Normal fetal heart rate during pregnancy
Heart rate (HR) is an important indicator that allows doctors to determine the health status of the unborn child.
You can hear the fetal heartbeat already 1 month after conception, but at this stage it is impossible to count the number of beats without special equipment. Heart rate differs at different stages of pregnancy. Accordingly, heart rate norms are determined by week.
Heart rate measurement methods:
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination). The most common way to evaluate the size of the fetus, gestational age, condition of the placenta, etc. Using ultrasound, they listen to heart sounds, examine the structure of the heart, and identify anomalies;
- auscultation. Involves listening to the heartbeat using a stethoscope. Determines the approximate heart rate, clarity of tones and presentation of the baby. Even a person without medical education can use the device, but it is effective only from the 3rd trimester. In some cases, auscultation is not possible. For example, if a pregnant woman is overweight, has a small or large amount of amniotic fluid;
- Cardiography (CTG). An informative method that allows you to determine the baby’s heartbeat, oxygen starvation and take timely measures. The CTG device is equipped with sensors for uterine contractions and fetal movements. They record the activity of the uterus and examine the waking and sleeping phases of the embryo. The first CTG is performed after 32 weeks. The second is immediately before childbirth. In rare cases, CTG is performed throughout pregnancy according to indications;
- echocardiography. It is carried out in the 2-3 trimester if heart defects are suspected in the fetus. EchoCG is an ultrasound examination that studies the structural features of the baby and blood flow.
Taking care of yourself
How can you tell if you're a boy or a girl by your heartbeat?
In order to finally dispel the myth about the existence of such a technique for determining the sex of an unborn child by heartbeat, even a small study was conducted with a group of women expecting a child.
Researchers have tried to determine a baby's sex using heartbeats at 20 weeks or earlier, but the results showed that the predictive value of this technique was only 50%. What does this number mean? The same as the statement of fairy-tale characters: “One of two things - either the patient is alive, or he is no longer breathing.” So there cannot be a positive answer to the question - is it possible to determine the sex of a child by heart rate.
Fetal heart rate table by week
The fetal heartbeat during pregnancy is checked for every woman registered. This indicator allows you to:
- confirm the fact of pregnancy. After the first delay, the woman is sent for diagnostics. According to ultrasound, from the 3rd week you can hear the heartbeat. If fetal cardiac activity is not observed, an ultrasound scan is performed again after some time. The absence of a heartbeat indicates a frozen pregnancy;
- assess the condition of the fetus. The child's heart is sensitive to changes. Stress, maternal illness, the amount of oxygen in the surrounding space, sleep and rest phases are immediately reflected in the heart rate. If the heart beats too fast for a long time, the blood supply to the fetus is disrupted. If it is slow, this indicates a deterioration in the baby’s condition. Correction methods largely depend on the period at which the heartbeat became pathological;
- monitoring the condition of the fetus during labor. During the birth process, the baby experiences severe stress and lack of oxygen. Heart rate monitoring allows you to identify difficulties such as umbilical cord compression, placental abruption, and take emergency steps to eliminate the consequences. During labor, the baby's heart rate is checked after each contraction.
There is a belief that the sex of the child can be determined by the fetal heart rate. Allegedly, girls have a heartbeat of 150-170 beats per minute, and boys - 130-150. Therefore, many people think that if, according to an ultrasound, the fetal heart is 146 beats per minute, or, for example, 137, 143, then a boy will be born. And who will be at 167 blows, or 158, 172 - a boy.
This hypothesis is not scientifically confirmed in any way. Gender can only be determined by heart rate with 50% confidence. Heart rate in boys and girls reflects the ability to fight the lack of oxygen. And gender has no influence on this ability.
If you want to find out the sex of your unborn child, contact an ultrasound specialist. Gender can be determined from 15-16 weeks.
The heart rate changes not only according to the baby’s activity phases, but also depending on the stage of pregnancy.
- at week 7 the norm is 115 contractions;
- on the 8th, the heartbeat can jump to 170 beats per minute;
- at 11 weeks, the heart rate usually remains at 150 beats. Minor deviations up or down are acceptable.
Starting from the thirteenth week, doctors constantly check the heart rate using ultrasound, checking the character and rhythm, location of the heart.
From the second trimester, the contraction frequency stabilizes and is 140-160 beats. If the pulse is fast, for example, 170-180, this indicates oxygen starvation. If it is low, less than 120, this indicates fetal hypoxia.
Observation by a doctor
Monitoring the heartbeat is mandatory during childbirth, especially in the presence of any pathologies. The normal heart rate is 140 beats. But sometimes it can reach up to 155.
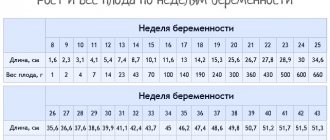
Baby's heart rate:
| Weeks of pregnancy | Number of contractions per minute |
| 4-6 | 80-85 |
| 6 | 100-135 |
| 7 | 115-130 |
| 8 | Heart rate 150 beats per minute. Indicators up to 170 are within normal limits. |
| 9-10 | 170-190 |
| 11-40 | 140-160 |
Thus, the number of 125 beats is the norm for the initial stages of pregnancy. At later stages, it is considered weak and requires additional examination.
A pulse of 153, 162, 166 beats per minute is natural for periods of 11-40 weeks, for 4-7 weeks it is pathological.
You can find out the sex of the fetus
When determining the heart rate, the doctor evaluates not only the fetal heartbeat, but takes into account additional factors: the presence of a disease in the mother, listening time, whether the baby is sleeping or is in an active state.
When the expectant mother wants to listen to the baby’s heart beat, it is not necessary to visit the clinic. The sound of embryonic development can be heard in the following ways:
- stethoscope. A regular obstetric tube is inexpensive and allows you to listen to the baby’s heart. A patient assistant will be required. It is important to learn to distinguish the heart from the sounds of the baby’s movements, pulse, and mother’s peristalsis. Effective from 18-25 weeks;
- fetal doppler. Suitable for those who do not have time to master a stethoscope. A portable ultrasound detector works on the CTG principle, but does not provide a graphic image. The kit usually includes headphones. This device is effective from 8-12 weeks, and you can use it until the 38-39th;
- putting your ear to your stomach. The method is suitable for late pregnancy, in the 3rd trimester. The place of application depends on the location of the fetus. If your baby is lying head down, place your ear below the navel. With breech presentation – higher. Usually this method is used by men to hear the life emerging in the womb.
Determining gender by heartbeat
Many women, being in an interesting position, believe that by their heart rate they can find out who they are having, a girl or a boy. There is a belief that in girls the frequency of beats per minute is from 150 to 160 times, and in boys it is slightly less and is 135-150 beats. The hypothesis has no scientific basis, which is why it has nothing to do with medicine.
The sex of the child can only be determined by ultrasound examination.
The fetal heart rate is, first of all, the body’s ability to cope with the fact that there is not enough oxygen. Gender has no effect on this.
If the expectant mother really wants to find out what color diapers and rompers she should buy, she can go to the hospital and have an ultrasound done.
Important seven-day periods
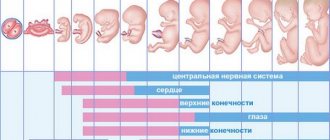
The fetal heart is one of the first to form. His work is a special indicator of the development and general condition of the child. Therefore, listening is carried out throughout pregnancy and during childbirth.
Regular monitoring of the heartbeat allows you to detect cardiovascular pathologies in the early stages.
Pronounced myocardial work begins from the 3rd week, but the heart rate can be calculated from the 5th-7th week using an ultrasound scan. At this time, the heart turns into a full-fledged four-chamber organ.
In the early stages, a transvaginal sensor is used to listen to heart rate; already at 6 weeks, an abdominal sensor can be used.
Waiting for a healthy baby
When determining heart rate during pregnancy, the following indicators are important:
- contraction frequency. Too fast heartbeat, up to 200 beats/min and above, or slow, less than 100 – these are pathologies that require examination and diagnosis;
- character of tones. A healthy heart sounds loud and clear. Blurred and dull tones indicate a disease;
- rhythm. Normally, the heart beats again at regular intervals. With acute and chronic hypoxia in the embryo and valve defects, arrhythmia is observed.
Women expecting a child undergo 2 screening ultrasounds, which also determine the heart rate during pregnancy.
The first test is carried out at 12-13 weeks, the second at 21 (some are carried out at 24), the third screening is performed at 32.
How can you calculate your heart rate?
So, you already know how to determine the sex of a child by heartbeat. The options proposed above can be grouped and combined with each other. However, to draw any conclusion, you must first calculate the baby's heart rate in the womb. This manipulation can be carried out in several ways:
- using a stethoscope (this option is suitable for measurements after 12 weeks of pregnancy, when the reproductive organ leaves the pelvis);
- using a tube (this method is used after 20 weeks of pregnancy, when the fetus is already quite large);
- cardiotocography apparatus (research and measurements are made after 30 weeks of pregnancy);
- using Doppler (the device is used after 15 weeks of child development and looks like a miniature ultrasound machine);
- during an ultrasound (diagnosis can be carried out in the earliest stages of pregnancy).
Why does tachycardia appear?
Arrhythmia of intrauterine fetal formation at different stages of pregnancy is associated with several negative factors.
- Systemic chronic and acute diseases of the mother: infectious processes in the body, respiratory pathologies with insufficient oxygen supply to the body, metabolic disorders, cardiovascular abnormalities, and very often the cause is hyperthyroidism.
- Fetal diseases: in the early stages of pregnancy, detection of tachycardia on CTG may indicate chromosomal abnormalities (Down syndrome at birth), in later stages (25 weeks or more) the cause may be fetal hypoxia, suffocation.
- Other causes: anemia, intoxication, fetal infection, oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios.
Advice! The tachycardia itself can be seen on CTG, and an ultrasound is performed to identify the cause.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of tachycardia during fetal development also apply to a pregnant woman, who also experiences a rapid heartbeat of more than 120 beats per minute. The fetus has a CTG reading of more than 220 beats per minute.
The first few weeks of pregnancy (before diagnosing any abnormalities of the fetus is difficult, but already at this moment favorable conditions for the appearance of tachycardia can form. In the early stages (8-12 weeks), pathological heartbeat more often indicates hypoxia (oxygen starvation).
Features of tachycardia during pregnancy:
- the process begins with an ectopic form of tachycardia;
- the abnormal focus is initially localized in the pulmonary veins or atrium;
- the deviation is accompanied by prolonged attacks and appears regularly;
- tachycardia is a clinical symptom of cardiovascular pathologies;
- a serious consequence of the pathology is fetal death or heart defects.
Advice! Tachycardia itself is not a disease and does not become a direct cause of abnormalities in intrauterine development. On the contrary, the resulting deviations lead to heart rhythm disturbances in the fetus.
Diagnostic methods
The main method for studying fetal cardiac activity is CTG (cardiotocography). This method is used to examine a pregnant woman after 8 weeks. CTG shows the heart rate at rest, during uterine contraction and under the influence of external factors. Cardiotocography allows timely detection of fetal hypoxia.
CTG is performed in two ways: external and internal. The external method is most often used without compromising the integrity of the skin. The procedure is carried out with an ultrasound sensor, which is attached to the pregnant woman's stomach. Indirect CTG has no contraindications and is performed at almost any stage of pregnancy.
Advice! The direct CTG method is used extremely rarely and only during childbirth.
Other methods for diagnosing cardiac disorders in the fetus.
- Ultrasound examination is the safest method for the fetus; it is used in the early stages (after 8 weeks) and late stages (35-39 weeks) of pregnancy without risks to the health of the unborn child.
- Echocardiography is an in-depth method of examining the fetus to identify heart defects.
- Radiography - determines the contractile function of the ventricles.
Detection of tachycardia requires differential diagnosis.
- Atrial flutter occurs in 25% of all cases of arrhythmia, the heart rate reaches 400 beats per minute, they are regular and associated with atrioventricular block. In other forms of arrhythmia, the contraction frequency does not exceed 250 beats.
- Ectopic form: formed in different segments of the atria, but most often localized on the lateral wall.
- Supraventricular reciprocal: occurs in late pregnancy (after 25 weeks).
Advice! Treatment of tachycardia in the early stages is successful with intravenous administration of drugs to the pregnant woman. In recent weeks, tachycardia is dangerous, and in some cases a cesarean section is indicated.
How to treat?
Mild arrhythmia, which is intermittent, is normal, and in this case no specific treatment is required; monitoring the woman and regular examination of the fetus is sufficient.
Complicated arrhythmia requires adequate treatment with antiarrhythmic drugs:
- The ventricular polymorphic form is treated with the following drugs: magnesium, proprolol, lidocaine. For the first two days, intravenous administration is indicated, after which the woman takes it orally.
- Severe attacks with a frequency exceeding 220 beats per minute require the appointment of sotalol, amiodarone, flecainide.
- If myocarditis is suspected, dexamethasone is prescribed, as other drugs can cause cardiac arrest and death.
The most effective option for eliminating arrhythmia in the fetus remains drug treatment, but in addition, the woman must reconsider her lifestyle and observe the prevention of exacerbations of chronic ailments. Maternal illnesses can worsen the arrhythmia and lead to death.
Advice! The use of beta blockers is ineffective, since drugs in this group do not penetrate the placenta well, so they are only suitable for treating a pregnant woman.
Consequences and prevention
Arrhythmia in 85% of cases indicates the onset of a serious pathological process in the fetus. The consequences of heart rate disturbances depend on the form of the deviation. With temporary tachycardia, which occurs once in the fetus, there are no risks, but atrial flutter or ventricular tachycardia with constant attacks does not go away without a trace.
Consequences of arrhythmia during intrauterine development:
- fetal death, miscarriage, stillbirth;
- hypoxia and suffocation;
- genetic abnormalities, Down syndrome;
- heart defects, underdevelopment.
It is possible to prevent the occurrence of arrhythmia, but prevention should be done even before pregnancy. A woman should avoid smoking, alcohol, serious physical activity, and stress. Together with the doctor, during pregnancy planning, nutrition is adjusted, vitamins and restorative drugs are selected.
If tachycardia could not be avoided, the woman should not panic, as this only aggravates the child’s condition. In this case, it will be useful to rest more, take walks in the fresh air, and remove all stress factors from yourself.
What is the danger of tachycardia in the fetus during pregnancy and how to deal with it
Dangers haunt a person not from the moment of his birth, but from the very moment of conception. A number of various problems can turn a healthy fetus into a disabled person from birth, and sometimes the development of events can be less favorable. That is why expectant mothers should not ignore the offices of obstetricians and gynecologists. There can be many problems, but it is important to notice and eliminate them in time.
One of the unpleasant problems that can beset a young mother is tachycardia in the fetus. It can occur both early (12 weeks) and late (38 weeks). However, whenever it is diagnosed, it must be dealt with in order to prevent the development of other heart pathologies. Today we’ll talk about why tachycardia is dangerous in the fetus, what methods are used to detect it, and how to treat such disorders.
Gender of baby based on heartbeat at 12 weeks. Determining sex by fetal heartbeat
When a representative of the fairer sex receives a positive pregnancy test, she has a number of questions and doubts. So, a woman thinks about how quickly her tummy will grow. The expectant mother is interested in her own well-being. Another important issue that worries a woman is determining the sex of her unborn baby. Will it be a boy or a girl? This article will tell you how to determine sex using the fetal heartbeat. You will learn the peculiarities of the rhythm of muscle contractions in boys and girls. It is also worth saying that the sex of the child is determined more accurately by the heartbeat at 12 weeks than earlier or later.
What is it and why does it occur?
Experts always evaluate not only the health of the mother, but also her unborn child. In this case, the heart rate must be monitored. It is carried out regularly, regardless of the timing. Monitoring the child’s condition must be thorough at every examination, because problems never come on time.
If the ultrasound gives the obstetrician cause for concern, the mother is sent for cardiotocography. If CTG shows 170-220 beats per minute in the fetus, this condition is called tachycardia.
This indicates not only the discomfort of the unborn child, but also the possible development of pathology, which urgently needs to be eliminated.
There are a huge number of reasons for tachycardia. First of all, it can occur due to some problems in the mother. It is the woman who influences the fetus throughout the entire period of its development, which means that her condition is mirrored on the condition of the child. And this may be the first reason for the development of tachycardia. In this case, the following factors should be highlighted:
- nervous overstrain and overwork cause the mother’s heart to speed up; The baby’s heart reacts in a similar way;
- increased concentration of thyroid hormones in the blood;
- anemia, which is a consequence of a lack of nutrients in the mother’s diet;
- vomiting caused by toxicosis dehydrates the body. Accordingly, the electrolytic composition of the blood changes, which is reflected in the baby;
- drinking strong tea or coffee;
- the effects of certain medications on the body;
- smoking.
Also, many residents of our country have chronic diseases. We may not even know about them before pregnancy. During this period, the body undergoes a restructuring, which is why all pathologies can appear. Particularly dangerous for a child are:
- Diabetes.
- Anemia.
- Thyroid disease.
- Leukemia.
- Cardiopathy.
- Hypertension.
- Hepatitis.
- Brucellosis.
- Myocarditis.
- Heart defect, etc.
However, one should not think that tachycardia occurs only because of problems with the woman’s body. The fetus can also develop all sorts of pathologies that are no longer dependent on the mother’s body. In particular:
- Intrauterine infection.
- Incorrect development of chromosomes.
- Anemia due to incorrect formation of the placenta.
- Incompatibility with mother by Rh factor, etc.
The highest risk of fetal tachycardia is at 36 weeks of age. Before this, the risks are considered moderate. The fact is that in the last trimester of pregnancy, gas exchange between mother and child increases. Plus, the mechanism of one’s own breathing is more actively developing, so an acceleration of the heartbeat at this stage is more likely than before.
Fetal tachycardia varies. There are two main types of it, in particular:
- supraventricular reciprocal form. As a rule, it is determined between 24 and 33 weeks. Further developments allow options for blockade, bradycardia, or a return to normal rhythm. Pathologies of this kind are typical for inflammatory foci in the heart muscle;
- ectopic form. The signal for excitation comes from the suprasinus zone. This is the lateral part of the atrium, near the ears. Chaotic extrasystoles from various areas of the heart muscle may be noted. Sometimes combined with the ventricular form.
So, we figured out what tachycardia is and why it can occur. Next, we’ll talk about how diseases of this kind are treated.
When does the fetal heart begin to beat?
Questions like “is it possible to determine the sex of a child by its heartbeat” arise due to ordinary illiteracy and lack of understanding of the physiology of intrauterine development. But this is quite fixable. If you sincerely want to give birth to a healthy child, you will definitely find time to read about the peculiarities of pregnancy, when the sex of the unborn baby is determined, when the mechanism of a barely formed heart starts working, and whether it is possible to find out the sex of the child by its heartbeat.
The pulse parameters of the future baby are regularly measured in the antenatal clinic as part of “pregnancy management”. This is done not with the goal of finding out the sex of the child by heartbeat, but to monitor the vital activity of the fetus and timely detection of problems with its health. This is especially true for women at risk for cardiovascular and other pathologies (with cardiac dysfunction, hypertension, etc.).
Reliably determining the sex of an unborn child is not an easy matter.
In obstetrics, the beginning of embryonic myocardial contractions is considered to be the 3rd week from conception. But it is impossible to hear it at this time, much less determine the sex of the child by the heartbeat at 12-14 weeks or any other period.
Listening to the fetal pulse becomes possible only at the beginning of the 6th week of pregnancy (the so-called obstetric one, which is calculated from the date of the last menstruation) during an ultrasound procedure. During this period, the baby's pulse should correspond to the mother's pulse (normal value is 83+/- 3 beats/minute). Is it possible to determine the sex of a child by the fetal heartbeat? It’s impossible, but you can calculate his gestational age, knowing that the heart rate increases by 3 beats every 24 hours with optimal development.
Treatment of pathology
The primary treatment is to change your own lifestyle. In particular, experts advise:
- change mode. Pregnant women need to spend more time in the fresh air and spend less time at the computer;
- diversify your diet. Tachycardia can occur if the diet lacks essential microelements, especially magnesium, potassium and calcium. You need to eat more plant foods, whole grain cereals, dried fruits, etc.;
- To calm and bring the body back to normal after stress, tea with lemon balm and mint helps.
To relieve an attack, the expectant mother is advised to sit down or lie down to relax. You need to breathe deeply. Antiarrhythmic drugs in this case are not used until the last minute, because they can harm the baby. As for the fight against tachycardia in the fetus, they also try to avoid drug treatment. Normalize your routine, change your diet, and everything should be fine.
If the cause of tachycardia is the formation of heart pathology, the use of antiarrhythmic medications is mandatory. The selection of drugs is based on the form of the disease. If inflammation of the heart wall is detected, steroid drugs are used. Application is carried out in courses - about a week and a half. Medicines can be in the form of tablets, or in the form of injection solutions or droppers.
Treatment is carried out in a hospital setting, under the constant supervision of a cardiologist and obstetrician-gynecologist. The unauthorized use of any medications is strictly prohibited! Violation of the dosage can lead to the most unpleasant consequences.
With correct drug treatment, in combination with the correct daily routine, fetal tachycardia can be overcome in 90% of cases. If the disease cannot be treated, transplacental administration of special drugs is used. Normalization of heart rate occurs after birth, in the first year of life.
Fetal tachycardia is a serious problem that needs to be dealt with. Don't delay this! At the first manifestations, immediately contact a specialist! Then, with a high probability, your baby will be born healthy and cheerful.
Source: serdcelechim.ru
Fetal pulse is normal and abnormal
The embryo's heart begins to beat on the 21st day of development. At 3-5 weeks it contracts 75-85 times per minute. Over time, the pulse quickens, and after the formation of the nervous system it gradually decreases. Normally, the indicators change as follows:
- At 5-6 weeks, the heart contracts 80-100 times every minute.
- At 6-7 weeks, the pulse is close to 100-120 beats per minute.
- At weeks 7-9, the heart rate reaches a peak of 140-190 beats every minute.
- At 10-12 weeks, the heart rate drops to 160-180 beats per minute.
- After 3 months of pregnancy, the fetal pulse does not exceed 140-160 beats every minute.
- By the 9th month, the heart beats 130-140 times per minute.
Fetal pathology is diagnosed if in the 2nd trimester the pulse is less than 110-120 beats per minute.
How to determine the gender of a baby at 12 weeks?
If you want to find out the sex of the baby by heartbeat at 12 weeks, then you need to do an ultrasound examination. During diagnostics, the specialist can turn on the sound of the device. This will allow you not only to calculate the number of contractions, but also to hear them.
The doctor can also display a curved line of the cardiogram on the screen. A special program measures and counts heartbeats. The operation of the technique allows us to avoid errors that could occur when counting blows by a person. So, how to determine the gender of the baby by heartbeat at 12 weeks?
What is typical for girls? During this period, the frequency of muscle contractions ranges from 150 to 170 beats per minute. The knocks are quick and muffled. The rhythm is chaotic and you have a hard time catching the monotony. Also, an experienced specialist may have his own ways of determining the sex of the baby by the sound of his heart.
What is typical for boys? The heartbeat is observed from 120 to 140 times per minute. The sound produced is clear and loud. The contractions are more like the beating of an adult human heart. A special rhythm is also determined. When the blood pressure rises or the mother becomes agitated, the baby’s heart begins to beat faster. This pattern is present in most cases.
Fetal bradycardia in early and late stages
If at 6-8 weeks of development and later the embryo’s pulse does not exceed 85 beats per minute, it is not bradycardia of the fetal heart that is suspected, but rather arrest or developmental defects. In other cases, a decrease in fetal heart rate that occurs in the early stages is not considered a pathology.
Bradycardia is diagnosed only after 20 weeks of gestation if the unborn baby’s heart beats less than 120 times per minute.
Types of embryonic disease
There are 3 types of embryonic bradycardia: basal, decelerant and sinus . Typically, these conditions develop due to fetal hypoxia, which occurs for the following reasons:
- due to compression of the head;
- due to maternal anemia;
- due to low blood pressure in the mother.
Basal bradycardia is diagnosed if the fetal heart beats less than 120 times per minute. If you treat the malfunction in time and eliminate its cause, you will be able to avoid harm to the woman and the fetus.
If the decelerant nature is violated, the heart rate of the embryo does not exceed 72 beats per minute. This condition requires hospital treatment with bed rest.
With the sinus form of the disease, the fetal pulse drops to 70-90 beats per minute. In this case, the woman needs urgent hospitalization with intensive care and observation until childbirth, because a failure threatens the fading of the pregnancy.
How to detect a slow heart?
Bradycardia of the mother and fetus manifests itself through symptoms of oxygen starvation. In this case, the pregnant woman faces the following ailments:
- with weakness;
- with dizziness;
- with headache;
- with noise in the ears;
- with shortness of breath;
- with low blood pressure;
- with chest pain.
An anomaly that exclusively affects the fetus does not affect maternal well-being . It can only be detected using modern diagnostic methods.
What will auscultation show?
After 18-20 weeks, each examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist includes auscultation - listening to the embryo's heart using a special stethoscope, a hollow tube made of wood or metal. To hear the heartbeat of the unborn child, the doctor proceeds as follows:
- Places one end of the stethoscope on the pregnant woman’s belly and puts her ear to the other end of the device.
- Finds the point at which the fetal heartbeat is clearly audible.
- It records the minute during which it counts fetal heartbeats.
The disadvantage of auscultation is its inaccuracy : diagnosis can be hampered by many factors, including maternal obesity and increased fetal motor activity during examination.
Ultrasound of the heart
Instrumental methods, such as ultrasound diagnostics, allow for more accurate research. In this case, a special sensor is used, which is applied to the pregnant woman’s abdomen or inserted transvaginally. It transmits data to the screen, which is decrypted by a specialist.
The following abnormalities indicate a slow pulse during ultrasound of the fetal heart:
- slow movements of the embryo;
- convulsions;
- stopping the movement of the embryo.
Rare breathing or heartbeat, as well as their periodic stopping, also indicate bradycardia. Ultrasound can be performed as early as 3-5 weeks of pregnancy.
CTG and other diagnostic methods
Cardiotocography is used for diagnosis from 32 weeks of pregnancy. The essence of CTG is recording and comparing the pulse of the unborn child with the frequency of uterine contractions. The results of the study are deciphered as follows:
- 8-10 points - the condition of the fetus is normal;
- 6-7 points - mild bradycardia occurs;
- 6 points or less - the fetus is in serious condition.
Another effective way to identify the disease is phonoelectrocardiography , in which the electrical impulses of the heart are recorded and analyzed. This method is a combination of ECG with phonocardiography - listening to heart murmurs.
When is an ECG used?
An electrocardiogram is resorted to if the pregnancy is proceeding with disturbances or there is a threat of any anomalies. From the embryo side, the following indications are distinguished:
- developmental delay;
- previously diagnosed cardiac pathologies;
- suspicion of developmental pathologies.
An ECG is performed on pregnant women who are over 38 years of age or have previously given birth to children with developmental defects. Also from the mother’s side there are the following indications:
- hypothyroidism;
- hyperthyroidism;
- diabetes;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- severe infections.
Bradycardia is indicated by the appearance of a P wave on the cardiogram, as well as a significant TP and PQ interval. The most accurate data is obtained by performing an ECG at 18-24 weeks of pregnancy.
Ultrasound at 12 weeks of pregnancy
Ultrasound during pregnancy shows not only the gender of the unborn child, but also its predisposition to various diseases.
The twelfth week of pregnancy is the time of approaching the equator of the period, when the fetus is already formed and is very similar to its parents in miniature.
Let's see what an ultrasound shows at 12 weeks of pregnancy.
- detection of fetal chromosomal abnormalities;
- embryo length (CTP – coccygeal-parietal size);
- fetal head size;
- symmetry of the brain hemispheres;
- assessment of brain structure;
- dimensions of the long bones of the fetus (tibia, ulna, radius, humerus and others);
- assessment of symmetry and motor activity of the fetal limbs;
- the location of the heart, stomach, and abdomen of the fetus is noted;
- identifying the fetus’s predisposition to heart defects (in the presence of a modern scanner and an educated, experienced ultrasound operator).
What does an ultrasound show at 12 weeks of pregnancy?
It is known that people with Down syndrome (trisomy 21) have a short nose, since the nasal bones form somewhat later than in a fetus with a normal (normal) cryotype. A fetus with Down syndrome has a shortened upper jaw, noticeable by the smoothness of the facial contours.
It also shows, using Doppler ultrasound, the pathology of the blood flow velocity curve in the venous system. The assessment of this value is a mandatory parameter during ultrasound of the fetus of a twelve-week pregnancy. Reverse blood flow is considered to be a pathology.
Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18) is characterized by early manifestations of slow fetal development and a predisposition to a slow heartbeat (fetal bradycardia). Moreover, until the eighth week of pregnancy, fetal development proceeds normally. The fetus has a noticeable omphalocele (prolapse of peritoneal organs into the umbilical hernial sac).
A fetus with Edwards syndrome is characterized by a lack of visualization of the nasal bones, and the frequent presence of one artery in the umbilical cord (Normally there should be two arteries and one vein).
23rd week of pregnancy what is happening, fetal development, weight gain, edema, cord blood
At-risk groups
Those who suffer from chronic diseases are prone to bradycardia. The risk group also includes women living in conditions of physical or psychological discomfort.
To reduce the likelihood of complications when carrying a child, you need to monitor the course of the underlying disease, give up bad habits and turn to physical therapy. In this case, regular visits to an obstetrician-gynecologist and other specialized specialists are required .
Bradycardia can lead to pregnancy loss or death of the woman. To prevent this from happening, expectant mothers should be careful about their own health. A timely visit to the doctor and correct diagnosis will allow you to identify the problem before it causes irreparable harm.
Source: oserdce.com