Hello friends! Lena Zhabinskaya is with you! We are always taught to be calm towards our children, especially very young ones. Of course, this allows you to soberly assess the situation and provide the necessary assistance in difficult times, but is this always possible? Sometimes things happen to babies that can cost them their health and even their lives, for example, moments when they choke on milk.
Moreover, doctors say that you need to think here not only about what to do if a newborn chokes on milk, but also about how to recognize these situations. Ultimately, time plays a huge role here.
When breathing problems appear in an adult, he can always tell others about it and, thereby, ask them for help; it’s another matter when an infant suffers from them. He himself is not yet able to recognize the danger threatening him and react correctly to it. Moreover, he does not know how to breathe and swallow at the same time, he often rushes, as his mother thinks, and ends up choking and then coughing.
Of course, nature helps him in this case. When liquid enters the respiratory passage, a reflex reaction comes into play, provoking the same cough that can help push the milk out. This cough is also evidence that everything is fine. The air passes through and most often the baby does not need help from adults.
Another thing is if the baby is choking and suffocating. In this case, the respiratory passage is completely blocked, the child is uncomfortable, but he cannot communicate about it. And not only coughing, but even crying. How to understand the full danger of the situation? It turns out that there are signs indicating that a child is choking and urgently needs help, namely:
- hoarseness, unusual sounds. When the airway is closed, the baby cannot cry out loud. Meanwhile, he is trying in every possible way to tell an adult about his problem, so he wheezes and hisses;
- panic and horror on the face. Sensing danger and experiencing difficulty breathing, the baby reflexively opens its eyes and mouth wide;
- increased salivation. Under such conditions, the baby is unable to swallow saliva; moreover, he may additionally choke on saliva;
- tummy tension. The inability to inhale is accompanied by retraction of the tummy;
- change in skin color. When air access is blocked, the child is unable to breathe. As a result, the skin of his face and lips turns blue;
- loss of consciousness. These are the most severe and extreme cases that require immediate medical intervention.
How does airway obstruction occur?
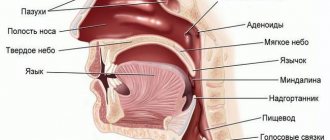
The human respiratory system, including that of a child, consists of the upper and lower respiratory tract. The first include:
- nasal cavity;
- pharynx;
- epiglottis;
- vocal cords;
- larynx.
The lower respiratory tract includes:
- trachea;
- bronchi;
- lungs (left and right);
- pleura.
Important! Anatomically, the human body is designed in such a way that some components of the upper respiratory tract are also involved in food intake. The pharynx, epiglottis, and the area close to the trachea where the vocal cords are located are the precursors of the esophagus. No wonder everyone knows what it means to choke.
Nasal passages
The nasal cavity is directly connected to the pharynx. Air entering the nasal passages descends through it into the trachea. When the flow moves backwards, for example, during a sneeze, the air rushes into the nose with a sharp push through the pharynx. If there is food in the mouth at this moment, its fragments will easily end up in the nasal passages.
Mouth
During swallowing, special cartilage protects the airways from foreign bodies and substances entering them. It is controlled by a conditioned reflex. If the epiglottis does not have time to close the entrance to the trachea, food enters the respiratory tract, which causes difficulty breathing, coughing and suffocation. This can happen if you laugh or talk while eating. Technically, it is enough to inhale when there is something in the mouth, because during inhalation the protective cartilage does not cover the trachea.
First aid for a child from 1 to 8 years old
For a child over one year of age, help is provided a little differently.
- You hold him on your hip, belly down, head below your torso.
- Strike with the heel of your palm (5 times) between the shoulder blades.
- Turn over onto your back and quickly (one press per second) press the sternum along the line passing between the nipples, also 5 times.
- After this, you examine the oropharynx, if you see a foreign body, try to remove it.
- And if successful, we begin to give the child artificial respiration. To do this, you take 5 breaths “mouth to mouth” or “mouth to nose”. The child's head should not be thrown back excessively.
- Repeat the entire cycle from the beginning until the foreign body is removed.
What are the risks of airway blockage?
What to do if the baby does not eat
Infants also differ from adults in that they cannot breathe through their mouths. Therefore, any difficulties with nasal breathing create insurmountable problems for the child. Many mothers know that children aged from birth to two months grunt and snore in their sleep. This happens because during sucking, milk often enters the upper parts of the back wall of the pharynx and into the nose. There it dries out and turns into crusts that interfere with nasal breathing, dooming you to wheezing. If the room where the baby sleeps were sufficiently humid and cool, crusts would not have time to form, and the milk that gets into the nose would easily flow down the back wall of the pharynx into the esophagus.
Attention! Blockage of a baby's nasal passages with dried mucus or milk is life-threatening because he does not yet know how to breathe through his mouth.
To relieve your baby of difficulty breathing, it is important to know what to do if a newborn chokes on milk. After finishing feeding, after some time, when the baby is still awake, you need to rinse your nose with saline solution. It’s easy to prepare: dissolve a teaspoon of salt in a liter of water and use a baby pipette to drip into your nose several times a day. The saline solution is safe for newborns, moisturizes the mucous membrane and washes away milk residues from the walls of the upper respiratory tract.
Nasal rinsing
First aid for loss of consciousness
Emergency assistance must be provided to a child if he or she loses consciousness as a result of choking on milk.
- Get on your knees. The adult's body position should be at right angles to the baby's chest.
- Place one hand on the child's forehead and gently tilt his head down. As a result, the baby's head and neck should be on the same line.
- Using the finger of your other hand, gently lift the child's chin.
- Check the baby's breathing (whether the baby is breathing through the mouth or nose). The procedure must be done quickly; all the above steps should take no more than 10 seconds.
- If the baby is not breathing, give him chest compressions or artificial respiration.
- At this time, another adult present at home should call an ambulance.
It is important to remember that it is very difficult to carry out resuscitation measures without prior training. Women are recommended to take first aid courses long before the birth of their baby. The ability to provide first aid to a child (or adult) in emergency situations can prevent the most unpleasant consequences.
What can a baby choke on?
Even in the maternity hospital, a woman is taught to place her newborn on her side, not on her back. This is done to prevent the baby from choking if he burps. This is not the only way a baby can choke. While sucking even the mother's breast, unpleasant situations can occur.
Milk
If a child has a temperature of 37 - what to do?
Happiness for the mother if she has abundant milk production, in which the baby is full. But in such cases, you need to know what to do if the newborn chokes while suckling. Most often, babies choke on milk in the first two months, when the mother’s breasts have not yet adjusted to the required volumes, and not at all because the baby cannot control breathing and swallowing, as mothers often write about this on forums. Swallowing is a reflex and does not need to be learned. From the first second after birth, when the baby takes a nipple or bottle, he can both breathe and swallow, thanks to the epiglottis. But, if the stream is excessively abundant, the child does not have time to swallow the portion, after which a second one has already arrived, which is why the child chokes.
Attention! The same applies to the water that children are given to drink. The pacifier on the bottle should be marked according to the child's age in months.
Pacifier for 3 month old baby
Saliva
At the age of about 3 months, the salivary glands begin to actively work in babies. This is not associated with teething, although it may coincide with this event. Saliva constantly flows down the chin, the child gets to know his hands by placing his fist in his mouth. If, with a mouth full of saliva, a child is surprised by something (father’s grimace, a bright toy), automatically, at the moment of surprise or joyful laughter, he will take a sharp and deep breath, which will allow saliva to enter the respiratory tract.
Regurgitation
After feeding, the baby needs to be held “soldier-like”, that is, in an upright position, so that the air that accidentally gets into the stomach comes out. As a rule, it comes out three times. Inexperienced or in a hurry mothers, having heard one burp from the child, put him on his back, after which he burps milk. This means that the remaining two portions of air did not have time to be released from the gastrointestinal tract and pushed out the milk with them. If a mother is in a hurry to go about her business, feeds the baby and immediately puts him on his back, there is a high probability that he will burp when he is no longer under supervision and will choke on the amount of milk that comes out. This is a very dangerous situation, especially because most young mothers have no idea what to do if their infant chokes.
Head on side in supine position
Interesting. Children, being in the womb in the last stages of pregnancy, are in such cramped conditions that for most, the skull remains crushed on one side of the back of the head for some time after birth. Because of this, babies from 1 month old, lying on their backs, still place their heads on the side, on the side that has become squashed. In most cases, this saves the life of a baby if he grows up in a family where little attention is paid to children, and there is no one to keep him as a soldier.
Foreign body
When feeding a baby with milk, in the sixth month of his life, relatives really want to diversify his diet with something very tasty. If at this age the two lower teeth have already come out, most adults believe that they can give the baby cookies, apples or carrots, without realizing that this is a real parental crime. If an adult ever tried to chew dry food, having only two lower and even two upper teeth, he would understand that this is impossible.
Instead, having given the baby the first apple, everyone is happy that he took a bite of it, which is not surprising - it’s not difficult to do this with two incisors. But what will happen next to this piece? The baby will try to swallow it all at once. The size of a piece of apple is often larger than the gap of the esophagus. Once in the throat, the apple can simply get stuck, blocking the lumen, which will not allow air to enter the bronchi, that is, the child will begin to choke, for this it is not at all necessary to run around with your mouth full and laugh - the usual swallowing of too large a piece is life-threatening. Therefore, until the baby has teeth intended for chewing (and they are located in a row after the fangs), dry and hard food cannot be given.
Baby and apple
Signs of danger
The danger of a foreign object getting into the baby's mouth is that it can block the respiratory passage. Blockage of the respiratory system causes suffocation. When liquid from a bottle, food or small objects gets into the respiratory tract, the child develops a protective reaction. At a reflex level, he begins to cough in order to get rid of excess body. If the baby is coughing, there is no need to help him. A cough is a sign that the airways are not clogged.
Closing the airway is a more dangerous situation. The breathing passage is closed and the main problem here is that it can be difficult to notice such a situation. The baby does not cry or scream at such moments. This emergency situation requires immediate and decisive action. There's not a minute to waste.
We list the main signs indicating a problem:
- The child cannot make loud sounds, including crying. The sounds are characterized by hoarseness and unusualness.
- The baby's eyes and mouth open noticeably. Such symptoms indicate a panic state in the newborn. You may notice increased salivation and futile attempts to breathe. Pay attention to your stomach - it is pulled in and tense.
- When a baby gags while feeding, the face takes on a characteristic red color. In the absence of air and the inability to take a breath, the face and lips acquire a bluish tint.
- The child may lose consciousness.
The fact that a baby is choking can be determined by wide open eyes and mouth.
Having noticed such symptoms in a child, parents should maintain composure and not panic. You need to act skillfully and decisively. Excessive excitement from adults will frighten an already frightened baby.
Signs that a child is choking
If an infant has already choked, the cough centers are triggered because they have been hit by an irritant - food in the respiratory tract irritates special villi, which tell the brain that something is bothering them. In other words, a cough begins, often accompanied by vomiting. This is a natural protective reaction of the body - to cough.
If a child is teething - signs
At times when breathing is difficult, the baby cannot take a breath in order to clear his throat. Therefore, you can understand that the toddler has choked by the following signs:
- lips turned blue;
- the child's mouth is open, but he does not make sounds;
- Older children tend to grab themselves by the throat with their hands;
- eye rolling;
- loss of consciousness;
- severe pallor or bluishness of the skin.
Attention! Babies under one month of age may shake their heads without blinking or open and close their mouths like a fish.
If a child chokes on water
You can choke on water in different places and under any circumstances, be it swimming in a natural pond or harmlessly splashing in the bathroom.
The first thing to do in such a situation is to pay attention to the child’s skin. If they have acquired a bluish tint, then we should talk about the presence of water in the lungs, which can come out in a foamy state through the oral and nasal cavities.
If the skin becomes pale without cyanosis, this is evidence of a lack of water in the lungs.
If there is water in the respiratory organs, immediate assistance should be limited to removing it from them. In this case, you need to do the following:
- Using a finger pre-wrapped in sterile gauze, excess mucus, dirt and sand particles are removed from the child’s mouth.
- The victim is placed with his sternum on a bent knee so that his head hangs down. Then, several times, you need to pat your back or press on it simultaneously carefully and forcefully.
- If the child is very small, you can simply turn him over by his legs and hold him upside down for a short time. At the same time, it is important to carefully close your mouth by pressing on the lower jaw. This must be done to avoid the tongue sinking, which can close the lumen of the larynx, thereby blocking the access of oxygen.
- After the water leaves the lungs, artificial ventilation is performed. If the child does not have a heartbeat, an indirect massage of the cardiac organ is required. If there is no effect, artificial respiration should be continued.
- If the first aid procedure is successful, the breathing process and heart rate are restored, after normalization of which it is necessary to dry and warm the child by giving him a hot drink.
Interesting: A child is choking: how to provide first aid
It is important to remember that an externally recovered child needs a mandatory examination by a medical specialist, who must exclude the possibility of possible complications. For this reason, in case of any outcome of an accident, it is advisable to call an ambulance.
What to do if your baby is choking
When the baby begins to choke while sucking, you need to stop feeding for a minute in order to give him the opportunity to cough and catch his breath. Human physiology is designed in such a way that it is easiest for the muscles of the respiratory tract to expel the irritant if the body is upright, with a slight tilt forward. The baby can be placed face down on your arm. The baby is able to remove milk and other fluids, including saliva, water or formula, from the respiratory tract on his own if he is not disturbed by tapping or patting. Only if the cough is unproductive or weak, you can start knocking on the back in a special way.
A choking baby who is unable to cough on his own needs urgent help from an adult, who should not be afraid for a minute, hesitate, or scold another, possibly guilty adult. It is required to immediately and confidently begin providing first aid to a baby who is choking:
- Place the baby face down on your arm so that the back and butt are higher than the head. For children who can stand, it is enough to lean forward, while with one hand the adult holds the child by the chest area.
- With confident, sharp movements, make sliding taps with the base of your palm in the area between the shoulder blades, in the direction from the shoulder blades to the head, 5 times. It is important to measure the force of the blow; you cannot hit too hard.
- Turn the baby onto his back. Turn the standing child to face you or walk around him independently. Using two fingers of your hand, sharply press the chest 5 times, just above the area between the nipples, so that the chest drops slightly. In infants it is pressed down by about 1 cm, in older children - by 3 cm.
- Look into the oral cavity. If a foreign object appears there, carefully remove it.
Attention! If an adult does not see a foreign object in the respiratory tract, but knows that it is definitely there, it is absolutely forbidden to reach into the throat and blindly try to get it out. This will only lead to the fact that it will be pushed lower, and it will be even more difficult to remove it.
Correct position for first aid
A popular pediatrician, Evgeny Olegovich Komarovsky, reminds in his book on emergency care that coughing is more effective than the given algorithm of actions, so all you need to do with a baby when he is choking is not to stop him from coughing if he is already coughing.
Unnecessary and necessary actions
Threatened situations are often created by the child’s parents. Teeth are being cut, and the infant is trying to chew everything that comes into view. Why should he chew on toys? You can keep your baby busy with a healthy and tasty apple, carrot, or cucumber. Many mothers, fathers and grandmothers think so. They are nearby, what could happen? Unfortunately, it happens in seconds.
If an infant has even the tip of a baby tooth showing, he will definitely bite off a piece of the apple.
He laughed, cried, and then the baby choked on his food.
Older children may get their hands on small parts from toys, but little ones explore and taste everything. And even just chewing something, a child can laugh or cry, inhale with a mouth full and choke. It is often necessary to provide assistance when a child chokes on candy.
- that is, you cannot ignore age restrictions on toys;
- You should not give your baby objects that can be chewed off;
- When eating, teach your child not to talk with his mouth full;
- You cannot play or fall asleep with candy in your mouth.
And yet, no matter how hard we try, we must be prepared for any situation.
If a child is choking and suffocating, we do not waste time and begin providing emergency assistance:
- if the baby chokes, but the cough persists, the skin is not blue (partial obstruction), urgently call an ambulance;
- and if you see bluish skin, weakness, ineffective cough, wheezing, when inhaling, retraction of the intercostal spaces (obstruction of the respiratory tract with breathing problems), if the child cannot speak, cough, or breathe (obturation) - start providing assistance immediately.
Ask someone for help to call an ambulance. If there is no one, and the child turns blue, first provide the first stage of assistance and then only call a medical team.
Prevention
There is a popular video on the Internet in which mothers whose children choke on milk during feeding due to excess flow are advised to breastfeed more often to reduce the accumulated volume. From a medical point of view, this advice is not only useless, but also dangerous, as it threatens the child with overeating, and, as a result, obligatory abdominal pain. If the baby is at risk of suffocating from the stream, it is better to first express the foremilk, reducing the pressure from the mammary glands, after which feeding will proceed calmly, the child will swallow food without difficulty.
When a baby is constantly choking on breast milk and saliva, it is important to pay attention to his emotional state. It is important to regularly visit a neurologist, pediatrician and other required specialists, who in the early stages will be able to detect problems with the development of reflexes or physiological features, such as cleft palate, that are the causes of endless choking.
It is important that during feeding the mother takes a comfortable position: sitting or lying on her side. She should not stand anywhere with the baby on her chest or do anything at the same time. It is important to ensure that the breast does not pinch the baby's nose. The baby's head should be raised above the body while eating. A calm environment is the key to healthy and peaceful feeding without choking.
Prevention of troubles
In order to avoid having to urgently remove all kinds of objects from the child’s respiratory tract, you need to take some precautions:
- choose soft toys carefully - the pile should not be too long and difficult to pull out;
- put off toys with small parts until a more conscious age;
- from a very early age, do not allow your baby to put everything in his mouth;
- teach your baby to eat carefully and not to indulge while eating;
- It is advisable to exclude any toys at the table; do not distract the child in this way so that he eats well;
- Grind the food offered to your child well, and thoroughly clean fish and fruits of bones and pits.
And one more important detail - there is no need to force feed the baby. The child will absolutely twist, struggle and resist, and this is another possibility of choking.
We also read:
- A child has a foreign body in the ear or nose - first aid rules
- What to do if a child has been bitten by mosquitoes, midges, bees, wasps - first aid for insect bites
- First aid for a child in emergency situations
We only told you about first aid for your child in an emergency. No matter what happens, calling an ambulance is simply a necessary measure. Even if the problem was resolved independently, it is impossible to answer unequivocally whether the child damaged the airways or not. Consulting a specialist will allow you to once again make sure that everything is in order.
Be sure to watch the video!
Safety comes first
Parents, without meaning to, often harm their baby. According to established stereotypes, they begin to act harmfully. We list the actions that should not be done if the baby is choking. We'll tell you what not to do and why:
- Do not try to reach the object with your hands or using devices. If there is a foreign body in the mouth, this still makes sense. Otherwise, parents risk pushing it even deeper.
- You should not hit your baby on the back when he is upright. A prerequisite for proper tapping is a tilted back and head. By slapping a child on the back in an upright position, there is a considerable risk that the object will settle even more firmly in the respiratory tract.
You can avoid possible emergency situations by properly organizing the meal process. Here's what you need to do to keep your little one safe:
- To feed your baby breast milk, choose a comfortable position so that the milk does not flow like a river. The baby's head should be higher than body level.
- When starting the introduction of complementary foods, organize it so that the child feels comfortable and calm. Don't let your baby play while eating. The sippy cup or bottle should be comfortable.
- Consider the age of the child to choose the right consistency of food.
- Use a special net to let your baby eat fruit.
- All small objects and parts from toys should be removed from the baby’s access. Develop fine motor skills under strict supervision.
Having studied all the possible options for techniques for choking and blockage of the airways, you are savvy in the question of how to help the baby if he cannot clear his throat and remove a foreign object. Do not forget about the general safety rules and never leave your baby unattended for a long time.
Bottle feeding can be dangerous
Breastfed babies are not the only ones at risk of choking. Babies who drink formula from a bottle are also at risk. We list the factors influencing this:
- The hole in the bottle nipple is too large. When purchasing pacifiers, pay attention to the indicated age. Newborn babies require the smallest opening, and today special anti-colic nipple systems have been developed. A properly selected pacifier allows the little one to calmly suck on the formula during feeding. Increasing the diameter of the hole will cause the baby to begin to choke.
- Consistency of the mixture. The choice of mixture also matters. The older the child, the more liquid his formula will be. Excessively thin milk can cause a month-old baby to choke and swallow excess air during feeding.
- Colic. The wrong choice of an adapted mixture leads to colic. They, in turn, affect discomfort during feeding, choking and swallowing air.