Premature babies are considered to be children with a gestational age of less than 28–37 weeks and weighing from 1 to 2.5 kg. At the same time, full-term babies often have low weight (up to 2.5 kg) - in the presence of congenital malformations or if the mother abused alcohol, tobacco, or drugs during pregnancy.
Prematurity is determined by distinctive features:
- lack of subcutaneous fat (plus impaired thermoregulation);
- immaturity of the respiratory system;
- softness of the ears;
- large size of the fontanelle;
- the presence of vellus cover;
- large parietal and frontal tubercles.
However, today such babies, with proper treatment and care, have every chance to grow into full-fledged, healthy, strong children - nature has awarded them with a phenomenal ability to compensate in order to catch up with their “timely” peers by the age of one year. How do premature babies develop month by month? How are they different from ordinary children?
Causes of premature birth
A baby born before 37 weeks is considered premature. There are a huge number of reasons and factors that can trigger premature birth. It is worth noting the most common ones:
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency. It is characterized by a pathological condition of the cervix, which does not allow the fetus to be retained.
- Various anomalies in the structure of the female reproductive organ. For example, bicornuate uterus, the presence of an intrauterine septum.
- Diseases suffered by a woman during the period of bearing a baby: acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, rubella, etc.
- Somatic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, hypotension, heart defects and other pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Toxicosis, which manifests itself in late pregnancy and is accompanied by swelling.
- Large fibroid or submucosal leiomyoma of the uterus.
Often, premature birth at less than 38 weeks is a consequence of Rh conflict.
Classification of prematurity
There are four degrees of prematurity depending on the gestational age, height and weight of the newborn:
- The first degree of prematurity (mild), in which the baby weighs from 2.1 to 2.5 kg and height ranges from 41 to 45 centimeters. First degree babies are usually born at 36-37 weeks of pregnancy.
- The second degree of prematurity is characterized by the weight of the newborn in the range from 1.5 to 2.1 kg. The baby's height is 36-40 centimeters. With these parameters, babies are born at 32-35 weeks.
- Third-degree premature babies are babies born between 28 and 31 weeks of pregnancy. The baby's weight does not exceed one and a half kilograms, and his height is no more than 35 centimeters.
- The fourth degree of prematurity includes babies born before 28 weeks. These are very premature babies, weighing less than one kilogram and height less than 30 centimeters.
The most common cases are first degree prematurity. These are children born at 7 months of pregnancy. How many weeks is this from the allotted forty? The seventh month ends at 32 weeks.
Development of underweight children
Low birth weight children have a high risk of abnormalities in the nervous and cardiovascular systems. And since such babies, due to their weakness, continue to gain weight poorly, their physical and mental development and the formation of immunity are also at risk.
Pediatricians and neonatologists draw a parallel between the parameters of weight and height of low birth weight children and their development:
- Children born with normal height but low weight usually have a restless character, low and uneven weight gain, but develop generally normally. By the time they are one year old, they are practically no different from their peers.
- Children who are low birth weight but whose height is only slightly below normal may lag behind their peers in psychomotor development. Inhibitory reactions of the body predominate in them.
- Children with proportionately low weight and height also develop more slowly. They also get sick for a long time and often due to reduced immunity.
- Children with severe delays in height and weight as a result of intrauterine development disorders. They have a delay in the development of bone tissue, psyche and other body systems.
Features of development in prematurity
Parents of a baby born prematurely need to understand that he will develop differently than other babies. This is due to the fact that a premature baby has not fully formed organs. In addition, in the first month or two of life, the weight of a seven-month-old child or one born at a later date does not increase so intensively, since the sucking reflex is developed rather poorly or is absent altogether, and the child cannot independently extract milk from the mother’s breast. If the baby has the second, third or fourth degree of prematurity, he spends the first weeks of life in a special incubator, which receives oxygen and the food necessary for growth and development. Neonatologists carefully monitor the baby in the first weeks of life. Parents of a premature baby need to understand that the newborn’s immune system is weakened and the body is susceptible to infections and viruses. That is why staff and parents should exercise maximum caution at first and carefully monitor hygiene.
Children born prematurely later catch up in the psychomotor and physiological development of their peers who were born on time. However, in the absence of unfavorable factors, premature babies catch up with the development of other babies by twelve months.
Caring for a premature baby at home. Principles
After discharge, parents are faced with one-on-one care for their baby. In order to help the baby get comfortable in the new world, it is necessary to take into account its physiological characteristics, which differ from full-term babies.
Features of feeding
Premature babies, whose development lags behind full-term babies by months, face a number of problems during feeding. In such babies, the sucking reflex is weakened, intestinal motility is reduced and the ability to absorb lactose is reduced.
The best nutrition is considered to be maternal colostrum, and later milk. For low birth weight babies, breast milk fortifiers are additionally prescribed to compensate for the lack of energy. The one-time volume of food gradually increases from 5 ml. A premature baby in the first days of life receives nutrition of 15 ml per day per 1 kg of weight.
Premature babies are fed on demand, but not less than every 2-2.5 hours. If the mother lacks milk, the baby is supplemented with a catheter or a specialized supplementary feeding system, which is attached to the mother's breast and given to the child along with the breast to form a sucking reflex.
Bottle feeding is not recommended due to the continuous flow and high pressure. Drip feed is suitable for premature babies.
It is important to monitor weight gain and if the dynamics are unsatisfactory, contact your pediatrician. If there is a lack of breast milk, it is necessary to transfer the child to specialized breast milk substitutes for premature babies.
To improve the functioning of the baby’s gastrointestinal tract, it is necessary to observe some nuances:
- Before feeding, place the baby on the stomach for 3-5 minutes;
- during feeding, the baby should be at an angle of 45 degrees;
- After feeding, the baby must be held in a column until air is burped.
Baby's sleep
The amount of daily sleep in a prematurely born baby is much greater than in full-term babies. The number of dreams and their duration depends on the degree of prematurity of the child. The weaker the baby, the shorter his waking time. In the first month of life, the amount of sleep can reach 22 hours. During sleep, the nervous system matures and organs strengthen.
By the second month, the baby forms shorter sleeps during the day and longer ones at night. From three months onwards, a premature baby should have at least 3 daily naps of 2-2.5 hours each and night sleep without moments of wakefulness, with possible intervals for feeding.
Premature babies over 4 months of age may show clear signs of fatigue. By observing the behavior of the baby, a dream routine is established. The waking time gradually increases and by 10 months there are 2 naps of 2 hours each.
Before they acquire the skills to roll over, premature babies are especially susceptible to bedsores and congestion of internal organs , so their position in the cradle must be changed every 2–3 hours.
Walking
Walking with premature babies should initially be coordinated with a pediatrician-neonatologist. In summer, walks with newborns from 2 kg are allowed, in winter - from 3 kg. Walking time is gradually increased, starting from 5 minutes a day. When the walk time reaches 2 hours, it is divided into two sessions - two walks of 1 hour each. In winter, it is not recommended to walk at temperatures below -10 C.
Bathing
Bathing babies is allowed after discharge. If at the time of discharge the baby weighs 2 kg or more, then water procedures can be started after 15–20 days, if the baby’s weight has reached 3 kg – after 7–10 days. The water temperature should be no lower than 37–38 degrees. It is not recommended to add herbs, potassium permanganate, etc. to the bath.
Complementary foods, mixtures
Children who have not completed the intrauterine development of the third trimester suffer from a lack of vitamins, enzymes, and minerals. To replenish the missing elements in the body, breast milk is not enough.
Adapted breast milk substitutes for premature babies are used as supplementary feeding or independent nutrition.
They are characterized by higher calorie content and a high content of vitamin-mineral complexes and nutrients. This promotes rapid weight gain for the baby. Breast milk substitutes for premature babies are labeled "0", "Pre", "Premature", "Neosure" and "Special care".
The protein content here is 1.5 times higher than in regular baby food of the first stage. The fat content is also increased. The composition contains polyunsaturated fatty acids, which promote the rapid development of body systems (nervous, visual).
Among vitamins, special emphasis is placed on:
- vitamin A, which promotes growth and weight gain;
- vitamin D for the prevention of rickets;
- B vitamins to prevent internal bleeding and anemia.
Formulas for premature babies are more concentrated, so they put a strain on the kidneys. Because of this, upon reaching normal weight levels, the child is transferred to a formula labeled “from 0.”
If the child, upon reaching 6 months, has caught up with his peers in most respects and has no digestive problems (excessive regurgitation, constipation, diarrhea), then the introduction of complementary foods can begin. Before starting, it is important to visit a pediatrician and neurologist to make sure there are no problems.
You can introduce green vegetables, then introduce porridge and fruits into the diet. If a significant weight loss is noted, it is recommended to start complementary feeding with cereals. If there are gastrointestinal disorders or other problems associated with prematurity, it is better to postpone the start of complementary feeding to 1-1.5 months later.
Calcium and vitamin D preparations
Although the skeletal system of a premature baby is often formed at the time of birth, the bones are not yet sufficiently mineralized and have a soft structure. A lack of calcium and vitamin D can lead to the development of rickets, deformation of bone tissue, and a slowdown in growth. It is replenished with medication.
Vigantol and Aquadetrim are common in medical practice. They are prescribed to children older than 2 weeks in a dosage of 2 drops per day (1000–1500 IU), regardless of the time of year. For children over 1 year old, preparations with calcium and vitamin D are recommended to be taken from September to May in a dosage of 1 drop.
It is recommended to take the vitamin in the morning with the first meal. Oil-based preparations, like Vigantol, have better absorption. "Aquadetrim" contains a small amount of alcohol, so it can affect the baby's anxiety.
Massage and gymnastics
Massage and gymnastics are prescribed to newborns to strengthen the body and unlock the potential of life systems. For premature babies, massage and gymnastics are prescribed with the permission of a neurologist and ophthalmologist at the age of 1 month. The set of exercises can be carried out by both a specialist and parents independently.
Exercises for a child in the first months of life:
- The child lies on his back. Light and rhythmic movements apply gentle pressure on the chest in a circle.
- Stroking movements of the inner and outer surfaces of the baby's arms in the direction from the fist to the shoulder.
- When the baby grasps the masseur’s thumbs in his fist, light pressure from the inside opens the fist. After stroking with the thumbs of both hands, gentle pressure is applied to the baby's palm. With this technique, the child should grab your fingers into a fist.
- Leg massage is carried out with stroking movements from the toes to the heel and from the foot to the thigh. Do not massage the kneecap.
- Stroking the abdominal area from left to right without pressing in the area of the right hypochondrium.
- Raise your arms to the sides, and then press them back to your chest.
- Laying on the stomach. Stroking the back and buttocks area alternately with the back and inside of the palm up and down.
- We place the baby on the fitball with his stomach and slowly rock him in different directions. Afterwards, the exercise is repeated lying on your back.
Between exercises it is necessary to take short breaks to restore the baby’s breathing. Each exercise is repeated 3-4 times.
Cloth
When choosing clothes for premature babies, it is important to follow several rules:
- naturalness of fabrics;
- no rough seams;
- warm and soft material;
- all parts of the body must be completely covered.
It is not recommended to swaddle a child so that the limbs have the opportunity to develop faster.
Nipples and diapers
For babies born prematurely, regular pacifiers are not the right size. Therefore, there are nipples that have an orthodontic shape that promotes the correct formation of the bite and closure of the upper arch of the jaw.
The shape of the pacifier resembles the shape of a mother's nipple. Holes in the pacifier and mouthpiece help air circulate and do not interfere with the newborn's breathing. Pacifiers for premature babies are sometimes equipped with special slots that allow you to place a probe tube or ventilator inside the pacifier if necessary.
Almost every manufacturer of baby hygiene products offers diapers for babies born prematurely. They are well suited for small babies, made from thinner and softer material, and do not contain additional flavorings. The belt of such diapers is made taking into account not to injure the umbilical wound.
Depending on the manufacturer, diapers for premature babies are marked either by weight category (up to 2-3 kg) or are marked with size “0”. Also in the names of these hygiene products there are the additions micro, before newborn, premature.
Appearance of a newborn born prematurely
Babies born prematurely have several external features and clinical symptoms. The degree of severity directly depends on the period at which premature birth occurred.
The skin of very premature babies is thin and has a bright red color. It is abundantly covered with vernix and fluff. The baby's skin turns pale only two to three weeks after birth.
The body structure of the baby is disproportionate. The head makes up about one third of the baby's body, and the limbs are short. The belly is large and its surface is flat.
In very premature babies, all fontanels and sutures of the skull are open. The ears are quite soft and bend easily. The nail bed is not completely covered by nails. The nipples and areolas are poorly pigmented and are barely visible on the baby's body.
Very premature babies may have underdeveloped external genitalia. As a rule, in newborns of the first and second degrees of prematurity, clinical symptoms do not appear so clearly.
Premature babies rarely cry and do not exhibit excessive motor activity. If a seven-month-old baby is born, his body weight will be approximately 1.5-2 kilograms. The weight of eight-month-old babies can exceed 2 kilograms.
What to feed your baby
New mothers and fathers need to know how to properly organize the diet of a seven-month-old baby. Parents should be prepared for the difficulties that may arise on the way to creating the most appropriate food intake regimen. A correct and balanced menu is necessary in order for the premature baby to actively increase in height and weight.
The best nutrition option for a newborn baby, regardless of the timing of birth, is breast milk. This is an absolutely natural product, the composition of which fully meets the requirements of the baby’s body. It is enriched with nutrients and rich in vitamins.
It is very difficult for a baby who is born ahead of schedule to suck mother's milk from the breast due to the fact that the corresponding reflex is developed quite poorly or not developed at all. That is why, in order to fully saturate a premature newborn, parents need to supplement their baby with expressed milk from a bottle.
If for some reason breastfeeding is impossible, new parents purchase special milk formulas, which form the basis of the baby’s diet for the first few months of life. For babies born prematurely, you can purchase special formulas for premature babies in pharmacies. The components of the product promote faster weight gain and stimulate the development of the baby. In addition, feeding special foods minimizes the risk of allergic reactions. Parents need to keep in mind that they can only purchase formula after consultation with a specialist. As a rule, upon discharge, the doctor gives the new parents of a premature baby the necessary recommendations and advises which formula is best to purchase.
In the first month, you need to feed your baby 10 to 15 times a day, in small portions. In some cases, the number of feedings can reach 20. From the second month of life, the number of feedings can be reduced to eight.
After the child reaches six months of age, it is necessary to introduce complementary foods to diversify the daily diet and enrich it with additional nutrients and vitamins. It is strictly not recommended to introduce new products before the specified period, since the digestive system of a small child is not ready to consume any components other than mother’s milk or formula.
But you shouldn’t delay expanding the baby’s diet. This is fraught with a deficiency of vitamins and minerals. The first complementary food should be dairy-free porridge. Then, starting from the eighth month of life, you can add vegetables and meat, and fresh juices to the baby’s menu. Closer to one year old, the baby’s daily diet can be expanded with fermented milk products. It is strictly forbidden to feed a small child sweet fruits or add sugar to food.
Child development calendar: what your baby learns every month from birth to one year
Children really grow up very quickly. Just yesterday, when you brought your newborn baby home from the maternity hospital, you didn’t even think about the fact that today a little one-year-old man would be running around your apartment. Of course, you are concerned about whether your child is developing correctly and acquiring the necessary skills on time.
By tracking your child's development month by month up to a year and comparing it with the recommendations of pediatricians, neurologists and psychologists, you will not miss anything and can detect and correct possible deviations in time.
To preserve the moments of growing up in your memory, keep a special notebook in which you will describe the child’s development month by month up to 1 year.
A table indicating the time of appearance of a particular skill will be of interest not only to you, but also to your grown-up child in the future.
First month
The first month of a newborn's life is also called the adaptation period. The child learns to live outside the familiar environment - the warm mother’s tummy. At this time the baby:
The task of the immediate family is to place the child in comfortable conditions: not to overheat or overcool. About this in the article temperature in the room for a newborn >>>, change diapers and feed on time.
Of course, it is important to give your baby your love: carry it in your arms, talk, sing songs.
By the age of one month, the child already pays attention to bright toys and can follow them with his eyes and turning his head. The article contains information about when a newborn begins to see>>> The first color that newborns see is red.
On a note! The following exercise will be very useful: take a bright, preferably red, toy, and move it at a distance of 30 cm from the child’s face from left to right, from bottom to top. A one-month-old baby can already follow the movements of the toy.
At one month old, the baby already turns his head towards the sound. Find out when your newborn begins to hear>>> You can check this by rattling a rattle to the left and right of the baby.
In the first month of life, the child retains some innate reflexes of the newborn, which will completely disappear by the fourth month of life:
- sucking reflex (can suck objects in the mouth);
- swimming (if you lower the baby into the water with his stomach down, the child will make movements reminiscent of swimming);
- grasping (if you touch your palm, the child will clench his fist);
- search reflex (if you touch the cheek, it looks for the mother’s breast);
- step reflex - if you put the child on his feet (while holding him), he can “step”.
If you put the baby on his stomach, he will try to slightly raise his head; trains your neck, back and shoulders.
By the age of one month, physically developed children already begin to hold their heads.
Read more about what a one month old baby should be able to do>>>
And also in my video tutorial:
Second month
The second month of child development is sometimes also called the “month of revitalization.” Your baby now sleeps less and can stay awake for up to 50 minutes.
The child’s vision and hearing improve, the baby is able to look at objects from a distance of 30 centimeters to half a meter. The baby can spend about 15 minutes in his crib, looking at a mobile phone or other toys.
- At the age of two months, babies already raise their head and hold it in an upright position for some time.
- Some babies already know how to roll over from their side to their back. Read more about when a baby starts to roll over>>>
- The child studies his hands - he can bring his fists to his mouth and suck them;
- Infant reflexes are still preserved, but begin to gradually fade away;
- The emotional sphere also develops. At two months, the so-called “revival complex” is formed. This skill takes pride of place on the child development chart; this is one of the most important milestones up to a year, confirming the normal functioning of the nervous system;
- The baby can already recognize his parents and is happy with them. When you bend over the crib, the baby begins to quickly and quickly jerk its arms and legs;
- In the second month of life, your child will most likely give you his first conscious smile. If this doesn't happen, no big deal; This means that this joyful event will happen a little later. Find out when your baby starts smiling>>>
- At two months, a child can walk - he makes melodious vowel sounds, sometimes he can even pronounce “agu”, “aha”, “abu”. Children like their own “speech” and listen to it with pleasure. The article contains information about when the baby begins to coo >>>
Communicate with your child more often, sing to him, you will see that the baby will sing along with you!
Source: https://uroki4mam.ru/razvitie-rebenka-po-mesyatsam-do-goda
Weight gain
One of the determining factors in the proper development of a baby born earlier than expected is weight gain. A good increase can be ensured only with well-established, nutritious nutrition for the child, which will include all the necessary vitamins and minerals and meet the energy needs of the newborn baby.
Doctors divide the newborn period for premature babies into three stages, in the first of which the child does not gain weight, but, on the contrary, loses it. Babies born at term lose no more than 5% of their original body weight, and the weight of premature babies can decrease by 10%, or even 15% (in very premature babies).
At the second stage, medical specialists together with parents try to achieve constant weight gain, which should be about 15 grams per day. Once the baby's body weight is 2.5 kilograms, the newborn and mother are discharged from the premature ward.
At the third stage, the baby’s weight returns to normal. The last period lasts up to a year. In premature babies, this stage lasts longer depending on the degree of immaturity.
In the first month of life, as a rule, the baby gains a little, on average 200-300 grams. From the second month, weight gain is about 700-800 grams. From the third month to six months, the monthly increase in body weight can reach 800-900 grams. On average, during the first year of life, a baby born prematurely gains about 8-9 kilograms. It is closer to a year when a premature baby catches up with its peers in development.
Psychomotor development as a criterion of neurological health of a premature baby
In recent decades, our country has seen rapid changes in the work of neonatology services. The widespread organization of resuscitation and intensive care units for newborns, the widespread introduction of mechanical ventilation, the involvement of resuscitation specialists in neonatology, the development of many new techniques related to the care of very premature babies - all this allowed doctors not only to reduce neonatal mortality to some extent, but also to guide in its work, using new, internationally accepted live birth criteria, to care for children with extremely low birth weight. All these children adapt poorly to extrauterine existence. Almost half of them have organic lesions of the central nervous system of hypoxic-ischemic origin in the form of intraventricular hemorrhages of varying severity, ischemic foci, and periventricular leukomalacia. Their treatment and care require large material costs and moral stress from the staff.
At the same time, our clinical experience and literature data show that only 10–15% of children have neurological pathology so serious already in the neonatal period (decompensated hydrocephalus, brain atrophy, developmental defects, intractable convulsive syndrome) that they require transfer to a specialized neurological hospital, and the unfavorable outcome of its development and disability can be established already within this period. The remaining children, after somatic adaptation, can and should be kept at home, although it is known that during almost the entire first year of life, these children retain changes in the bronchopulmonary system, hemodynamic instability, a tendency to viral-bacterial infection, a high incidence of rickets, anemia , dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, biliary dyskinesia, prolonged dysbacteriosis, fermentopathy. In addition, most of them have problems with hearing and vision and perinatal damage to the central nervous system. That is why these children deserve special attention from doctors and society as a whole.
However, today we have a significant gap between scientifically proven high technologies for caring for premature babies, used in specialized clinics, and their subsequent observation in the general outpatient clinic network. An analysis of outpatient observation cards that we carried out over 2 years showed that these children cause great concern among local doctors. The lack of a scientifically based methodology for managing such patients causes great difficulties in identifying priority tasks aimed at correcting their somatic condition. An even more serious problem is the complete lack of scientific data regarding the characteristics of their neuropsychic and motor development, the concept of corrected age and its comparison with the actual one. Thus, there are 2 options for assessing the development of children and, accordingly, 2 forecasts. The first option is a “compassionate, calm attitude”: “the child is very small and may lag significantly behind his peers.” This approach in some cases leads to late diagnosis of gross developmental disorders, and therefore special treatment begins already at an advanced stage, when the child’s condition is difficult to correct.
The second option, more common, is to “exaggerate” neurological pathology, developmental delay, and overdiagnosis of pathological conditions, such as intracranial hypertension or hydrocephalus (not confirmed by functional studies). In accordance with this, it is often observed that the prescription of long-term dehydration is not always justified, and the early inclusion of an arsenal of stimulants, which can lead to the opposite result and slow down the development of children. In addition, the current system of separate monitoring of such a child - a pediatrician, a neurologist, a gastroenterologist, a pulmonologist, etc. - leads to the fact that each specialist, focusing only on “their” pathology, prescribes drugs that, in total, the child simply cannot “learn”, and in some cases it turns out that they are simply incompatible.
Thus, there is an urgent need to develop an ideology as well as a methodology for the observation, treatment and rehabilitation of premature infants.
The problem is that at 3-4 months of postnatal life of a premature baby, the doctor cannot predict the likelihood of an “adverse neurological outcome”, since the development of the disease is determined by 3 main points - perinatal brain damage, brain plasticity and adequate assistance, i.e. rehabilitation and corrective measures carried out at the right time and using the right means.
Currently, in the domestic and foreign literature there are many studies devoted to identifying risk factors for unfavorable neurological outcome in premature infants. Knowledge of these factors is certainly important for a specialist, but this does not yet make it possible to conduct an individual assessment and predict how the child’s condition will change further. In addition, almost any premature baby is, to one degree or another, at risk of developing neurological diseases. This determines modern guidelines regarding his follow-up in the general outpatient clinic network, which can be formulated as follows: “A premature baby is a obviously sick child, and he requires, taking into account the many unfavorable factors that he suffered in the perinatal and neonatal periods, constant stimulating treatment, and therapy should begin as early as possible in order to activate the compensatory capabilities of the brain.”
Current ideas practically do not allow a differentiated approach to the condition of children, since there are no criteria for their individual “health” that can be objectively assessed and controlled.
The first year of any child’s life is characterized by completely unique processes that manifest themselves in the child’s acquisition of many psychomotor skills: combination and purposefulness of actions, verticalization and stability, the formation of abstract thinking (searching for a hidden object), associations (comparing an animal object with one drawn in a book), play activities and social contact (reflection of the child’s relationship with adults “friend or foe”), etc. In order for the baby to acquire all the above skills and in 1 year of life turn from an absolutely defenseless newborn into a charming, active, active, inquisitive child, they must the most complex processes of the formation of intrahemispheric and interhemispheric connections within the brain, connections with peripheral centers, neuromuscular signal transmission will be realized, the functioning of the neuroendocrine system will improve and much more, which we, unfortunately, do not know and which is the great mystery of development.
The assessment and concept of development in all other periods of a child’s life determine the differentiated level of realization of the brain’s capabilities. But in the first year of life, this is, first of all, the formation of capabilities, which means that any new skill that a child acquires is a function of his psychoneurological health. In other words, the progressive psychomotor development of a child in accordance with monthly standards for acquiring skills can serve as the main criterion for the health of any child in the first year of life. This also applies to premature babies.
However, for the widespread introduction of this methodology into practice, first of all, it is necessary to resolve 3 main issues: how to assess the development of a premature baby, what is the “norm” for a premature baby and in what case and what therapy should be carried out.
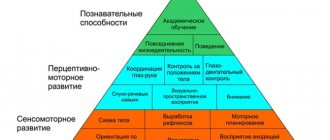
There are many scales used to assess child development. They are based on the mandatory identification of various lines of development, i.e., the versatility of the assessment, which makes it possible to timely determine the cause of the lag and direct efforts specifically at correcting the identified disadvantage. Thus, we must evaluate (from the first month of life) how successfully the formation of cognitive function, visual, eye-hand coordination, motor function, maturation of the auditory-speech analyzer, and what the social integration of the child is. In this case, it is necessary to test all children in the same way. In all cases, it is advisable to only listen to the parents’ words, but the child’s response should be assessed for himself, since the parents’ ideas and desires may not coincide with how neurologically the child is able to perform a particular action. In order for the child to react to the proposed action, it is necessary to come into contact with him, so testing should be carried out before the general examination, without undressing the child. Tests should have high sensitivity and specificity, be easy to perform, not require any additional equipment except 1-2 toys, and take no more than 7-10 minutes from the doctor so that the child does not get tired. Of all the available scales, the CAT/KLAMS scale meets the requirements to the greatest extent. It was developed by the American Academy of Pediatrics and is a compilation of all common scales, as unified and simplified as possible, in accordance with the objectives. For a more in-depth study, such a scale is certainly not suitable, but it is indispensable for screening and quick assessment of the dynamics of the development of a child’s skills and has a high degree of reliability.
This technique, which allows assessing the development of skills in solving visual (CAT section) and speech (CLAMS section) problems, as well as the development of a child’s motor skills (macromotor development scale), was created for testing children under 2 years of age. By comparing the developmental age with the actual age, the development coefficient is determined, which is equal to the ratio of the developmental age to the actual age, multiplied by 100. The development coefficient is calculated separately according to the 3 parameters described above. If they coincide and correspond to the actual age, or if the development coefficient is greater than or equal to 75, the child is considered to have normal development. For full-term children, a development coefficient below 75 indicates that the child is lagging behind, and with different indicators in 3 systems, it indicates developmental dissociation and allows one to choose the appropriate tactics for corrective measures.
The most difficult task is to determine the “standards” for the development of premature infants. This is especially true for extremely premature children born at less than 32 weeks of gestation and with a body weight of less than 1500 g. It is clear that, taking into account the degree of prematurity, morphofunctional immaturity, and perinatal pathologies, the standards for the development of psychomotor functions in these children differ from those of their full-term peers.
Special studies were conducted with retro- and prospective analysis in a large group of specially selected children with extreme prematurity, who had minimal disorders in the peri- and neonatal period (in the absence of organic damage to the central nervous system and severe somatic pathology) and by 2 years of life were equal to their full-term counterparts. peers.
When analyzing the development of children in this group, the following patterns were established, which can serve as a starting point when examining any premature baby. First of all, it is advisable to begin assessing his motor and psycho-emotional capabilities only after reaching the age of 40 weeks of gestation (on average, in children with a gestational age of 26–28 weeks, this is 3 months of their actual postnatal age). The norm for these children can be considered to be 1 month (4 weeks) of development according to the CAT/KLAMS scale. In the next 2-3 months (i.e., almost until 5-6 months of actual age), there is no significant increase in psychomotor skills - this is the so-called “plateau-like period of development of a premature baby” associated with the “accumulation of brain connections.” At this stage, in common practice, doctors most often think about drug intervention. However, functional and electrophysiological studies show that the absence of external manifestations of skill formation does not exclude the possibility that complex processes may occur in the brain that predetermine the child’s further spasmodic development. In addition, this period of a premature baby’s life requires special attention to somatic problems (issues of feeding and adaptation of the gastrointestinal tract, prevention and treatment of anemia, rickets, vitamin and mineral disorders, etc.), which most often appear at this time and may potentiate developmental delay.
From the seventh to eighth month of actual age (corrected age - 4-5 months), a pronounced leap in psychomotor development is noted. Thus, the increase in functional capabilities begins to outpace the corrected age by 3-4 weeks, by the 12th month of life - by 5-6 weeks, and by 18-20 months children are no different in development from full-term peers 12-14 months old. Achieving the level of full-term peers in motor development occurs by 18–20 months of actual life, in cognitive development by 20 months, and in speech development by 24 months of life.
The development of language function in premature infants also has certain features. Thus, only from the fourth month of corrected age (6-7 months of actual age) do they begin to develop the intonation of dissatisfaction, and other types of intonation expressiveness are formed, such as humming and then babbling. This indicates the activation of specific cortical speech structures. The appearance at the same time of an adequate reaction to the intonation of adults indicates the maturation of the auditory analyzer. In other words, the development of the mechanisms of the intonemic field occurs in accordance with the corrected age, and the phonemic field is delayed against the background of dysfunction of the stem structures, which determine the pronounced immaturity of the articulatory apparatus, but is always progressive in nature. Despite the fact that these features are characteristic of all very premature children, it is imperative to establish early speech therapy supervision over them in order to timely correct these deviations.
You can most clearly imagine the dynamics of the formation of psychomotor skills in the form of development graphs for corrected age (Fig.).
Identification of deviations from the “conditional” standard during mandatory monthly monitoring and examination of the child is an indication for a more in-depth analysis and comprehensive examination, the purpose of which is to identify pathology that can disrupt a certain line of development. So, if a child has an isolated slowdown in the formation of motor skills, one can limit oneself to physical methods of influence - massage, physiotherapy, swimming, etc. If there is no effect, a further differential diagnostic search should be carried out.
When there is a delay in cognitive development and secondary motor delay, it is first necessary to assess which tests are causing difficulties. This will make it possible to identify conditions associated with impaired functioning of the visual analyzer, with genetic diseases, with organic lesions of the central and peripheral nervous systems. In the absence of humming and babbling, it is necessary to exclude hearing loss.
In this way, a monitoring system for premature babies is formed. The child must be examined monthly, with an assessment of his psychomotor development and skills that were acquired during the month, parameters of physical development, somatic condition, neurological status, etc. If deviations are identified, the possible cause of the problem is assessed (this can not only be truly “neurological” diseases, but also past infections, feeding disorders, teething and even an unfavorable home environment), and therapeutic efforts are directed towards its correction.
Based on the above, it is possible to propose not only an algorithm for monitoring and identifying possible pathology in a premature baby, but also therapeutic tactics.
Thus, children are usually in the second stage of nursing until 40–44 weeks of gestation, which corresponds to 2–3 months of their postnatal life, depending on the degree of prematurity. It is during this time that they are transferred to outpatient observation in the general polyclinic network or in specialized centers. In the next 3 months of their life, in the absence of acute neurological conditions (a sharp increase in head circumference, outpacing the growth of chest circumference, an increase in the size of the ventricles of the brain according to ultrasound, clinical signs of acute intracranial hypertension - vomiting, throwing back the head, incessant screaming, hyperthermia, convulsions - all this requires hospital treatment) the child is recommended to undergo corrective measures. This is, first of all, nutritional selection, treatment of gastrointestinal dysfunction - biological products, enzymes, simethicone preparations, etc. It is necessary to start early prevention of rickets by prescribing vitamin D, preventing anemia, taking folic acid, selecting a complex of vitamins A, B and E. To improve cellular metabolism, the drug Elkar (L-carnitine) is indicated. To improve cerebral blood flow, vascular agents (Cavinton or cinarizine) are used. In our experience, the use of dehydrating agents requires more stringent indications, and their effectiveness is questionable.
Massage during this period should be gentle, short-term (no more than 10–20 minutes) and aimed at improving blood circulation in the skin and muscles. It should be remembered that therapeutic massage can provoke a deterioration in adaptation with the development of regurgitation syndrome, disruption of the circadian rhythm, an increase in excitement, in some cases turning into convulsions, as well as disturbances in cardiac activity, up to the re-opening of fetal communications.
At 5-6 months of corrected age, premature infants begin to clearly demonstrate a delay in the formation of motor skills due to a slower normalization of tone.
During this period, after the necessary examinations - ECG and EEG, you can begin to carry out a complex of intensive rehabilitation measures - therapeutic massage, physiotherapy, water procedures. Among medications, nootropic drugs are used, for example Pantogam, and if necessary, a course of Cerebrolysin is prescribed. In the future, when the condition normalizes and the formation of skills accelerates in accordance with the above standards, the child may not receive active therapy. At the same time, the lack of effect from the treatment serves as the basis for further examination, repeated rehabilitation measures with diagnosis of the cause of developmental delay and the inclusion of the entire arsenal of drugs used to treat a specific disease
This approach, successfully used at the Center for Correction of Development of Infant Children at the Moscow Research Institute of Pediatrics and Pediatric Surgery, can significantly reduce the likelihood of prescribing unnecessary treatment to a child. This is especially important, since when using drug therapy and using physical stimulation techniques in children with low birth weight, a large number of adverse, paradoxical reactions and complications are observed, up to the development of seizures, which parents should be warned about and which requires great responsibility from doctor
For questions regarding literature, please contact the editor.
E. S. Keshishyan , Doctor of Medical Sciences, Doctor E. S. Sakharova , Candidate of Medical Sciences Moscow Research Institute of Pediatrics and Pediatric Surgery of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Center for Correction of Early Childhood Development, Moscow
How to care for a newborn born prematurely
In order for a child born earlier than expected to catch up with his peers faster, parents need to know how to properly care for the baby and what conditions need to be created for him. Improving the functioning of organs and systems of seven-month-old children and the development of their psyche largely depends on parents, especially in the first year of life.
First of all, parents should take care of the microclimate of the room in which the newborn will live. It should be bright and spacious enough. The air temperature in an apartment or house should be in the range from 20 to 25 degrees. The room must be regularly ventilated. Drafts must be avoided.
In addition, new mothers and fathers need to maintain air humidity. Its level should be in the range from 50 to 70%. Too dry air often causes a runny nose. A humidifier, which can be purchased at any hardware store, can make the task easier.
Some children may require additional warming. A heating pad is ideal for these purposes.
Hygienic procedures in the first month of life are not recommended for those babies whose initial weight was less than 2 kilograms. To care for a baby's skin, cotton swabs soaked in warm water are suitable. After completing hygiene procedures, you need to wipe the baby’s skin dry and use baby cream.
Babies weighing more than two kilograms should be bathed every other day in a small bath. The water temperature should be 36-37 degrees. It is best to boil water for hygiene procedures. If desired, you can add chamomile and calendula to the bath. After a few months, it is allowed to use special herbal solutions, which can be purchased at any pharmacy without a doctor's prescription.
You can go for a walk with a baby born prematurely three to four weeks after arriving home. The baby should be dressed according to the weather. In the summer, you do not need to go outside from 11 a.m. to 3 p.m. to avoid overheating. For walks, it is better to choose morning or evening time of day.
You should not walk with a baby whose weight is less than three kilograms, at temperatures below ten degrees. After the baby’s weight reaches this value, you can take walks at minus fifteen degrees. You should not choose crowded places or areas where there are a lot of cars driving around. There is no need for the baby to breathe exhaust fumes. And this will not be beneficial for a nursing mother.
From month to month
These and other disturbances in the functioning of organs and systems require special attention to babies born prematurely. However, with a relatively small prematurity (gestation period of more than 35 weeks), children have every chance of leveling off in development at about one year of age with their peers.
The development of such babies month by month will take place according to the following scheme.
- 1 month. The baby's sucking activity is still weak, and besides, all organs and systems are experiencing adaptation stress. Therefore, the child gains little weight and spends most of his time sleeping. If such a baby is already at home, the main concern of parents is to protect him from viruses, germs, drafts, and temperature changes.
- 2 months. During this period, the child begins to actively gain weight and get stronger (which can be considered the main sign of proper development); it is already allowed to start laying him on his tummy.
- 3 months. The child's first facial reactions appear. He tries to focus his gaze on his mother’s face and raise his head. There is no smile yet, but the baby is sensitive to tactile contact. A grasping reflex appears, and visual and auditory concentration gradually develops. Now it is important to change the baby’s position more often so that the head is not constantly turned to one side, and to provide him with enough food and rest. Your weight should double by this time.
- 4 months. The baby begins to make the first sounds, raise and hold its head, and grasp the toy. Now it is possible to increase muscle tone, which is well relieved by gymnastics and massage.
- 5 months. The baby begins to smile and become interested in the world around him. He can already hold a toy in his hand. His vision improves slightly, and more sounds appear in his speech. The baby is already trying to turn its head in the direction of the sound, determining exactly where it comes from.
- 6 months. The baby is trying to roll over from his back to his tummy. He develops a “revival complex” at the appearance of relatives whom he already recognizes. The child talks more actively. His weight has already tripled by this point. With the support of his armpits, he rests his legs on the surface, squatting slightly.
- 7 months. The baby is already quite active, can roll over on his tummy, and tries to crawl with his “belly.” He holds the toy confidently. Now he may have his first teeth.
- 8 months. The child gets on all fours, tries to sway, tries to sit down on his own, and strives to communicate with adults. He understands if he is asked to show something. Loves songs, nursery rhymes, fairy tales, listens to words and intonations.
- 9 months. Now the baby is sitting almost confidently and is trying to crawl “for real.” He needs communication even more. The baby's speech develops - the first repeating syllables appear.
- 10 months. The child can stand and move independently with support, but for now he mostly crawls. He reacts quickly to various sounds and loves to watch bright toys moving in front of his eyes. Reacts to his name.
- 11 months. The baby has learned to sit down and stand up, even stand without support (some babies can take several steps without support), but still loves to crawl. Begins to be interested in pyramids and cubes, toys that move. He gravitates more and more towards communicating with his family.
- 12 months. Many premature babies begin to walk independently by this age - they were able to catch up with their lag within a year. It should be borne in mind that in mental development, premature babies are still 1–2 years behind their peers. This is considered normal.
Do not rush to consider it a deviation if your baby has not mastered any of these skills by a certain month. The development of each baby is individual, it depends on the degree of prematurity, the presence of complications and health problems, and the general condition of the toddler. The greater the degree of prematurity and weakness, the later the skills appear. If you are concerned about anything, consult your pediatrician.
Features of care
A premature baby requires more attention and precautions when caring. First of all, seven-month-old children, whose development depends largely on their parents and the environment, should grow up in a favorable environment, in love and warmth.
Clothing and related products (caps, socks, etc.) must be made exclusively from natural materials. Fasteners should be in the form of buttons and located on the outside. There should be no tags or labels inside the vests and rompers. They can injure the baby's delicate skin. For premature babies, you need to purchase special clothes, since standard size baby onesies and rompers are too big for them.
Hygiene products deserve special attention. Preference should be given to hypoallergenic compounds, the quality of which is confirmed by certificates. For babies born earlier than expected, it is possible to purchase size zero diapers in baby stores, which are intended for newborns whose weight ranges from one to three kilograms. There are also diapers for children whose birth weight was less than one kilogram.
A massage would be helpful. It will help increase muscle tone, strengthen all ligaments and bones, improve metabolism and the functioning of the digestive system. A child up to one year old can have a massage that includes stroking movements. In any case, before carrying out any manipulations, you must contact a medical institution for the advice of a qualified pediatrician. Some parents provide professional nursing care for their premature baby. A medical professional will not only be able to better assess the development of the baby in the first weeks of life, but also, if anything happens, alert the parents to the occurrence of any problem.
Alarming symptoms. What to do?
Normal behavior for a newborn is periodic drowsiness or moodiness. This depends on weather conditions, environmental conditions or maintenance regime. But, frequent such behavior by a baby can be an alarming symptom.
If the baby's lethargy or excitability is accompanied by convulsions, crying when touched, or lack of visual-auditory attention (for a child older than 2 months), such symptoms may be signs of early autism. This condition requires immediate consultation with a neurologist and psychologist.
In addition, a mandatory reason for contacting a doctor or emergency medical care will be:
- systematic long-term refusal of the child to breastfeed or another method of feeding;
- presence of profuse vomiting;
- yellowness of the skin and whites of the eyes;
- long painful cry;
- sudden cardiac and/or respiratory arrest;
- lethargy and pallor.
If any of the above symptoms are present, it is necessary to contact medical personnel as quickly as possible and act in accordance with their recommendations before providing medical assistance.
Why is it better to have a seven-month-old baby than an eight-month-old baby?
There is an opinion that it is better to give birth to a seven-month-old baby than an eight-month-old baby. Why? Let's turn to embryology. 7 months is how many weeks of pregnancy? As already noted, this period lasts from 28 to 32 weeks. The child is actually fully formed and can easily live outside the mother’s womb. However, its organs are not fully developed, the systems do not function to their full potential. Only the stomach and intestines are fully formed. The cerebral cortex is actively developing.
For a long time, doctors argued that the likelihood of successfully nursing a seven-month-old baby is much higher than saving an eight-month-old one. This is actually a myth. At 8 months, the baby’s vital stages of development are behind him, and he is almost ready to be born. The only organ that continues to actively mature is the brain. Experts say that the likelihood of successful nursing of a premature baby depends not even on the period at which he was born, but on his indicators at birth. First of all, it depends on the child’s height and body weight.
Medicine has come so far that doctors are now able to save and deliver babies born at 28-29 weeks of pregnancy. Seven-month-old children, whose development is not complicated by unfavorable factors, with proper care and regular monitoring by medical personnel, after some time are able to catch up with their peers.
Prevention of premature birth
Every woman carrying a child should know about measures to prevent premature birth. This will allow you to carry the long-awaited baby and give birth on time.
At the moment, the most informative way to determine the risk of premature birth is a test based on the determination of the glycoprotein fibronectin in cervical mucus after 20 weeks. The presence of this substance in the cervical mucus is considered a harbinger of imminent labor. The most accurate study is a couple of weeks before the expected delivery. The testing accuracy is more than seventy percent. Women need to understand that such a study is carried out exclusively within the walls of a medical institution and only on the advice of the doctor who is caring for the pregnancy.
Another test that can help prevent early labor is an ultrasound scan done transvaginally. An ultrasound can measure the length of the cervix. If the indicator is more than three centimeters, the likelihood of premature birth is reduced to zero.
The woman herself can prevent early birth, not only during pregnancy, but also during pregnancy planning. Before conception and while carrying a child, it is best for a woman to give up alcohol and cigarettes. Narcotic and psychotropic substances are out of the question. You should not use any medications while planning a pregnancy. It is also better to avoid antibiotics. You need to be very careful about your health during the period of pregnancy. A woman’s immunity is weakened, which means she is susceptible to viruses and infections. Any unfavorable factor can provoke premature birth.
During pregnancy, it is best to avoid wearing high heels. In winter and spring, when there may be ice on the roads, you should give preference to boots and shoes with non-slip soles. This will avoid falls and, as a result, injuries. An accidental fall can cause premature birth.
Low birth weight fetus - causes and consequences: what to do if the baby is developmentally delayed?
The weight of the fetus is one of the criteria by which the doctor can determine the level of its development and condition. The closer it is to the norm, the higher the chances of a natural birth without negative consequences for the child. A baby whose weight is more than 10% less than normal is considered low birth weight. Why might intrauterine growth retardation occur? What should a mother do if she is diagnosed with this?
Norms of fetal body weight at different stages of pregnancy
In the first weeks of pregnancy, the doctor cannot determine the weight of the fetus because it is too small, and this parameter is not important for diagnostic purposes. Its information content increases in the second and third trimester. The norms for fetal weight throughout pregnancy are shown in the table.
| Week of pregnancy | Weight, g | Week of pregnancy | Weight, g |
| 11 | 10–15 | 26 | 850–1000 |
| 12 | 15–20 | 27 | 1000–1200 |
| 13 | 20–30 | 28 | 1200–1350 |
| 14 | 30–50 | 29 | 1350–1500 |
| 15 | 50–75 | 30 | 1500–1650 |
| 16 | 75–115 | 31 | 1650–1800 |
| 17 | 115–160 | 32 | 1800–1950 |
| 18 | 160–215 | 33 | 1950–2100 |
| 19 | 215–270 | 34 | 2100–2250 |
| 20 | 270–350 | 35 | 2250–2500 |
| 21 | 350–410 | 36 | 2500–2600 |
| 22 | 410–500 | 37 | 2600–2800 |
| 23 | 500–600 | 38 | 2800–3000 |
| 24 | 600–750 | 39 | 3000–3200 |
| 25 | 750–850 | 40 | 3200–3500 |
Causes of fetal weight deficiency
Fetal body weight may differ from normal, and this does not necessarily indicate pathology. However, if the weight is significantly below the average, doctors talk about a low-birth-weight child. Reasons for this condition:
- heredity;
- multiple pregnancy;
- maternal malnutrition;
- bad habits (especially smoking, which causes a narrowing of the diameter of the placental vessels);
- infections and chronic diseases of the mother;
- woman's age under 18 and over 35 years;
- anemia accompanied by hypoxia of the baby;
- failure of the placenta to perform its functions due to preeclampsia or hypertension;
- exposure to stress and fear;
- severe toxicosis;
- work in hazardous production;
- the baby has a disease that leads to developmental delay.
How to fix the situation?
If the fetus is low in weight, this can have serious consequences, including intrauterine death. Fortunately, this rarely happens. However, such children have a harder time with childbirth and are often diagnosed with asphyxia and neurological diseases. If a low birth weight baby experiences hypoxia, he may develop lung disease.
Regardless of the reason for the low fetal weight, the situation can be corrected. Pregnant women are prescribed:
- drugs to relax the muscles of the uterus (its contractions lead to deterioration of blood flow);
- vasodilators;
- medications that increase the child’s resistance to hypoxia;
- hyperbaric oxygenation and medical ozonation to saturate the mother's blood with oxygen.
A woman should increase her consumption of fruits, vegetables, and foods with animal proteins. It is recommended to limit physical activity and spend at least 6 hours a day on your side to improve blood flow in the placenta. Treatment is most often successful. If the baby still doesn't gain weight or is too weak to pass through the birth canal, doctors perform a caesarean section.
Prevention of fetal developmental delays
In order to prevent the baby from lagging behind in development, a woman at the stage of pregnancy planning must cure chronic diseases or at least stabilize her condition. While carrying a baby, she should:
- to refuse from bad habits;
- monitor your weight;
- Healthy food;
- keep chronic diseases under control and undergo examinations more often;
- avoid contact with toxic substances.
Women with their first pregnancy in adolescence or after 30 years, or who gave birth to low-birth-weight children, are recommended to take a course of vitamins and drug prevention of fetoplacental insufficiency. It is prescribed for up to 12, 20 and 30 weeks.
Source: https://www.OldLekar.ru/beremennost/plod/malovesnyj-prichiny-i-posledstviya.html