Pregnancy is a great joy for future parents, but you still shouldn’t forget about following the regimes, and you should also pay special attention to any ailment or painful feelings, because the baby must be healthy and strong.
Let's talk about pain, such as a pulling sensation in the lower abdomen in the early and late trimesters. What does this mean and what to do?
Why does your stomach hurt at 12 weeks of pregnancy?
The second trimester begins. The child's body is formed. The heart is beating. Nutrition is absorbed. There is still a long way to go before he is born. Development of the nervous system, respiratory center, digestive organs at the very beginning. They are formed in the fetus, but are little active.
A woman may experience nagging pain. The uterus has become enlarged. This is an unpaired hollow organ that consists of muscle tissue. The inner epithelium is covered with a mucous membrane.
The center of gravity has shifted forward. There is pain in the lower back. The increased load causes aching sensations in the joints and muscles of the pregnant woman’s limbs. The roundness of the abdomen is not noticeable. The scales show the expectant mother's weight gain of up to three kilograms.
Possible discomfort is associated with infection. A sign of the disease will be an unpleasant smell of discharge and its unusual color. By this time, the woman must register with the antenatal clinic.
If there is such discharge, you need to make an appointment with your obstetrician-gynecologist. Treatment will include the use of special vaginal suppositories.
The doctor may order additional examination if he is not sure of the initial diagnostic conclusion.
The list of planned activities may include:
- Analysis of urine;
- blood for HIV infection, syphilis, hepatitis;
- blood chemistry;
- ultrasound examination (screening).
The first ultrasound is important because it determines the presence of possible physical abnormalities. If there is a threat of miscarriage or placental abruption, an ultrasound will determine this.
Screening also allows you to accurately determine the time from the moment of conception by measuring the fetus from the tailbone to the crown. Based on the data, the estimated date of birth (DAD) is determined.
The mother is given recommendations on the correct lifestyle during pregnancy:
- Question of diet, permitted foods.
- Sexual activity.
- Performing physical exercises to strengthen the muscle corset and maintain muscle tone.
- They will determine the level of fluid you drink per day so that there is no swelling, stagnation, and enough to carry out metabolic processes.
- Sleeping and waking patterns.
If the cause of pain is a disease that is not associated with the patient’s special situation, she is referred for examination and diagnosis to general practitioners.
If the following symptoms appear, you should call an ambulance rather than wait for an appointment or get to the medical center yourself:
- vaginal bleeding;
- fever above 38 degrees;
- discharge with an unpleasant odor and streaks of blood.
Delay can have life-threatening consequences. For example, with inflammation of the appendix, acute pain in the abdomen is localized closer to the right side.
It is accompanied by high fever, vomiting, and impaired consciousness. Pain in this case is one of the symptoms, but not the disease itself. Emergency hospitalization and urgent surgery to prevent peritonitis were prescribed.
↑
What about the fruit?
Around this time, gynecologists began to call the embryo a fetus.
How is it developing?
All organs by this period have already been formed and are developing further.
The development of the embryo is associated with the beginning of the 2nd wave of cytotrophoblast invasion, due to which the uteroplacental blood circulation increases. This leads to an intensive increase in the weight of the fetus and its main organs. The child begins to receive more oxygen and nutrients necessary for intensive growth. In addition to red blood cells, leukocytes begin to appear for the first time in the circulatory system, forming the prototype of the immune system. The cartilage gradually calcifies and turns into bone. Calcification starts from the middle of the bone and will continue as it grows. The process will be completed only during puberty.
The fingers and toes have finally separated, nails are actively growing, the rudiments of future molars are forming, and signs of hair appear in the eyebrow area. The ribs are formed, and the skeletal system further develops.
The fetal pituitary gland begins to produce most hormones. The brain develops, which by this week begins to resemble the tiny brain of an adult. The simplest reactions have already developed: although the child does not open his eyes yet, he is already reacting to light; touching the wall, he pushes off from it.
The liver is already beginning to produce bile, peristaltic movements begin in the intestines for the first time, and the small intestine can already absorb sugar and glucose. In the kidneys of the embryo, the loop of Henle is activated, which is responsible for filtering urine. The baby drinks amniotic fluid and unnecessary substances are excreted in the urine; the necessary substances are absorbed in the tubules of the loop. The child begins to practice breathing, swallowing amniotic fluid - the chest rises.
The fetus begins active movements and exhibits facial expressions. The child begins to move, may squint, move his fingers, open and close his mouth, and make sucking movements. Mommy will be able to feel the baby’s movements for the first time only after another couple of months.
The genital organs are also differentiated. This week, the male embryo develops a vaginal process - a special protrusion of the peritoneum, which will take part in the process of lowering the testicle into the scrotum. With a successful combination of circumstances, you can already see the sex of the baby on an ultrasound.
What does it look like?
The child looks already fully formed, only slightly disproportionate - the head is much larger than the body. The figure can already be compared to that of an adult. The face has pronounced features and a neck has appeared. The ears are still in their infancy, the nostrils are set wide apart.
Fetal weight and height
During this period, the fetus reaches a size of approximately 9 cm. Weight can reach 19 g. From this period, the gynecologist will more closely monitor the mother’s weight and the dynamics of uterine growth - factors indicating the growth of the child.
What causes nagging, aching pain during pregnancy?
Pregnancy is the brightest time for most women. They are waiting for the miracle of the birth of their own child. But at the same time, this is a period when it is difficult to walk.
The woman feels weak and tired. It's hard to even stand for long periods of time. Periodically there are attacks of discomfort and pain.
Associated with physiology. The uterus expands in proportion to the rate of fetal development. The skin, muscles, and ligaments are stretched. The uterus puts pressure on other organs. A nagging pain appears.
With weight gain, the stress experienced by the pregnant woman's skeleton increases significantly. From constant fatigue, muscles, joints, and lower back begin to ache.
↑
https://gidpain.ru/bolit/zhivot-12-beremennosti.html
The mood of the expectant mother
During this period of time, hormones are still raging in the expectant mother’s body, affecting her mood and psychological state. In general, the end of the 1st trimester is a relatively calm time. During this period, for most women, fears regarding the condition and development of the fetus disappear, and their mood improves.
At the 12th week of pregnancy, the most sentimental and impressionable expectant mothers are characterized by a state of increased anxiety, rarely a depressive mood, which is easily corrected by the support and attention of loved ones.
What does dull, pulling, point or cutting pain in the abdomen indicate?
Stomach pain during pregnancy is due to changes in the body, in organs associated with hormonal changes, changes in the position of internal organs, and obstetric pathologies.
Many types of these sensations do not pose a threat to the health of the mother or the condition of the fetus. Others cause significant harm and even death to the woman and the unborn child.
Pain is a reaction of the nervous system to stimuli. A symptom of many diseases, including obstetric pathologies during pregnancy. A pregnant woman experiences hormonal changes and a restructuring of many systems. They are also accompanied by this feeling.
If discomfort and pain occur, it is better to consult with your doctor about the nature of these sensations and appropriate treatment. During pregnancy, a woman is responsible not only for her own health, but also for the health of the baby.
Nature has determined that the mother’s body tries to protect the fetus from all negative influences. A plug formed from mucus in the cervix prevents pathogenic microorganisms from entering.
Umbilical cord nutrition is formed in such a way that harmful chemical compounds do not enter the fetus. The uterus itself protects the child from external mechanical influence.
At the same time, during the period of bearing a baby, the woman herself may regularly experience pain of varying intensity and nature. Each type of discomfort indicates the presence of different pathological conditions, with the exception of harmless obstetric ones associated with changes in the maternal body and preparation for childbirth.
Based on the nature, intensity of pain, and gestational age, we can talk about how dangerous the condition is.
For example, pulling, extending to the lower back and groin, may indicate a risk of miscarriage. An additional sign of the condition will be the presence of bloody discharge.
When do you need to see a doctor urgently, and which doctor will help?
Cases of pain where medical intervention cannot be avoided:
- Cramping attacks of a pulling nature (especially in the first trimester of pregnancy) - you need to immediately seek help. There is a high risk of miscarriage or placental abruption. The presence of mucous discharge mixed with blood is a reason to call an ambulance for immediate hospitalization of the patient.
- Shingles with a return to the lower back in the presence of a burning sensation at the time of urination - signs of the development of pyelonephritis. Long-term treatment may be required. Signs of illness should be reported immediately.
- In the later stages, accompanied by contractions and increased uterine tone - a sign of premature birth.
Regardless of the stage of pregnancy, the appearance of bleeding from the vagina with or without pain - you should definitely call an ambulance.
Consulting a pregnant woman and caring for the patient during pregnancy is the responsibility of the local obstetrician-gynecologist. They work in district antenatal clinics.
You can get an appointment with them in the following ways:
- through an electronic appointment system;
- by calling the registration number of the medical institution;
- Some consultations retained the journal recording system.
If the pain is not associated with the course of pregnancy and does not affect the development of the fetus, then you need to contact your local physician. It is important that treatment is selected taking into account saving the life and health of the mother and child.
↑
Top medications to reduce abdominal pain during pregnancy and breastfeeding, painkillers
Painkillers are not advisable during pregnancy. Especially in the first months, when the main formation of organs and tissues of the future person occurs. However, the process of experiencing discomfort caused by constant negative factors also does not bode well.
Before purchasing analgesics, consultation with a specialist is required. It is advisable to try non-pharmaceutical ways to cope with discomfort.
The least dangerous drug is Paracetamol. Suitable for use throughout the entire gestation period. Toxic components are in minimal concentration and are quickly excreted in the urine.
Ibuprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Prescribed with caution during the second trimester. Contraindicated for the first and third trimester. Use may cause a number of dangerous side effects. If your condition changes slightly for the worse while taking an analgesic, you should inform your doctor.
Indomethacin also belongs to the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. It is subject to the same restrictions as Ibuprofen. If taken continuously, there is a risk of damage to the child's kidney function.
For the first two trimesters, it is permissible to use creams and ointments based on:
- Diclofenac.
- Ketoprofen.
- Ketorolac.
In the third trimester, you can only use local products based on herbal ingredients. It is forbidden to apply them if they contain bee or snake venom.
Ointments with an irritating effect that stimulate increased blood circulation can also have a negative effect. There is a risk of developing uterine tone and high blood pressure.
The most powerful painkillers are classified as narcotic substances and are prohibited for free sale. Their use occurs only in a hospital with extremely severe pain. These are drugs based on morphine and codeine.
The list of chemical compounds for pharmaceutical use during pregnancy is extremely limited. Before you start taking it, you should read the instructions for use in detail and strictly follow the manufacturer’s recommendations on dosage and method of use.
It is important to familiarize yourself with the provisions on common side effects and contraindications.
It is possible to use folk and non-traditional methods of getting rid of suffering. For example, yoga for pregnant women, acupuncture, light massage, aromatherapy. Traditional methods are also used. But their use also needs to be discussed with a specialist.
Preventive measures to avoid abdominal pain
The basis of prevention is the correct lifestyle of a pregnant woman:
- No stress factors. The mental state of the mother is the key to the health of the child. The fetus inside a woman reacts sensitively to changes in the mother’s emotional background. He is not able to recognize the causes of depression or fears, but he is aware that adverse events are occurring. If the mother is very worried, there is a risk of pathological changes during the formation of the future person. Neurological and psychological problems are possible.
- Elimination of physical fatigue. Pregnant women are not recommended to attend training regularly. During active sports, blood pressure levels increase noticeably. This will provoke the development of uterine tone, which will inevitably lead to adverse consequences. You can go for walks in the fresh air.
- Properly designed diet and nutrition schedule. It must be balanced. You should not consume fast food products or preservatives; it is recommended to reduce the amount of tea and coffee. It should consist of vegetables, fruits, animal and plant protein. It is worth taking vitamins prescribed by a doctor for those who are pregnant. Weight control is required, since the percentage of subcutaneous fat outside the normal range negatively affects the functioning of the cardiovascular system and gastrointestinal tract. The feeding processes of the fetus are disrupted. With rapid weight gain, nutritional correction and a special diet may be prescribed. Excess weight contributes to decreased activity, bad mood, and additional pain in the back and joints. Make sure there is no overeating.
- Maintaining a sleep and rest schedule ensures that a woman is highly active. She does not feel tired and overwhelmed, which means she has a positive morale.
- Regular observation by an obstetrician-gynecologist according to the established schedule, passing mandatory tests, compliance with received medical recommendations. Undergoing developmental ultrasound examinations and other diagnostic measures.
- Tracking the development of chronic pathologies that were diagnosed before pregnancy.
- Prompt treatment of colds, bacterial and viral diseases acquired during pregnancy.
- Eliminate all bad habits, such as alcohol, smoking, and drug use. Failure to comply with this rule results in a developmental delay in the baby.
- Monitoring blood pressure for hypertension (high blood pressure) or hypotension (low blood pressure). Monitor your sugar levels if you are diagnosed with diabetes.
- Do not take a hot bath or shower, or a contrast shower. A sharp change in ambient temperature threatens a rise in pressure and disruption of the cardiovascular system.
Compliance with these rules will ensure comfortable and proper pregnancy. The pain will be considered obstetrically safe. But even if you follow all the recommendations, you need to carefully monitor your own condition and, if there are reasons, seek medical help.
↑
Medical and lifestyle advice
You can lead an almost ordinary life - all the main troubles are left behind. A pregnant woman just needs to monitor her diet and follow some recommendations:
- avoid taking medications without consulting a gynecologist;
- You should not take medicinal herbs without consulting a doctor - some can cause a miscarriage;
- walk more in the air, lead a moderately active lifestyle;
- monitor your weight and avoid overeating;
- exclude fast food, soda, food rich in chemicals, spicy, salty, fatty foods from your diet. However, if you crave salty or spicy foods, you don’t need to torture yourself either - spicy foods, for example, reduce heartburn.
Scheduled doctor visits
If a pregnant woman has not yet registered, she should do so this week. If a woman is registered, then starting this week, she will have to go to the doctor once every 4 weeks. If you haven’t already, you need to undergo a gynecological examination and examination by a therapist. Consultation with a dentist, endocrinologist, or ENT specialist is also necessary.
Necessary studies and analyzes
If a pregnant woman is just registering, she needs to be tested for HIV, syphilis, blood group and Rh factor, and determine her sugar level.
In the near future you need to submit:
- UAC and OAM;
- blood for pregnancy hormones - free-B-hCG and PAPP.
A test for placental lactogen may show an increase to 1,550 ng/ml. The coagulogram will show an increase in fibrinogen levels. Analysis of AFP during this period will show its peak amount, which will remain at this level until the 16th week.
The doctor in the residential complex conducts an examination with a mirror on a chair and takes smears for cytology and flora. The presence of STDs is determined - gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, etc.
Diet
The diet does not need any changes or restrictions.
The main thing is weight control. To prevent a decrease in hemoglobin levels, it is necessary to increase the amount of iron-containing foods in the diet - liver, veal, beef tongue, buckwheat, apples, pomegranates. To maintain the required amount of calcium, you should increase the amount of dairy products you eat. To reduce the amount of constipation, you should definitely eat soup. You definitely need to give up heavy foods and fast food, reduce the amount of fatty, fried, flour, and smoked foods.
Lifestyle
In the absence of contraindications, you can continue a moderately active lifestyle. During this period, many expectant mothers give up their usual sports activities - running, fitness - and switch to yoga or fitness for pregnant women. Moderate activity is useful for maintaining tone and preparing for childbirth. In addition, trained mothers will be able to recover faster after childbirth.
What's prohibited?
The following should be completely excluded:
- drinking alcohol;
- smoking;
- coffee;
- hard physical labor;
- X-ray, fluorography and CT;
- strength and injury-prone sports;
- stressful situations and experiences.
Taking vitamins
If before this time the mother took folic acid, then the time has come for special multivitamin complexes for pregnant women. You can take them on the recommendation of a doctor. Not all women are recommended to take vitamins.
They are usually recommended for the following groups:
- who do not have the opportunity to eat fully;
- those who previously suffered from iron deficiency anemia or B12 deficiency anemia, as well as similar conditions;
- women whose pregnancy previously ended in miscarriage;
- over 35 years old.
The most popular multivitamin complexes are vitamins Elevit, Vitrum Prenatal and Prenatal forte, Alphabet.
What does sudden abdominal pain mean?
The suddenness of the development of pain is a sign of an acute form of pathology. If the sensation is localized on the right side, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, dizziness, there is a risk of developing inflammation of the appendix.
Immediate hospitalization and surgical intervention are required before perforation begins. Removing appendicitis is a common procedure for surgeons. It passes without complications.
During pregnancy, the operation is performed in compliance with all required patient safety criteria.
Non-obstetric types of pathological pain of a sudden acute nature include:
- intestinal obstruction;
- peritonitis.
As with appendicitis, acute pain accompanied by vomiting and general weakness. The syndrome extends to the lower abdomen, lower back, sacrum, and groin.
Unilateral, accompanied by bleeding from the vagina - a sign of ectopic pregnancy.
Additional signs of a dangerous condition:
- cramping character;
- increased symptoms in a horizontal position of the body;
- severe vomiting;
- shortness of breath at rest;
- frequent heartbeat, which in frequency goes above 100 beats per minute.
In the absence of medical attention, the fallopian tube ruptures. Internal bleeding begins.
↑
Changes in the mother's body
In a woman, the volume of the anterior pituitary gland, the organ responsible for the production of prolactin, increases. This happens so that from the 12th week prolactin accumulates in the body, which is largely responsible for the growth of the mammary glands. In the future, the hormone will promote the onset of lactation.
Brownish spots of various shapes begin to appear on the face and neck - this is chloasma or skin hyperpigmentation.
Due to the increased level of estrogen, vascular changes begin to appear:
- telangiectasia – dilatation of small vessels;
- stars;
- swellings of a reddish hue with radiating rays (angioma).
They can suddenly appear on the face, neck, arms, and upper chest area. Stars on the palms are called palmar erythema. They will all disappear after childbirth.
Although the fetus begins to move at this time, the mother cannot yet feel them. Some pregnant women say that they feel fetal movements from twelve weeks - however, this is a purely psychological phenomenon.
Attitude to sex
Sex during this period begins to require some restrictions.
For example, positions on the stomach are contraindicated for women. Even just lying on your stomach is no longer worth it from this period. However, if a pregnant woman wakes up face down at night, there is nothing particularly terrible about it. There are no more restrictions on sex during this period if there are no pathological symptoms. You cannot have sex if placenta previa is diagnosed. If discomfort appears after intimacy, it is better to consult a gynecologist. Sex is not recommended for mothers with multiple pregnancies.
hCG
If during the first screening a decrease in hCG levels is detected, this indicates a risk of Edwards syndrome or placental pathology. Elevated human chorionic gonadotropin may indicate a risk of developing Down syndrome. With twins, hCG may also be elevated. The normal level of hCG in the blood at 12 weeks is 13.4 ng/ml -128.5 ng/ml.
Progesterone
The norm at the twelfth week is from 38.19 nmol/l to 47.41 nmol/l. Low progesterone levels at this time may indicate:
- problems with the placenta;
- ongoing chronic inflammatory processes in the female reproductive system;
- fetal hypoxia;
- ectopic.
A high level may indicate:
- developing hydatidiform mole;
- presence of corpus luteum cysts;
- adrenal gland disease;
- multiple pregnancy.
Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner lining layer of the uterus to which the chorion is attached. The thickness of the endometrium plays a big role during pregnancy. During pregnancy, the thickness of the layer also changes and is about 2 cm. The thickness of the endometrium is measured by ultrasound. If the endometrium is thin, the doctor will prescribe medication to help it grow.
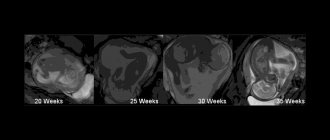
Ultrasound, photo of the baby
If a woman has just registered, then the first screening is immediately carried out, including an ultrasound examination.
The timing of diagnosis in the first trimester is limited: from the 1st day of the tenth week to the 6th day of the thirteenth. At the first ultrasound screening:
- calculate the length of the embryo, its CTP - coccygeal-parietal size;
- assess the size of the head;
- look at the symmetry of the brain hemispheres and the presence of structures required for this period;
- measure the length of the femur, humerus, as well as the forearm and lower leg;
- check the location of the stomach and heart;
- measure the size of the heart and abdomen.
Normal ultrasound findings:
- CTE - from 51 mm to 59 mm exactly at 12 weeks and from 62 mm to 73 mm - on the last day of the twelve week period;
- thickness of the collar zone – from 1.6 mm to 2.5 mm;
- nasal bone (an indicator important for diagnosing Down syndrome) – at least 3 mm;
- Heart rate – from 150 to 174 beats per minute;
- biparietal size – not less than 20 mm.
Based on the results of the 1st trimester ultrasound, they look for markers of chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus and analyze the period at which the baby’s development corresponds. 3D ultrasound can already show the sex of the fetus. If you had a 3D ultrasound, you can ask for a photo of your baby.
If the first screening ultrasound was done earlier, then at the 12th week it is repeated for pregnant women in whom pathology was identified during the first ultrasound examination. The thickness of the nuchal translucency is examined again to identify severe malformations or chromosomal abnormalities. In this case, the question of terminating the pregnancy may arise. In this case, ultrasound examination data must be confirmed by amniocentesis - a biochemical, immunological, genetic and hormonal study of amniotic fluid.
Well-being
During this period, everything should be normal. A pregnant woman becomes less irritable, her state of toxicosis subsides, nausea disappears, the urge to urinate decreases, and her quality of life improves. It is necessary to constantly monitor pressure and temperature. The pressure should be slightly lower, and the temperature should not be higher than 37.5. Your weight may not change during this period, but even if it increases slightly - up to 3.6 kg - then this is normal.
For the first time, an expectant mother may experience the unpleasant phenomenon of heartburn - a burning sensation in the stomach. During pregnancy, the placenta produces large amounts of progesterone, which relaxes the muscular valve between the esophagus and stomach. When a woman lies down, gastric secretions begin to flow into the esophagus, causing irritation.
Chronic diseases not treated before pregnancy can worsen during this period. The load on the liver, kidneys and heart increases. The uterus puts pressure on the intestines and inhibits its peristalsis, which can cause constipation.