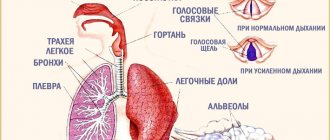
The existing division into hind and foremilk causes anxiety among nursing mothers. And not in vain, a deficiency of one or another milk is equally harmful to a growing organism. The posterior is responsible for weight gain, normalization of intestinal microflora, and the psycho-emotional state of the baby. With a regular lack of foremilk, dehydration occurs. In order for the breastfeeding period to be comfortable for the woman and beneficial for the baby, it is necessary to teach the child how to latch onto the breast correctly and not limit him in the time of feeding.
Differences between foremilk and hindmilk
The breast produces only one type of milk, but due to the “flushes” the percentage of fat in it changes. If you pump for a long time, you can notice a metamorphosis in the color and consistency of the nutrient fluid. Particles of fat stick to the walls of the alveoli in the upper part of the mammary gland. Meanwhile, watery milk continues to move towards the nipple, filling the lower cavity of the breast. As it moves through the ducts, fat molecules come off the walls, and the flow force decreases. It is the fat content that distinguishes foremilk from hindmilk. The latter provides the baby with a feeling of fullness and timely weight gain, and the anterior one serves to quench thirst.
Foremilk
Foremilk has a bluish tint, contains a lot of lactose, water-soluble minerals, and is rich in proteins and carbohydrates. The taste is a little sweet. Lactose is a carbohydrate of the disaccharide group that promotes the absorption of iron and calcium; the substance has antifungal and antibacterial effects. Therefore, do not underestimate the benefits of milk that is released in the first minutes of feeding. First, the baby must “drink”, only then get to the rich hindmilk. Due to the fact that fats are necessary for the proper intellectual and physical development of the baby, expressing foremilk while breastfeeding is not recommended.
Hind milk
It is many times fatter than the front one, so it looks thick and has a rich white or yellowish color. Produced through prolonged breastfeeding. Hind milk contains fat-soluble enzymes that make it easier for babies to digest and absorb nutritional fluids. Fats are the source of strength for babies. They are responsible for the state of the immune system and saturate the body with cholesterol, necessary for the synthesis of vitamin D. Small children suck out hind milk slowly, literally drop by drop. A nutritious treat causes drowsiness. It usually looks like this: the baby sleeps, lightly sucking on the breast.
Baby feeding rules
Only breast milk satisfies the needs of babies 100%, so even in the maternity hospital, young mothers are taught the basics of feeding. Experienced mothers in labor and pediatricians share their knowledge; some advise feeding the baby every 2.5–3 hours, i.e. according to a schedule, others – on demand. Each newborn child is an individual; the woman herself must determine the optimal frequency of attachments. A properly organized breast sucking process saves a woman from many troubles, such as cracks and abrasions on the nipples, blockage of the milk ducts, and the development of mastitis or mastopathy.
Correct application
The first time the baby is placed next to the mother is immediately after birth. In the first minutes of his life, the child feeds on colostrum, a thick yellow liquid. Its composition is close to infant blood serum - it contains immunoglobulin, leukocytes, vitamins, and a lot of proteins. Women devote the entire first month of their baby's life to learning how to latch onto the breast correctly.
Advice for young mothers:
- Before feeding, take a comfortable position and turn your baby's body towards you.
- Position his head and neck in one straight line so that food flows smoothly into the stomach.
- Then you need to bring the baby closer to the breast - the smell of milk stimulates the baby's feeding instinct and he himself will open his mouth wide.
- Place the nipple in your baby's mouth so that the entire lower part of the areola is not visible.
- Adjust the position of the mammary gland; it should not interfere with the baby's breathing.
Children under six months of age do not eat only during the day. The side-lying position is ideal for relaxed night feedings. The “reclining” position is preferred by women with a voluminous bust; the pose is suitable for poor breast grip, for example due to a shortened frenulum of the tongue.
How to alternate breasts
To avoid problems with lactation, one breast should not wait longer than 4 hours for its turn. Experts recommend starting feeding from the breast that was the last in the previous session. For good weight gain and overall development, the baby needs nutritious hind milk. If the baby begins to swallow less often, about once every three or four sucking movements, it’s time to change breasts.
A second breast can be offered if the child:
- Smacking or licking lips after feeding.
- He sucked out a sufficient amount of milk and released the nipple, but continues to stay awake and fuss.
- Poor weight gain.
Not all babies respond well to the change of gland during one feeding session. Alternating “in a circle” is suitable for newborn babies. To make it easier for a tired mother to remember which side she last latched the baby on, it is better to leave herself “reminders” in the form of notes in a notebook. With hyperlactation, it is necessary to alternate breasts even less often - once every 3-5 hours, depending on the rate of milk production.
How long should a child eat?
Newborn babies should eat 8–12 times a day. Over time, the baby becomes stronger and sucks more milk. It is best to feed your baby on demand, on average every one and a half to three hours.
It is necessary to monitor the eating interval, it should be 3-4 hours even at night.
The duration of the break depends on the individual characteristics of the mother’s body (volume and quality of milk, the rate of its release), appetite, mood and well-being of the baby. Typically, a newborn “hangs” on one breast for 20–40 minutes; as the skills of quickly eating food develop, the baby gets full faster. But we must not forget that hind milk reaches the nipples after about 15 minutes of feeding.
Why doesn't the baby eat?
If a child does not eat enough, then the main reason is usually a violation of the milk formation process and its lack. It is necessary to identify the reason for the decrease in level. As a rule, the main reason is the mother’s disrupted diet, insufficient diet.
A newborn may stop breastfeeding if the taste of the milk is changed. It depends on the products that the mother eats. Therefore, you need to take your diet very seriously, for example, avoid spicy, spicy foods, alcohol, etc.
Normal milk production also does not guarantee satiety of the baby. Its volume may not be enough for the baby to feel full. This can be caused by improper grip of the nipple with the lips, uncomfortable position of mother and baby during feeding, or incorrect choice of diet. In fact, the child should receive the breast immediately at the first urge, which is characterized by crying.
Milk may disappear or the child may reject the breast due to psychological problems: unpreparedness for breastfeeding, painful sensations when the child bites the nipple, the occurrence of cracks - ultimately creating an unfavorable background.
What to do if your baby is too lazy to breastfeed
Small children sometimes fall asleep while feeding, but this does not mean that the child is lazy. A cause for concern is a complete refusal of the breast or a “reluctant” meal, during which the baby sucks only foremilk. At the same time, the baby is capricious, cries, spits out the nipple, demanding an easier supply of food.
If you suspect that the baby is not eating enough, you can purchase a sling (a long scarf used to carry the child in the first months of life and up to 2–3 years). With the help of this simple device, the baby can spend as much time with the breast in his mouth as he needs to be completely saturated. If the baby is already familiar with artificial formula, you need to remove all bottles and nipples from his field of vision. With sluggish sucking, it is useful to practice co-sleeping. A child, half asleep, instinctively sucks and smacks his lips. If during the day he quickly falls asleep under the breast, “wake him up” by encouraging him to continue sucking. With lactostasis, it is necessary to eliminate milk stagnation in any way in order to ensure the baby an easy flow of nutrient fluid through the ducts.
Solution
First of all, it is necessary to track the feeding process itself, if lactation is normal, but the child shows signs of malnutrition. The baby will not receive the required portion of milk if he latches onto the nipple incorrectly and begins to suck in air with the milk. If the baby is hunched over or his position is twisted forward, then the milk will not be distributed normally in the esophagus and stomach, hiccups will occur, and the baby will refuse to suckle.
The most correct option is when the baby, along with the nipple, also grabs a part of the halo with a diameter of at least 2 centimeters. The nose should touch the chest, but breathing should not be difficult. The nipple should move freely in the baby's mouth, with the lips turned outward and tightly to the breast. You cannot force breastfeeding; the baby will only eat when he accepts the breast on his own. Forcing will lead to incorrect grip and undesirable consequences.
If the level of milk production is insufficient, then it is necessary to stimulate it. There are many ways to improve the lactation process without harming the baby. Here are the most effective of them:
- It is necessary to protect yourself from dehydration and drink more fluid than normal. Particular attention should be paid to the consumption of warm and sweet drinks; milk and honey are ideal. This will also help strengthen the immune system. 1.5-2 liters is the minimum total volume of liquid consumption for a nursing mother. Any liquid counts, as well as various soups and broths.
- Diet violations are unacceptable. First of all, the balance of all elements is important. Vegetables, meat and fish are required to be consumed. Excessive spice of foods, oversalting, and flour products can have a negative effect on the formation of milk. In addition, they significantly change the structure of milk and its taste for the baby.
- Walking in the fresh air and light exercise are the best ways to combat stress. Swimming in a pool or safe water is perfect. Yoga and Pilates in moderate loads will allow you to quickly return to your prenatal body shape and have a positive effect on vitality;
- Stimulation of the mammary glands. As a rule, stimulation is used not only to increase the speed of the lactation process, but also to gently resolve lumps and stagnation of milk. Priority is given to circular movements. The fact is that stagnation leads not only to the loss of the opportunity to breastfeed, but also to disruption of milk production and the development of mastitis. Prevention is regular self-massage.
- The baby should be fed not according to schedules, but according to the baby’s demands. Typically, feeding is carried out 9-10 times a day in small portions and about 4 times at night;
- The taste of the breast itself, and not the milk, should be pleasant to the child. It is not advisable to wash your breasts with soap with a caustic taste and a high alkaline composition. If you don’t wash off the soap well, the baby will begin to reject the breast, first for a reason, and then as a reflex. It is best to wash your breasts with liquid, light, colorless and odorless soap, and dry your breasts with paper napkins or a white felt towel.
- Cumin decoction and fennel infusion are an effective folk remedy. The main thing is that fennel or caraway seeds do not cause the baby’s allergies through a reaction to milk. It is better to consult a doctor. Specialty teas are often recommended.
It is very important to maintain a calm emotional background and try to abstract yourself from all life’s problems and stresses. You need to understand that now all attention should be focused not on yourself, but not on the child.
This will be the main incentive. But postpartum depression is a serious obstacle. Added to this is a regular lack of normal sleep, anxiety, and fatigue. Taken together, this is a powerful negative criterion. It is necessary to turn the situation around on your own and not resort to the help of sedative medications. The rule applies: what the mother eats, the baby also eats. The sedative will affect not only the calmness of the nurse, but also the properties of the milk.
Stressful situations are best overcome with the help of aromatic baths, aromatherapy, spa and light massage; walks in the fresh air are great help
But if you cannot do without medications, then you can use valerian, glycine no more than half a tablet per day, or a decoction of natural motherwort.
Milk imbalance
An imbalance between foremilk and hindmilk can cause lactase deficiency. The condition is manifested by increased gas production, pain, bloating in the abdomen, frequent foamy stools, weight loss or poor gain. Troubles arise due to the “overload” of the baby’s digestive tract with lactose, which is found in foremilk. In addition, the latter contains a lot of water and little fat, which contributes to too rapid movement through the gastrointestinal tract. Once in the large intestine, the enzymes do not have time to react, and lactose remains undigested.
Many breastfeeding consultants believe that there is no milk imbalance; the main thing is not to limit the child’s feeding time. To solve the problem, it is enough to teach the baby to grasp the nipple correctly and not offer one breast or the other at random, ignoring the prescribed two to three hour interval.