into the uterus. At the end of the second week, it attaches to the lining of the uterus. This insertion sometimes causes minor bleeding.
3 week
On the 18th day, the embryo’s heart begins to pulsate. The embryo separates from the membranes and actively develops. The nervous, skeletal, and muscular systems are emerging.
4 week
Often it is during this period that a woman finds out about her pregnancy. Signs of pregnancy appear and menstruation is absent.
5 week
The length of the embryo is 6-9 mm. The brain and spinal cord develop, and the central nervous system is formed. The heart, head, arms, legs, tail, and gill slit appear. You can consider a face with holes for future eyes, mouth, nostrils.
A pregnant woman should consume enough folic acid to prevent neural tube defects in her baby. By the end of this week, the heart begins to beat.
week 6
The placenta is formed, which is the lungs, liver, stomach, and kidneys for the fetus. The placenta is also called the baby's place.
week 7
The expectant mother's breasts are significantly enlarged. The length of the fetus reaches 12 mm, weight - 1 g. The fetus already has a vestibular apparatus, the rudiments of the abdomen, chest, and eyes. The brain and fingers are developing. The fruit begins to move.
8 week
The length of the embryo reaches 20 mm. The fetal body is formed. The face, nose, ears, and mouth are different. The skeleton continues to grow, the nervous system improves.
Skin sensitivity appears in the area of the mouth, face, and palms. The gill slits die off, and the rudiments of the genital organs appear.
Week 9
All fetal muscles develop. The fingers and toes already have marigolds. Sensitivity affects the baby's entire body. He touches his body, the umbilical cord, the walls of the amniotic sac. Thus, the tactile sensations of the fetus develop.
10 week
This is one of the most important stages in a baby's development. The nervous system and almost all organs develop. His eyelids are half-open and will fully form over the next few days.
It is very important for the mother not to drink alcohol or other toxic substances during this period. The placenta does not yet fully protect the baby, so significant harm to his health can be caused.
11 week
The amount of blood in a pregnant woman's body increases. The hormones produced during this period affect the body's thermoregulation. Therefore, a woman increasingly experiences changes in blood pressure, dizziness, weakness, and stuffiness.
The fetus has formed eyelids, arms, and legs. He is already making swallowing movements.
12 week
There are already red blood cells in the baby’s blood, and the production of leukocytes begins, which will be responsible for protecting the body. In the meantime, antibodies protect the baby from infection. They come from the mother through the blood and are passive immunity.
Week 13
The expectant mother already wears her protruding belly with pride. The fetus actively develops its skeleton and growth. This causes increased calcium intake. Therefore, a pregnant woman must take special medications to replenish this microelement.
The baby begins to hear thanks to special vibration receptors that are located on the skin. The fetal vocal cords begin to form. The baby's pancreas begins to produce insulin, and the liver begins to produce bile. Villi are formed in the intestines, which are of great importance for digestion.
Week 14
The fetus begins to develop training movements that are very important for the development of the lungs - inhalation and exhalation. The kidneys, bladder, and urethra begin to function. The urine excreted is eliminated by the placenta. The baby's body begins to become covered with lanugo. This is a fluff that performs a thermoregulatory and protective function for the fetal body.
In girls, the ovaries move to the pelvis. In boys, the prostate gland develops. Blood forms inside the baby's bones. Hair growth begins on the scalp.
Week 15
The baby's hematopoietic system is actively developing. Veins and arteries supply all organs and systems with blood. The fetus's heart beats twice as fast as the mother's, while passing about 23 liters of blood per day. The first foci of hematopoiesis appear in the walls of the gallbladder. You can find out the child's blood type and Rh factor.
Week 16
The baby exhibits greater physical activity. The child's eyes open. There is still no subcutaneous fat layer at all. The baby's skin is very thin, with blood vessels visible through it. The fetal skeleton consists of a flexible rod and a network of blood vessels.
Week 17
During this period, the fetus experiences rapid eye movement. In this regard, scientists claim that a child can dream. They are associated with his physical activity during the day.
Week 18
The length of the fetus reaches 14 cm. The baby blinks, opens its mouth, and makes grasping movements. He moves a lot in his mother's belly. All parts of the body are clearly visible, the face, the skin of the body turns pink.
Week 19
The mother feels the baby move. Later the movement turns into tremors. The strength of the shocks varies. It depends on the mother’s mood, activity, and time of day. On average, the baby makes 20-60 pushes in half an hour. The baby's brain is actively developing. He starts sucking his thumb.
Week 20
At this time, expectant mothers are seriously thinking about childbirth. It’s good to choose courses for expectant mothers.
21 weeks
The length of the fruit already reaches 20 centimeters. The fetus's kidneys are working, and meconium is produced in the intestines - pseudo-feces.
Week 22
The child hears his mother’s voice, her breathing, her heartbeat. All this is due to the fact that the auditory ossicles have ossified and become capable of conducting sounds.
The weight of the fetus increases and fat deposits accumulate.
Week 23
The length of the fetus reaches 30 cm, and the weight is 650 g. The lungs are quite developed. In case of premature birth during this period, the baby will be able to survive in the intensive care unit.
Week 24
You can hear the baby's heartbeat by placing your ear to the mother's belly. During this period, the placental blood circulation of the child is of primary importance. The dimensions of the child's pelvis and lower extremities are relatively smaller than the upper part. This is due to the fact that the upper part of the body is better supplied with lower arterial blood. At the same time, the lungs receive very little of the blood.
Week 25
Still soft cartilage of the nose and ears. The skin of the fetus is wrinkled, covered with grease, and vellus hair forms on it. The child is already falling asleep and waking up.
Week 26
The baby has a well-developed sucking reflex. He often sucks his thumb. This activity calms him down and strengthens his jaw and cheek muscles. Depending on the finger of which hand the child sucks, we can assume that he will be right-handed or left-handed.
The baby pushes, explores the space that surrounds him. At this time, the normal number of kicks for the baby is 10 times per hour.
The mother's uterus has quadrupled in size. It expands the lower ribs, resting on the hypochondrium.
Week 27
The length of the fetus reaches 350 mm, weight -900-1200 g. The child’s eyes open slightly and perceive light. The mouth and lips become even more sensitive.
The boys' testicles have not yet descended into the scrotum. In girls, the labia minora are not yet covered by the labia majora.
Week 28
The hair on the head becomes thicker. Although some children are born almost bald. All these are variants of the norm. Lanugo practically disappears. Although in some places there may still be fluff on the body, which will disappear in the first weeks after birth.
Week 29
The baby has eyelashes. His eyelids are already closing and opening. Toenails grow on my feet.
Week 30
The child reacts to sounds from the external environment and may cry. The central nervous system controls body temperature and breathing rhythm. The lungs can already breathe normal air.
31 weeks
While awake, the child opens his eyes. Closes them during sleep.
Week 32
The length of the fetus reaches 450 mm, its weight is about 2500 g. From this period, the baby is actively growing and gaining weight. His skin becomes thicker, pinkish, smooth.
Week 33
During this period, the brain mass, depth and number of convolutions increase significantly. The most important functions of the fetus are controlled by the spinal cord and parts of the central nervous system. After birth, the functions of the cerebral cortex will develop.
34 week
The child can lift and turn his head due to increased muscle tone. Actively reacts to light, can squint from direct rays of the sun.
Week 35
The baby's lungs are fully developed. The fetus quickly develops a grasping reflex.
Week 36
A pregnant woman may experience the first signs of future birth. “Prolapse” of the abdomen occurs when the height of the uterine fundus decreases. The mucus plug from the cervix may come off. Characteristic during this period is an increase in urination and defecation. Not only does the uterus put pressure on the intestines and bladder. Also, prostaglandins (hormones produced at that time) periodically cause the desire to have a bowel movement.
The child pushes and moves less. The cervix shortens and becomes softer. Sometimes the external os of the uterus can open 1-2 cm.
Week 37
The length of the child reaches 47 cm, weight - 2600 g.
Week 38
The fetus is already quite viable, ready to be born. There can be hairs up to three cm on the head. Its skin is pale pink and has a layer of subcutaneous fatty tissue. The child performs about 70 thyreflex movements.
Week 39
The baby reacts very sensitively to all movements and the psychological state of the mother. He responds with his movements to her anxiety, joy, fear.
40 week
The length of the child reaches 480-520 mm, weight - from 3200 to 3600 g. In girls, the labia minora are covered by the labia majora. The boys' testicles dropped into the scrotum. The cartilages of the nose and ears are elastic, the nails on the fingers. The baby is ready to be born.
In the first weeks after the birth of the baby, it is very important to stroke his body and gently hold him close to you. The child cannot yet feel himself and really misses being touched.
The baby's memory retains very well the sound and rhythm of the mother's heart. To calm the baby, sometimes it is enough to put it on the left side of the mother's body.
- and here is Lennart Nilsson’s book “A Child is Born!” The miracle of the birth of a new life."
Lennart Nilsson also filmed short videos about embryo development; I found them when I was studying information from his official website.
A selection of books about pregnancy and childbirth: - Mommy is Me, or the Diary of a Pregnant Woman about the most secret things. L. Lomanskaya
— A big book about pregnancy. McCarthy Jenny
If you liked the article, subscribe to updates, it will take less time than taking a pregnancy test =))
Fetal position at the end of pregnancy
The successful process of childbirth depends on the final position of the fetus in the mother's uterus.
Main options:
- longitudinal position of the fetus;
- transverse arrangement;
- oblique position.
The longitudinal position is considered the norm. With it, the baby is vertical in the uterus. It involves the smooth passage of the fetus through the birth canal. Transverse position – horizontal. Oblique position - the baby is placed in the uterus at an acute angle. Oblique and transverse positions are extremely rare and undesirable. The decision on the type of birth in such cases is made by the doctor.
Second and third trimester of pregnancy
The child continues to grow and bile is already being produced, the urinary system is functioning, the heart and blood vessels are working.
- 13 weeks. From this moment on, protection in the form of the placenta is added; it protects against unwanted influences.
- 14 weeks. The eyes are covered with eyelids, they will remain in this state for another three months.
- 15 weeks. The soft ears are modified to a normal silhouette, the legs and feet have grown noticeably.
- 16 weeks. Nothing yet interferes with the free movements of a child weighing 120 grams.
- 17 weeks. The glands that lubricate the skin with a sebaceous layer are already working. Soft hairs are visible on the body.
- 18 weeks. Fatty tissue is formed under the skin.
- 19 weeks. Inside the intestines there is something like feces with bile.
- 20 weeks. The endocrine system begins to work, and a more intense heartbeat is heard. Such a child, if it had to exist outside the womb, could produce breathing.
- 21 weeks. The body is actively growing. At birth at this stage, there is a high probability of fetal survival, subject to the availability of professional supervision and special devices.
- 22 weeks. Fat deposition and weight gain continue to occur.
- 23 weeks. The baby is about 32 centimeters tall and weighs no more than 650 grams.
- 24 weeks. At the end of the sixth month, the weight reaches 900 grams.
- 25 weeks. A rapidly growing child is able to distinguish voices and hear the mother’s heartbeat.
- 26 weeks. Preparations are underway to leave the uterus. The child tries to open his eyes a little; his height is approximately 40 centimeters.
- 27 weeks. Eyelashes have grown. There is a high probability that the fetus is already positioned head down.
- 28 weeks. Weight has gained more than a kilogram, the skin is all wrinkled.
- 29 weeks. In the womb there is a one and a half kilogram baby with thick hair.
- 30 weeks. The fetus will now live in somewhat cramped conditions due to weight gain.
- 31 weeks. By the middle of seven months, a two-kilogram baby is already in the womb.
- 32 weeks. At this time, the nails reach normal length, the skin is smooth and pink.
- 33 weeks. The fluff is gradually coming off the expanding body.
- 34 weeks. The eighth month is coming to an end, and it can almost be said that the weight reaches more than two and a half kilograms.
- 35 weeks. At this age, the child is able to tenaciously grasp objects, his limbs are in a bent state.
- 36 weeks. The foot lengthens, the toenails are completely retracted, the body is no longer covered with wrinkles, the ears harden, and in most cases a sucking reflex is formed. When born, the baby is already capable of screaming loudly.
- 37 weeks. Parietal-sacral height is 35 centimeters.
- 38-40 weeks. The ninth month has ended, babies most often at this stage weigh about three and a half kilograms (at least two and a half kilograms), height is more than 52 centimeters (at least 47 centimeters).
14 week 18 week 20 week 33 week
A child who has lived inside the uterus for forty weeks has every chance of successfully passing through the birth canal and feeling great outside next to his mother. Normally, such a baby, just born, shows high motor activity, screams loudly, opens his eyes, and is able to intensively suck his main food - milk.
Fetal presentation
The position of the fetus relative to the cervix, called presentation, also matters. It can be cephalic (the baby's head is below), and pelvic (close to the mother's cervix - the baby's buttocks). Head presentation with a longitudinal position is the key to an easy and natural birth, experts say.
Considering the location of the fetus in the uterus by week, it can be noted that it is active from 7 to 24 weeks. By week 36, the baby in the uterus becomes almost motionless. The expectant mother cannot independently predict the final position and presentation of the fetus. Only a doctor can draw a conclusion by conducting regular examinations and using ultrasound results.