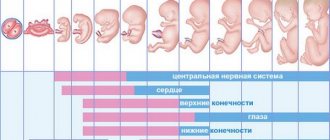
16 weeks of pregnancy is how many months? - you have a week until you reach the fourth month of pregnancy. Your chances of miscarriage have dropped to one percent, so get ready for exciting times. Your baby may hear your voice and you may start to feel his kicks! The 16th obstetric week of pregnancy differs from the usual one, since gynecologists count from the date of the last menstruation.
What happens at 16 weeks of pregnancy?
At the end of the fourth month and the beginning of the fifth, the uterus gradually begins to emerge into the abdominal cavity, as a result of which the pregnancy may become noticeable to others. The growth of the uterus leads to increased stress on the spine, which can cause pain in the lower back.
The 16th week of pregnancy is the time when it is already possible to determine the baby’s gender using an ultrasound examination, since the external genitalia are formed. The child has grown noticeably since the previous week, and over the next month there will be a sharp jump in weight and height.
Typically, in the middle of pregnancy, women feel good and their appearance noticeably improves. Sensations in the abdomen at 16 weeks of pregnancy become less pronounced. Nausea goes away and odor intolerance decreases. The only problem that remains with a woman almost until childbirth is constipation.
Scheduled examinations
Pregnancy 16-17 weeks is the time when an expanded list of tests is prescribed.
In addition to regular research:
- general clinical examination of urine;
- body weight measurements;
- blood pressure measurements.
Additional tests may be ordered for:
- hCG;
- AFP;
- Estriol-A.
This is a so-called triple biochemical test, which allows timely detection of the presence of genetic abnormalities and serious malformations of the fetus. A significantly elevated hCG in the blood of a pregnant woman may be due to the fact that the fetus has Down syndrome.
The mechanism of increased hCG in this chromosomal pathology of the fetus has not yet been clarified, but it is known for sure that the level of hCG is the most sensitive marker of fetal Down syndrome. If a woman is 16 weeks pregnant and the fetus is developing abnormally, then a triple biochemical test will help identify a predisposition to the following pathologies:
- Down syndrome (hCG level is more than doubled, other markers are low);
- Edwards and Patau syndromes (low levels of all markers);
- Turner syndrome (normal hCG level with low levels of other markers).
In addition to biochemical blood tests, an ultrasound can be performed at 16 weeks of pregnancy, although, as a rule, this study is prescribed at 18-20 weeks. An ultrasound may be prescribed in the following cases:
- if the first scheduled screening has not been completed;
- if there is a suspicion of premature cervical dilatation;
- to determine the sex of the baby. Of course, the study is not carried out to satisfy curiosity, but to exclude hereditary pathologies transmitted to a child of a certain sex.
In addition, ultrasound allows you to measure the body parameters of the unborn baby, examine its internal organs and evaluate the development of the placenta.
If, as a result of tests and ultrasound, a high risk of developing pathologies is revealed, the expectant mother should not be upset ahead of time. It is impossible to make a diagnosis based on the results of these tests. To get reliable results, you should undergo additional examinations, which may include:
- chorionic villus biopsy;
- cordocentesis;
- amniocentesis.
In addition, genetic counseling is necessary.
Changes in a woman's body
The uterus has increased even more, and its weight is about 250 g. It is located at a distance of 7-8 cm from the navel. By the end of the fourth month, the mother’s belly usually increases by 2-2.5 kg, but there should not be a sharp increase yet. Weight gain occurs due to an increase in the volume of blood and lymph fluid, as well as the mass of the distended uterus. However, if weight gain occurs quickly enough, you need to consult a specialist - this may be a sign of preeclampsia.
At this stage, carpal tunnel syndrome, itching in the abdomen, palms, feet, swelling of the fingers, face, and ankles are also often observed. Due to the lethargy of the muscle wall, intestinal function becomes difficult. Since constipation threatens the normal development of the fetus, you need to carefully approach the issues of regular bowel movements and proper nutrition.
The hormonal influence of progestron can cause pyelonephritis, which increases the risk of premature birth, so you need to carefully monitor your health and be careful about various infections.
The 16th week of pregnancy is characterized by interesting sensations. During pregnancy, the mammary glands actively prepare for upcoming breastfeeding. The milk ducts become enlarged, which leads to swelling in the breasts. Other possible changes could be:
- darkening of the nipples and areolas, as well as the appearance of small Montgomery nodules;
- the formation of a thin venous network, which is due to increased blood supply to this organ.
- Tiredness appears in the legs. The center of gravity of the body shifts, weight is gained - the load on the legs significantly increases. It is at this time that a woman develops the so-called duck gait.
Feel
They can still be very individual for each woman. In addition to toxicosis and emotional instability, painful sensitivity of the breasts and/or nipples may now completely disappear.
- Appetite is noticeably better. Food whims may persist, but are not so acute. For example, you might want to eat a bowl of ice cream. But this desire will not bring you to tears. You can calmly wait until you can go and buy what you want.
- The uterus presses slightly on the diaphragm. Sometimes this makes it difficult to breathe. Just make sure that when you suffocate, your hands don’t get cold, your fingertips don’t turn blue, and you don’t feel like you’re about to faint.
- Physiological runny nose in pregnant women may not go away until childbirth. Do not use vasoconstrictors. Carry a small aerosol can of sea water with you.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome may occur, that is, pain and numbness in the wrist.
- Another specific sensation is itching in the palms and soles.
- The arms, legs and face may swell slightly. It is safe if it only happens occasionally and goes away quickly.
- Constipation almost always occurs; you just need to loosen your diet a little.
And the most important thing! Skinny mothers, especially those who are not pregnant for the first time, can feel the first movements of the baby! Be sure to check your sensations, because light, barely noticeable tremors of your baby can be confused with manifestations of flatulence. In any case, the antenatal clinic doctor will certainly ask if you are mistaken. Are you sure the baby is moving? Write down the date, it is important.
It happens differently. Mothers are worried and complain to doctors: “It’s been almost four months, but I don’t feel any movement.” This is just normal. The practice of obstetricians and gynecologists shows that most often the first fetal movements are felt at 20 weeks in women who are expecting a child for the first time and at 18 weeks in subsequent pregnancies.
What can hurt
Just a little, without disturbing, almost everything hurts from time to time:
- lower back - due to changes in the body;
- ribs – if you have been sitting in an uncomfortable position for a long time;
- legs – after a long walk or long standing;
- the stomach below or on the sides - with a sudden change of position;
- head - in case of overwork, any experience.
If pain, even minor pain, almost never stops, tell your doctor about it. Do the same if you experience severe pain.
What happens in the stomach - a woman’s sensations
The first sensations of fetal movement appear. They are not yet sharp, and you can only feel them at rest. Since the baby is in the free space of the uterus, and all its movements are “smoothed out” by the amniotic fluid, the first movements resemble “movements of a fish,” “fluttering of a butterfly,” or “bursting of bubbles.”
The 16th obstetric week of pregnancy is accompanied by slight malaise, weakness or dizziness, which is due to the active growth of the fetus. It is important to eat right and avoid long breaks between meals.
At the end of the fourth month, a woman may still have mild toxicosis, and some expectant mothers may continue to experience morning sickness until delivery. By this period, the hormonal levels have stabilized; the sensations at the sixteenth week are no longer accompanied by mood swings, anxiety, tearfulness, and irritability.
What does your body look like
You are beautiful! Don't look for flaws in yourself and don't think that you have become unattractive. Yes, the body changes noticeably, but this is the norm.
Breast
She looks fuller. You feel its heaviness. The skin around the nipples has probably darkened and yellowish-white bumps are visible. Dark veins may clearly appear under the skin of each breast. Make sure there are no stretch marks. To prevent them, use any special cream or good olive oil.
Stomach
Your waist is rounded and your tummy is visible in any tight clothing. You should already have comfortable maternity pants and perhaps special blouses and sweaters. Depending on the season and climate in your area, special tights may be required. And in the heat, choose beautiful and comfortable sundresses.
When pregnant with twins, the belly grows faster and becomes noticeable earlier.
Leather
The thin strip between the border of pubic hair growth and the navel is still clearly visible. Pigment spots may appear. But often you may be simply amazed at how amazingly soft the skin throughout your body becomes. Due to an increase in blood volume, it may acquire a special pink tint (instead of the original light color).
Photos of bellies:
Discharge from the genital tract
At the 16th obstetric week of pregnancy, the discharge may change its character: it acquires a milky color and increases in volume. But at the same time, their consistency and smell remain the same. The appearance of such discharge is due to stretching of the walls of the uterus and ligamentous apparatus. If there is red, brown, yellow, green or bright yellow discharge with a pungent odor, accompanied by pain, a woman should visit a gynecologist for a comprehensive examination.
To prevent possible problems, the expectant mother needs to take care of her hygiene and wear only natural cotton underwear. If necessary, you can use intimate hygiene products, panty liners, and tampons should be abandoned.
Ultrasound
Between 16 and 20 weeks, the woman undergoes a second screening examination, which includes ultrasound scans and tests. It allows you to assess the viability and proper development of the fetus, as well as the presence/absence of any pathologies.
An ultrasound scan can already determine the gender of the fetus, since the external organs have formed. Sometimes this can be quite difficult to do, since the child may cover himself with his arms or be in a position that is inconvenient for visualization.
At the sixteenth week, Doppler ultrasound is performed as indicated, which is necessary to assess blood flow in the umbilical cord. This test shows whether the fetus is receiving enough nutrients and oxygen from the mother.
Second screening
At this time, a second screening can be performed to identify pathologies of fetal development.
It is not obligatory for everyone, it is carried out at the request of the woman, and also in cases where:
- On a previous ultrasound, abnormalities in the development of the fetus were noticeable.
- The expectant mother suffered from influenza, ARVI or other infectious disease.
- The pregnant woman has been diagnosed with any tumors.
As part of the screening, an ultrasound examination is performed, which reveals progress in fetal development. The formation of bone tissue, heart function and other important indicators are assessed. The doctor also carefully examines the placenta to make sure that it provides the fetus with full nutrition and oxygen.
A biochemical blood test helps to more accurately determine the condition of the mother and fetus and exclude the presence of serious pathologies. In order for the result to be as reliable as possible, a couple of days before donating blood, you need to limit the consumption of seafood, citrus fruits and chocolate - they can distort the results of the study.
What happens to the fetus at 16 weeks of pregnancy
The child is already about 109-117 mm in height, and weighs at least 80 g. It is similar in size to an avocado, but still moves freely in the uterine cavity. The volume of amniotic fluid is about 250 ml.
A thin muscle layer is formed in the fetus, so it already knows how to hold its head straight and turn it to the sides. The muscles on the face have also strengthened, and the child can make active facial movements - frown, open his mouth, and also wink. In girls at this stage, the ovaries descend into the pelvic area, the vagina, uterus and fallopian tubes are developed. In boys, the external genitalia are formed, but the testicles are still located in the abdominal cavity.
The child actively swallows amniotic fluid and can taste it. The kidneys and bladder work well, so the fetus pees approximately once every 45 minutes. The amniotic fluid itself is renewed up to 10 times a day. The umbilical cord, which connects the mother to the fetus and transfers nutrients, is located slightly lower in this period than before.
The 16th obstetric week of pregnancy is the time when the ligamentous vocal apparatus begins to form, but the baby will make its first sounds only after birth. Nerve endings develop in the skin, so it becomes very sensitive. In case of any irritation, the baby clenches his fingers into a fist, moves his arms and legs away under mechanical influence on the amniotic sac.
The fetal blood has already been formed, and at this stage it is already possible to determine its group and Rh factor. But the child still produces fetal hemoglobin, which is similar in structure to oxygen. Usually, by the end of the baby’s first year of life, it is completely replaced with a normal one.
Fetal development
Now the baby is actively growing from head to toes. Besides:
- the skeleton is actively ossifying;
- legs lengthen;
- all muscles are improved;
- some systems work quite “adult-like”: for example, a baby swallows amniotic fluid, it turns into urine and is excreted;
- the heart beats about twice as fast as mom’s and pumps blood perfectly;
- more and more new blood cells are formed in the baby’s blood, special fetal hemoglobin begins to be produced;
- the genital organs are developing, and if the baby turns successfully during an ultrasound, an experienced doctor will tell you whether you are expecting a girl or a boy;
- the eyelids have almost completed their development and are ready to open;
- the child moves his limbs, sucks his thumb and grimaces.
In addition to the overall size of a small body, during an ultrasound, the doctor also checks individual parameters. For example, a baby’s forearms are 12-18 mm long, and the head circumference is 11-13 cm.
All movements of the fetus are unconscious, spontaneous. The baby's face is already quite human, only the eyes look too bulging.
The umbilical cord is now about half a meter long and has a diameter of 20 mm. It is flexible and durable.
Frozen pregnancy
Under unfavorable conditions, the fetus may die in the uterus. Main reasons:
- infections;
- severe developmental abnormalities;
- Rhesus conflict;
- other negative factors (unhealthy lifestyle, unfavorable environment).
When pregnancy fails, the dead fetus remains in the uterus and poses a threat to the woman’s life. If the development of pregnancy stops, the doctor will issue a referral to the hospital. There, artificial birth will be induced using special drugs.
Women who have experienced a frozen pregnancy are not recommended to plan to conceive within the next year.
Possible problems
At 16-20 weeks, a pregnant woman undergoes a second screening and triple test, which can determine the presence of certain pathologies, serious anomalies or Down syndrome. If, based on the test results, the doctor suspects a problem, the woman will need to undergo a special test - amniocentesis. It is carried out using a special thin needle, which removes a small amount of amniotic fluid. This process is controlled using an ultrasonic device. Before the procedure, local anesthesia is applied to the puncture site. After this, a test for 40 defects is carried out. The risk of miscarriage associated with amniocentesis is no more than 3%.
Other possible problems during this period include:
- isthmic-cervical insufficiency;
- primary placental insufficiency.