Obstetric pathology is an important aspect of modern medicine. And among all diseases, miscarriage holds a special place. For women who hoped for a successful conception and further development of the child, this becomes a heavy blow. A similar situation can occur in the early stages, when a non-developing pregnancy of the anembryonic type occurs, which indicates the absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg. Why this happens and what actions should be taken are questions that the doctor will answer. And a woman should follow his recommendations.
Where it all begins
When a woman is planning a pregnancy, she cannot even imagine a fertilized egg without an embryo. However, representatives of the fairer sex often have to face this problem.
At the moment of ovulation, the female cell leaves the follicle - the place of its development. Heading towards the uterine muscle through the fallopian tubes, it meets the male reproductive cell. At this moment, the sperm merges with the egg, resulting in the formation of a zygote. Continuously dividing and multiplying, the cells move towards the uterus, where they are firmly attached to the walls for all subsequent months of pregnancy. With normal development and proper growth of the embryo, the happy couple will see their baby after forty weeks of pregnancy.
Attachment of the fertilized egg can occur both to the anterior wall of the uterus and to the rear. This will not affect the course of pregnancy and the birth of the baby.
Possible pathologies
During pregnancy, various situations may arise when the condition of the embryo turns out to be incompatible with life. Let's look at the most common of them.
For example, if the fertilized egg attaches outside the uterine cavity, then this is called an ectopic pregnancy. This condition can pose a threat to a woman’s life, so it should be diagnosed and corrected as early as possible.
A woman can also have an arbitrary miscarriage for one reason or another. In this case, the lady also needs urgent medical care.
Another pathology is a fertilized egg without an embryo. This condition has been occurring quite often lately. Out of a thousand pregnant women, one hundred do not have an embryo.
Anembryony
This diagnosis can be made to a woman when the fertilized egg develops and grows over weeks, but does not have an embryo.
Under the influence of certain factors, cell division stops at a certain level, and the embryo stops growing. In this case, its size is so small that even an ultrasound machine cannot detect it. Then the doctor announces this terrible diagnosis to the woman: a fertilized egg without an embryo.
There are also cases when the embryo not only stopped developing at the very initial stages, but was completely absent. Then the pregnant woman is also diagnosed with anembryonia. With this type of pathology, the fertilized egg may not meet its due date for weeks or may develop and enlarge without contents.
Fertilized egg without an embryo: why does this happen?
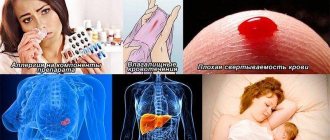
The reasons for the development of anembryonia are still not fully understood. However, there are several prerequisites that can provoke the death of an embryo in the early stages of its growth.
Bad habits
This point includes nicotine addiction, excessive consumption of alcohol. Harmful destructive substances pass through the blood of the expectant mother to the fetus and have an irreversible effect on it, as a result of which development stops.
Genetic abnormalities
A fertilized egg without an embryo may be due to initial disturbances in cell division after fertilization. In this case, the woman is unable to influence the situation and somehow prevent herself from such a pathology. It is also possible to develop a similar defect if fertilization occurred with the cells of a blood relative.
Hormonal disorders
When stopped, the size of the fertilized egg usually does not correspond to the term. The reason for this may be a lack or excess of certain hormones in the female body. Only that representative of the fair sex in whose body the production of hormones is in perfect order can bear a child.
Causes and mechanisms
The causes of undeveloped pregnancy are diverse and complex. It is difficult to single out one factor that has the greatest impact on a woman’s body before and after conception. Most often we are talking about an association of several reasons. Of these, the following are important:
- Infections (viral-bacterial, chlamydial, fungal).
- Chromosomal abnormalities (trisomy, monosomy, tri- and tetraploidy).
- Endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, adrenogenital syndrome).
- Autoimmune disorders (antiphospholipid syndrome).
- Intoxication with chemicals.
- Heavy physical activity.
- Radioactive exposure.
- Taking certain medications.
The sensitivity of the embryo to external unfavorable factors is greatest in the early stages. There are critical periods during pregnancy when the risk of pathology is significantly higher. This is mainly observed 7–12 days after conception, during implantation of the fertilized egg into the uterine mucosa, and from 3 to 8 weeks of gestation, which is associated with active processes of embryogenesis.
Among the mechanisms of development of anembryonia, the main role belongs to disruption of the life support processes of the embryo, which leads to its death. This occurs against the background of cessation of chorionic blood flow, involution of the villous membrane and exudative-fibrous reaction of the endometrium. The latter, instead of decidual transformation, acquires signs of glandular-cystic hyperplasia. If the pregnancy is not rejected, the fertilized egg without an embryo can persist in the uterus for a long time, increasing the risk of complications.
Anembryonia is a type of non-developing pregnancy. And its causes include external and internal factors that have an adverse effect on the fetus in the early stages of gestation.
Fertilized egg without embryo: signs of pathology
At the initial stage of development of the pathology, the woman does not experience any discomfort. During the development and growth of the fertilized egg, a pregnant woman produces a certain hormone. Under its influence, a woman experiences all the “delights” of pregnancy. She may be tormented by morning sickness, intolerance to certain smells, and the desire to eat something “like that.” The absence of an embryo in the egg does not affect these characteristics in any way. Therefore, a woman may not suspect anembryonia until the last moment.
For some representatives of the fair sex, the opposite happens. The body, realizing that the condition of the embryo is incompatible with life, begins to reject the fertilized egg. At this moment, the pregnant woman may feel pain in the lower abdomen, as well as observe red or brown discharge from the genitals.
Absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg - reasons
In most cases, many doctors find it difficult to answer the question of why there is an absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg. In general terms, it can be assumed that there is a genetic anomaly, exposure to an infectious agent or other negative environmental influences. Hormonal dysfunction also plays a role in the pathological process. In some sources, the absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg is called anembryony. So, the main reasons for diagnosing this pathology are:
- Various infectious agents of viral or bacterial origin. Typically, this process is dangerous in the early stages of the formation of the fertilized egg. During this period of time, the virus has a negative impact on the embryo itself, or provokes a negative impact on it. High temperatures at the time of a woman’s illness simply have a tremendously negative effect on the pregnancy process. Febrile fever literally destroys the embryo.
- Radiation exposure at the time of formation of vital systems and organs in the fetal body.
- Toxic poisoning that has a detrimental effect on the fetus.
- Failure of hormonal genesis, which is also observed in the early stages of gestation.
- Drinking alcohol, smoking cigarettes, using psychotropic substances and drugs.
- Hereditary predisposition.
To approximately establish the cause of the pathological process, a histological study is carried out. Taking tissue from a pregnant woman increases the chances of identifying the origin of the pathology. Anembryony of the second ovum is also detected in some women.
In order to avoid anembryonic pregnancy, it is necessary to fully examine the partners. The genetic formula is being studied, materials are being collected to determine what could influence such a pathology. The woman's sperm and reproductive cells are also taken to the laboratory. If the ultrasound machine does not show an embryo in the fertilized egg, then we can say that the pregnancy was unsuccessful.
What surprises medical experts the most is pathological pregnancy in prosperous and healthy partners. Usually, if further, during a second pregnancy, if there are huge chances of conceiving a future child, without any pathological processes. If there is no embryo in the fertilized egg for 8 weeks, then take urgent medical measures.
To get a positive result, you need to wait a certain period after the first unsuccessful attempt. This period of time is needed so that the woman’s body can fully recover and gain new strength for the next pregnancy.
Diagnosis of pathology
If a woman is not bothered by any symptoms, then she will find out about anembryonia at the next examination using an ultrasound sensor. The doctor discovers that the size of the fertilized egg does not correspond to the term.
If signs of an ongoing miscarriage appear, the woman usually turns to a specialist herself. To begin with, the obstetrician-gynecologist conducts a physical examination on the gynecological chair and notes the condition of her cervix. After this, the patient is prescribed an ultrasound examination. The doctor records the fertilized egg on the screen - what it looks like, what size it is - and notes the absence of an embryo.
If a woman doubts the doctor’s competence, she can undergo a re-examination in a few days. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the intensity of the discharge and exclude bleeding. If repeated diagnostics show a fertilized egg without an embryo - a photo of the empty ring is visible on the screen - then there is no doubt about the assumption of anembryony.
After a diagnosis is made, a woman definitely needs medical correction.
Additional diagnostics
Additional methods are of decisive importance in the diagnosis of anembryonia. And the main role in this is played by ultrasound examination of the uterus. Based on its results, the following signs of pathology are determined:
- The absence of an embryo is an “empty” fertilized egg.
- Areas of chorionic detachment.
- Discontinuity of the decidua.
- Enlarged amniotic sac.
- Fuzzy visualization of the embryo.
- Deformation of the fertilized egg, uneven structure.
- No heartbeat.
If the doctor said that the woman does not have an embryo according to ultrasound, but clinically the pregnancy is progressing normally, then the study must be repeated after 7 days. In the absence of pathological changes, the fetus will grow, and it will become not only visible, but also audible (at 8 weeks there should already be a heartbeat). Therefore, you should not rush to conclusions and focus only on the results of a one-time procedure.
According to ultrasound data, there are two types of anembryonia. The first is characterized by the fact that the diameter of the fertilized egg does not exceed 25 mm, the size of the uterus corresponds to 5–7 weeks of pregnancy, but lags behind the actual period. In the second type, the egg grows at a normal speed and reaches 50 mm by 2.5 months, but the villous chorion is not visualized.
In addition to instrumental research, diagnosis includes determination of the hormonal spectrum and biochemical blood parameters. The following indicators may indicate anembryony:
- Low levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), absence of its peak concentration at 10–11 weeks.
- Decrease in prolactin, progesterone, estradiol, cortisol.
- A drop in the level of trophoblastic β1-globulin.
- Decrease in the concentration of placenta-specific α1-microglobulin.
It must be said that increased hCG, as well as other biochemical markers, indicate a normal course of pregnancy. And if even on an ultrasound the embryo is not yet visible - this happens up to 6-7 weeks - then the woman should not worry. Perhaps this is due to her individual characteristics or the imperfection of the apparatus.
To find out why the fertilized egg may be absent, a study of the immune status (immunoglobulins, lupus anticoagulant, cardilipin and antiphospholipid antibodies) is prescribed, and a genetic analysis (karyotyping) is performed. For early detection of complications, analysis of the coagulogram (clotting time, prothrombin index, fibrinogen) is necessary.
Anembryony can be confirmed only by instrumental and laboratory methods. But even their results should be considered in the context of the clinical picture and individual characteristics of the body.
Treatment of anembryonia
There are two ways to correct this pathology.
Drug treatment
If the pregnancy has not reached six weeks, then the patient may be offered. In this case, the woman drinks the necessary medicine under the supervision of a doctor and waits for cramping pain to begin. The contents of the uterus are rejected and come out.
The patient should remain under the doctor's supervision for several more days until the bleeding is completely completed. Next, the woman is examined by a doctor using an ultrasound sensor and determines the cleanliness of the uterine muscle.
Surgical intervention
In most cases, doctors choose this particular method of treatment, since during it it is possible to thoroughly clean the internal cavity of the uterus without developing complications.
The doctor puts the patient to sleep using general anesthesia and begins the procedure. This manipulation lasts from five to twenty minutes. Using special instruments, the gynecologist scrapes out the upper uterine layer with the pathological fertilized egg. Within a few hours after such a manipulation, the woman can be discharged.
After the bleeding is completed, an ultrasound should be performed to ensure that there are no parts of the fertilized egg left in the uterus.
Fertilized egg: what is it and why keep an eye on it?
A fertilized egg is a fertilized egg surrounded by membranes. It constantly undergoes division - first into 2 parts, then into 4, etc. As a result of this process, the size of the embryo constantly increases. Before fixation in the uterus, which occurs 7 days after conception, the fertilized egg receives the necessary substances from the yolk sac. The term “gestational sac” changes to “fetus” after 12-14 weeks of pregnancy.
Tracking the size of the ovum week by week is not a whim or a safety precaution for scrupulous doctors and their patients. This information helps:
- determine the duration of pregnancy;
- name the expected date of birth;
- make sure that the growth of the embryo is normal;
- detect the appearance of pathologies;
- prevent involuntary termination of pregnancy, that is, miscarriage.
Do not put off ultrasound examination until later. After all, the woman herself, who is preparing for imminent motherhood, is primarily interested in obtaining the above information.
If an ultrasound does not show an embryo in the fertilized egg, what does this mean?
Very often, a fertilized egg without an embryo is diagnosed in the uterine cavity in young and healthy girls. Why is the fetus not visible on an ultrasound, and is it possible to avoid a frozen pregnancy?
There are a huge number of reasons for this phenomenon. This can be caused by infections of various etiologies, exposure to toxic substances, etc. You can minimize the possibility that an embryo will not be visible on an ultrasound by planning your pregnancy in advance in order to accurately calculate the gestational age. Also, you need to undergo examinations and cure all existing infections before planning to conceive a baby.
This is especially important for women who are planning a pregnancy over the age of 35. This category has a significantly higher risk of developing chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus
The absence of an embryo in the fertilized egg often does not give the woman any symptoms during pregnancy. Blood discharge may appear if a miscarriage occurs. Even a gynecologist during an examination will not be able to say for sure whether there is an embryo in the fertilized egg or whether it is empty. The diagnosis of anembryonia can only be made by a doctor who performed an ultrasound examination no earlier than 5-6 weeks. If the gestational age is calculated from the first day of the last menstruation, then the doctor will be able to visualize the embryo using ultrasound at 1-2 weeks of delay.
It is extremely rare for a patient to be given an incorrect diagnosis after an ultrasound, so if there is no embryo in the fertilized egg, it is necessary to check the result a week later using other equipment if there are any doubts about the professionalism of the doctor or the quality of the ultrasound machine. An error cannot be ruled out for other reasons: short pregnancy or late ovulation, excess weight of the woman and hypertonicity of the uterus.
What numbers create a “portrait” of a tiny embryo?
Medical science has long known the norms for various indicators of the development of the fertilized egg in the first 3 months of expecting a child. When examining the embryo visualized on the monitor, the doctor will first of all pay attention to its shape - at a minimum, it resembles a circle. Next, you need to measure the internal diameter of the fertilized egg and tell the woman how long the long-awaited “resident” has been inside her. But this diameter is not the same for everyone, as it depends on the individual characteristics of the body. Therefore, if you rely only on this indicator when establishing the time elapsed after conception, an error of 1.5 weeks is possible.
Thanks to modern transvaginal ultrasound devices, it is possible to detect a fertilized egg measuring 2-4 mm. What period does this measurement confirm? No more than 2-3 weeks after the start of development and 5-6 weeks from the date of the last menstruation.
What to do if the fetus is not visible on ultrasound and what could this mean?
There are situations that during an ultrasound, the embryo is not visualized inside the fertilized egg, and sometimes the fertilized egg itself is not visualized. First of all, you need to try not to panic. There may be no pregnancy at all, or there was an error in calculating its duration, so it is still difficult to diagnose. If a frozen pregnancy is not definitely confirmed, there is no need to rush into cleaning. First, it is better to undergo an ultrasound again, in another clinic. It may be necessary to conduct one or more studies. The best option is when the level of hCG in the blood is monitored in parallel with the diagnosis. If pregnancy develops without deviations, then its level increases. This helps specialists exclude a possible frozen pregnancy.
When is women's anxiety justified?
A woman who has recently learned about her new situation does not always hear good news on an ultrasound. What could darken her hope for successful motherhood?
Irregular shape
Before the 5th-6th week of pregnancy, the doctor sees the fertilized egg in the form of a rounded figure. But when the baby’s gestation period approaches 2 months, during a longitudinal scan the embryo will look oval, although during a transverse scan it will remain round. Other deviations from the normal form are also possible. This pathology most often develops in the presence of tumors in the uterus or partial detachment of the placenta.
Placement violations
The fertilized egg should be fixed in the fundus of the uterus or on its posterior wall, less often in the internal pharynx or in the upper part of the organ. If the embryo is positioned differently, the doctor assesses how dangerous it is and makes a decision about the future fate of the baby.
Size pathologies
If the egg in the membrane is smaller or larger in size than the above values, this indicates possible developmental disorders. But since these indicators can fluctuate even during the normal course of pregnancy, only a specialist can make a conclusion about how significant the deviations are.
False ovum
In the case of an ectopic pregnancy, the doctor can still see the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity. But in fact, this formation consists of an accumulation of mucus and secretion from the glands of the fallopian tubes. You can recognize the “deception of the body”: this egg will differ in wall thickness and shape from a normal fertilized egg.
Empty fertilized egg
At 1-2 weeks the fetus is not yet noticeable, so it will not be possible to understand whether it is developing. But an empty egg at a later stage is an alarming sign. Most likely, a medical termination of the pregnancy will be required. Among the reasons for this sad situation are the woman’s age, genetic disorders, and taking medications that are contraindicated for pregnant women.
30 hours after fertilization, the egg splits in two. Further division occurs every day, and subsequently the cells form a fertilized egg.
The fertilized egg reaches the uterus on the fourth day and consists of 12 cells. It then implants itself into the wall of the uterus and continues dividing. After six days, the egg already consists of more than 100 cells.
At first, the egg is a liquid substance filled with an embryo and anatomical fluid.
Diagnosis of pregnancy
In modern medicine, there are two main methods for diagnosing pregnancy in the early stages. After the first days of missed menstruation, an analysis of the level of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) helps determine the presence or absence of pregnancy.
HCG is a hormone that begins to be produced immediately after implantation of the fertilized egg into the uterine wall. For diagnosis, you can use either a simple pregnancy test or laboratory analysis. The latter method helps not only to obtain a result about the presence or absence of pregnancy, but also to establish the exact date.
Another very common diagnostic method is ultrasound. Ultrasound helps to collect the necessary information about the nuances of pregnancy: embryo development, term, possible pathologies and abnormalities, etc. Monitoring also gives an idea of the size of the fertilized egg. Numerous studies have made it possible to establish what diameter is typical for each trimester of pregnancy.
However, often in the first weeks there are errors in determining the date and size of the fertilized egg. For example, if the fertilized egg is 3 mm, it is very difficult to determine the period.
You can see the fertilized egg on the monitor of an ultrasound machine no earlier than a week after the delay. During this period, it already occupies ¼ of the entire space of the uterus and is well visualized. As for the embryo, at such an early stage it is not yet visible.
Due to the inaccuracy of determining sizes using ultrasound, many experts advise testing for hCG. It is worth considering that at the end of the first trimester, fluctuations in the growth of the hormone change, and the study becomes less informative.
With each subsequent week, the fruit becomes larger. Thus, ultrasound monitoring becomes more effective and allows you to monitor the process in more detail. After 20 days, the fertilized egg occupies 1/3 of the uterine cavity. At the 10th week, you can see the arms, legs, head and torso of the fetus.
Diagnosis of the death of the fertilized egg
It is quite difficult to detect the early death of the fertilized egg and its retention in the uterine cavity; in the absence of characteristic manifestations, this requires dynamic observation. If severe symptoms appear: bloody vaginal discharge, heavy bleeding, acute pain, the patient is urgently hospitalized.
The main sign of a non-developing pregnancy is: cessation of uterine growth, determined by repeated studies. It is recommended to test the blood levels of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), the level of which constantly increases during normal pregnancy. Echo signs of a non-developing pregnancy during ultrasound may include the following indicators:
- lack of fetal heartbeat;
- the fertilized egg is wrinkled;
- no fertilized egg was found;
- “sleeping” uterine cavity.
If the fertilized egg has died, there is a disappearance of subjective symptoms of pregnancy: cessation of nausea, shrinkage of the mammary glands, lack of pigmentation of the areolas.
Fetal death in the second half of pregnancy is characterized by cessation of the heartbeat and movement of the fetus, delayed growth of the uterus, and also, in some cases, a crunching sound when palpating the skull due to separation and mobility of the bones.
Timely diagnosis will help to detect this pathology in time, which requires immediate hospitalization for further observation and prevention of complications.
When a long-awaited pregnancy occurs, the fertilized egg descends into the uterine cavity and attaches to its wall. Thus, the development of an embryo occurs, surrounded by a fertilized egg. The first month, from the date of fertilization, the embryo is so small that it is very difficult to visualize it. That is why the first ultrasound is done at 6-7 weeks, so that the embryo can be examined and pregnancy can be confirmed.
Size of fertilized egg by week
If the size of the fertilized egg is 4-3 mm, then this indicates a very early period - up to 5-6 weeks. At the 6th week, the fertilized egg has a diameter of up to 18 mm; on the 7th - from 18 to 26 mm; on the 8th - from 27 to 34 mm; on the 9th - up to 35 mm; on the 10th - approximately 50 mm.
Below is a table of the development of the fertilized egg with the gestational age.
It is worth considering that in one pregnant woman the fertilized egg can reach a size of 20 mm at the end of the 6th week, and in another - at the end of the 9th. This is the norm. The most accurate determination of the period is possible for patients whose cycle is 28 days and is regular.
What are the developmental anomalies of the fertilized egg?
Problems with the fertilized egg can arise on the way to the uterus. If the speed of movement of an egg through the fallopian tubes is too high, then its membranes do not have time to fully mature and such an egg is not able to attach to the wall of the uterus. Then a miscarriage occurs.
The fertilized egg may attach low. When the egg is low, there is no particular threat to either the fetus or the mother, but in this case, cervical pregnancy often develops. But with a cervical pregnancy, you should hurry up and terminate it, since there is already a direct threat to the mother: in the future you will have to perform a hysterectomy, that is, remove the uterus.
A false ovum can be detected during an ectopic pregnancy. There is no embryo in this egg; there is only an accumulation of glandular secretion from the fallopian tubes or blood. If a specialist does not see the embryo in the first or second week, then there is nothing to worry about - it should not be visible there. And if there is a truly false fertilized egg, it makes no sense to continue the pregnancy.
Quite often, during echoscopy, a fertilized egg is detected that is deformed. What is the reason for the deformation? This defect develops with increased tone of the uterus, and there are plenty of reasons for hypertonicity: stress, infections of the woman’s genital organs, imbalance of sex hormones.
A small fertilized egg can be a diagnostic sign of a frozen pregnancy. However, it should be borne in mind that this anomaly is determined taking into account the relationship between the size of the egg and the gestational age, so you need to be sure that the exact period is determined correctly.
Sometimes a specialist sees during an ultrasound session that the fertilized egg is larger than the embryo. This may indicate a frozen pregnancy. BUT in this case, you should also keep in mind that the gestational age may not be accurate, the egg simply did not have time to grow and is not visible on the device now. In this case, it is advisable to repeat the echoscopy in the seventh week.
Normally, the fertilized egg has a round shape. An elongated ovum indicates a possible loss of the embryo, that is, a frozen pregnancy. In this case, too, you should not rush to have an abortion. If the contraction of the embryonic heart is visible, it is worth observing the dynamics of its further development. Of course, echoscopy will have to be done repeatedly and quite often.
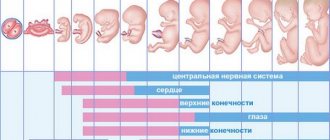
Embryo size and date of birth
Around the 6th week, the embryo becomes visible on the ultrasound monitor. From now on, it becomes the main factor determining the term. The size of the embryo during this period already reaches 5 mm. Despite its very small size, you can already hear its heartbeat. It is possible to determine the exact size of the fertilized egg, embryo and set the date of birth as early as 12-14 weeks of pregnancy. Next, the embryo enters the stage of fetal formation and the following data become the source of information: head circumference, fetal movements, formation of limbs and blood vessels.