Surely you approach the cradle more than once during the night, listening to your baby’s breathing - Is he breathing?! Everything is fine! We bet that young parents monitor materials about newborns, checking to see if everything is fine with the baby. Sometimes symptoms of a variety of disorders are found, especially if the mother’s anxiety level is high.
What color should a breastfed baby's stool be, why does a baby hiccup, how to tell if a newborn is cold, why wheezing... - these are perhaps the most popular queries in a search engine in the first 3 weeks of a baby's life.
Paying attention is good because you can diagnose problems at the stage of their appearance. But it’s better to find an experienced pediatrician about the birth of your baby and ask him questions. But of course, you need to have basic knowledge, read, analyze, compare, double-check.
What is wheezing?
This term usually refers to extraneous noises heard during breathing. They can be more difficult to identify in children than in adults. Firstly, the sounds made by the respiratory organs at different ages are different (which is considered normal). For example, children from one to seven often experience symptoms characteristic of ARVI in adults. It's about hard breathing. They go away on their own with age. Secondly, wheezing in a child without fever can be difficult to listen to, since the baby feels well and does not want to sit quietly for a whole minute and breathe at the command of parents or doctors.
What are they?
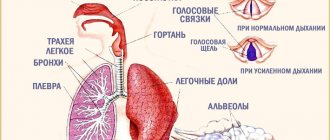
Wheezing in children, as in adults, is divided primarily according to its localization. They are pulmonary, bronchial or tracheal. There are often cases when extraneous sounds when breathing come from the nasopharynx or throat. This happens after long screams (they say that the child is hoarse). Either the symptom is a clear sign of an allergic reaction or an incipient acute respiratory viral infection.
Wheezing in a child without fever, regardless of the source, does not require emergency medical attention (provided that he is able to breathe independently and there are no signs of asphyxia). However, it won’t hurt to show it to your treating pediatrician, especially in cases where neither the cause of noisy breathing nor its source is clear.
In addition to localization, wheezing can be dry and wet, constant and intermittent, whistling and crepitating. Sometimes they are heard when you inhale (then they are called inspiratory), and sometimes when you exhale (expiratory).
Common causes of wheezing
With pathological wheezing, the child will show anxiety.
The most common diseases that occur with wheezing are presented in the table:
| Causes of wheezing | |||
| Dry wheezing | Wet wheezing | Wheezing after mechanical impact | Wheezing due to physiological disturbances |
| Develop after inflammatory processes, spasm of the muscular wall of the bronchi and bronchioles occurs, swelling of the mucous membrane | Occurs against the background of diseases such as bronchitis: in this case, sputum passes freely | Appear due to the closure of the respiratory tract by a foreign object | Develops after inflammatory diseases: sputum accumulates, preventing the free passage of air in the lungs |
It is not always the case that a child’s cough with wheezing occurs due to serious inflammatory infectious processes. Often the physiological development of young children contributes to the appearance of such symptoms, but they will not be a sign of disease. For example, it is normal for newborns to have a wheezing cough within a few months of life (see Newborn Cough: When to Worry).
A cough without wheezing in a child less than a year old is often associated with the irritating effect of mucus draining from the nasal cavity along the back wall of the throat. This is also a common condition for children of this age. But if wheezing of a different nature, which does not disappear for a long time, appears in an older child, then you should immediately consult a doctor.
The most common causes of pathological processes associated with wheezing:
- Respiratory infectious diseases.
When a child develops a hoarse voice and cough, ARVI is often the cause. Inflammation affects the upper part of the respiratory tract, bronchi, and alveoli. The appearance of wheezing is preceded by the appearance of fever and severe intoxication (especially in young children). As a cough develops, the child may refuse to eat;
- Inflammation of the nasopharynx, tonsils (pharyngitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis).
The child may experience wheezing when breathing, but there may be no cough at all. You should be attentive to the manifestations of inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx in children. Their entrance to the trachea is so small that when the mucous membrane swells (which can occur with intense crying), the lumen becomes very narrow or disappears altogether. Subsequently, the child develops wheezing, a barking cough develops, and respiratory failure increases.
- Low air humidity.
Another cause of wheezing in babies. It typically appears in the summer months, when parents, fearing that the child will catch a cold, do not properly ventilate the room. Due to the heat and circulating dust in the room, allergic reactions appear, which are often characterized by an unproductive cough and wheezing in the lungs.
- Ingestion of a foreign body into the respiratory tract;
One of the serious causes of wheezing with cough, requiring immediate medical attention). Wheezing in children of all ages (especially young ones) requires timely diagnosis and treatment.
How to hear wheezing?
Medical workers do this using a special device - a phonendoscope. It allows you to locally amplify sounds. Often, pulmonary or bronchial wheezing can be clearly heard if you simply lean your ear against your back or chest. There are also diseases in which gurgling in the chest cannot be ignored even at some distance from the patient.
If the source of the sound is the throat or nasopharynx, the noise is usually accompanied by pain, voice distortion and difficulty breathing.
“Grunting” with the nose is a symptom of adenoiditis in a child
During inflammatory processes in the upper respiratory tract, the nasopharyngeal tonsil (adenoids) grows. But even in this form, this organ can only be seen with the help of special instruments. Most often, inflammation of the tonsil occurs in children 3–7 years old. The disease is called “adenoiditis”; it is caused by a runny nose and sore throat.
Signs and symptoms of adenoiditis:
- The inflammatory process in the nasopharynx makes nasal breathing difficult and provokes coughing.
- Pallor of the skin occurs due to low hemoglobin levels.
- The child speaks through his nose but there is no snot, his voice becomes nasal.
- Inflammation may affect the middle ear cavity.
- The child sniffs and breathes through his mouth.
- The baby is restless and does not sleep well at night.
- Appetite decreases.
Doctors pay attention not only to the listed external symptoms. To determine an accurate diagnosis, a small patient is given an X-ray of the nasopharynx and an examination of the nasal cavity is performed - rhinoscopy. Sometimes the degree of adenoids is determined by an experienced ENT doctor by palpation examination.
Wheezing in a baby
In early childhood (especially up to one year), it can be very difficult to diagnose and treat diseases. The baby cannot say what exactly is bothering him. At the same time, wheezing in an infant can be the result of either prolonged crying or a complex (and sometimes even dangerous) disease.
It is not always easy for a mother to understand whether her baby is choking or has simply been crying for too long. Doctors advise paying attention to other symptoms. If the baby, once in your arms, immediately calms down, looks healthy and behaves normally (despite wheezing), there is no need to worry. In the case when a bluish tint appears on the skin, and breathing is clearly difficult, you need to sound the alarm. This may be a symptom of a cold or infection, or a more serious illness. Such signs also sometimes indicate that foreign objects have entered the respiratory system. It is important that in all these cases emergency assistance from a specialist is required.
How to get rid of "grunting"
Preparations based on sea water, such as Aqualor, saline solution or sea salt solution, work well on the nasopharyngeal mucosa. A ready-made preparation based on saline solution for a newborn or a child over 1 year old can be purchased at a pharmacy. The bottle must be warmed to room temperature, then the liquid must be injected into the child’s nasal passages through the tip. If the baby “grunts”, then rinsing the nose should be done twice a day - morning and evening.
The solution is called “physiological” because its concentration is the same as blood plasma. When 9 g of table salt is dissolved in 1 liter of water, a liquid of similar composition is obtained. Seawater is usually a more concentrated solution. For example, the Black Sea contains on average 18 g/l of salts (chlorides, carbonate sulfates). Saline solution is prepared in pharmacies using distilled water; it is a clean and safe liquid.
How to rinse a newborn's nose:
- Warm the saline solution carefully to room temperature.
- Place the baby on his back, holding his chin with his hand.
- Carefully inject 2-4 drops of the solution into each nostril using a baby dropper.
- Raise the child or pick him up and hold him in the “column” position.
- After 5–10 minutes, use cotton wool to clean each nasal passage.
Daily wet cleaning and aquariums with water will help to avoid the harmful effects of dry air on the baby’s nasopharyngeal mucosa. It is advisable to install a special humidifier in the room or place a bowl of water over the heating device.
The baby needs to be turned from back to side until he learns to do this himself. It’s good if the baby regularly changes position, this reduces the likelihood of mucus hardening and drying in the nasopharynx. A light massage of the baby's back and abdomen helps breathing.
When to start worrying
Wheezing when breathing in a child is not in itself a reason to panic. But in combination with some other symptoms, they require immediate medical attention. An ambulance should be called if severe wheezing in a child is accompanied by a high temperature (38 or more), repeated vomiting, noticeable difficulty breathing (there is a risk of asphyxia) or under the age of one year (if it does not go away within 5 minutes to exclude “false alarm” caused by prolonged screaming).
In all other cases, there is no need for urgent specialist intervention. If a child has a cough with wheezing, a fever (within acceptable limits) and other signs of a respiratory infection, it is enough to call a local doctor.
Self-medication is acceptable when all the symptoms have already been observed before, a specialist has made a diagnosis and prescribed treatment. You will still have to schedule a visit to the clinic if the cough does not go away within a week, despite all the measures taken. A doctor should be invited to your home, even if the baby’s temperature is not very high, but it has not been normalized within 7 days.
Dry indoor air
The baby’s nasal canals are still very narrow, so dust and crusts quickly accumulate in them. The reason for this may be dry air in the room. Active attempts to protect the child “from drafts and hypothermia” often lead to infrequent ventilation. Then the air stagnates and becomes polluted. Dryness can also be a consequence of this state of affairs, plus hot weather, heating in winter, insufficient natural sources of moisture. The mucous membranes dry out, crusts form, dirt accumulates - and then the child “grunts.”
It is recommended to ventilate and also use humidifiers, frequently do wet cleaning, water the flowers on the windowsills, get rid of dust collectors - heavy curtains and carpet.
You can also get aquarium fish. Having an aquarium in your home is a great way to humidify the air. By the way, the ideal indoor humidity is 50-60% and the temperature is 22 degrees Celsius.
How to treat wheezing in a child?
The most correct answer to this question is what the specialist prescribes. However, knowing modern mothers (as well as grandmothers), it is worth assuming that no one will really listen to him, and their own knowledge will be used.
If wheezing when breathing in a child occurs as a result of a common viral infection, then they can be treated with medications (expectorants and anti-inflammatory drugs), folk methods (honey with milk, herbs, rubbing) and other methods (warming, inhalation). In some cases, it is necessary to use more serious drugs - antivirals and antibiotics. They should be prescribed by a doctor in accordance with the diagnosis and condition of the child.
Adenoiditis is one of the causes of developmental delays
It happens that the child sniffles through his nose, but there is no snot, the temperature is normal. The pharyngeal tonsil responded to infection in the upper respiratory tract by growing (hypertrophy). When the inflammatory process subsides, the adenoids may remain enlarged.
Why does adenoiditis occur in children:
- Untreated acute inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx.
- Dry, dusty air in the children's room.
- Wrong diet.
- Weak immunity.
- Hypo- and vitamin deficiency.
Nasal congestion and wheezing at night quite often occur in children with enlarged nasopharyngeal tonsils. A high degree of proliferation of adenoids becomes the main cause of mouth breathing in the absence or small amount of discharge. There are several consequences of poor adenoid health that parents should pay attention to. This is difficulty in nasal breathing and hearing impairment.
In the chronic form of adenoiditis, intoxication of the body occurs and the child’s development slows down.
There are 5 important points to consider:
- If a child has had ARVI or other acute inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract, the adenoids do not immediately return to normal.
- Acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI) must be treated until complete recovery.
- The children's room needs to be ventilated daily, remove dust, and use a humidifier.
- Hardening helps strengthen the immune system and better resist ARVI.
- Good nutrition helps prevent adenoiditis.
Drug treatment
If a child has a cough with wheezing, and even a dry one, folk remedies will most likely not be enough. After showing the baby to a specialist and making sure that this is the result of a common cold, you can start taking an expectorant mixture or syrup. The last option is good because most of these drugs have a pleasant sweet taste, so the child will drink the medicine without harm. Although potions can be more effective (especially those that are sold in powder form and require dilution with boiled water). But children sometimes refuse tasty medicines, so they certainly won’t drink unpleasant ones, much less bitter ones.
For older children, expectorant medications in tablets or powders are quite suitable. Or a medicine for adults (it is important not to make a mistake with the dosage). If the doctor has prescribed additional anti-inflammatory drugs, you should not refuse them either.
ethnoscience
If, as a result of a complication of a viral infection or hypothermia, wheezing occurs in a child, treatment may not be medicinal (provided the temperature is normal). We are talking primarily about decoctions of medicinal herbs. When coughing, coltsfoot, thyme, licorice, and elecampane help well. You can relieve inflammation with regular chamomile. There are also special herbal preparations that are sold in any pharmacy.
In addition, inhalations of pine buds or potato peelings help against coughing and wheezing. But they are contraindicated at elevated body temperatures. Pine buds brewed in milk (a tablespoon per liter of liquid) are consumed orally, 50 ml every 2 hours. An untreated dry cough can go away in just a day.
In the absence of an allergy to honey, eggnog is effective. Children eat it with pleasure, perceiving it as a delicacy. A tablespoon of honey is mixed with softened butter and ground until white with the yolks of 2 eggs. A mixture of 20 grams is enough; it is consumed half an hour before meals. A contraindication may be an allergy to eggs or honey. Radish can also perfectly cure wheezing in children. Using a knife, a hole is made in it, which is filled with honey. After a couple of hours, a sweet syrup forms in this place, which children drink with pleasure. The procedure can be repeated throughout the day, after which a new radish is taken.
Dangerous situations
Now let's talk about wheezing, which requires immediate consultation with a doctor. The newborn’s body is weak and susceptible to many external factors that can provoke infection and the development of any pathology. In this case, as a rule, wheezing is accompanied by additional symptoms: cough, difficulty breathing, anxiety, lack of appetite, elevated body temperature, etc.
To protect your baby from colds and wheezing, you need to follow simple rules during:
- you should not walk in windy weather;
- dress your baby according to the weather using the “+1” principle. That is, the child should be wearing 1 more clothes than you. If your child is dressed too warmly, he or she may become sweaty and easily get sick. A lightweight version of clothing if it’s cold outside is also not suitable, as the baby will simply freeze and get hypothermia. Many mothers, when dressing their children “lightly”, argue that the child should be toughened up. This is a controversial issue, and it also needs to be hardened correctly and competently;
- avoid drafts. Even if the baby is in a stroller, you need to provide it with protection from wind, rain and snow;
- Avoid contact between your baby and people with a recent, or even ongoing, viral disease.
The cause of wheezing can be pneumonia or bronchitis, which is very dangerous for an infant, since all diseases in babies under one year of age develop rapidly and doctors do not always have time to stop dangerous symptoms.
A newborn's wheezing may also occur due to allergies or more serious conditions such as asthma, in which the airways become swollen and produce excess mucus.
A child develops hoarseness, coughing and wheezing if a foreign object gets into his larynx or respiratory tract, and such wheezing appears suddenly. Never leave your baby alone with small toys, candy or other items that could cause choking! If this does happen, you should not panic, but urgently call an ambulance to prevent respiratory arrest.
Compresses
When a child has wheezing in the chest and breathing is difficult, ways to ease it can be not only medicinal. Compresses are used mainly at night, provided that the body temperature is close to normal. This method of treatment is good for both infants and older children.
The simplest and most pleasant compress is potato. To do this, the vegetable is peeled and boiled. Then they are pounded (without adding any salt or fat) and placed in a plastic bag, which is tightly tied. Then you need to wrap it in several layers of fabric (a towel will do) so that it is warm, but not hot. The bundle is placed on the baby's chest and held for about an hour. From time to time you need to remove 1 layer of cloth, adjusting the temperature as the potatoes cool.
Children are sometimes given mustard-honey cake, which also has a good warming effect. Take vegetable oil and vodka in equal parts. Add the same amount of honey and mustard powder, as well as flour, to make a dense but soft dough. A flat cake is formed from it and placed on the chest or back (you can make 2). Having secured it with a bandage, you can leave it until the morning. If you are allergic to honey, this remedy is contraindicated.
Inhalers
They come in steam and aerosol. The former allow you to treat inflammatory processes in the upper respiratory tract using hot herbal decoctions or special solutions. They are used both for mild forms (laryngitis, ARVI, tracheitis) and for more severe diseases, for example, bronchitis. Aerosols are prescribed by a pediatrician when diagnosing complex forms. This applies to bronchitis and bronchial asthma. Any type of inhaler can be purchased at a pharmacy. It is usually used in combination with other types of therapy. The essence of this device is to turn the drug into steam (by raising the temperature or under pressure) and deliver it directly to the respiratory tract.
Wheezing as a feature of the body
In a newborn, the tissues of the respiratory tract are not yet sufficiently formed, and the respiratory tract itself is quite narrow. This feature of a small organism can cause wheezing, for example, during sleep or during breastfeeding. When all the cartilage of the larynx is formed, the wheezing will go away. This will be around 1.5-3 years. Although the immaturity of the respiratory organs can become aggravating circumstances in acute respiratory viral infections and inflammatory processes. Therefore, it is better to consult a doctor, especially if there is a suspicion that the virus has nevertheless attacked.
Physical exercise
If a child is breathing with wheezing, has a dry cough and does not clear sputum, therapeutic exercises are often used to alleviate the condition. Basic expectoration exercises are performed upside down. For example, you can take a child by the legs and lead him around the room in your arms. Then they perform the “birch tree”. If there is a horizontal bar in the apartment, you should hang upside down on it (but not for very long). Lightly tapping on the baby's chest and back can also be effective. As a rule, if he does not have a fever and his overall health is within normal limits, the baby will like this exercise.
When talking about a baby, they take him by the legs and shake him slightly upside down. Then tap on the chest and back. It will be useful to spread the child’s arms to the sides, then cross them over the chest. Massage of the chest and back (in the area of the shoulder blades) is no less effective. For babies it is done with their hands, stroking and tapping. Older children are given a vacuum massage using a can. The procedure is very unpleasant and even painful, but very effective. Helps even with bronchitis and pneumonia.
Diseases with the symptom of wheezing and what to do
If the baby wheezes, has snot and cough, the temperature rises, the baby behaves lethargically, refuses to eat, then most likely the diagnosis will be “acute respiratory viral disease.” In this case, only a doctor should decide on the necessity and correctness of treatment. All that is required of you is not to force the child to eat, provide him with plenty of fluids and strictly follow all the doctor’s recommendations regarding the treatment of a wheezing child.
If the newborn wheezes quite strongly, coughs with a “barking” cough, wheezes when he breathes, and when the baby inhales, the intercostal spaces are drawn in, and a high temperature (above 38.5 degrees) is observed, then doctors, as a rule, talk about pneumonia. If such symptoms are noticed, it is necessary to call a pediatrician to make a correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. It often happens that the baby has to be hospitalized.
If the child’s voice is hoarse, the baby is breathing heavily, he has a fever, a strong dry cough and “whistles” in the chest, while all of these symptoms are aggravated at night, then you can suspect the baby has croup (difficulty in breathing, which is caused by inflammation and narrowing of the chest). lumen of the upper respiratory tract). When such an attack begins, it is necessary to call an ambulance or a pediatrician. While waiting for medical help, the child should be allowed to breathe humidified air. To do this, you can use a humidifier or fill the bathroom with hot water to make steam and bring the child into the bathroom for a couple of minutes. Afterwards, drip the nose with vasoconstrictor drops and provide an influx of cool fresh air. You can also give your baby anti-allergy drops, for example, Fenistil.
Children under one year of age may develop a disease such as bronchiolitis. In this case, small areas of the bronchi become inflamed. In this case, there is a strong cough that does not subside for a long time (sometimes several hours), difficult hoarse breathing, there are signs of a cold such as snot and sore throat, which is why the baby refuses to eat, is very irritated and capricious.
If the baby’s poor health does not go away after a few days, then it is necessary to call a pediatrician for an examination. If the diagnosis is confirmed, hospitalization may be required
If the baby still has wheezing after a runny nose, the baby snores at night, his nose is constantly stuffy, and one of his relatives suffers from asthma or allergies - this may indicate that the child has developed bronchial asthma. You need to consult a pediatric allergist and carry out the necessary examinations for further treatment.
Also, when the baby breathes through the mouth, he has a runny nose, he snores in his sleep, suffers from frequent colds, clear nasal discharge and otitis media, is whiny and irritable, it is likely that his adenoids are enlarged or he is allergic to some irritant. In this case, only the pediatrician will be able to determine the cause of the child’s unsatisfactory well-being, that is, determine whether it is a runny nose, allergies or inflammation of the adenoids. After making the correct diagnosis, the doctor will be able to prescribe adequate therapy.
During illness, a child should drink a lot, this will reduce intoxication of the body. And also breathe fresh and humidified air. Dr. Komarovsky constantly emphasizes this. He argues that during the acute period of illness (fever and severe malaise), it is necessary to provide such conditions at home, and after the onset of a lasting improvement in well-being (even if there is still a cough with phlegm, but the temperature has dropped, the child has regained his appetite and good mood) do not forget about walks in the open air. You need to remember that a hoarse baby can be taken outside for 20-30 minutes in windless, sunny weather and be sure to choose the right clothes so as not to overheat or overcool the child.
Particular attention should be paid to the fact that the above describes not exact diagnoses, but their possible variants, in which the child may become hoarse. Therefore, it is strictly not recommended for parents to independently treat wheezing in their baby, much less give him any medications without consulting a pediatrician! Such an irresponsible approach will pose a threat to the life and health of the baby. You can help a small child if you accurately determine the main cause of the illness. Therefore, you should not refuse additional examinations if the doctor suggests them.
Wheezing, bubbling, squelching - these are the sounds heard in the baby’s nasopharynx when he has a cold or an acute respiratory infection. The following situation often happens: the child grunts, but there is no snot, the temperature is normal. The cause may be untreated inflammatory processes in the upper respiratory tract, enlarged adenoids, and allergies.
Almost forty years ago, the whole country sang along with Valentina Tolkunova, who first performed the song “Snub Noses.” Children snoring peacefully while sleeping evokes affection. But what will mom say when quiet sounds give way to strange wheezing? Of course, this causes concern, especially for parents of young children.
If a newborn baby grunts through his nose, but there is no snot, then extraneous sounds are most often associated with imperfections in the structure of the baby’s respiratory organs. The respiratory tract is just developing, like other organs; the nasal passages are still short and narrow. Discomfort is caused by dried mucus on the walls of the nasopharynx.
The baby wheezes when air passes through the upper respiratory tract, when the mucus in the nasopharynx dries out, forming crusts.
Why does the mucous membrane in a child’s nasopharynx dry out:
- dry air, especially during the heating season;
- parents do not clear mucus from the baby’s nose;
- the children's room is poorly ventilated;
- Wet cleaning is rarely carried out.
Dry mucous membranes cause discomfort to the baby, and strange sounds when breathing make the mother worry about the health of the baby. To help, you need to rinse the baby’s nose and instill solutions that act as antiseptics and moisturizers. Vasoconstrictor drops will not be useful in this case!
Allergic cough
Often, wheezing in children, cough, runny nose and swelling of the nasopharynx are the result of contact with external irritants. Allergens can include plant pollen, animal hair, clothing, toys, food and medications. Often, with age, allergies go away on their own. Sometimes it stays for life. Allergies are difficult to treat, and since their manifestations are often accompanied by fever, swelling of the respiratory system and the risk of asphyxia, the first priority is to combat the symptoms.
If a child experiences a similar reaction to any irritants, then contact with them should be minimized (ideally, eliminated). The first aid kit should have the appropriate medications - we are talking about decongestant and antiallergic tablets, nasal drops, etc. It is better to use them on the advice of a specialist, since self-medication in this case is the most dangerous.
Mucus in the nose
In older children, mucus comes out freely from the nasal passage, but in infants it can linger, also forming crusts, which can become another cause of wheezing. That is why, after each bath, parents need to carefully remove the crusts using cotton wool soaked in oil.
Also, 2-3 weeks after birth, parents may notice that the child has a runny nose. If there are no other symptoms other than mucus in the nose, most likely this is a “physiological runny nose” and the mucous membrane is adapting to new conditions. If the baby attaches to the breast without any problems, then all that parents need is to maintain the optimal temperature and humidity in the room, as well as drip sea drops (BUT! only after consultation with a pediatrician). Sometimes milk gets into the nose (during regurgitation, for example) and also forms crusts. Therefore, toileting the spout is an important daily procedure.
Prevention
Of course, all parents dream about the health of their children. But very few take concrete actions aimed at maintaining it. We are talking primarily about proper nutrition, regular physical activity, active recreation, walks in nature and hardening. Children do not need to be bundled up and given antibiotics at the first symptoms of a cold. After all, immunity is developed precisely at this age. If it is constantly suppressed by excessive care and chemicals, then as a result, a sick child will turn into an adult with a bunch of chronic diseases.
Wheezing in children can be a sign of a variety of ailments, ranging from a common respiratory infection to complex bronchitis, pneumonia and even asthma. Therefore, if they do not go away and are accompanied by fever and other symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
Diagnosis of diseases
To diagnose the cause of pathological wheezing, there are instructions that hospital doctors follow, which include the following data:
- History of the disease;
- Objective examination;
- Laboratory tests (general blood and urine tests, biochemistry, allergy tests);
- Instrumental studies (radiography, bronchoscopy, etc.).
Depending on the cause, which is fundamental in the development of wheezing in children, appropriate therapy is prescribed.